Features of the disease
Lymphadenitis is a very common pathology, during which inflammation develops in the lymph nodes.
To understand the etiology of the disease, it is necessary to understand in more detail the physiological processes occurring in the human body. Lymph nodes represent a kind of barrier that restrains the spread of pathogenic microflora from the nearest focus of the inflammatory process throughout the system. However, there are cases when the lymph node itself becomes a source of infection in the event of suppuration. As a result, patients often require hospitalization and possibly surgery. It is quite difficult to obtain statistical data regarding the prevalence of pathology. The fact is that the disease often becomes a complication of other pathologies, for example, tonsillitis or purulent wounds, and its course is not very difficult. In such situations, therapy is aimed at the underlying disease, and lymphadenitis disappears without specific treatment. Therefore, patients with a very serious degree of pathology, which already requires serious medical and often surgical intervention, turn to a specialist.
Causes of pathology
As already indicated, in the vast majority of cases, inflammation occurs as a complication after an infectious process that has already been suffered.
This occurs for physiological reasons, when pathogens are carried by the lymph current to the nearest lymph node. If the body functions correctly and appropriate therapy is carried out, then the bacteria arrive there already in a weakened or killed state, or die directly in it. In this case, inflammation does not develop further. However, if the process is not stopped and the pathogen is very active, then inflammation is already developing in the node itself. In such a situation, lymphadenitis is secondary. However, there are cases when the pathology is primary.
This can occur as a result of trauma to the lymph node area, during which the strain penetrates through the site of injury. It should be noted that such pathologies are very rare and occur against the background of reduced immune defense. The cause of nonspecific lymphadenitis in most cases is staphylococcal and streptococcal infections .
The nodes enter through the flow of blood or lymph. The most common foci of primary inflammation include: carbuncles, boils, infected wounds, thrombophlebitis, osteomyelitis and others. A specific type of pathology is caused by a special type of pathogen that provokes the appearance of specific diseases, for example, gonorrhea, syphilis, tuberculosis, plague, anthrax and others. In such situations, the localization of the inflammatory process occurs in the node closest to the site of infection. So, in case of a sexually transmitted disease, the inguinal nodes are the first to react.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes
To understand which antibiotics should be used for a particular pathology, it is necessary to pay attention to certain factors. There is clinical evidence that in most cases, nonspecific lymphadenitis is caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal microorganisms. That is why it is customary to prescribe antimicrobial agents that are most effective against them.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the severity of the disease, the patient’s age and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Despite the fact that lymphadenitis has a very clear clinical picture, its features vary somewhat from patient to patient. Elderly people, young children and patients with chronic decompensated conditions are very prone to the formation of sepsis, which may well be fatal. Therefore, in such situations, a more powerful medication, or a combination of both, is often prescribed.
A characteristic feature of each type of antibiotic is the place where they accumulate. Due to the characteristics of the disease, it is preferable to use a product with a concentration in the human lymphatic system. For the best effect, it is also recommended to take into account the patient’s medical history and medication history. If a few months ago the patient already underwent antimicrobial therapy, then it is necessary to select a drug from a different group.
Modern tactics for treating pathology involve dividing drugs into first and second lines. Initially, safer drugs with a broad spectrum of action are prescribed. However, if they turn out to be ineffective or cause an allergic reaction, then you have to move on to second-line drugs.
For lymphadenitis use:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides;
- fluoroquinolones;
- lincosamides;
- aminoglycosides.
Penicillins
This class of antimicrobial agents was found earlier than others and has been widely used in medical practice for many decades. They have a very wide spectrum of bactericidal effects. However, due to long-term use, many pathogens have developed resistance to these medications.
Ear congestion
Fungus
Allergy
29212 04 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Ear congestion: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Congestion in the ear or ears occurs as a result of a violation of sound perception and is characterized by various sensations, which may include deafness, a feeling of squeezing and heaviness, and the sound of one’s own voice being too strong. Ear congestion, regardless of the causes of its occurrence, is difficult for the patient to tolerate and, as a rule, requires the help of a specialist.
Types of ear congestion
Blockage in one or both ears may be accompanied by pain, tingling, noise or ringing in the ears, and dizziness. In some cases, congestion disappears after swallowing.
A dangerous symptom is ear congestion accompanied by fever, headache, discharge from the ear (purulent or bloody), and foreign body sensation.
Ear congestion does not always indicate a pathological process.
This condition can be caused by water getting into the ear, pressure changes
during air travel or diving to depth.
Sometimes too strong and incorrect blowing of the
nose from two nasal passages at the same time leads to a blocked ear (ears), which is associated with an increase in pressure in the middle chamber of the ear due to a sharp intake of air from the Eustachian tube.
