How to cure periodontal disease forever?
Treatment of any disease begins with diagnosis. In the case of periodontal disease, which is often asymptomatic, the following procedures are performed to make a final diagnosis:
- examination of the oral cavity;
- probing of the gingival sulcus;
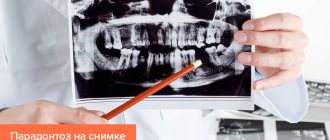
- X-ray examination (orthopantomography);
- biomicroscopy of the gums to determine the degree of microcirculation impairment.
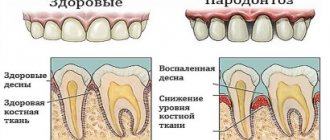
The main factor confirming the presence of periodontal disease is a uniform decrease in the height of the interdental septa with alternating foci of osteosclerosis and osteoporosis in the deep parts of the alveolar process and the body of the jaw, as well as in other bones of the skeleton. As a rule, all these manifestations are displayed on an x-ray. The patient will also need additional consultation with a general practitioner and an endocrinologist to identify and treat metabolic disorders, diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine systems, which often accompany the disease.
How to get rid of periodontal disease and finally prevent bone tissue destruction? Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely say goodbye to the disease. For this reason, treatment of dental periodontal disease is usually aimed at slowing down the process of periodontal dystrophy and preventing tooth loss, tissue inflammation and purulent bone damage.
Consequences of periodontal disease - why is it dangerous?
- Firstly, due to the absence of pronounced symptoms, this disease can progress unnoticed over many years and lead to total destruction of the teeth and jawbone - and then teeth fall out with periodontal disease.
- Secondly, the destruction of bone tissue leads to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract with the subsequent occurrence of diseases of the digestive system.
- Thirdly, advanced periodontal disease can provoke periodontitis - acute inflammation of the tissue and tooth loss.
In addition to the above consequences, generalized periodontal disease in an advanced stage causes another dangerous disease - osteomyelitis, that is, purulent bone damage.
Treatment methods for periodontal disease
The development of the disease can be slowed down by treating periodontal disease with medications and carrying out the following procedures:
- professional hygiene for timely removal of dental plaque;
- splinting to normalize occlusal relationships;
- the use of drugs for periodontal disease, vitamins and agents to improve microcirculation in tissues (nicotinic acid, aloe extract, heparin);
- massage to strengthen gums during periodontal disease;
- grinding of teeth;
- prosthetics;
- darsonvalization of gums;
- filling erosions.
Modern methods
The most effective treatment for periodontal disease is based on the use of more modern methods, listed below:
- exposure to high pressure oxygen in hyperbaric chambers;
- ultrasonic device for the treatment of periodontal disease;
- local hypo- and hyperthermia;
- diadynamic currents;
- amplipulse therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF therapy.
Which doctor treats periodontal disease? Most patients do not know the answer to this question. A doctor who treats periodontal disease is called a periodontist. Be sure to contact this specialist if you notice pale coloration and receding gums, increased tooth sensitivity, or a wedge-shaped defect. Where to treat periodontal disease? Of course, in a dental clinic.
Surgical treatment of periodontal disease
Is it possible to cure advanced periodontal disease? The answer to the question is also negative. However, when treating advanced periodontal disease, surgical intervention is most appropriate. We are talking about the stage of the disease when the alveolar process is almost completely atrophied, and in order to prevent the loss of all teeth, the patient undergoes an operation to restore bone tissue during periodontal disease, which will keep the teeth in their places.
Causes of periodontal disease in adults
Periodontal disease is a systemic disease that indicates not so much problems in the oral cavity, but rather malfunctions in the functioning of various organs. In most cases, pathology develops due to poor circulation in the gums. This is due to age-related changes, deterioration of immunity or certain diseases: diabetes, atherosclerosis, malfunction of the endocrine system, etc.
