Tooth displacement: reasons
The median straight line, which divides the face into two halves, should coincide with the interincisal median lines - that is, with those lines that can be conditionally drawn between the front teeth. All teeth should be symmetrically located relative to this line. If at least one tooth moves away from these lines, this is a malocclusion. In addition, there should be no increased spaces between the teeth; they should not overlap each other in the dentition.
The question of why teeth shift has long been of interest to orthodontists. In the 18th century, the French physician Pierre Fauchard, personal dentist of Louis XV, in his book “The Dentist-Surgeon, or Treatise on the Teeth” (1728), recommended tying abnormally growing teeth with silk threads to a strip of metal. At the end of the 19th century, Edward Engle proposed a classification, diagnostic methods and an apparatus for correcting occlusion, which was sold in American catalogs for about a hundred years - until the 1980s.
As doctors have established, heredity plays a large role in the occurrence of tooth displacement - if one or both parents had bite defects, then there is a high probability that they will appear in their children. In addition to heredity, the following reasons for displacement are distinguished:
- too late eruption of both milk and permanent teeth;
- disruption of the process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones - for example, very early removal of a baby tooth;
- lack of space in the jaw arches (often leads to crowding of teeth);
- developmental anomalies of one or both jaws;
- abnormalities in tooth size;
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint;
- injuries to teeth and jaws.
In adults, tooth displacement can also occur due to injury or due to tooth loss or extraction. Neighboring teeth begin to shift towards the empty space, forming a malocclusion. This is one of the reasons why dentists, when teeth are lost, strongly recommend restoring them with prosthetics.
Why do teeth shift?
The most common reason is a violation of the integrity of the dentition
. As a result, antagonist teeth cease to participate in the chewing process, and the load on other (working) teeth increases. The contact of the teeth (occlusion) is disrupted and becomes traumatic, destroying the ligaments and stretching the collagen fibers that hold the tooth. A tooth that does not have contact when the jaws are closed begins to move vertically. So, if the lateral upper teeth are missing, then the lower ones move vertically upward. And if there are no lower teeth, the upper ones are displaced. For large defects (6 or more missing teeth), the movement is strictly vertical. But almost every tooth has a main and secondary antagonist. They prevent the tooth from moving strictly vertically. With small defects (1-3 teeth), there is also a tilt towards the lost units. The displacement of teeth after extraction becomes more pronounced the longer prosthetics are delayed. Therefore, dentists recommend restoring the dentition without delay.
Other reasons:
- Caries of occlusal surfaces
(points of contact when closing the jaws)
The more the crown is destroyed, the less the tooth participates in the chewing process, up to its complete exclusion from it. Then the displacement mechanism develops according to the same pattern as with dentition defects.
- Increased enamel abrasion
A change in tooth height, even by one or two millimeters, changes the entire articulatory picture, disrupting the occlusion and leading to the same results as in the first two cases.
- Periodontal disease
The periodontium is a ligamentous-muscular apparatus that holds the tooth in its socket. With periodontitis, the ligaments weaken and cannot hold the teeth in their original position. They begin to stagger and “move apart” to the sides. A classic example of combined movement during periodontal inflammation is the fan-shaped discrepancy of the upper frontal teeth.
- Wisdom teeth
They begin to grow after the dentition has formed. An obstacle in the form of a neighboring tooth can stop growth, or turn the “eight” to the side. Abnormally located teeth are not in the bite and violate the occlusion. An impacted (unerupted) tooth can cause the front teeth to shift and become crowded.
- Wisdom teeth removal
One of the complications is tooth displacement after wisdom tooth removal. Extraction can disrupt the occlusion by moving the adjacent tooth, the “seven,” to the vacant space.
Types of tooth displacement
While everything is quite clear about why teeth shift, many people are confused about the types of this problem. All bite defects are divided into 3 large groups.
