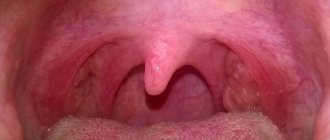
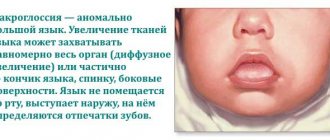
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Pain on the tip of the tongue
There may be several reasons for the occurrence of such pain:
- Mini tip injury . In first place in terms of prevalence are mini-injuries of the tip of the tongue. Most often, patients inadvertently bite the tip of their tongue or burn it with too hot food. Such mini-injuries are painful and cause a lot of trouble for patients; the papillae hurt, and sometimes eating becomes impossible for a while due to severe pain. Over time, everything heals and passes without a trace.
- Glossalgia is a serious disease in which the tip of the tongue most often hurts, less often its sides. The pain is manifested by a burning sensation; patients often complain that their tongue hurts, like after a burn. Sometimes the painful sensations spread to other organs of the oral cavity; the patient’s tongue and gums, sometimes lips and cheeks, hurt. If such symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor, since glossalgia is difficult to treat and exhausts the patient with its symptoms.
- Glossitis is an inflammatory disease of the tongue. When it occurs, the tip of the tongue can be very painful, because the infection that causes inflammation usually gets into the wound, and the tip of the tongue is bitten much more often than other parts of it.
- Stomatitis is also accompanied by severe pain in the tongue, which becomes covered with painful ulcers located over its entire surface.
- Allergy . Allergic reactions are also common causes of pain.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
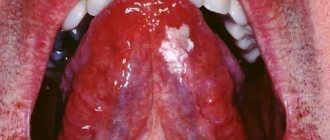
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
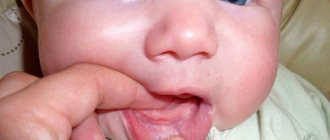
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Pain after puncture
Recently it has become fashionable to pierce the tongue, it is called piercing. We will skip moralizing on this topic and tell you briefly what this threatens.
Many patients complain that their tongue hurts for a long time after the puncture. This is considered normal, since a puncture, even the most skillful one, is a kind of injury that takes time to heal. In addition, the tongue is literally riddled with nerve endings, so the puncture site hurts especially strongly. It is impossible to say exactly how long the pain continues after the puncture; this happens individually for everyone: for some, the pain stops 2-3 days after the puncture, for others the pain lasts for 10-12 days. If your tongue is swollen and painful immediately after the piercing, this is normal. However, severe pain and swelling should gradually subside and disappear completely 4-5 days after the puncture. If the pain does not subside after a week or is acute and throbbing, you should immediately consult a doctor, as the possibility of infection cannot be ruled out.
Causes of pain after piercing:
- damage resulting from puncture of nerve endings located in the tongue;
- infection in the wound and development of the inflammatory process;
- allergy to the metal from which the jewelry is made.
In order to prevent the development of complications, you should contact only professionals. After all, not every cosmetologist knows how to properly pierce the tongue without damaging the nerve or developing inflammatory processes. If, after the piercing, the pain when speaking and swallowing does not go away, you should consult a dentist or surgeon.
It should be warned that the closer to the edges of the tongue the puncture is made, the more painful and dangerous complications it is. The easiest way to heal is a puncture made in the center of the tongue, because along the edges of the tongue there are arteries, damage to which can even lead to death. How far from the tip the puncture is made also plays a role. The closer to the root the tongue is pierced, the more it swells and hurts.
- If after piercing your tongue hurts on the side, left or right, you should definitely consult a doctor to see if the lateral arteries are damaged or if they are being pressed by a barbell.
- If the patient is suffering from pain in the tip of the tongue, but it is not swollen and there are no signs of inflammation, such pain must be endured and the puncture site must be given time to heal.
- If the tongue was pierced in the root area, you should expect that the pain at the base will be prolonged, and the healing itself will take 4-6 weeks.
