Symptoms
The feeling of suffocation in the throat rarely comes alone.
Most often it is accompanied by other symptoms, sometimes no less unpleasant. Let's find out what these additional symptoms are. During a conversation, a persistent feeling of discomfort appears. It is difficult for a person to speak; there is a feeling that something in the throat is preventing this.
Feeling of a lump in the throat. Moreover, this “lump” not only interferes with speaking, but also makes it difficult to swallow and interferes with breathing.
In the video, the appearance of a lump in the throat:
When swallowing, painful sensations appear. Sometimes this even leads the patient to a complete refusal to eat due to too uncomfortable sensations during this process. Such refusal is especially dangerous for children, as it leads to weakness and rapid weight loss in the child.
You may feel heaviness in the back of your head, headache, and even loss of consciousness. The last symptom is expressed if there are disturbances in the circulatory system or central nervous system. Symptoms of pharyngeal neurosis may also include numbness and partial or complete absence of the pharyngeal reflex.
A feeling of numbness in the limbs is a symptom that is also sometimes associated with a feeling of suffocation. This symptom develops due to circulatory problems or neurological causes.
All additional symptoms can help the doctor make a diagnosis faster and more accurately and begin treatment. Therefore, at an appointment with a specialist, voice all the symptoms that worry you. And the doctor will be able to draw the appropriate conclusion from them.
Feeling of a lump in the throat with VSD
Very often you can find in people suffering from VSD the sensation of a lump in the throat. It's one thing when there is a logical, although there may be an unpleasant and frightening explanation, for example, a tumor or severe inflammation that causes a narrowing of the larynx. But what to do in cases where there is a lump, but there are no reasons for it, and turning to a variety of specialists gives the same result: the person who contacts them has no reason to feel a lump.
What are the symptoms of a lump in the throat?
This symptom of VSD, like a lump in the throat, appears completely suddenly. One fine morning there is a feeling that something is interfering, preventing you from swallowing and breathing deeply as usual. At the same time, five minutes ago everything was in order, but any ordinary or everyday situation, accompanied by a little excitement, an increase in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate - and now, the feeling that someone is squeezing the neck. All you have to do is drink a sedative, come to your senses a little, and your condition will return to normal. But in any other stressful situation, the feeling of a lump in the throat appears again.
Unpleasant sensations can be either constant or periodic. At the same time, the sensations may differ from person to person; it may be a tickling sensation, a tingling sensation, a feeling of squeezing, or the inability to swallow, whether it is saliva or solid food.
Sometimes the feeling of a lump can develop into a state in which a person may realize that he has forgotten how to swallow and cannot do it. Then it comes to a panic attack. So, over time, a fear of swallowing in general and eating solid food may develop.
Causes of a lump in the throat with VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia in itself is a nervous disorder; suffering from VSD, a person is constantly in panic and fear of something. This, in turn, is triggered by the release of large doses of adrenaline into the blood.
Which part of the body the adrenaline will choose to express itself is not clear. For some, this manifests itself in pain in the chest area, for others, the gastrointestinal tract suffers, and for others, they experience spasms of the laryngeal muscles, which is the very sensation of a lump in the throat.
It is worth remembering that no other disease, for example, an enlarged thyroid gland, osteochondrosis or aneurysm, gives symptoms similar to a coma, no matter what anyone says.
What could be bothering your throat?
People who first feel a lump in their throat first think of the worst, of course, cancer. What else could create such sensations of interference if not a tumor? And the more panic moods grow in a person, the stronger the lump is felt.
You need to know that the most important difference between a lump in the throat during VSD and any serious disease of the larynx, esophagus or other respiratory organs is that during sleep the lump is not felt at all. When I wake up, everything is fine too. But as soon as you get up and feel more energetic, the sensations return. The whole point here is that until the brain woke up, the body felt good, but as soon as the brain returned to working condition, it remembered that there should be a lump, and the patient felt it again.
It is the normal state of the throat in the first five minutes after waking up that should assure a person that the issue here is not some mythical disease, but the state of the nervous system.
How to treat a lump in the throat?
In fact, it is very difficult for any person suffering from VSD to admit to himself that the problem is not a disease at all, but a disorder of the nervous system. Treatment for coma is the same as for VSD therapy.
- Taking psychotropic medications that reduce panic attacks to a minimum and have a calming effect in a dosage that is relevant for a particular patient.