- Violation of the position of the teeth: normally there are very narrow spaces between the teeth, and each tooth, except the last in the row, has 2 contact points with its neighbors. If there are enlarged spaces (tremas, diastemas) or teeth are crowded, then this is a defect that needs to be corrected - otherwise it will lead to problems with the gums and increased tooth wear,
- Violation of the development of dentition - they can be either narrowed or expanded.
- Abnormalities affecting the size or position of the jaws. These include:
a) cross bite - the jaws close in a cross direction horizontally, i.e. the teeth overlap;
b) mesial bite - the lower jaw protrudes forward;
c) distal bite - the upper jaw protrudes forward.
If any tooth has changed position as a result of injury or removal of an adjacent tooth, this is also a malocclusion that can be corrected by orthodontists.
Causes of dislocations
Dislocation always occurs under the influence of a directed force, the source of which is:
- a blow to the tooth during a game, a fall, a fight, an accident, an industrial accident;
- the load acting on the tooth when chewing bones, unshelled nuts, or opening beer bottles with the teeth;
- incorrect tooth extraction technique;
- pressure on a moving tooth when biting hard food.
When dislocation occurs, the position of the tooth root in relation to the walls of the socket changes, periodontal fibers are completely or partially torn, and the neurovascular bundle is damaged; often a dislocation is combined with a fracture of the tooth crown or maxillofacial injuries. Based on the nature of tooth displacement, incomplete, complete and impacted dislocations are distinguished.
Correction of misaligned teeth
What to do if you see, for example, how the teeth on the lower jaw have shifted?
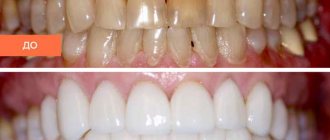
It seems to many that it is no longer possible to correct the situation in adulthood - the teeth will still return to the wrong position, and besides, correcting the bite is long, difficult and unaesthetic. Fortunately, orthodontists today are successfully correcting misalignments in adult patients. To do this, they use 2 orthodontic systems, which, using the pressure of a calculated force, carefully move the teeth to the correct position.
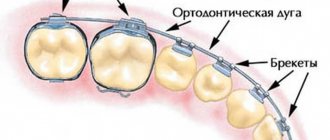
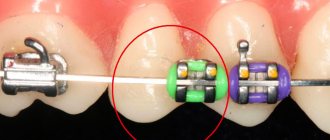
- Braces
A classic non-removable system that consists of a metal arch, braces - elements that are fixed to each tooth, and locks or ligatures that secure the arch in the braces. Today, these systems have become much more compact and comfortable, and we are no longer talking about long years of correction, since the average treatment period is only 1.5–2 years. Doctors have metal, ceramic, sapphire and combined systems at their disposal. There are also lingual braces - they are fixed on the lingual side of the teeth and are not visible when you smile. - Aligners
A removable system of aligners developed about 3 years ago that are worn on the teeth. For each patient, based on photographs and impressions of the jaws, an individual set of aligners is created, which the patient himself changes according to a schedule drawn up by the orthodontist. Unlike braces, aligners can be removed for 2 hours a day to eat and brush your teeth.
However, in any case, after removing the orthodontic system and completing the bite correction, a period of retention follows - when the patient wears retainers that prevent the teeth from returning to their previous position.
In our Center, we apply the principles of an integrated approach when planning treatment.
For the process to be successful, the patient receives consultation from several specialists. The process involves an orthodontist, an implantologist, and an orthopedist. They draw up a joint treatment plan, taking into account the volume of the bone, the distance between the teeth for the implant and the crown. If you do not take into account these nuances, you will have to re-install braces.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
It is important to consider how long ago the tooth was removed:
- If a tooth has been missing for a long time, and the neighboring ones have changed position and left no room for an implant, orthodontic treatment is aimed at freeing up space for an artificial root and crown.
- If implantation is planned after the braces are removed, a spring is placed on the adjacent teeth to prevent them from approaching each other and to leave space for the implant.
- If an implant is already in place and its position interferes with tooth movement, orthodontic treatment becomes more difficult. When trying to move an artificial root, there is a risk of its rejection, the development of inflammation, and tissue injury.