Stitching pain in the tongue after piercing should alert you, as they most often indicate the development of an acute inflammatory process due to infection. Without timely treatment, an abscess may develop.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Diseases of the throat and ear, in which pain in the throat radiates to the ear
| Pathology causing symptoms | What is it characterized by? |
| Lymphadenitis | Inflammatory damage to the lymph nodes due to damage by bacteria or viruses. It can occur in acute or chronic form and manifests itself:
|
| Rhinitis | Inflammatory processes of the nasal mucosa, which can develop due to viral lesions. They appear:
|
| Sinusitis | Inflammation that covers the paranasal sinuses, developing when they are damaged by bacteria, viruses or fungi. Depending on the localization of pathological processes, sinusitis is divided into sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, and ethmoiditis. Their clinic provides for increased body temperature, headaches, sore throat, radiating to the organ of hearing. |
| Tonsillitis | Inflammatory lesion of the tonsils, developing as a result of damage by pathogenic microorganisms. The pain during the disease is acute and radiates to the ear, and in the chronic form it is sticky. The patient's throat has a burning sensation and soreness, and a reflex cough develops. |
| Otitis | Inflammation that affects the external, middle or internal parts of the hearing organs, and occurs in acute or chronic form. Pain with it is accompanied by a significant deterioration in well-being. Often otitis media occurs along with tonsillitis, causing a sore throat. |
| Pharyngitis | Inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx due to damage by bacterial or viral agents. Very often it occurs together with tonsillitis and, in addition to pain in the ear and throat, is manifested by the following symptoms:
|
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you should consult a dentist. If the cause is not of a dental nature, then you need to undergo an examination to identify the true causes of the disease. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- collection . At the first visit, the patient outlines complaints, existing allergic reactions or injuries, chronic diseases, etc.
- Visual inspection. The doctor assesses the patient's condition based on the existing signs. If it is possible to eliminate the problem immediately, surgical manipulations are carried out. For example, removing a bone from the tongue.
- A clinical blood test to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
When a disease is detected, the doctor determines treatment tactics.
Treatment of sore throat and ear
To relieve a patient of a sore throat, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause that provokes it. CELT specialists conduct comprehensive diagnostic studies that eliminate the risk of error. For this, the patient is prescribed to undergo general laboratory tests, bacterial culture, X-ray and pharyngoscopy. Treatment tactics are developed based on the results obtained and the patient’s individual indications.
| Pathology | Treatment |
| Lymphadenitis | The acute form is treated conservatively: taking antibiotics and vitamins, as well as UHF. The purulent process is opened and drained. The chronic form requires elimination of the underlying disease, which provokes inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes and pain. |
| Rhinitis | The acute form is treated with medications, heat treatments and antibiotics if a bacterial agent is identified. As for chronic, it requires the use of astringents, antibacterial ointments, instillation of antiseptics and UHF. According to indications, cauterization of the nasal mucosa or cryodestruction is performed. |
| Sinusitis | Treatment is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and ensuring the outflow of purulent masses from the paranasal sinuses. The latter allows you to eliminate pain. The patient is prescribed antibacterial or antiviral drugs, and a maxillary sinusotomy is performed according to indications. |
| Tonsillitis | Treatment tactics are selected depending on the form and stage of the disease and provide an integrated approach. In the process, local procedures and drug treatment with the use of immunostimulants and immunocorrectors are used, which reduces pain and improves the general condition of the patient. Surgical treatment is aimed at removing the tonsils and is carried out according to indications if lymphoid tissue has been replaced by connective tissue. |
| Otitis | Treatment depends on which part of the hearing organ is affected. It is possible to use antiseptics that are injected into the ear canal. In addition, warm compresses, physiotherapeutic procedures, and the use of topical anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended. If the above does not give the desired result, the eardrum is pierced to ensure the drainage of pus. This automatically reduces pain and the patient feels relief. |
| Pharyngitis | It is important to eliminate the factors that provoke the disease. The patient should avoid consuming foods that can cause irritation to the mucous membrane. If a bacterial agent is detected, antibiotic therapy is administered. Local treatment involves rinsing with antiseptics and inhalation. |
Having decided to undergo a course of treatment for chronic pain in the throat and ear at CELT, you will have an appointment with doctors of the highest category and candidates of medical sciences. They will help you get rid of unpleasant symptoms by eliminating the cause of their development. You can make an appointment with them online or by contacting our operators.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Our doctors
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
20 years of experience
Make an appointment