Causes of unpleasant odor
An unpleasant odor can occur for various reasons: from stress suffered by a child to a disease of the digestive system. To eliminate an unpleasant odor, sometimes you need to carefully observe oral and dental hygiene. From a very early age, that is, when the baby’s first baby tooth appears, the child should be taught to brush his teeth twice a day.
If the smell from the mouth becomes persistent, then the child should be shown to a dentist, who will check the condition of the child’s gums and teeth. If the teeth are healthy and the gums do not bleed, the dentist will give a referral to a specialized specialist to diagnose the causes of the child’s bad breath.
What diseases cause purulent sputum?
Purulent sputum when coughing can appear for various reasons. Mostly this is caused by serious problems in the body, so you should not treat the symptom yourself. Why does a purulent cough appear:
- pneumonia;
- disturbances in lung function;
- bronchitis;
- tuberculosis;
- asthma;
- tumor.
A healthy person may expectorate a small amount of mucus per day. Normally it is transparent and odorless. Depending on its color, sputum indicates the presence of certain diseases. For an accurate diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo the necessary tests. What does yellow-green sputum indicate:
- allergy;
- pneumonia;
- untreated flu;
- asthma;
- bronchitis;
- pharyngitis;
- lung abscess.
Sputum that is rusty, red, or brown:
- pulmonary edema;
- tuberculosis;
- pneumonia;
- lungs' cancer.
A cough with white sputum indicates the presence of a fungal infection or tuberculosis. It is important to remember that self-medication is contraindicated when coughing with purulent sputum. You should immediately seek help from a doctor.
- Cough with sputum - how to treat in adults and children
Types of bad breath
Parents should pay attention if the child's mouth emits a specific odor, which may be:
- acetone, appearing against a background of high temperature. This smell should especially alert parents. The child should be immediately shown to a doctor, as it appears when acetonic syndrome occurs, which is a serious disease;
- A putrid odor occurs due to poor oral hygiene, a sore throat, tonsillitis or pharyngitis. With these diseases, the oral cavity, including the tongue and tonsils, become covered with a white coating, which also appears in cases of stomatitis and caries, and increased stomach acidity. The child should be seen by a doctor for advice and to understand how to act in case of such diseases.
- A purulent odor occurs during chronic inflammation in the child’s nasopharynx, when the tonsils become covered with purulent plaque, and purulent plugs form in the child’s throat, emitting a purulent odor.
- A sour smell occurs when the stomach is too acidic or when inflammatory processes occur in it. The second cause of sour odor is reflux, when gastric juice enters the baby's esophagus.
- A sweetish smell indicates liver disease or the development of cirrhosis.
- A chemical smell appears when there is a disease of the digestive system, especially when there is a disease of the gallbladder.
- The smell of chlorine occurs when gums bleed and periodontal disease develops. In this case, it is necessary to check the condition of the child’s gums and teeth.
Oral diseases
The appearance of an unpleasant rotten or rotten odor, both with and without a cough, may indicate oral diseases or insufficient hygiene. Irregular brushing of teeth leads to the appearance of plaque on them, as well as rotting food particles that remain in the small crevices of the oral cavity even several hours after eating. The unpleasant odor from the mouth becomes especially pronounced after sleep.
Other causes of odor include the following oral diseases:
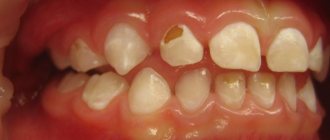
- Stomatitis,
- Caries,
- Gingivitis,
- Tartar, formed from plaque due to insufficient oral hygiene,
- Gum abscess,
- Periodontal disease.
Pathologies of the oral cavity often become causes of disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. This is possible because, passing through diseased teeth, food carries some pathogenic microorganisms into the stomach.
- How to treat a dry cough in an adult that lasts for a long time without fever
ENT pathology
Almost all ENT diseases arise as a result of exposure to pathogenic microorganisms on the mucous membrane. These can be either viral or bacterial, most often coccal, infections. When they infect the human mucosa, they actively multiply in it. The result of the vital activity of pathogenic microflora is the appearance of purulent inflammation.
The main ENT diseases that provoke the appearance of cough with an unpleasant odor and pus are:
- Sinusitis. Pus accumulates in the maxillary sinuses and remains there constantly,
- Tonsillitis. It is characterized by inflammation of the tonsils and the appearance on their surface of accumulations of pus, consisting of dead bacteria, dead epithelial cells and leukocytes.
The appearance of small, foul-smelling lumps when coughing most often indicates tonsillitis. With sinusitis, pus is most often excreted in sputum.
