The appearance of an infant’s first milk teeth is a difficult period for both him and his parents. The baby often cries, is capricious and demands increased attention from mom and dad. Teething is often accompanied by an increase in temperature. It lasts for 1-3 days, after which the child’s condition stabilizes.
Teething can be called a purely individual process. In some children it is completely asymptomatic, while in others very unpleasant symptoms appear that significantly worsen the baby’s life - diarrhea, hyperthermia, loss of appetite, inflammation of the gums and others. This clinical picture often confuses parents - they cannot understand whether these signs are related to teething or whether the child is developing some kind of pathology.
Parents' biggest concern during teething is temperature. It can rise to dangerous levels - 39-40°C. To alleviate the child’s condition, it is necessary to be able to provide him with first aid, as well as to recognize in time the signs indicating that you urgently need to either call an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself.
Why does the temperature rise
Teething is a traumatic process. Dental units damage the gum mucosa and inflammation occurs, which in medicine is called aseptic (microbial-free). This process is accompanied by an increase in temperature. In addition, during teething, some processes occur in the baby’s body that stimulate hyperthermia:
- at the site of localization of future milk teeth, specific substances necessary for softening the bone tissue of the jaw begin to be actively produced;
- Since all the forces of the child’s body are aimed at teething as quickly as possible, the immune system weakens a little. During this period, infectious agents present in the body may become active and diseases will begin to progress. Many of them are accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Damaged gums are the “entry gate” for infection. Through them, pathogenic microflora can penetrate the body and provoke the development of a septic inflammatory process. The body also responds to such an attack with an increase in temperature. To prevent infection, it is recommended to take more careful care of your baby’s gums during this difficult period for him. Pharmaceutical companies now produce many drugs that have a triple effect - relieve pain, reduce inflammation, fight viruses, bacteria and fungi. But before using these medications, it is recommended to consult your pediatrician.
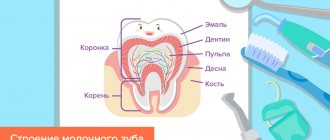
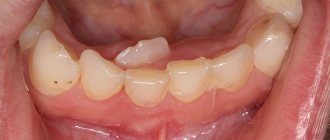
Loss of baby teeth in children, replacement scheme with permanent ones
We all remember those sleepless nights when our dear little one was teething for the first time. Teething is a rather long and quite painful process. But everything turns out to be behind us around the age of 3, when your baby can boast of 20 bead-like teeth. These are temporary teeth, called milk teeth. Starting from the age of 6, they begin to fall out in order to make room for permanent ones. But this is a completely natural and painless process that should not frighten parents. Usually, baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth around the age of 4 , when the child’s third molars begin to erupt.
It is this period that can be considered the beginning of the process of baby teeth falling out. We will consider below which teeth change in a child. In general, the process of losing baby teeth is quite long and can last from five to eight years . This period depends on:
- Genetics of the child
- Varieties of diet
- Quality of drinking water consumed
No matter how many milk teeth a child has, by the age of 13-14 they are completely replaced by permanent ones.
Teething symptoms
A child's first teeth begin to erupt between 4 and 8 months. There are exceptions. Sometimes children are born with several teeth, while others show them only after a year. Teething is a difficult process for a child. It can be accompanied by various symptoms, but the most common are the following:
- How long does it take for drugs to leave the body?
- Increased nervousness. The child cries for no reason, whines. Teething may be accompanied by painful sensations that prevent him from sleeping normally. As a result, the regime of wakefulness and rest is disrupted.
- Heavy salivation. This is a protective process. Saliva has anti-inflammatory and bactericidal properties. Hypersalivation helps protect inflamed gums from infection. Sometimes there is so much saliva that it flows down the chin onto the neck and chest. You should not constantly rub your baby's delicate skin. It is permissible to periodically carefully blot with dry wipes.
- Loose stools. During teething, the baby may experience diarrhea. It is caused by increased salivation, changes in intestinal microflora, or increased bacterial activity due to a decrease in the body's immune defense.
- Decreased appetite. Often, due to pain in the gums, infants refuse to eat. In this case, it is a little easier for those who are breastfed, since the sucking process calms and pacifies the baby.
- Inflammation of the gums. This is the natural state of affairs at the time of teething. If a white stripe appears in some place of the gum, the tooth will soon come out.
- Runny nose. Sometimes swelling and inflammation from the gums spreads to the nasal mucosa. As a result, the baby begins to snot.
- Itching in the gums. The baby puts all the objects that come to hand into his mouth. This is how he scratches his gums. To make his task easier, you can purchase special teething toys in stores.
