Most dental patients want to have not just a healthy, but also an attractive smile. Unfortunately, not everyone can boast of this.
Back in 1984, some components that are necessarily inherent in a “beautiful smile” were identified:
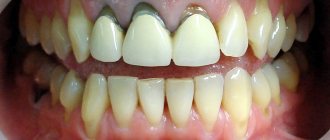
- The smile should expose almost 100% of the coronal part of the tooth and the gingival papillae, while the gum itself should not be visible (otherwise, when the gum is exposed, we are talking about a “gummy smile”).
- The gingival contour should be symmetrical, smooth, the edges of the gums at the central incisors and canines should be located at the same level, and at the second incisors - 1-2 mm lower.
- The length of the tooth crown should not be less than 11 mm, and the width should correspond to the “golden ratio”.
- The gum contour should be in harmony with the smile line.
If the patient's smile does not fit into these standards, then it can be significantly improved by changing the edge of the gingival contour and increasing the length of the dental crown.
What is lengthening of the clinical crown of a tooth?
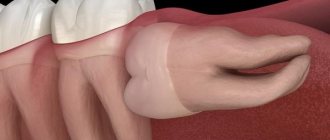
Lengthening the crown of a tooth is a tooth-preserving dental intervention, as a result of which the required amount of subgingival tooth tissue is exposed and a new gingival contour is formed.
A radical alternative to this manipulation is to remove the problematic tooth and install an implant of the required length in its place, forming the most aesthetically pleasing gum contour. But do not forget that not a single most beautiful artificial tooth can compare in functionality with your real teeth, so resorting to such a radical method is only in exceptional cases.
The need for surgery
An operation to lengthen the crown of a tooth is prescribed to a patient for several reasons:
Aesthetic reasons:
- the gum frame is damaged;
- discrepancy between the height of the gum and teeth;
- improving dental hygiene;
- not fully erupted teeth.
Preservation of teeth:
- the need to restore the length of a dental unit lost as a result of abrasion;
- the presence of caries under the gums;
- the need for dental restoration work.
Periodontal causes:
- effective periodontal treatment.
In what cases is it necessary to lengthen the clinical crown of a tooth?
Lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth may be prescribed to a patient for the following reasons:
- Aesthetic
- "Gummy" smile.
- Violation of the gum contour of one or more teeth.
- The natural crowns of the teeth are too short - after eruption the gums did not rise and remained “lowered” on the tooth.
- Under-eruption of one or more teeth in the dentition.
- To improve dental hygiene.
- Tooth-preserving
- The need to restore the length of teeth that was lost as a result of pathological abrasion (bruxism, increased tone of the masticatory muscles can lead to this).
- The presence of caries in the subgingival part of the tooth, i.e. below the gum line.
- The need to carry out and maintain high-quality tooth restoration using any of the methods, because to maintain periodontal health, such restoration should not go below the gum level.
- For high-quality prosthetics, in case of complete destruction of the tooth crown, for reliable “full” capture of the hard tissues of the tooth and to prevent future problems with the crown.
- As one of the components of complex surgical treatment of periodontal diseases for the removal of periodontal pockets.
What could be the consequences?
The problem most often manifests itself exclusively from an aesthetic point of view - psychological problems arise, the patient wants to correct the pathology as quickly as possible, especially if it is pronounced. That is, if the teeth and gums are healthy, then such discomfort is the only consequence of the problem.
If the short size of the crowns is caused by an abnormal structure of the teeth, problems with the gums, or abrasion of the enamel, then the consequence of this condition may be inadequate chewing of food, which will inevitably lead to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, premature aging of the face and the appearance of deep wrinkles near the mouth, and general deterioration dental conditions and even their loss.
Methods for lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth in modern dentistry
In modern dentistry, there are 4 methods of lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth:
- Orthodontic – involves “pulling” a tooth from the bone using a brace system, which can be installed on several teeth or on the entire jaw. This method is used when there is free space between antagonist teeth, mainly to lengthen the crown of one “under-erupted” tooth, the length of which differs from the rest. The disadvantage of this method is the need to wear braces, a long treatment time - 2-3 years, and the presence of a retention period.
- Surgical - is an operation to remove part of the gum and/or bone and give a new shape to the gingival contour. The main types of surgical intervention are gingivectomy or gingivoplasty, as well as bone resection.