Taking certain medications
(antibiotics, psychotropic substances) has a toxic effect on the ear, causing the development of congestion and hearing loss.
Diseases that can cause ear congestion.
Earwax
blocking the ear canal. Attempting to remove earwax yourself using improvised objects significantly increases the likelihood of pushing the plug deeper into the ear and sticking to the eardrum (this increases the risk of injury to the eardrum, which leads to complete or partial hearing loss). In these cases, the condition of congestion in the ears is accompanied by excruciating pain, noise, dizziness and nausea.
Mycotic, or fungal, infection of the external auditory canal
. Infection with fungi can be complicated by narrowing or blockage of the ear canal with a feeling of fullness in the ears. The spread of fungi in the ear is aggravated by hearing aids, in-ear headphones, and inflammatory diseases of the ear. The main signs of the disease are itching, ear congestion and resulting hearing loss, and increased sound of one’s own voice in the affected ear.
Damage to the external auditory canal and middle ear structures
may be accompanied by hearing loss and congestion. Bleeding and the formation of a blood clot that blocks the ear canal lead to deterioration in sound transmission. In addition, injury to the eardrum is possible during cleaning of the ear canal, a sudden change in pressure, or a strong blow to the outer ear. In this case, sharp pain occurs, which is replaced by congestion, ringing, noise and hearing loss.
Acute inflammatory diseases
accompanied by swelling and sometimes the formation of purulent contents.
They can lead to ear congestion and hearing loss. In particular, with otitis media of the middle ear (tympanitis),
the tympanic cavity and auditory tube are involved in the inflammatory process. Swelling, which narrows the lumen of the auditory tube, and suppuration of the soft tissues cause ear congestion and hearing impairment. As a rule, the infection enters this sterile cavity from the Eustachian tube, which is directly connected to the nasopharynx.
In children of the first and second year of life, acute otitis may occur when breast milk or formula enters the nasopharynx during regurgitation.
In older children, otitis media and congestion can be caused by
inflammation of the adenoids
, the lymphoid tissue responsible for the local immunity of the nasopharynx and closing the openings of the auditory tubes in the nasopharynx. The anatomical proximity of the adenoids and the auditory tube ensures the rapid transition of infection from the nasopharynx to the ears. In addition, enlarged adenoids can block the openings of the auditory tube, which causes a feeling of stuffiness.
Allergic reactions
can also lead to acute inflammation and swelling of the middle ear.
Otitis externa
characterized by inflammation of the external auditory canal. Congestion in the ear in this case occurs due to swelling of the tissues of the ear canal.
If the disease is caused by a foreign body entering the ear canal
, then swelling and congestion are complemented by a picture of severe irritation. The patient complains of severe itching, pain, a feeling of fullness, and heat in the ear area. The pain intensifies with chewing movements.
For furunculosis
In the external auditory canal, the picture of the disease is aggravated by a closed space where the inflammatory process develops. Increasing pain in the ear is complemented by its irradiation to the corresponding half of the head. The patient cannot lie on the painful side. Due to severe swelling of the tissues of the external auditory canal, sound transmission into the affected ear is disrupted, and a feeling of stuffiness occurs.
Among the anatomical and postoperative defects
that cause ear congestion include deviated nasal septum, narrowing of the nasal passage due to hypoplasia of the nasal wings, and stenosis of the external nasal valve.
Impaired nasal breathing leads to frequent runny nose, infection of the nasal sinuses and, as a consequence, to the transition of the inflammatory process to the auditory tube.
Ear congestion in these cases appears on the side of the narrow nasal passage. The same consequences occur after operations in the nose area.
Sensorineural hearing loss
occurs due to damage to any part of the auditory nerve. Most often, this is an irreversible phenomenon, the symptoms of which include imbalance, dizziness, nausea, fullness and noise in the ear, and poor perception of low sounds. The causes of sensorineural hearing loss can be previous infectious and vascular diseases, tumor processes, injuries, and toxic effects of various substances.
Meniere's disease
is a non-purulent disease of the inner ear, which is accompanied by congestion. An increase in the volume of lymph in the labyrinth of the ear leads to increased pressure and attacks of progressive deafness, tinnitus, and sudden dizziness. In most cases, one ear is affected first. The disease begins either with attacks of dizziness or with deterioration of hearing, which is completely restored between attacks. However, after a few years, hearing loss becomes irreversible.
Myofascial pain syndrome, temporomandibular joint diseases
. Patients with myofascial pain syndrome, which is associated with disruption of the masticatory muscles and limited mobility of the lower jaw, may also complain of ear congestion. In addition, the disease is accompanied by headaches and facial pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and clicking in the temporomandibular joint.
The root cause of the syndrome is spasm of the masticatory muscles.
