Causes of the problem
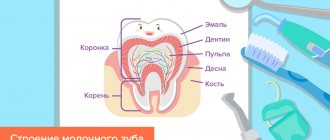
Enamel is the hardest tissue in the body, which is continuously exposed to mechanical, thermal and chemical stress. There are many reasons for its destruction and they can all be divided into two groups: carious and non-carious.
Carious causes
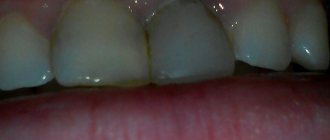
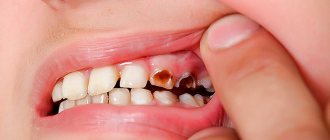
Most often, it is caries that destroys teeth, and in children this happens very quickly - in a few months, snow-white milk teeth can turn into black “stumps”. Bottle caries is a problem in the first years of life, when the use of a bottle with formula or sweet liquids at night creates a favorable atmosphere for an increase in the number of bacteria, leading to the development of caries and destruction of tooth enamel.
Non-carious causes
Often teeth are destroyed due to a lack of minerals in the enamel: calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, which enter the body with food.
The main non-carious reasons why baby teeth crumble:
Enamel hypoplasia is a serious problem in which the enamel layer on a tooth may be completely or partially absent due to abnormal processes that are formed during the formation of the rudiments of teeth. The reason is a difficult pregnancy, stress, bad habits and a lack of vitamins in the body of the expectant mother.
Visually, enamel hypoplasia looks like grooves on the enamel, through which dentin shines through. Such teeth are not protected and are more susceptible to physical and chemical stress.
Fluorosis is a disease that develops due to excess fluoride in the body. The child's teeth are covered with bright white spots. This problem is caused by drinking water with high levels of fluoride content.
Non-carious lesions also include:
- poor nutrition (lack of important substances);
- lack of fat-soluble vitamins;
- high levels of phytic acid;
- excessive sugar consumption;
- excess fluoride in the body;
- enamel defects or absence;
- heredity;
- taking antibiotics during the mother's pregnancy;
- poor oral hygiene;
- the habit of chewing on everything - pencils, pens, toys, nuts, candies;
- problems of intrauterine development;
- low quality of drinking water;
- jaw injuries resulting from a fall.
Why do baby teeth crumble?
In addition to the typical adult causes of tooth decay in children, factors are added that affected the fetus in the mother’s womb. Teeth crumbling in children is often observed due to the fact that the expectant mother during pregnancy:
- had an addiction to alcohol and tobacco;
- experienced a deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the diet;
- suffered severe toxicosis or infectious diseases;
- suffered from anemia, a condition in which there are not enough red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood;
- experience chronic stress [2].
It will no longer be possible to completely stop the influence of these factors after the birth of a child, and he will be at risk. Therefore, it is very important for the expectant mother to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, follow the schedule of examinations with the attending physician and follow all his recommendations.
How to prevent tooth decay
What to do to prevent chipping/decay of teeth:
- ensure high-quality oral hygiene;
- limit the amount of sweets in the children's diet;
- teach your child to brush their teeth and rinse their mouth after eating;
- take your child for preventive examinations to the dentist.
Expectant mothers need to eat well, take vitamins, and treat all their teeth that need it - after all, a child’s teeth are formed in the early stages of pregnancy. Vitamins that a child should receive from food:
- Group A – butter, yolk, offal, fish, fish oil;
- Group D – pork, salmon, yolk, beef liver, fish oil;
- Group E – meat by-products, nuts, seeds, green vegetables;
- Group K – liver, yolk, butter, nuts, seeds, broccoli.
As for babies, it is necessary, if possible, to eliminate night feedings and teach them to drink water at night. You can also use xylitol - containing wipes for treating teeth, if such feedings are still present.
What to do if your teeth are crumbling?
The first and main thing to do if teeth are crumbling in adults and children is to consult a dentist for an examination and professional consultation. The doctor will advise how to strengthen the teeth so that they do not crumble, if necessary, he will carry out therapeutic procedures (remineralization, fluoridation), and if the process is advanced, restoration. In addition, this problem often requires concomitant treatment of the gums, since sometimes dental tissues suffer due to inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, and vice versa, dental diseases lead to problems with the gums.
You also need to pay attention to the following points:
- Normalization of nutrition with the development of a certain food regimen and revision of the diet in the direction of increasing “healthy” foods in it (fermented milk products, eggs, sea fish, herbs, legumes).
- Thorough oral hygiene includes not only mandatory brushing twice daily, but also rinsing your mouth after meals, using dental floss and toothpicks.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the endocrine and digestive system, adherence to the diet indicated in such cases.
- Consultations with an endocrinologist and therapist to identify possible causes of tooth enamel destruction.
- Rejection of bad habits.