- An attempt to come to terms with the fear of death and liberation from oppressive terrible thoughts. You can seek advice on this issue from a psychotherapist, but you will have to work on yourself on your own.
The feeling of a lump in the throat will not go away on its own and will poison your life.
He needs to be treated. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
What happens in the body
What is suffocation? This is a difficulty in breathing. This condition can develop for a number of reasons, from harmless to requiring urgent medical intervention. The cause of suffocation may be problems from:
- respiratory tract,
- of cardio-vascular system,
- thyroid gland,
- nervous system.
The feeling of suffocation in the throat occurs due to severe irritation of certain groups of nerves located in the larynx.
- Compresses the throat (feeling of suffocation) - causes and treatment
If choking in the throat has causes related to the respiratory system, then most often it begins with swelling of the mucous membrane, which can be triggered by various factors. The most common are inflammatory diseases of the throat, allergies, irritation from polluted air. Allergic reactions pose a particular danger. Laryngospasm can be very strong, and there is a possibility of developing Quincke's edema with complete occlusion of the airways.
Most often, a feeling of suffocation in the throat appears due to inflammatory diseases. It could be a sore throat, pharyngitis or laryngitis. The swelling that accompanies these diseases narrows the airway, making it difficult for a person to breathe.
Inflammation can lead to irritation of the nerves responsible for muscle contraction, then a spasm develops, which also disrupts the free passage of air, and a feeling of suffocation appears.
Symptoms accompanying inflammatory processes
- A sore throat,
- Runny nose, cough,
- Increased body temperature
- General weakness
- Possible enlarged lymph nodes.
Periodic spasms of the throat, accompanied by choking, may be a sign of the development of myocardial infarction. The thyroid gland can cause a feeling of choking in the throat. This occurs with endocrine disorders, accompanied by its increase. As a rule, this is no longer the initial stage of the disease, so symptoms characteristic of damage to this organ are also present:
- increased irritability,
- cardiac dysfunction,
- problems in the gastrointestinal tract,
- weight loss or gain,
- deterioration of the condition of the skin, nails and hair.
Choking in the throat due to the thyroid gland can be caused not only by the pressure of the enlarged gland itself on the larynx, but also by inadequate reactions from the nervous system, because with diseases of this organ, the nervous system is the first to be hit. Attacks of choking in the throat can have causes associated with overload, both physical and psychological. With any overexertion, the body reacts with muscle spasms. If such spasms occur in the throat area, they are often accompanied by suffocation. The feeling of suffocation is also dangerous because it can cause severe fear in a person, leading to the development of a panic attack, which leads to even greater muscle spasm.
Women, as well as people with an anxious and suspicious character, are more susceptible to panic attacks. Any stress, work overload, conflict can lead to such a person’s emotional reaction resulting in a panic attack and severe muscle spasm.
Acute laryngitis - symptoms and treatment
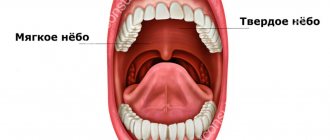
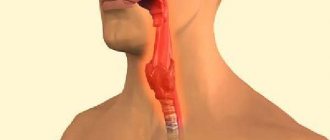
The larynx (Larynx) is a conventional boundary separating the upper and lower respiratory tract. This is a kind of musical instrument in the human body that gives voice. It is built on the principle of a movement apparatus - it contains a skeleton (cartilages of the larynx) and its connections (ligaments and joints). This frame has two bands of muscle (vocal cords) that run along the top of the windpipe (trachea). The movements and vibrations of these muscles allow us to speak, sing and whisper.
In addition to the voice-forming function, the larynx also performs a protective function. When we swallow, the larynx closes its opening so that food and liquids enter the esophagus rather than the airways [4].
Regardless of the cause, inflammation causes swelling of the vocal cords and narrowing of the space between them. Protein breakdown occurs, which leads to an increase in osmotic and oncotic pressure in damaged tissues. Due to the difference in pressure, fluid rushes into the damaged area, which leads to the appearance of edema. Changes appear in the mucous membrane of the larynx:
- Catarrhal (associated with inflammation of the mucous membranes): hypersecretion of the mucous glands, swelling, redness. Observed during viral infections.
- Severe swelling - with allergies.
- Infiltrative (accumulation of cells mixed with blood and lymph in the tissues of the body) - characteristic of neoplasms and chemical lesions (when exposed to acids, alkalis and other caustic liquids);
- Purulent - for bacterial infections [5].