What is dental transposition?
So, all the described problems that you observe in a child or in yourself: improper growth of teeth, teeth out of place - this is transposition of teeth
.
Transposition of teeth in dentistry is a situation when neighboring teeth change their places during the process of eruption. For example, the first premolar erupts at the site of the canine, and the canine, respectively, at the site of the premolar.
Transposition of teeth is a fairly rare occurrence. It occurs in both men and women. Transposition can be unilateral, but there are also bilateral options when the teeth are swapped on both sides. Strangely, I personally have encountered the right-sided version of the anomaly in the vast majority of cases.
Most often, the process of transposition involves the upper canine and first premolar, which can partially or even completely exchange not only crowns, but (!) also roots. Other forms of anomaly, such as rearrangement of the canine and lateral incisor, are extremely rare.
Among the causes of tooth transposition in the literature, the most often described are:
- Hereditary predisposition, which is apparently associated with the atypical position of the tooth buds
- Violation of the order of change and eruption of teeth
- Injuries
Diagnosis of transposition is based on clinical examination and X-ray examination. The most preferred method would be computed tomography (CBCT), which allows the most comprehensive and comprehensive study of the situation of abnormal tooth growth.
In most sources, “destructive” methods are most often proposed as possible treatment methods: from grinding, veneers, covering teeth with crowns - to tooth extraction. Orthodontic correction options are rarely mentioned. This is understandable - the process of moving teeth from an incorrect position to the correct one is always long, complex, and requires the doctor to have certain skills, experience and patience, and strict control at all stages of treatment of transposition. And the risk of complications (gingival recession with exposure of the neck of the tooth, root resorption) is still high. However, orthodontic movement will be a pathogenetic treatment option, and therefore the most correct one. It will allow you to achieve the maximum result from an aesthetic and functional point of view.
Possible consequences
Have you noticed that your front tooth has begun to protrude slightly beyond the row? Do not delay visiting a doctor, as malocclusion is very dangerous. When an incisor or canine is displaced, the following problems are often observed:
- chewing function is impaired,
- the risk of gastrointestinal diseases increases,
- a diastema is formed,
- gum tissue becomes inflamed.
Don't wait for a significant change in the position of the crown - make an appointment with your dentist at the first sign of a problem.
Content:
- Why is there a problem?
- Other reasons
- Is it necessary to remove a loose tooth?
- How to save a loose tooth
Only children with primary occlusion can react calmly to a loose tooth. For everyone else, this is a serious problem that requires immediate dental attention. If measures are not taken in time, you may encounter partial edentia - the movable unit will simply fall out at some point, which will negatively affect the functioning of the maxillofacial apparatus and, of course, the appearance of the smile. You should not decide on your own whether to remove a loose tooth. Only a qualified dentist, after an in-person examination, can tell you what to do correctly in a particular situation. Today, thanks to a large number of innovative treatment techniques, doctors most often manage to save even loose units.
Why is there a problem?
Among the reasons causing loose teeth:
- Periodontitis. With this disease, even healthy canines, molars and incisors lose their former stability in the socket. Other characteristic symptoms of the disease are the appearance of bad breath and bleeding gums.
- Periodontal disease. A diagnosis in which atrophy of the jaw bone tissue is detected. The gums become inflamed, red, and swollen. This subsequently leads to loosening of individual units.
- Periodontitis. A condition that affects the roots of teeth. It is in them that the destructive process begins. The pathology is very insidious and, in the absence of adequate therapeutic measures, leads to the need to remove a loose tooth.
- Flux or periostitis of the gums. It manifests itself as an accumulation of purulent masses in the tissues of the periosteum. For this reason, the roots lose their ability to be firmly held in hard tissues, the hermetic contact is broken - loosening occurs.
- Cyst. A fairly common dental problem. Affects the area adjacent to the root. If drug correction does not provide positive dynamics, the surgical method is used. An advanced cyst affects a large area of the jaw, which has a bad effect on the stability of teeth and the well-being of a person in general.