- Hyperthermia. The temperature rises in 80% of cases. It is important to ensure that it does not reach critical levels. Once every 1-2 hours, it is recommended to measure it not with an electronic, but with a mercury thermometer, since it is more reliable.
All these symptoms frighten parents, as they are similar to the signs of many other diseases of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract. These symptoms are typical for teething. But you need to monitor the baby’s condition very carefully, and if the clinic is accompanied by other alarming symptoms, you need to immediately contact your doctor.
Is there a pattern for tooth loss?
It is believed that the first permanent tooth appears immediately after the baby tooth falls out. Actually this is not true.
“At the age of five or six years, children’s first molar teeth erupt,” comments a pediatric dentist at the “All Yours!” Dentistry. Victoria Arutyunova. - This is the sixth tooth, which is located behind all the milk teeth. And only after this the change from the milk bite to a permanent one begins.”
This happens in a certain order:
- the first stage at 6-7 years . The central incisors change, first on the lower jaw, then on the upper;
- second stage at 7-8 years . Time to change the second incisors, which will also fall out first at the bottom and then at the top;
- third stage at 8-9 years . There are fangs immediately behind the incisors, but they will not change now. At this stage, the “fours” located immediately behind the fangs should change;
- fourth stage at 9-10 years . Time to change canines, and then molars;
- fifth stage at 10-11 years . By this age, the child should have replaced molars. The process of tooth loss in children is completed.
“At the age of 10-11, the last milk teeth fall out, and the bite becomes permanent,” notes Victoria Arutyunova. - But the growth of molars does not end there. There are still “sevens” and “eights” left - the second painters, who erupt at 12-13 years of age. And also wisdom teeth or third molars, which grow after 18 years. But in general, we can say that by the age of 12, all the teeth in the child’s mouth will be permanent.”
pixabay.com/
Symptoms indicating pathology
An increase in temperature during teething is a natural process. This is a kind of protective reaction of the baby’s body. At this time, it is necessary to carefully assess the general condition of the child. Sometimes dangerous pathologies can be hidden behind teething syndrome. Therefore, parents should know the symptoms indicating the progression of the pathological process:
- Vomit. Single vomiting can occur at high temperatures. But if it recurs, the baby feels very bad and has diarrhea, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. These are signs of intestinal infection or poisoning.
- Nasal congestion or discharge of thick yellow-green snot. This is not the norm, it is a pathology that requires adequate and immediate treatment.
- Coughing. During teething, a lot of saliva is released. Often children simply do not have time to swallow it, and they may choke. A cough appears reflexively, which is not pathological. But if wheezing is heard and a certain amount of sputum is released during coughing, this indicates the development of diseases of the upper respiratory tract (tracheitis, bronchitis and others).
- Stomach ache. With normal teething, this symptom should be absent. If the baby is restless, capricious, cries, or pulls his legs toward his stomach, these are alarming signs. Especially if the abdominal pain is accompanied by repeated vomiting. This symptom complex indicates the development of an intestinal infection. The child could pick it up through toys and other objects that he pulled into his mouth.
- Red throat. Swelling from the gums does not spread to the palate. It can spread to the nasal cavity. If the throat and palate are hyperemic (reddened) upon examination, this is the first sign of the development of pharyngitis.
If you have at least one of these symptoms, you should immediately contact your doctor or go to a medical facility. There the child will be examined by a pediatrician and prescribed the correct treatment. It is prohibited to give any medications (except antipyretics) at home without prior approval from the doctor.
How long does the temperature last
During teething, the temperature rises on average to 37.7°C. This has practically no effect on the general condition of the child. He is active, eats well, plays. But hyperthermia can also reach high numbers - 39-40°C. In this case, the baby is lethargic, capricious, and refuses to eat. It is better to take measurements every 1-2 hours. If the increase is critical, an antipyretic drug should be given. Normally, the temperature during teething can last up to three days. If hyperthermia is present even on the 4th day, you cannot do without the help of a doctor.
When it all begins
The process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones begins much earlier than the first one falls out. The roots gradually weaken and dissolve.
Baby teeth are no longer firmly anchored in the gums and begin to wobble. This process lasts 2 years. The first permanent teeth are the third molars. Normally this happens after 4 years.
The main factors on which the course of the process depends:
- Baby food;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Composition of drinking water;
- Existing diseases.
If there are no deviations in this part, then by the age of 5, more noticeable gaps should form between the child’s teeth than before. This is how the jaws prepare for the appearance of permanent organs.