In response to irritants, the mucous membrane of the larynx begins to produce mucus, which can also clog the respiratory lumen, like a plug. Mucus is produced by special cells called goblet cells. They are located in the mucous membrane and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells from infectious agents, allergens and irritants. This is why smokers suffer from a constant cough with sputum production. Increased mucus secretion in the respiratory tract is a marker of many common diseases, such as acute respiratory viral infections or allergies.
Due to swelling of the mucous membrane, the vocal cords thicken and cannot vibrate, the voice changes, becomes hoarse or disappears altogether. In severe cases, the ligaments can practically close, causing shortness of breath and noisy, hoarse breathing due to the inability to take a breath. This condition is called laryngeal stenosis, another name is false croup (from the Scottish “croup” - to croak). This life-threatening condition, which is characterized by a barking cough, is often accompanied by inspiratory dyspnea (difficulty breathing) and hoarseness of the voice. Usually observed in children aged 6-36 months, most often against the background of a viral infection: parainfluenza - 50%, influenza - 23%, adenovirus infection - 21%, rhinovirus infection - 5% [6].
Methods for treating a feeling of choking in the throat
To cope with the feeling of tightness in the throat, it is imperative to treat the underlying pathology. The choice of medications and procedures directly depends on the diagnosis.
So, if the functioning of the thyroid gland is impaired, iodine preparations must be prescribed . If autoimmune thyroiditis is diagnosed, therapy is more complex. In some situations, a person has to take hormonal medications for the rest of his life.
If the reason lies in damage to the cervical spine, it will not be possible to do without therapeutic exercises . The doctor may also recommend physical therapy - vacuum treatment, manual techniques, reflexology, laser therapy. Normalizing your lifestyle and following the rules of a healthy diet is of no small importance.
- Choking in the throat and neck area: diagnosis, causes, treatment, prevention
The most dangerous condition is the formation of a malignant tumor. In such a situation, it will not be possible to do without radiation and chemotherapy. In some cases, there is a need for surgical intervention.
When gastroenterological problems occur, treatment consists of following a special diet and using medications. However, if a hernia forms in the esophagus, surgery may be necessary.
With the development of inflammatory lesions of the otolaryngological organs, it is necessary to evaluate the nature of the disease - it may be of viral or bacterial origin. Based on the results of the studies, antibacterial drugs or other medications may be prescribed.
In addition to the main therapy, gargling with infusions of medicinal plants, preparations containing iodine or salt can be used. All of these products are distinguished by pronounced anti-inflammatory and healing characteristics. In some situations, warming compresses will help to enhance drug therapy.
If the feeling of tightness in the throat is due to psychogenic factors, therapy involves the use of medications and psychotherapeutic agents. If a patient is diagnosed with depression, he is prescribed antidepressants and tranquilizers.
If breathing problems occur that are associated with the appearance of panic attacks, measures are taken to eliminate the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
It is recommended to do breathing exercises on your own, which provides effective relaxation. To do this, you need to breathe with your stomach or use a bag, holding your breath for a certain time. The exact set of exercises will be selected by your attending physician.
When a coma occurs for the first time, you can perform several breathing exercises, trying not to focus attention on this condition. At the same time, it is important to control swallowing movements - they should not become more frequent. An additional remedy to improve the condition would be herbal infusion or tea. Subsequently, it is recommended to perform exercises for the muscle tissue of the neck and larynx.
How to get rid of the feeling of a lump in your throat
Not enough air - treatment methods
If it is difficult to breathe for physiological reasons, but there are no diseases, no special therapy is required. Many people are interested in what to do if breathing is a little difficult, but there are no serious disorders in the body. To improve your well-being, you should use simple methods (ventilation, humidification, taking sedatives, agreed with the doctor).
Patients who have difficulty breathing due to certain diseases are prescribed complex treatment. Main goals of therapy:
- eliminate foci of infection and inflammation;
- clear the airways;
- speed up the discharge of sputum;
- improve blood composition;
- stabilize the functioning of the heart muscle;
- normalize the condition of blood vessels.
To eliminate lack of air during breathing, specialists at the KRH Dental & Medical clinic use effective and safe medications and prescribe effective procedures. Each patient is guaranteed attentive attention and an individual approach. After the treatment is completed, recommendations are given to correct the lifestyle and prevent the recurrence of the pathology.
Causes of tightness in the throat
A feeling of tightness in the throat can appear under the influence of various factors, which are divided into 2 main categories - somatic and psychogenic. The first group of reasons is considered the most extensive and occurs most often.