Remedies for periodontal disease
There is no best cure for periodontal disease, and a specific cure has not yet been invented. At the moment, relief from the symptoms of this disease is achieved only through special procedures and complex treatment of periodontal disease with drugs rich in amino acids, proteins and antioxidants. Taking vitamins for periodontal disease also helps accelerate metabolism in periodontal tissues. What vitamins can a doctor prescribe? Typically, as part of drug treatment for periodontal disease, dentists recommend taking the following vitamins and minerals:
- vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 – if periodontal disease develops against the background of pathologies of the digestive system, diabetes mellitus, neurasthenia;
- folic acid – to activate all metabolic processes in the body;
- zinc – for bone tissue regeneration;
- calcium – for mineralization of bones and teeth;
- selenium - for antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects.
You should not self-medicate. The doctor determines which drugs for periodontal disease should be used in each specific case, based on the results of dental diagnostics and the general condition of the patient’s body.
Causes of gum disease
Factors that increase the risk of developing gingivitis:
- Insufficient oral hygiene.
- Hormonal changes in the body. They create a favorable environment for the formation of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. That is why teenagers and pregnant women most often suffer from gingivitis.
- Damage from impacts, burns, incorrectly installed fillings and dentures.
Periodontitis occurs if gingivitis is not properly treated in time. The inflammatory process, under the destructive influence of pathogenic bacteria, spreads to other areas of the periodontium.
Periodontal disease develops due to poor blood supply to the gums and poor nutrition. The most common causes of periodontal disease:
- gastrointestinal diseases,
- diabetes,
- heart and vascular diseases,
- taking anticonvulsants and other medications that reduce salivation.
The problem may also be hereditary.
Antibiotics for periodontal disease
Patients are often interested in whether antibiotics are used for periodontal disease in adults? In the initial stages, this is not necessary, since there is no inflammatory process. However, severe degrees of the disease are sometimes accompanied by inflammatory complications. Here, treatment of periodontal disease with antibiotics is considered justified. What antibiotics do doctors usually prescribe for periodontal disease with inflammatory complications? These can be various drugs that help quickly stop inflammation.
The next stage is the removal of dental plaque above and below the gums.
The main cause of the inflammatory process during periodontal disease is the presence of a large amount of plaque. Its formation is a consequence of insufficient oral care. Therefore, it is impossible to achieve effective treatment unless the root cause is removed. The optimal way to treat tartar and plaque in modern dentistry is the use of ultrasound.
The next stage of eliminating periodontal disease is therapy aimed at relieving inflammation. As a rule, it lasts about 10 days.
The course consists of rinsing the mouth for an antiseptic effect.
Algorithm:
- After breakfast, brush your teeth thoroughly for 3-6 minutes.
- Rinse mouth with chlorexidine (0.05%).
- Dry the gums using a clean cotton swab.
- Apply a special gel to the gums.
- Do not eat for at least 2 hours, drink only clean water.
Such step-by-step treatment is prescribed for mild cases of the disease. If the development of periodontal disease has reached its climax, you will need to take antibiotics (7-10 days). The doctor may prescribe tablets or intramuscular injections.
Injections into the gums for periodontal disease
In addition to drug treatment, injections for periodontal disease are also used. These are injections of aloe extract, which is an effective biogenic stimulant. Typically, the course of treatment consists of 20 - 25 injections with a break per day. What injections for periodontal disease are prescribed if the disease has become severe? In the presence of an inflammatory process in the later stages of the disease, dental periodontal disease can be treated with injections with synthetic tissue regeneration stimulators according to the same scheme.
Recipes for strengthening bone tissue:
- Take 20 g of myrrh, add 15 g of chopped mint and raspberry leaves. Dilute a mixture of 80 g of wine alcohol and 25 g of vinegar. Stir and pour into a glass jar. Leave for 3 days in a dark place. Afterwards, rinse your mouth twice a day.
- Pour 50 g of chopped sage into 100 g of boiling water. Leave covered for an hour. Rinse your mouth thoroughly.
- Chop fresh plantain leaves and crush well. Soak a clean cotton swab with the resulting juice and wipe the gums with it.
- Pour 30 g of dried calamus into 0.5 liters of vodka. Leave for a week in a dark place, then strain. Add 3 tbsp. l. mixture into a glass of water and rinse your mouth for 3-6 minutes.