A similar clinical picture is also given by diseases of the joint itself caused by malocclusion. Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, increased blood pressure
. Congestion in the ears due to damage or narrowing of blood vessels is explained by a deterioration in the blood supply to all tissues, as well as impaired circulation in the area of the inner and middle ear.
Vasomotor rhinitis, or runny nose during pregnancy
occurs under the influence of hormonal changes and is characterized by impaired vascular tone and the release of mucous secretion. With allergic rhinitis, the clinical picture of the disease is almost the same, but the provoking factor is not hormones, but a specific allergen. Swelling of the mucous membrane and narrowing of the nasal passages lead to obstruction of the auditory tube and cause ear congestion.
Tumors in the area of the auditory canal, auditory tube and inner ear
– the most serious cause of ear congestion. Among them should be called cholesteatoma - a tumor-like formation that consists of epidermal cells impregnated with cholesterol. Cholesteatoma is characterized by slow but steady growth. Forming in the middle ear, it can spread to the outer and inner ear, causing congestion and a feeling of heaviness in the ear, purulent discharge, swelling and redness of the auricle.
Which doctors should I contact if I have ear congestion?
If ear congestion occurs, you should contact an otolaryngologist. In the future, you may need to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or allergist.
Diagnosis and examinations for ear congestion
To diagnose the disease that caused ear congestion, a careful questioning of the patient, examination of the outer ear and ear canal to the eardrum, and an audiometric examination are necessary. The infectious nature of the disease is determined on the basis of the clinical picture, otoscopy data and culture of the discharge.
Rules for taking antibacterial drugs
Antibiotics are among a number of drugs, the use of which is strictly prohibited without a doctor’s prescription, as they can lead to the development of serious side effects. In addition, the choice of antibacterial agent depends on the pathogen, so the patient cannot choose it independently.
Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed for lymphadenitis in a course. The minimum duration of therapy is five days, the maximum is four weeks. It is prohibited to discontinue the drug before completing the full course, because this can lead to a worsening of the condition and the development of sepsis.
It is advisable to take the antibiotic at the same time, so that equal intervals are maintained between doses. If for any reason the time was missed, then the tablet must be taken as soon as possible and then continue the course as usual. You can take the drug only with clean water; any other liquid can affect the absorption of the active substance.
What antibiotics can you take during pregnancy?
The period of waiting for the birth of a child is very important in the life of every mother, and the main task of the therapist when prescribing treatment is the safety of the fetus and the woman. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly understand what is prescribed for inflammation of the lymph nodes during pregnancy and lactation.
In most cases, penicillins are used for antimicrobial therapy. They are allowed to be used at any stage of pregnancy, including the first trimester. However, the prescription must have clearly defined indications.
For infections of the respiratory tract, urinary system and ENT organs, beta-lactam antibiotics and cephalosporins are used in most cases. In some cases, the use of Erythromycin is permitted.
WHAT DOES LYMPHADENITIS THREATEN?
22.Mar.2021
The infection can enter the lymph node from a wound, boil (boil), panaritium, diseased tooth and other sources. The inflammatory process is accompanied by pain and enlargement of the lymph node, headache, weakness, general malaise, and increased body temperature.
In the case when suppuration of the lymph nodes themselves occurs, the symptoms become more pronounced: intense pain appears, the skin over the lymph nodes becomes red, the previously clearly defined nodes merge with each other and the surrounding tissues, and become immobile.
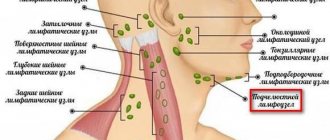
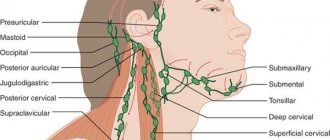
Of practical importance are primarily superficial and deep lymphadenitis of the face and neck. In the facial area, there are buccal, parotid and mandibular lymph nodes.
In the tissue on the outer surface of the body of the lower jaw and in front of the place of attachment of the masticatory muscle, the so-called supramillary or mandibular lymph nodes are located. The deep nodes are located between the lobules of the parotid gland, corresponding to the level of the earlobe.
Acute inflammation begins with a feeling of some awkwardness when moving the head, dull pain in the area of the affected node or group of nodes. Enlarged lymph nodes are clearly visible on palpation, but they are somewhat painful and have a dense elastic consistency. General disturbances at the beginning of inflammation may be absent or mild.
If the course is unfavorable, the inflammation can turn purulent: the node becomes inactive, “fused” with others, forming a group. Body temperature rises to 37.2-37.8 °C. Changes characteristic of ulcers appear in the blood. The patient becomes unwell, weak, loses appetite, etc. In turn, the inflamed lymph node gradually melts and leads to the formation of a fistula tract (with the disease becoming chronic).