- What is a “lump in the throat” and how to get rid of it
Inflammatory processes in the throat area
Any inflammation provokes swelling of the tissues, as a result of which a person develops a pressing lump in the throat. This process can be acute or chronic and indicate the development of laryngitis or pharyngitis. Also, the reason may lie in the appearance of follicular tonsillitis.
In some cases, the patient's condition worsens and paratonsillitis or an abscess develops. This situation poses a serious danger, since there is a risk of severe edema, which will create difficulties with the access of oxygen to the organs of the respiratory system.
Tumor formations
Constriction may be associated with the development of benign or malignant tumors. And if in the first case conservative methods of therapy are usually sufficient, then in the second the situation can be much more serious. For treatment to be successful, the disease must be treated at the initial stage of development.
In some cases, a feeling of choking in the throat is the only sign of a dangerous disease. However, in some cases additional symptoms occur:
- rapid fatigue of the ligaments during a conversation;
- difficulty swallowing;
- the appearance of hoarseness in the voice;
- bad breath;
- formation of bloody streaks in sputum;
- breathing problems;
- the appearance of shooting pain in the ear.
Most often, such problems are localized in the larynx, trachea or oropharynx. If you suspect the presence of tumor formations, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Thyroid dysfunction
With iodine deficiency there is a risk of damage to the thyroid gland. This organ increases in size and compresses the throat. This pathology is called goiter. The second name is Graves' disease.
To identify pathology, the doctor conducts an examination. In addition to visual signs, people experience decreased appetite, protruding eyes, and weight loss. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests and ultrasound are prescribed.
Also, a feeling of choking in the throat is sometimes associated with other lesions of the thyroid gland - inflammatory processes or increased production of thyroid hormones. These pathologies are also accompanied by a sensation of a foreign object in the throat.
Osteochondrosis
Quite often there is pressure in the throat with the development of cervical osteochondrosis. The causes of this disorder are most often associated with lack of movement, poor diet and bad habits.
Cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by pain in the back, head and neck. In some cases, the pathology even provokes nausea, vomiting, and pressure changes. Only a doctor can diagnose the disease.
To cope with the pathology, long-term treatment is carried out. Therapeutic gymnastics and massage are highly effective. You definitely need to watch your posture. For sleeping, you should use an orthopedic pillow and mattress. In difficult cases, it is not possible to do without medications.
Digestive system diseases
If your throat is choking, the reasons may be due to gastroenterological problems. If this symptom appears after eating, there is a very high probability of developing pathologies of the digestive system.
As a rule, these disorders are accompanied by other symptoms. These include belching, heartburn, sour taste in the mouth and stomach discomfort.
Reflux
A sore throat is often caused by reflux. When this chronic disorder occurs, acidic contents enter the esophagus from the stomach. As a result, symptoms such as belching, nausea, and flatulence occur.
To cope with the violation, experts advise reviewing your menu. First of all, you need to give up coffee, chocolate, carbonated drinks and any other irritating foods. Losing weight and following a diet is important.
Esophageal hernia
If the throat is compressed, the reasons may lie in the occurrence of a hiatal hernia. This disorder is associated with excess weight, constipation, lifting heavy objects and severe coughing. Also, a provoking factor can be severe stress, which leads to muscle spasms. In such a situation, it is enough to drink a glass of warm milk with honey.
A hernia is often accompanied by chest pain. In such a situation, the doctor should do a cardiogram to rule out heart disease. In some cases, in addition to a lump in the throat, hiccups occur.
Traumatic injuries
If your throat is tight and it is difficult to breathe, the cause may be damage to the esophagus or larynx. So, rough food can injure the esophagus. In addition, the reason may lie in improper gastroendoscopy. As a rule, such symptoms disappear on their own after about a week.
Allergy
There is a lump in the throat that seems to be suffocating due to Quincke's edema. This condition is life-threatening. In such a situation, swelling quickly increases, which can lead to suffocation. Time in such cases passes literally in seconds. Only urgent administration of antihistamines can save the patient’s life.
Other reasons
If your throat seems to be squeezing, you can look for reasons in the following:
- Worm infestation . It is generally accepted that parasites most often live in the intestines. However, sometimes they lay eggs in other places. The throat is no exception. As a result, a person has a feeling of a foreign object in this area.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. This factor quite rarely provokes such problems, but it cannot be completely excluded. This is especially true if there are other signs of damage to the cardiovascular system - for example, pain in the sternum.