Diabetes
The appearance of a cough with a specific odor from the oral cavity is also possible with diabetes. In this case, the cough itself occurs due to constant dry mouth that accompanies the pathology, and the foul odor is a reaction to dehydration.
In diabetes mellitus, cough may be accompanied by the aroma and taste of acetone. This phenomenon occurs when the mucous membranes are dry due to fasting or lack of fluids, especially with excessive sweating.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A foul odor, as well as a cough, can occur in a person due to slow digestion, low acidity of gastric juice, and also due to rotavirus infection. The smell of rotten eggs occurs when coughing and belching due to fermentation and rotting of undigested food. Coughing in such cases is often accompanied by the flying out of small lumps of rotting food. The pathology may also be accompanied by vomiting.
Sour belching and a cough with a sour smell may indicate gastritis or a peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum.
Strange smell from the mouth during an acute respiratory viral infection
When an acute respiratory viral infection occurs against a background of high temperature, a purulent odor emanates from the child’s mouth. This occurs because the tonsils and tongue are covered with a coating that emits the smell of pus. With an inflammatory process in the lungs or sinusitis, halitosis may worsen, which disappears after the child recovers. Rinsing your mouth with antiseptic solutions will help speed up recovery.
Causes of cholitosis in children
Halitosis can develop in children of different ages and for various reasons: from poor oral and dental hygiene or the presence of a foreign object in the baby’s nostril. A doctor who examines a child can determine several causes of cholithosis:
- an incorrectly chosen diet, from which it is necessary to exclude fatty, fried foods flavored with garlic and onions;
- the stressful situation experienced by the baby causes dryness in the baby's cavity, and can cause cholithosis. In case of stress, the child should be given acidified water to drink or the child should be given a slice of tangerine so that he can suck on it;
- unpleasant smell in the morning. Bad breath after sleep is caused by the fact that a sleeping child does not produce saliva, which is a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. After the morning hygienic brushing of teeth, the smell disappears.
Why does a child have bad breath, what does this phenomenon mean?
Osostomy never occurs by accident; there is always some reason behind it. Above we discussed some of them, based on the nature of breathing. Now we propose to consider several factors leading to this disease. Knowing them will help you prevent the next occurrence of halitosis.
Little moisture in the body
If the baby does not consume enough fluid, this negatively affects the functioning of all organ systems. In particular, saliva becomes more viscous, which is why it poorly wets food, and it cannot be digested normally. This provokes disruption in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Among other things, the salivary compartments themselves, due to their viscosity, are not swallowed completely, but remain on the root of the tongue, where they oxidize and emit a corresponding odor.
Newborns receive a sufficient amount of moisture from their mother’s milk; only in hot weather they need additional water. At 4-5 years old, a child needs to consume about one and a half liters of fluid daily.
Insufficient hygiene
Some parents neglect this procedure until the baby's entire set of teeth erupts (otherwise, what's the point of brushing them). But this logic is incorrect: even if only one incisor appears, it also needs to be looked after. You can do this until you are 2-3 years old; perhaps the baby will not immediately get used to the process and will have to work hard. But soon this will become a regular thing for him, just be patient. Then treatment for the child’s terrible bad breath will not be necessary.
In the third year of life, it is necessary to show children the correct technique for brushing their teeth, or even better, to master it themselves: it is easier for little ones to learn when they have the opportunity to repeat after their parents.
Poor nutrition
You need to understand that a child’s body cannot absorb everything that adults consume. He should not be given too fatty, fried or spicy food. Provide nutritious meals, increase it appropriately and do not forget about maintaining a drinking regime.
Stressful situation
The younger the child, the more difficult it is for him to experience strong emotions, especially fear. It also causes halitosis, as the oral cavity becomes very dry. This can be fixed quite easily: you just need to give the baby a little water. For better salivation, you can add a few drops of lemon to it, and soon the freshness of your breath will be restored.
Unpleasant smell in the morning
This phenomenon is also familiar to adults; it is again associated with a lack of moisture in the mouth during sleep. Reducing the intensity of salivation is a normal and natural process. You just need to brush your teeth in the morning for this trouble to go away.
Chronic rhinitis
Some children suffer from constant nasal congestion: their breathing is often difficult, and a lot of dried mucus accumulates inside. The latter provokes halitosis, but this is not so scary. You just need to humidify the air more often, ventilate the rooms and remove dust.
What to do?