- 6 tbsp. l. Mix crushed pine needles with a liter of boiling water. Bring to a boil, strain and set aside. Rinse your mouth morning and evening.
Plates for periodontal disease
Often solutions and ointments for the treatment of periodontal diseases are not effective enough, as they are quickly removed from the mouth with saliva. Therefore, it is necessary to apply products in the form of applications for periodontal disease. However, modern treatment of periodontal disease involves the use of an alternative form of drugs that allows active substances to better penetrate the epithelium to achieve a high regenerative effect. These are plates made from natural polymers (gelatin, collagen, sodium alginate) and medicinal substances that improve metabolic processes in tissues and increase vascular tone (mineral components, enzymes, herbs, vitamins, amino acids, organic acids, phytohormones).
How is periodontal disease treated with plates?
The product is applied to the gingival margin after brushing the teeth and gently pressed into the interdental spaces. Thanks to their adhesive properties, the plates can be held on the gums for 6 to 10 hours. Then their remains are removed with warm water.
The instructions for these plates say that they are intended to protect and improve periodontal tissue. But is it possible to cure advanced periodontal disease with their help? The answer is negative. This product is not intended specifically for the treatment of periodontal disease. It has a general strengthening effect on the entire periodontium as a whole and is more suitable for alleviating the symptoms of gingivitis and periodontitis in the form of bleeding and inflammation of the gums.
How to treat periodontal disease with folk remedies?
Treatment of dental periodontal disease with folk remedies will not bring results. No rinses or decoctions can cope with bone tissue degeneration. And following advice from articles on the Internet that recommend using hydrogen peroxide or other chemicals to eliminate periodontal disease is not only pointless, but also dangerous to your health. It is important to understand in time that this is a serious disease that requires qualified assistance from a periodontist, and to seek treatment for periodontal disease at the dentist.
Possible complications
If you ignore the symptoms of periodontal disease for too long and do not take measures to solve this problem, the disease can lead to very disastrous consequences. Pathology leads not only to aesthetic problems, but also to the complete impossibility of carrying out hygienic procedures, and nutritional problems (due to pain that occurs when mechanical action is applied to exposed roots).
An advanced form of the disease can even lead to tooth loss. Atrophic processes and destruction of the ligamentous apparatus deprive the teeth of natural support. As a result, they become very loose and fall out. To prevent such an outcome, it is important to promptly seek professional help from a specialist.
Prevention of periodontal disease
There are few preventive measures to prevent the appearance and development of periodontal disease, since the pathology is associated with genetic predisposition and metabolic disorders in the body. In general, doctors recommend maintaining overall oral hygiene through regular brushing and flossing.
You should also follow a certain diet for periodontal disease and to prevent the disease. It is recommended to eat more milk, vegetables, seafood, unrefined vegetable oils, and limit carbohydrate intake. The diet for the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease in adults should include a sufficient amount of raw vegetables and fruits, which promote self-cleaning of teeth from plaque and have a massaging effect on the gums, improving their microcirculation.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation, irritation and redness. Because gingivitis can be mild, you may not be aware that you have inflammation. But it's important to take gingivitis seriously and act quickly. If you do not undergo careful treatment, gingivitis may eventually develop into a more serious disease – periodontitis. Ultimately, this can all lead to complete tooth loss.
The most common cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene. Good habits such as brushing, flossing at least twice a day, and regular dental checkups can help prevent gingivitis.
Symptoms
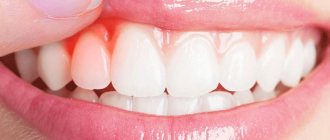
Healthy gums are firm, painless and pale pink in color. If your gums are puffy, dark red, and bleed easily, you may have gingivitis. Because the disease is rarely painful in its early stages, you may have gingivitis without even knowing it.
Signs and symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Swollen gums
- Soft, plump gums
- Sensitive gums
Gums that bleed easily when you brush or floss.
Redness or pinkishness on the brush or toothpick is sometimes seen.