- Excess weight . When an impressive layer of fatty tissue appears under the skin, a lump in the throat may occur.
- Hit by a foreign object . This could be a bone or a tablet.
Psychogenic factors
Such reasons also often cause constriction in the throat. Before making such a diagnosis, the specialist conducts a detailed examination of the patient to exclude somatic factors. If the internal organs are working correctly, one can suspect the psychogenic nature of the problem.
In such a situation, a person faces difficulty swallowing saliva; constriction, scratching or soreness appears in the throat. In some cases, breathing problems and difficulty eating solid food occur.
At the initial stage, these manifestations are rather weakly expressed, but after some time they increase. This condition can persist for a very long time. Moreover, a person may have suspicions of developing cancer or other dangerous diseases. As a result, anxiety increases, which leads to a worsening of the clinical picture.
A feeling of tightness may occur periodically. In such a situation, panic attacks are observed, blood pressure increases, heart rate increases, and fear of death arises. At the same time, the feeling of suffocation and oxygen deficiency only increase fear. In such a situation, signs of depression arise. They manifest themselves in the form of depression, isolation, and tearfulness.
When panic attacks occur, pain in the throat is accompanied by increased heart rate and pulse. You may also experience numbness in the limbs, dizziness, pain in the left side of the chest, and a feeling of lack of air. Such attacks have an acute onset and last a maximum of half an hour.
To determine the exact causes of the problem, the doctor must study the influence of psycho-emotional factors on the patient’s condition. In this case, stressful situations, difficult situations at work and at home are important.
What to do if you feel a feeling of choking in your throat
Neurogenic respiratory disorders: hyperventilation syndrome
History of the study of hyperventilation syndrome (HVS). The first clinical description of HVS was by Da Costa (1842), who summarized his observations of soldiers participating in the Civil War. He observed breathing disorders and various associated unpleasant sensations in the heart area, calling them “soldier’s heart”, “irritable heart”. The connection between pathological symptoms and physical activity was emphasized, hence another term - “effort syndrome”. In 1918, Lewis proposed another name, “neurocirculatory dystonia,” which is still widely used by therapists. Manifestations of HVS such as paresthesia, dizziness, and muscle spasms have been described; a connection between increased breathing (hyperventilation) and muscular-tonic and tetanic disorders has been noted. Already in 1930, it was shown that pain in the heart area with Da Costa syndrome is not only associated with physical activity, but also with hyperventilation as a result of emotional disturbances. These observations were confirmed during the Second World War. Hyperventilation manifestations were noted in both soldiers and civilians, which indicated the importance of psychological factors in the genesis of HVS.
Etiology and pathogenesis. In the 80–90s of the twentieth century, it was shown that HVS is part of the structure of the psychovegetative syndrome [1]. The main etiological factor is anxiety, anxiety-depressive (less often, hysterical) disorders. It is mental disorders that disrupt normal breathing and lead to hyperventilation. The respiratory system, on the one hand, has a high degree of autonomy, on the other, a high degree of learning ability and a close connection with the emotional state, especially anxiety. These features underlie the fact that HVS is in most cases of psychogenic origin; extremely rarely it is caused by organic neurological and somatic diseases - cardiovascular, pulmonary and endocrine.
Complex biochemical changes play an important role in the pathogenesis of HVS, especially in the calcium-magnesium homeostasis system. Mineral imbalance leads to an imbalance in the respiratory enzyme system and contributes to the development of hyperventilation.
The habit of breathing incorrectly is formed under the influence of cultural factors, past life experiences, as well as stressful situations suffered by the patient in childhood. The peculiarity of childhood psychogenies in patients with HVS is that they often involve respiratory dysfunction: children witness dramatic manifestations of attacks of bronchial asthma, cardiovascular and other diseases. In the past, patients themselves often have an increased load on the respiratory system: running, swimming, playing wind instruments, etc. In 1991, I. V. Moldovanu [1] showed that with HVS there is instability of breathing, a change in the ratio between the duration of inspiration and exhale.
Thus, the pathogenesis of HVS appears to be multilevel and multidimensional. A psychogenic factor (most often anxiety) disrupts normal breathing, resulting in hyperventilation. An increase in pulmonary and alveolar ventilation leads to stable biochemical changes: excessive release of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the body, the development of hypocapnia with a decrease in the partial pressure of CO2 in the alveolar air and oxygen in the arterial blood, as well as respiratory alkolosis. These shifts contribute to the formation of pathological symptoms: impaired consciousness, autonomic, muscular-tonic, algic, sensory and other disorders. As a result, mental disorders increase and a pathological circle is formed.