If a child has persistent bad breath, he or she should be shown to a doctor for a comprehensive examination. Usually, when you establish a drinking regime and exclude sweet foods from your diet, the unpleasant odor disappears. Parents should be alarmed by the unpleasant odor emanating from the baby’s mouth, which should be immediately examined by a doctor.
Causes of halitosis.
In the mouth.
There are more than 600 types of microorganisms in the average person's mouth. About a hundred of them can produce a stench even when grown in a laboratory.
Solobacterium moorei is a microorganism that is recognized by some researchers as the most active producer of stench.
This stench is produced mainly due to the decomposition of proteins into individual amino acids with their further decomposition into odorous substances.
For example, the decomposition of cysteine and methionine produces hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan, respectively. Volatile sulfur compounds have been shown to be statistically related to the degree of halitosis and usually disappear with adequate treatment.
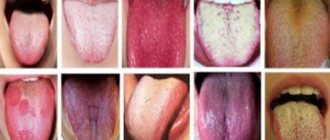
1.1. The tongue is where odor in the mouth appears in most cases.
A significant amount of natural microflora is localized in the villi and folds of the back of the tongue, especially on the back (root of the tongue).
This part of the tongue is relatively poorly cleaned and the bacterial population multiplies here on food debris, dead cells and nasal mucus.
Such a nutritional environment on the back of the tongue is ideal for anaerobic bacteria that produce a specific gas, the components of which are:
- putrid odor of indole substances,
- skatola,
- polyamines;
- “rotten egg” smell of volatile sulfur compounds (hydrogen sulfide, methyl mercaptan, allyl methyl sulfide and dimethyl sulfide).
Cleaning the tongue.
Chewing gum, sprays, rinses, etc. can only temporarily muffle the odor produced by bacteria on the root of the tongue, but cannot eliminate halitosis because they do not eliminate its cause.
To neutralize the release of the above-mentioned volatile sulfur compounds, it is necessary to remove plaque from the back of the tongue along with the aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms contained in it.
Typically, a tongue scraper or toothbrush is used for this.
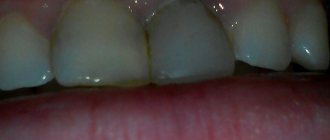
1.2. Gum diseases (periodontitis).
There is some controversy regarding the role of gum disease in the formation of bad breath. However, advanced periodontitis is always the cause of halitosis.
The waste products of anaerobic bacteria developing in periodontal pockets have a disgusting odor and, as has been clinically proven, lead to severe halitosis.
Removing calculus (tartar) and loose gums has been proven to significantly freshen the smell of your mouth. It is desirable that this event be accompanied by subgingival scaling, root planing and tissue irrigation with antimicrobial agents.
1.2.1. Particular attention should be paid to pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth.
- inflammation of the gums around the eighth tooth that has not fully erupted. After the exacerbation is relieved, it is reasonable to remove these teeth.
1.2.2.
Fetid sore throat and
Vincent's stomatitis.
Tonsils (chronic tonsillitis).
In general, suppuration from the tonsils is considered statistically insignificant in the occurrence of halitosis (only about 5%). About 7% of the population suffers from tonsillar plugs, small pieces of calcified material in the folds of the tonsils.
They smell extremely unpleasant and when released can cause halitosis.
Nasal passages.
The nose is the second major cause of halitosis due to sinusitis and foreign bodies. In this case, the smell rather comes from the nose and is different from bad breath.
Esophagus.
The cardiac valve between the stomach and esophagus may not close well when the stomach herniates into the esophagus, allowing acid and stomach gases to leak into the mouth. With diverticulosis (false pouch) of the esophagus, deposited food debris can cause halitosis.
Stomach
Rarely is the cause of halitosis; belching should not be confused with the latter. With reflux (backward release of stomach contents), an odor may appear.
Liver.
Hepatic respiration (fetor hepaticus) is a condition associated with portal hypertension and liver failure. In this case, odorous digestive products (mercaptan, ammonia, ketones), instead of being destroyed in the liver, enter the lungs and, accordingly, into the exhaled air.
The breath has a sweetish, fecal tint. In this case, the fight against symptoms is no longer relevant.
Lungs and bronchi in acute and chronic inflammation and tumors (carcinoma).
Other diseases:
- renal failure,
- diabetes,
- metabolic diseases.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of cholithosis, the child must follow some preventive measures:
- brush your teeth twice a day (morning and evening);
- parents should organize a diet that contains vegetables and fruits containing phosphorus and calcium;
- observe drinking regime;
- be systematically checked by a dentist and, if you have sick, damaged baby teeth, have them treated, since rotten teeth can be a source of bad breath from the child’s mouth.