- Changing the color of your gums from a healthy pink to red
When to see a dentist
Most dentists recommend regular exams to screen for gingivitis, tooth decay, and other dental diseases. The doctor eliminates the causes of the disease - treating only the symptoms of the disease at home can lead to more serious problems. If you notice any signs and symptoms of gingivitis, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your dentist. The sooner you seek medical help, the better your chances of reversing the damage from gingivitis and preventing it from progressing to periodontitis.
Causes
The most common cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which contributes to plaque formation. Plaque is invisible - it is a sticky film consisting mainly of bacteria. Plaque forms on teeth when starches and sugars in foods interact with bacteria normally found in the mouth. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing every day are recommendations from any dentist. Plaque requires daily removal because it forms quickly, usually within 24 hours.
Plaque that remains on the teeth for longer than two or three days can harden under the gums into tartar. Tartar can also develop as a result of minerals in saliva. Tartar makes plaque more difficult to remove and creates a protective shield for bacteria. You usually can't get rid of tartar by brushing or flossing—you need ultrasonic teeth cleaning to remove it.
The longer plaque and tartar remain on your teeth, the more they irritate the gums around the base of your teeth. Over time, your gums become swollen and bleed easily. It can also lead to tooth decay.
Risk factors
Gingivitis is common and anyone can experience this condition. Many people first experience gum problems during puberty and then to varying degrees throughout their lives.
Factors that may increase your risk of developing gingivitis include:
- Insufficient oral hygiene
- Tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Elderly age
- Decreased immunity due to leukemia, HIV/AIDS
- Some medications
- Some viral and fungal infections
- Dry mouth
- Hormonal changes that are associated with pregnancy, the menstrual cycle, or the use of birth control pills
- Poor nutrition
- Alcohol or drug abuse
- Unsuitable dental restorations
- Poor quality prosthetics
Complications
In its chronic form, gingivitis can progress to gum disease that spreads to the tissue and bone of the jaw, which can lead to tooth loss.
Periodontitis and poor oral hygiene in general can also affect your overall health. Also, today it is not entirely clear whether this is true, but the disease may be associated with:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Lung disease
- Premature birth or the birth of a child with low body weight or other pathology
Tests and diagnostics
Dentists usually diagnose gingivitis based on complaints and an examination of your teeth, gums, mouth and tongue. Your dentist will look for plaque and tartar on the teeth and check the gums for redness, swelling and bleeding - this will help him make an accurate diagnosis and determine the form and extent of the disease.
If it is not clear what caused your gingivitis, your dentist may recommend that you get a physical examination to check for underlying health conditions.
Procedures and drugs
Prompt treatment usually reverses the symptoms of gingivitis and prevents it from progressing to more serious gum disease and tooth loss. Effective treatment requires professional care followed by oral hygiene at home.
Professional prevention includes:
- Initial assessment and thorough teeth cleaning to remove all traces of plaque and tartar
- Instructions for effective home flossing
- Regular professional inspections and cleanings
- Special cleaning in places where crowns and fillings are attached, implants installed
Your initial professional cleaning will include the use of dental instruments to remove all traces of plaque and tartar.
Uneven teeth or poorly fitting crowns, bridges or other dentures can irritate your gums and make at-home plaque removal more difficult. If problems with your teeth or dentures are contributing to gingivitis, your dentist may recommend correcting these problems.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Steps you can take at home to prevent and reverse gingivitis include:
- Regular professional dental cleanings on a schedule recommended by your dentist.
- Using a soft toothbrush—replace it at least every three to four months.
- Using an electric toothbrush, which may be more effective at removing plaque and tartar.
- Brushing your teeth twice a day, or better yet, after every meal.
- Use toothpicks at least once a day.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash if recommended by your dentist.
If you are consistent with your home hygiene, you should see the return of pink, healthy gum tissue within a few days or weeks. You will need to practice good oral hygiene every day.
Prevention
The best way to prevent gingivitis is a good oral hygiene program that is followed consistently throughout your life. Brushing and flossing for three to five minutes is as much a daily ritual as eating.