Clinical manifestations of HVS. HVS can be paroxysmal in nature (hyperventilation crisis), but more often hyperventilation disorders are permanent. HVS is characterized by a classic triad of symptoms: respiratory disorders, emotional disturbances and muscular-tonic disorders (neurogenic tetany).
The first are represented by the following types:
- "empty breath";
- violation of breathing automaticity;
- labored breathing;
- hyperventilation equivalents (sighs, coughing, yawning, sniffling).
- Emotional disorders are manifested by feelings of anxiety, fear, and internal tension.
Muscular-tonic disorders (neurogenic tetany) include:
- sensory disturbances (numbness, tingling, burning);
- convulsive phenomena (muscle spasms, “obstetrician’s hand”, carpopedal spasms);
- Chvostek syndrome II–III degree;
- positive Trousseau test.
In the first type of respiratory disorder - “empty breath” - the main sensation is dissatisfaction with inhalation, a feeling of lack of air, which leads to deep breaths. Patients constantly lack air. They open the vents and windows and become “air maniacs.” Respiratory disorders intensify in agoraphobic situations (subway) or social phobia (exam, public speaking). Breathing in such patients is frequent and/or deep.
In the second type - a violation of the automaticity of breathing - patients have a feeling of stopping breathing, so they continuously monitor the act of breathing and are constantly involved in its regulation.
The third type - shortness of breath syndrome - differs from the first option in that breathing is felt by patients as difficult and performed with great effort. They complain of a “lump” in the throat, failure of air to pass into the lungs, and constriction of breathing. This variant is called "atypical asthma." Objectively, increased breathing and irregular rhythm are noted. The act of breathing uses the respiratory muscles. The patient looks tense and restless. Examination of the lungs does not reveal any pathology.
The fourth type - hyperventilation equivalents - is characterized by periodically observed sighs, coughing, yawning, and sniffling. These manifestations are sufficient to maintain prolonged hypocapnia and alkalosis in the blood.
Emotional disturbances in HVS are mainly of an anxious or phobic nature. The most common disorder is generalized anxiety disorder. It, as a rule, is not associated with any specific stressful situation - the patient experiences various mental (feelings of constant internal tension, inability to relax, anxiety over trifles) and somatic manifestations for a long time (more than 6 months). Among the latter, respiratory disorders (usually “empty breath” or hyperventilation equivalents - coughing, yawning) may form the core of the clinical picture - along with, for example, algic and cardiovascular manifestations.
Respiratory disturbances reach a significant degree during a panic attack, when a so-called hyperventilation crisis develops. Disorders of the second and third types are more common - loss of automatic breathing and difficulty breathing. The patient experiences a fear of suffocation and other symptoms characteristic of a panic attack. To diagnose a panic attack, four of the following 13 symptoms must be observed: palpitations, sweating, chills, shortness of breath, suffocation, pain and discomfort in the left side of the chest, nausea, dizziness, a feeling of derealization, fear of going crazy, fear of death, paresthesia, waves heat and cold. An effective method for relieving a hyperventilation crisis and other symptoms associated with respiratory failure is breathing into a paper or plastic bag. In this case, the patient breathes his own exhaled air with a high content of carbon dioxide, which leads to a decrease in respiratory alkalosis and the listed symptoms.
Agoraphobia is often the cause of HVS. This is fear that arises in situations that the patient regards as difficult to help him. For example, a similar condition can occur in the subway, store, etc. Such patients, as a rule, do not leave home unaccompanied and avoid these places.
A special place in the clinical picture of HVS is occupied by an increase in neuromuscular excitability, manifested by tetany. Tetanic symptoms include:
- sensory disorders in the form of paresthesia (numbness, tingling, crawling, buzzing, burning sensations, etc.);
- convulsive muscular-tonic phenomena - spasms, contractions, tonic convulsions in the hands, with the phenomenon of “obstetrician’s hand” or carpopedal spasms.