Chronic specific lymphadenitis, as a rule, affects the mandibular, submandibular, premaxillary and cervical nodes. Sometimes it is combined with damage to the lymph nodes in other parts of the body, including bronchial and retroperitoneal. The course of chronic lymphadenitis is very diverse, which depends on the stage of the disease, the number of affected lymph nodes, the reaction of the tissues surrounding the node, etc. The diagnosis of inflammation of the lymph nodes is established only during a medical examination. Self-treatment is also contraindicated.
Elena Averkina
, oncologist, Nyagan City Clinic
What antibiotics are prescribed for children?
Lymphadenitis in children develops in childhood in most cases as a result of infectious lesions of the respiratory tract, and they, in turn, are accompanied by respiratory viruses.
Uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents for respiratory infections in children often leads to the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Due to the improper use of antibiotics, children may experience dyspeptic symptoms. In severe cases, it can lead to acute liver failure, enterocolitis or erythema multiforme.
Prescription of antibiotics is necessary for:
- bacterial pneumonia;
- meningitis;
- infections of the genitourinary system;
- purulent tonsillitis.
In childhood, the use of Cefuroxime and Amoxicillin is permitted. The first is used to destroy streptococcus, pneumococcus and staphylococcus, which often cause inflammation of the throat and mouth. The second belongs to the class of penicillins and is widely used in the treatment of tonsillitis, infections of the ears, nose and throat, as well as inflammation in bone tissue and the bloodstream.
Lymphadenitis - a lump in the groin area
11.11.2021
There are many unusual inflammatory tumors, malignant and benign neoplasms on the human body. Neutralizing each of them requires its own special approach. A lump in the groin area can be represented by either a small swelling or a massive formation.
In any case, such an anomaly should be shown to an experienced doctor . During the examination, the latter will probably prescribe a number of medical procedures. Well, then everything will depend on the type of growth that appears. Most likely, the formation will disappear on its own after a few days, but there are situations when surgical removal is clearly unavoidable.
Lump in the groin in men - causes and treatment
A lump in the groin in men is the very first symptom of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes. And in this case, it clearly smells like hernia Diagnosis of such a disease is carried out through self-examination or medical examination. This will only give a superficial idea of the severity of the disease. Next you need to undergo a more serious examination.
This type of formation appears in men in the upper part of the inguinal fold. The size of their healthy lymph nodes can be compared to a bean, but when it becomes inflamed, the size increases, literally, to a walnut. When a lump appears in the groin, males feel a sharp or dull pain in this area. In addition to the above symptoms of the inflammatory process, there is also a significant increase in body temperature.
Lymphadenitis in the groin area can occur due to infection with a variety of genital infections. Among the latter, viruses are often observed. In this case, treatment will be more predictable than in the presence of malignant or benign tumors. Lymph nodes can become inflamed during prostatitis . And during the course of various types testicular A male lump in the groin is more rarely observed as a consequence of swelling of the scrotum. But for children (boys), this disease is explained by the fact that the testicle does not descend from the abdominal cavity.
Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the male inguinal lymph nodes), which appears between the groin and also the leg, can be removed by modern doctors not only through surgery. There are many medications on sale, the use of which promotes complete resorption of inflammatory formations.
A lump on the pubis in representatives of the stronger sex may also appear after a sudden weakening of the muscles that are located in the wall of the abdominal cavity. Moreover, such a nuisance can provoke not only enormous physical exertion, but even a severe cough. Because of all this, intestinal loops often protrude directly under the skin. Thus, a hernial sac is literally instantly formed and unprecedented pain appears in the groin, which is unbearable. When a hernia is subjected to excessive stress under the influence of physical stress, the skin that is located above it swells very quickly, acquiring a red tint. If a hernia is strangulated, you obviously cannot avoid surgical medical intervention.
Lump in the groin in women - causes and treatment
A lump in the groin in women can also occur due to a variety of factors. There are a lot of variations in the process of treating a lump near the groin. Most often, representatives of the fairer sex discover such formations on their own. Well, then, it’s up to the doctors . Most likely, they will diagnose you with harmful enlarged lymph nodes. In this case, it is necessary to identify the causes of damage to these natural protective barriers of the body. Viral infections are considered the most common of them.
In case of inflammatory processes in the organs of the female reproductive system, a lump under the skin in the groin can be treated faster and more productively than in the case of cancer. The most trouble awaits you when malignant processes appear in the body. Even the use of high-precision instrumental examination, including computed tomography or biopsy, does not always help to identify all the nuances regarding tumors.
And finally, remember that it is better to show the above abnormal formations that appear on the body to a doctor , since only medical professionals can promptly save you from the serious consequences of illnesses. And it doesn’t matter whether the lump is in the groin on the right, left or in the center - the main thing is that such an anomaly needs to be eliminated.
Published in Lymphology Premium Clinic