- Granuloma. Inflammatory formation at the apex of the tooth root. In fact, this is an advanced and complicated cyst. The disease has the following symptoms: unsteadiness of individual units, sore gums, swelling, decreased overall performance.
Is it necessary to remove a loose tooth?
In some situations this procedure cannot be avoided, but the main thing here is not to rush. Before drawing up a treatment plan, the dentist conducts an in-person diagnosis - examines the oral cavity, takes X-rays and studies the condition of the roots. The less damage is detected, the greater the chances of successful prosthetics. You won’t be able to do without deletion if:
- pronounced mobility;
- the infectious process is severely advanced.
At the same time, patients at dental clinics should understand that doctors are doing everything possible to maintain the integrity of their bite. Therefore, it is important to trust your doctor and strictly follow all his instructions. This approach will allow you to get excellent results in a short time.
How to straighten teeth without braces?
Children's teeth trainers
Trainers act directly on the perioral muscles, thereby creating conditions for the formation of a correct bite. Children's trainers contribute to:
- normalization of breathing, swallowing, speech, chewing functions;
- restoration of muscle balance in the maxillofacial area.
Due to this, conditions are created for the normalization of jaw growth, the formation of dentition and the functions of the dental system in the removable and emerging permanent dentition.
Trainers are removable orthodontic devices made of silicone. They include:
- “tongue” is a special protrusion to put the tongue in the correct position;
- lip bumpers – silicone pads to protect teeth from excessive lip pressure;
- tongue stopper – prevents the tongue from inserting between the teeth;
- special thickenings in the area of chewing teeth - to reduce the load on the joint;
- breathing holes.
Pre-orthodontic trainer
This is a universal removable orthodontic device that covers two jaws. The trainer method includes the following devices.
- Soft (blue, transparent or green).
Has greater elasticity to adapt to the mouth. It has holes in the front section, which allows it to be used when breathing is difficult. Helps normalize breathing, swallowing and eliminate hyperactivity of the chin muscle. The trainer is used during sleep and during the day (at least 1 hour) for 6-8 months. Then it is replaced with a hard trainer. - Hard (pink or red).
It has the same design as the soft trainer, but without breathing holes. Made from more elastic material. It corrects the position and shape of the teeth. The duration of treatment is from 6 to 12 months.
LM activator
In its design, the LM activator resembles a preorthodontic trainer. It is presented in two modifications:
- low model – for correction of deep bite;
- high model – for the treatment of open bite.
There are 13 sizes of the low model and 11 of the high model. This allows you to accurately select a model for each patient.
“Myobrace” device
This is a removable orthodontic device with a two-layer design:
- outer layer – soft flexible silicone;
- internal elastic frame.
Myobrace devices are available in six sizes. When using them, maximum straightening occurs in the frontal region.
Preventive myogymnastics
The muscles surrounding the dentition (tongue, lips, cheeks) can either contribute to the normal development of the bite or disrupt it. With the help of special gymnastics, muscle function is restored and the development of malocclusions is prevented. Myogymnastics is suitable for children aged 4-7 years, when the child can understand what is required of him and perform the exercise.
Preventive myogymnastics performs the following tasks:
- restoration of physiological tone of muscle tissue;
- normalization of the functions of the muscles involved in the movements of the lower jaw;
- normalization of the function of the orbicularis oris muscle and tongue muscles;
- adaptation of the joint and muscles to the orthodontic apparatus.
The child performs exercises such as protruding the lower jaw, clenching the teeth, and massaging the lips. The nature of myogymnastics depends on the muscle group that needs to be affected. However, you should adhere to the general rules:
- exercises must be done systematically and regularly (several times every day);
- the intensity of muscle contraction should be sufficient, but not excessive;
- muscles should be tensed slowly and smoothly;
- each exercise should be performed several times until a feeling of slight fatigue appears;
- the number of exercises and their duration increase over time.