These manifestations often occur in the picture of a hyperventilation crisis. In addition, increased neuromuscular excitability is characterized by Chvostek's symptom, a positive Trousseau cuff test and its variant, the Trousseau-Bahnsdorff test. The characteristic electromyographic (EMG) signs of latent muscle tetany are essential in the diagnosis of tetany. An increase in neuromuscular excitability is caused by the presence in patients with HVS of a mineral imbalance of calcium, magnesium, chlorides, and potassium, caused by hypocapnic alkalosis. There is a clear connection between increased neuromuscular excitability and hyperventilation.
Along with the classic manifestations of HVS, paroxysmal and permanent, there are other disorders characteristic of the psychovegetative syndrome as a whole:
- cardiovascular disorders - pain in the heart, palpitations, discomfort, chest compression. Objectively, lability of pulse and blood pressure, extrasystole are noted, and on the ECG - fluctuation of the ST segment; acrocyanosis, distal hyperhidrosis, Raynaud's phenomenon;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: increased intestinal motility, belching of air, bloating, nausea, abdominal pain;
- changes in consciousness, manifested by a feeling of unreality, lipothymia, dizziness, blurred vision, in the form of fog or a grid before the eyes;
- algic manifestations, represented by cephalgia or cardialgia.
So, to diagnose hot water supply, confirmation of the following criteria is necessary:
- The presence of polymorphic complaints: respiratory, emotional and muscular-tonic disorders, as well as additional symptoms.
- Absence of organic nervous and somatic diseases.
- Presence of psychogenic history.
- Positive hyperventilation test.
- Disappearance of symptoms of hyperventilation crisis when breathing into a bag or inhaling a mixture of gases (5% CO2).
- Presence of tetany symptoms: Chvostek's sign, positive Trousseau test, positive EMG test for latent tetany.
- Change in blood pH towards alkalosis.
Treatment of hot water supply
Treatment of hot water supply is comprehensive and is aimed at correcting mental disorders, teaching proper breathing, and eliminating mineral imbalances.
Non-drug methods
- The essence of the disease is explained to the patient, they are convinced that it is curable (the origin of the symptoms of the disease, especially somatic ones, and their relationship with the mental state are explained; they are convinced that there is no organic disease).
- It is recommended to quit smoking and drink less coffee and alcohol.
- Breathing exercises are prescribed to regulate the depth and frequency of breathing. To carry it out correctly, several principles must be observed. First, switch to diaphragmatic abdominal breathing, during which the “inhibitory” Hering-Breuer reflex is activated, causing a decrease in the activity of the reticular formation of the brain stem and, as a result, muscle and mental relaxation. Secondly, maintain certain relationships between inhalation and exhalation: inhalation is 2 times shorter than exhalation. Thirdly, breathing should be rare. And finally, fourthly, breathing exercises should be carried out against the background of mental relaxation and positive emotions. At first, breathing exercises last for several minutes, then for quite a long time, forming a new psychophysiological breathing pattern.
- For severe hyperventilation disorders, breathing into a bag is recommended.
- Autogenic training and breathing-relaxation training are shown.
- Psychotherapeutic treatment is highly effective.
- Among the instrumental non-drug methods, biofeedback is used. The feedback mechanism with the objectification of a number of parameters in real time allows you to achieve more effective mental and muscle relaxation, as well as regulate your breathing pattern more successfully than with autogenic training and breathing-relaxation training. The biofeedback method has been successfully used for many years in the Clinic of Headache and Autonomic Disorders named after. acad. A. Veina for the treatment of hyperventilation disorders, panic attacks, anxiety and anxiety-phobic disorders, as well as tension headaches.