When to lower the temperature
There is no need to lower the temperature to 38.5°C. If it rises higher, you need to take action. Hyperthermia affects many processes in the human body. During fever, the water-salt balance is disrupted and the load on the heart increases. In severe cases, convulsions may occur that can lead to respiratory arrest. In no case should this be allowed to happen, as this would pose a threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the little patient.
- How many days does a baby's teething temperature last?
When to give antipyretic drugs:
- temperature exceeded 39°C;
- breathing rate increases;
- the baby sleeps for a very long time;
- the child is restless, cries, cannot calm down;
- drying of mucous membranes, redness of the skin;
- the occurrence of convulsions (in this case, they give an antipyretic and immediately call an ambulance).
If the child has already had convulsions once, the temperature must be brought down when it exceeds 38°C.
Replacing baby teeth with permanent ones: what should parents pay attention to?
The process of replacing children's milk teeth with permanent ones requires increased attention from parents. It is necessary to monitor the child’s adequate nutrition and oral hygiene, and if there are deviations from the norm, immediately contact a dentist
Every person in childhood goes through a period when temporary teeth are replaced with permanent ones. In most cases, this process does not cause any problems. However, parents should still know what exactly to pay attention to when a child’s baby teeth fall out and permanent teeth appear.
Causes of loss of baby teeth
There are very specific reasons for the process of changing a set of teeth after a certain age. The fact is that children erupt their first teeth before they reach the age of one, when more dense foods than milk appear in the diet. However, the child’s jaws at this time are still quite small, and the first teeth that grow have a corresponding size. And milk teeth themselves, which have weak enamel, are not very strong.
Gradually, as the baby grows up, the chewing load on the teeth increases due to the intake of increasingly solid foods. This requires the formation of an appropriate masticatory apparatus. By this time, the growing child's jaws are just large enough to accommodate the entire set of permanent teeth. Therefore, the process of loss of milk teeth and the appearance of stronger molars, necessary for a full future life, begins.
At what age do baby teeth change?
Parents often mistakenly believe that the process of changing primary teeth begins with the loss of the first milk tooth. As a rule, this occurs at the age of 6-7 years. However, doctors take as a starting point the appearance of the first permanent teeth - third molars, which are absent in the “deciduous bite”. This process is observed at the age of 5-6 years. It is at this time that the process of resorption of the roots of temporary teeth begins, which lasts approximately 2 years. Gradually, baby teeth begin to loosen, and by the time the molars appear, they fall out.
The age at which teeth change varies from person to person, and the time difference is sometimes up to 2 years. Experts note that this factor may also depend on the region of residence: in warmer climates, permanent teeth appear earlier. It is also known that girls replace their baby teeth with molars a little faster than boys.
What to pay attention to during the period of teeth change?
Proper nutrition
The process of final formation of enamel during the eruption of permanent teeth takes several years. And during this period, proper nutrition becomes extremely important, thanks to which the child must receive all the substances necessary for the body.
Parents should pay attention to the following points:
- the child’s daily diet should include foods with a good calcium content - milk, cottage cheese, cheeses;
- the diet should be supplemented with fresh fruits and vegetables to obtain the required amount of vitamins and microelements;
- at least 1-2 times a week, to obtain a sufficient amount of phosphorus, you need to include fish dishes in the menu;
- Until the final formation of the enamel of the molars, it is advisable to give up sweets, chocolate and sweet pastries. Sweet soda is also extremely dangerous for young enamel;
- The child should eat some food, such as fruits and vegetables, in solid form. The load on the teeth will stimulate the resorption of the roots of baby teeth, helping the eruption of molars;
- in some cases, for example, if a child does not eat dairy products well, the baby’s diet should be supplemented with a multivitamin complex with calcium.
It is better to exclude the hardest or most chewy foods, such as nuts or toffees, from the diet completely during the period of teeth change. Their use can lead to injury or early loss of primary teeth, which will interfere with the proper growth of permanent teeth.
Oral hygiene
As already mentioned, permanent teeth appear with weak, not yet fully formed enamel. Therefore, oral care to prevent tooth decay is very important.
Proper oral hygiene in a child involves morning and evening brushing of teeth using children's toothpastes that have an optimal content of calcium and fluoride. To avoid injury to the gums, it is better to choose a toothbrush with soft bristles. It can also be helpful to teach your child how to use children's dental rinses. Ideally, it is advisable to rinse your mouth every time after eating - this will optimally prevent the formation of plaque.