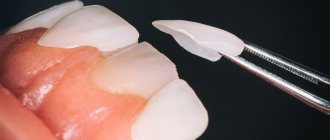
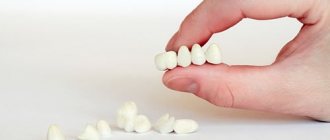
- Orthopedic - involves building up the crown of a tooth using orthopedic structures - veneers/lumineers or dental crowns, due to the installation of which the bite is raised, i.e. the tooth is lengthened from the cutting edge, without involving the gingival zone. This method of lengthening dental crowns is used in the presence of an erased cutting edge and in the restoration of significant defects in damaged and chipped teeth. The doctor will also choose this technique if the patient has short teeth, but at the same time an ideal gingival contour.
- The therapeutic method is composite augmentation of the incisal edge. Effective for minor chips and chips on single teeth.
This technique is used to “raise” the gum level when correcting a gummy smile, and before caries treatment and restoration that need to be performed below the natural gum level.
When should you see a doctor?
Dentist help is necessary if one of the incisors is in a high or low position. In children, this defect can disappear without any intervention when replacing milk teeth with molars. If different lengths of the front teeth persist despite a fully formed bite, you should consult a doctor.
You should also contact a specialist:
- when the enamel darkens,
- increased sensitivity of teeth,
- acute toothache,
- cutter mobility,
- formation of a sharp cutting edge.
The dentist will conduct an examination, determine the cause of the problem and help solve the problem.
What does a patient need to know about lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth?
In order for the tooth crown lengthening procedure to be successful, it must be carefully and comprehensively planned - this applies to all methods of its implementation. In planning such treatment, depending on the chosen intervention technique, several specialists will take part - a periodontist, a dental surgeon and/or an orthodontist, a dental therapist and/or an orthopedic dentist.
When planning to determine the volume and type of intervention, the following are taken into account:
- Current and future health status of periodontal tissues.
- The proportions of the tooth itself, the aesthetics of the patient’s smile.
- The structure of the roots of the tooth and the ratio of the length of the root and crown. It is IMPORTANT that its root part is no less visible.
- Condition of the jaw bone.
- Biological width is the distance from the bottom of the gingival sulcus to the crest of the tooth-bearing bone, and in order for the tooth to be stable in the future, its value must be at least 3 mm.
Therefore, lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth requires a very careful diagnosis, because the procedure should not disrupt the stability of the teeth on which it will be performed.
Diagnostics before tooth crown lengthening includes:
- Assessment of periodontal condition (diagnosis by a periodontist).
- Diagnosis by a surgeon – if a surgical lengthening method is proposed.
- Consultation and diagnosis with an orthopedist – in case of need for extensive restorations, prosthetics or the use of an orthopedic lengthening method.
- Consultation with an orthodontist and orthodontic diagnosis, if the crown will be lengthened by installing a brace system
One of the mandatory studies during diagnosis will be a 3D CT scan - computed tomogram, to determine the length, location of the tooth root and the condition of the jaw bone tissue.
What should you pay attention to?
The procedure must be performed flawlessly, as even a minor mistake can cause cosmetic defects and loss of tooth stability. It is important to conduct thorough preparation, including extensive diagnostics. It includes a computed tomography scan, consultations with an orthopedist, surgeon and periodontist. This will allow you to correctly assess the condition of the jaw tissue and determine the length of the roots.
When preparing for lengthening, all points are taken into account:
- bone condition;
- aesthetics;
- condition of periodontal tissues;
- the distance between the bone crest and the gingival sulcus (should not be more than 3 mm);
- anatomy of dental roots and their relationship to the coronal part.
What awaits a patient undergoing a clinical crown lengthening procedure?
Read about the orthodontic, orthopedic and therapeutic method of lengthening the crowns of teeth in the relevant sections - on orthodontics (installation of braces), prosthetics with crowns and veneers, and restoration. In this article we will focus on surgical lengthening of the crown of one, and more often, several frontal teeth.
Basically, in this case, they resort to gingivoplasty - a surgical operation during which part of the gum is removed along the gingival contour, often this intervention also requires the removal of part of the bone.
This manipulation is performed by a dental surgeon in a surgical office, on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia and, sometimes, sedation.