Medicinal methods
Hyperventilation syndrome refers to psychovegetative syndromes. Its main etiological factor is anxiety, anxiety-depressive and phobic disorders. Psychotropic therapy has priority in its treatment. In the treatment of anxiety disorders, antidepressants are more effective than anxiolytic drugs. Patients with anxiety disorders should be prescribed antidepressants with pronounced sedative or anxiolytic properties (amitriptyline, paroxetine, fluvoxamine, mirtazapine). The therapeutic dose of amitriptyline is 50–75 mg/day; to reduce side effects: lethargy, drowsiness, dry mouth, etc., the dose should be increased very slowly. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors have better tolerability and fewer unwanted side effects. The therapeutic dose of fluvoxamine is 50–100 mg/day, paroxetine is 20–40 mg/day. Their most common unwanted side effects include nausea. To prevent it or more successfully overcome it, it is also recommended to prescribe the drug at half the dosage at the beginning of therapy and take it with meals. Given the hypnotic effect of fluvoxamine, the drug should be prescribed in the evening; Paroxetine has less pronounced hypnogenic properties, so it is often recommended to take it with breakfast. The four-cyclic antidepressant mirtazapine has a pronounced anti-anxiety and hypnotic effect. It is usually prescribed at bedtime, starting with 7.5 or 15 mg, gradually increasing the dose to 30–60 mg/day. When prescribing balanced antidepressants (without pronounced sedative or activating effects): citalopram (20–40 mg/day), escitalopram (10–20 mg/day), sertraline (50–100 mg/day), etc., their combination is possible for a short period of 2–4 weeks with anxiolytics. The use of such a “benzodiazepine bridge” in some cases makes it possible to accelerate the onset of action of psychotropic therapy (this is important, given the delayed effect of antidepressants by 2-3 weeks) and to overcome the increase in anxiety symptoms that temporarily arise in some patients at the beginning of therapy. If the patient has hyperventilation crises during an attack, along with breathing into the bag, anxiolytics should be taken as abortive therapy: alprazolam, clonazepam, diazepam. The duration of psychotropic therapy is 3–6 months, if necessary up to 1 year.
Psychotropic drugs, along with a positive therapeutic effect, also have a number of negative properties: unwanted side effects, allergization, development of addiction and dependence, especially to benzodiazepines. In this regard, it is advisable to use alternative means, in particular, means that correct mineral imbalance, which is the most important symptom-forming factor in hyperventilation disorders.
As agents that reduce neuromuscular excitability, drugs that regulate calcium and magnesium metabolism are prescribed. The most commonly used are ergocalciferol (vitamin D2), Calcium-D3, as well as other medications containing calcium for 1–2 months.
The generally accepted view is that magnesium is an ion with clear neurosedative and neuroprotective properties. Magnesium deficiency in some cases leads to increased neuro-reflex excitability, decreased attention, memory, convulsive attacks, impaired consciousness, heart rhythm, sleep disorders, tetany, paresthesia, and ataxia. Stress - both physical and mental - increases the need for magnesium in the body and causes intracellular magnesium deficiency. A state of stress leads to depletion of intracellular magnesium reserves and its loss in the urine, since an increased amount of adrenaline and norepinephrine promotes its release from cells. Magnesium sulfate has been used in neurological practice for a long time as an antihypertensive and anticonvulsant. There are studies on the effectiveness of magnesium in the treatment of the consequences of acute cerebrovascular accident [2] and traumatic brain injury [4], as an additional remedy for epilepsy, and the treatment of autism in children [3, 7].
Magne B6 contains magnesium lactate and pyridoxine, which additionally potentiates the absorption of magnesium in the intestine and its transport into cells [6]. The implementation of the sedative, analgesic and anticonvulsant effects of magnesium-containing drugs is based on the property of magnesium to inhibit excitation processes in the cerebral cortex [5]. Prescribing Magne B6 both as monotherapy, 2 tablets 3 times a day, and in complex therapy in combination with psychotropic drugs and non-drug treatment methods, leads to a decrease in the clinical manifestations of HVS.
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
E. G. Filatova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of MMA named after. I. M. Sechenova, Moscow
Treatment of throat spasms and choking
How to quickly get rid of painful spasms in the pharynx that accompany the pathological condition?
The following tips are most effective in this case:
- The first step is to ensure peace and quiet for the patient.
- Open the window to allow fresh air into the room.
- To bring a person to consciousness, you can use ammonia.
- Give the patient a little water (about 100 ml) at room temperature to drink.
- If a person’s condition does not return to normal, you should pat him on the back without making too much effort.
- To relieve severe spasm in the larynx, you can artificially induce vomiting or place the patient in a warm bath.
- If the pathological process occurs against the background of a stuck bone in the throat, then the patient should be urgently sent to the surgical department of the nearest hospital.
- The periodic occurrence of convulsions in the upper respiratory tract should be a reason to immediately call an ambulance. Sometimes this indicates the presence of a serious illness.
If you are confident that asphyxia will develop due to nervous tension, then you should use the most effective treatment methods:
- psychotherapy;
- treatment with medication (an antidepressant and a tranquilizer will quite quickly remove a person from a pathological condition).
If the cause of convulsive spasms is allergic edema, then specialists usually prescribe effective drugs such as:
- Diphenhydramine;
- Suprastina;
- Tavegila.
When spasms appear against the background of pronounced bronchial asthma, it is most advisable to use drugs that help normalize the functioning of the bronchi.