Visiting the dentist
Special attention should be paid to the medical prevention of dental diseases during the period of teeth change. For preventive purposes, dentistry for children should be visited at least 2 times a year. And if there is a need to treat a child’s teeth, then you need to go to the doctor as quickly as possible. After all, caries in children with teeth with still weak enamel can develop very quickly.
Early and late change of primary teeth
Sometimes situations arise when the replacement of temporary teeth with permanent ones in children occurs in violation of the deadlines. Let's consider what parents should do in such cases.
Early tooth loss
The loss of baby teeth can be called early if it occurs before the age of 6 years. As a rule, such situations arise due to injury, dental disease, or intentional loosening of a tooth. The main problem here is that when a baby tooth disappears, free space appears in the dentition. And if the permanent tooth does not begin to grow after the loss of the temporary one, then gradually the neighboring milk teeth will begin to move, filling the resulting volume. In the future, this will lead to the fact that the molars will not have enough space for normal eruption, and the dentition will be uneven.
With the early loss of a temporary tooth, pediatric orthodontics comes to the rescue. Currently, modern techniques are available to doctors to prevent the displacement of adjacent teeth. Therefore, in case of early loss of a baby tooth, it is advisable to immediately go for a consultation with an orthodontist. After all, correcting cosmetic defects and correcting the bite will bring much more trouble in the future.
Late replacement of primary teeth
There are two possible scenarios here. The first is when molars do not appear in a timely manner, even if the milk teeth have already fallen out. There may be several reasons for this anomaly, from a physiological delay in the appearance of new teeth to incorrect positioning of the tooth inside the jaw apparatus. The second scenario is when the molars began to erupt before the baby teeth fell out. The result can also be the formation of bite defects.
If a child shows signs of a delayed change of teeth, it is necessary to contact a dentist to identify the causes of the deviations. As a rule, the doctor will be able to tell about the causes of the anomaly after an X-ray examination, after which appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
What can you do to bring down the temperature?
An increase in a child's temperature is always a reason for panic among his parents. But it is important to control yourself and be able to properly help your child. To normalize body temperature, you can resort to methods of traditional and folk medicine.
Medications
For young children, it is best to give the medicine in syrup form or use rectal suppositories. Both the baby and the older child will refuse to take the bitter pill, and giving it to him will be problematic. If you don’t have anything else at hand, then you can try mixing the medicine with something tasty - honey, fruit puree.
Medicines for fever in a child
To normalize a child's body temperature, medications based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are used in pediatrics. The first can be given to a baby from the first days of life, the second - from three months. Before use, you should consult with your doctor, and also study the instructions for the drug in detail, paying special attention to side effects and dosage.
Traditional methods
If you don’t have the required medications in your medicine cabinet at the right time, you can resort to traditional methods of lowering your temperature. They allow you to reduce the heat by 1-2 degrees. This is often enough to stabilize the child’s general condition.
Effective methods:
- Toothache and fever
- Physical cooling with a diaper or sheet. This method can hardly be called purely folk, since it is also used in medical institutions. Its essence is to cool the “burning” human body. It is necessary to wet the diaper in warm water and wrap it around the baby.
- Rubbing with warm water. It is necessary to prepare a sponge and a deep container with water. Her temperature should be 36-37 degrees. Water that is too cold can cause chills and even trigger cramps. Hot water will not bring the expected effect. Take a little warm water into a container, moisten a sponge in it and carefully wipe the child’s feet and hands, elbows and knees, and armpits.
- Cabbage leaves. They need to be kept in boiling water, and then beaten a little, cooled and applied to the baby’s body.
- Linden blossom. It can be given even to children under one year old. It has a pronounced diaphoretic effect. As a result, the child sweats and body temperature decreases. Use after consultation with a specialist and in the absence of an allergic reaction to this plant.
It is best to use traditional methods of treatment in tandem with traditional ones. This will not only achieve the desired effect, but also quickly improve the child’s condition.
What not to do when teething
It’s hard to look at a child when you know that he’s feeling bad right now. Therefore, many parents try to take some measures to somehow help their child. But not everything goes to his advantage. During the teething period, you cannot rush the course of events. Teeth will erupt in any case. If you try to speed up this process, you can only do harm.
What not to do:
- give adult medications to bring down the temperature;
- wipe the child with vinegar or alcohol;
- massage the gums;
- make cuts on the gum so that the tooth emerges faster;
- give the child dry bread crust (it can scratch the swollen tissues in the mouth and infection can penetrate through the wounds).
Now in children's stores there are a sufficient number of various “rodent” toys, as well as pain-relieving gels that will help simplify the teething process and reduce pain and inflammation. It is to them that you need to resort if there is a need to help the baby.
“Rodents” for teething children