Such an operation is prescribed after a thorough diagnosis, in most cases - as a stage in complex treatment and the formation of an aesthetic smile.
- Before any surgical intervention, professional hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity are carried out to reduce infection in the oral cavity and speed up healing.
- The patient is given anesthesia.
- After which, if resection (removal) of a part of the bone is required, the mucoperiosteal flap is peeled off and an osteotomy is performed. A new gingival contour is formed, which is located above the previous one.
- The wound is sutured and a gum bandage is applied.
- In the postoperative period, for a speedy recovery, the patient is prescribed antiseptic rinses and painkillers, and a course of antibiotics may be prescribed. It is necessary to limit physical and chewing activity.
- The stitches are removed after about 7-10 days.
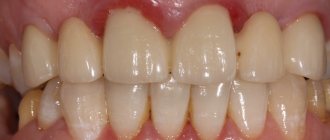
- Immediately after the wound has healed, a temporary restoration or prosthetics is performed, and after a few months the temporary structures are replaced with permanent ones.
- Complete restoration of the new natural gum margin occurs in 1-3 years.
Preparation for the procedure
For the procedure to be successful, an examination must be carried out before it begins. It includes an assessment of the structure and condition of the tooth roots, their relationship with the crown, the condition of the jaw bones and gum tissue. The patient’s oral cavity is also examined for carious lesions and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
For more effective diagnosis and treatment, an additional consultation with an orthopedic dentist, periodontist or surgeon may be required. A CT scan is also performed to see the length and location of the roots hidden under the gum tissue. The last stage of preparation is professional teeth cleaning and antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
Contraindications to lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth
In some cases, after weighing all the pros and cons, the dentist may refuse to lengthen the patient’s dental crowns.
The following reasons may serve as the basis for this:
- After tooth crown lengthening, the appearance and health of adjacent teeth will deteriorate.
- Regardless of the lengthening, restoration of this tooth is still impossible.
- Insufficient biological width.
- A tooth with a short crown has a short root.
- During orthodontic lengthening, there is no space between the tooth that is planned to be lengthened and the opposing tooth.
- The ratio of the effort required to lengthen the crown of a tooth and its value is not in favor of preserving the tooth.
- The patient is unable to maintain the required level of periodontal health.
Contraindications
Lengthening is not suitable in some cases, so dentists do not recommend surgery in the presence of the following conditions:
- the tooth has a short root;
- the biological width of the dental element is not enough;
- in cases where the expended efforts and resources are not justified and it is easier to carry out prosthetics;
- there is not enough space between the tooth and the antagonist;
- if the appearance of the tooth or adjacent elements deteriorates.
Professional dentists determine the feasibility in each case individually.
The main stages of the teeth extension procedure
The tactics chosen by the dentist when extending teeth directly depend on the degree of destruction of the dental crown.
Partial tooth damage
In cases where only partial damage is detected on its surface (small chips, cracks, thinning of the enamel), as well as when there is a need to eliminate wide gaps between adjacent teeth, the tooth is restored with composite materials.
Severe damage
In cases where the tooth is too damaged, extensions are made by implanting a pin into the tooth root and applying composite materials to form the tooth.
Stage 1 – professional teeth cleaning
At the first stage of treatment, the patient undergoes professional teeth cleaning, dental tissues affected by caries are removed and the canals are treated.
Stage 2 – application of reflective material and polishing
After this, a light-curing material is applied layer by layer to the remaining tooth tissue (or to the pin), and each portion of it is illuminated with a special lamp. After restoration of damaged tissues, the extended area is grinded and polished using paste and special brushes.
In most cases, tooth augmentation is carried out using the direct method, that is, all activities related to the restoration of dental crowns are carried out directly in the oral cavity of the client of the dental clinic.
Moreover, to restore a tooth, only one visit to the doctor is required.
Indirect restoration is performed only in situations where there is a need to manufacture additional orthopedic structures (pins, inlays) in a dental laboratory.
Postoperative recommendations
After the teeth lengthening procedure, the following recommendations should be followed:
- follow all doctor's instructions to prevent infection;
- Avoid spicy, sour, solid foods that can irritate or injure tissue;
- stop smoking;
- do not overheat in the sun, in a bath or sauna, postpone taking hot baths;
- minimize heavy physical activity;
- perform oral hygiene with caution;
- treat the oral cavity with antiseptics.