Professional treatments
To stop tooth decay, experts recommend strengthening the enamel with the help of remineralizing agents:
- fluoridation – periodic coating with solutions containing fluorine and other useful microelements;
- artificial saturation of the enamel surface with calcium and other minerals - the dentinal tubules are sealed and the density of the enamel increases;
- ozonation – destruction of bacteria in the affected tooth tissues without injuring soft tissues, helps stop destruction and cure caries at the initial stage;
- filling of dental defects;
- prosthetics – a decaying tooth is covered with a crown to isolate it from aggressive environments and stop crumbling.
- fissure sealing – sealing the chewing surface of molars with a special filling material;
The dentist chooses the appropriate treatment method, depending on the condition of the teeth and the age of the patient.
If your teeth have already begun to decay/crumple or the first signs of caries have appeared (stains on the enamel, changes in its color), do not delay your visit to the dentist. This is when time matters!
How is deep caries treated for young children?
If a one-year-old child is diagnosed with deep caries, it cannot be treated like a superficial one, without drilling. In this case, the teeth are filled with photopolymer composite or glass ionomer cement. To ensure that the baby sits still or as calm as possible during treatment, sedation or general anesthesia is used. Unfortunately, any anesthesia has a number of side effects, so it is better not to start caries and treat it in the early stages, when you can do without preparation and filling.
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion in children
When it comes to damage to baby teeth, remineralization therapy comes first.
The enamel is saturated with fluoride and calcium using special gels and applications. If necessary, the procedures are supplemented by taking medications with appropriate microelements. Damage to permanent teeth also requires remineralizing treatment. In case of deep erosions, restoration is carried out using composite (filling) materials, veneers or crowns.
It is important to eliminate the provoking factor: endocrine pathology, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment for crumbling teeth
The method of treating tooth decay depends on the cause of this process. If it is caused by general somatic or chronic diseases, the dentist may involve specialized specialists in treatment. In addition, organizing a balanced diet and generally strengthening the immune system are of great importance. To restore damaged teeth, photopolymer filling materials are usually used, and in case of significant destruction, teeth are restored with artificial crowns.
At the ARTOX dental clinic, you can always get advice from a qualified dentist about crumbling teeth in patients of any age and carry out a course of treatment. The experience of our specialists and advanced technologies will allow you to eliminate problems effectively and safely.
Make an online appointment with a doctor or call: +7,.
View prices
Making an appointment with a dentist
Symptoms of tooth erosion in children
The severity of symptoms largely depends on the degree of destruction and activity of the process. With a shallow lesion, tissue changes are invisible; a specific yellowish coloration is visualized only in the dentist’s office after drying the surface and/or treating it with iodine.
As the process spreads, round or oval lesions resembling a bowl begin to appear on the surface of the teeth. Initially they are whitish in color, but as they approach dentin they acquire a yellowish or light brown tint.
Subjective complaints arise in the active phase of the process with moderate or deep damage. The child pays attention to the increased sensitivity of the teeth to hot, cold, sour foods, and discomfort when brushing the teeth.
How to prevent caries in one-year-old children: preventive measures
Simple preventive measures will help prevent the development of this pathology, which can lead to the loss of several baby teeth at once:
- Clean your baby's teeth and gums with a special fingertip immediately after eating.
- Do not bottle feed a 1 year old child.
- Dentists note that bottle caries can also develop in one-year-old breastfed children. What's more, breast milk contains more sugar than formula, so prolonged breastfeeding can be damaging to children's teeth.
- Brush your teeth immediately after teething. First, use a soft toothbrush with fluoride-free toothpaste; after two years, you can use baby toothpaste with fluoride.
- Brush your child's teeth or supervise this process until he is at least eight years old.
- Don’t give sweet drinks, it’s better to teach them to drink plain water and unsweetened tea.
- Do not feed your baby at night. At night, the production of saliva, which has a bactericidal effect and fights germs, decreases. If necessary, you can give your child clean water to drink at night.
- Do not share a spoon with your child or put his pacifier in his mouth to avoid the transmission of cariogenic bacteria.
- Check your teeth regularly. If you notice white spots on them, lines on the tooth enamel near the gums, be sure to contact your dentist.
- Visit your dentist regularly, even if there are no stains on your teeth.
Follow all preventive measures, and you can prevent caries in children under one year old and maintain oral health.
Classification and stages of development of tooth enamel erosion in children
Depending on the depth of the lesion, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- initial: only the top layer is affected;
- medium: the pathological process involves the entire enamel;
- deep: destruction affects the upper layer of dentin.
The activity of the process allows us to distinguish two clinical stages of erosion development. In the active stage, relatively rapid destruction occurs: defects spread over the surface and become deeper. The enamel takes on a matte appearance, and in severe cases changes color to yellowish. In the stable phase, the teeth are not externally changed, there are no obvious symptoms, but when examined under a microscope, the lesion is clearly visible.
Diagnostics
For a basic diagnosis, a dental examination is sufficient, during which the doctor identifies characteristic changes in the appearance of the enamel. To clarify the diagnosis, a drying test (iodine test) is performed. In some cases, microscopic examination and x-rays are used. As a rule, at the same time, the child is sent for a consultation with an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist to rule out stomach pathology, accompanied by the reflux of acid into the oral cavity, or diseases of the thyroid gland.