Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
For many years, every second person in the street was convinced that a good toothpaste must certainly contain fluoride. Our grandparents stubbornly insisted on the importance of this element. But is fluoride really necessary in toothpaste, or does the harm of this microelement still outweigh its benefits? Let's try to figure it out.
The history of fluoride in toothpastes
Fluoride was first used in toothpastes more than 100 years ago, in 1914 in the USA. At the beginning of the 20th century, scientists found that this element is an excellent protection against caries and its use reduces the rate of tooth decay by an average of 30-45%. Under the influence of fluorine, enamel became resistant to acids and more durable.
Why is fluoride needed in toothpaste?
Surprisingly, the same element can be both healing and destructive to the body. And fluoride is just that: the substance can both restore and strengthen tooth enamel, and cause irreparable harm to it. It is thanks to fluoride that the strength of bone tissue in the body is maintained; this element plays a key role for the health of hair, nails and teeth. Fluoride is very important in the growth and development of a child: without it, his skeleton does not develop normally.
In addition, fluorine has a beneficial effect on metabolism: without this element, the body cannot remove heavy metals. The substance also helps absorb iron and supports immunity.
When there is a lack of fluoride in the body, bones and teeth are the first to suffer. Bones bend, become brittle and brittle, and in the event of a fracture they heal very slowly. With a lack of fluoride, the enamel gradually becomes thinner, it is increasingly affected by plaque bacteria, and caries develops faster and faster.
In fact, it is not difficult to provide the body with its daily requirement of fluoride. Products high in this substance include:
- a variety of fruits, such as grapefruits and apples;
- nuts;
- dairy products;
- various types of meat (especially liver);
- various vegetables - pumpkin, spinach, potatoes;
- buckwheat and oatmeal porridge;
- honey;
- any types of tea.
By drinking enough water per day and eating right, you can provide yourself with fluoride. Therefore, the need for toothpastes with fluoride should only be determined by a dentist. As a rule, fluoride products are prescribed to smokers and people who abuse coffee.
Pros of fluoride toothpastes
Many people specifically choose hygiene products with fluoride to strengthen their teeth and prevent the development of caries. Indeed, in some cases, this element protects the enamel from the action of harmful bacteria and strengthens it. Under the influence of fluoride, less acid is released, which affects the enamel. Therefore, anti-caries toothpastes often contain fluoride.
The main benefits of fluoride toothpastes include:
- antiseptic effect;
- improvement of metabolism;
- improvement of the remineralizing effect of saliva;
- stimulation of the salivary gland;
- inhibition of the transformation of soft plaque into tartar.
Harm of toothpastes with fluoride
Unfortunately, many of us forget that toothpaste is not the only source of fluoride. This element is found in many foods and even in ordinary tap water.
Before you buy even the best toothpaste with fluoride, it is important to understand your need for this element: its daily intake should not exceed three milligrams. In order to get this dose, it is enough to drink two liters of water a day.
For a person who eats right and drinks enough water, it is not at all necessary, and often even harmful, to use toothpastes with fluoride. The fact is that this element in excess amounts is toxic to the body. The substance accumulates in tissues, including tooth enamel. If too much fluoride accumulates in it, fluorosis appears, the process of destruction of enamel.
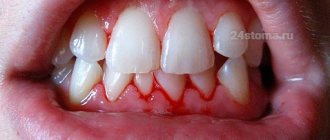
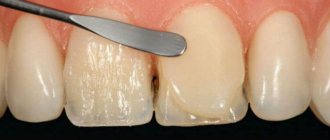
Fluorosis is very easy to recognize. The disease manifests itself as white spots on the surfaces of the teeth. These spots grow quickly, turn yellow and begin to corrode the enamel. In case of fluorosis, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible - remineralizing therapy, photophoresis or the use of special applications.
Often, teeth with fluorosis require additional whitening, because it is almost impossible to cope with such a problem with the help of professional cleaning.
Fluorine is the 9th element of the periodic table
Fluorine is a chemical element from the halogen group. Actively contacts with other substances. As a result, bright reactions appear: combustion, explosion, boiling. Research by dentists has revealed the presence of fluoride at approximately 0.02% in tooth enamel. The population of regions where the water contains insufficient amounts of fluoride is more susceptible to caries. At the same time, its excess is manifested by darkening of the teeth and the presence of white spots on them (fluorosis). Over time, the enamel begins to gradually deteriorate.
Indications for the use of fluoride pastes
Of course, in some cases, toothpastes with fluoride will be useful to patients, but, as we have already said, only a dentist should prescribe them. The specialist will assess the condition of the enamel and oral cavity, and then determine whether the teeth have enough fluoride and what kind of toothpaste they need.
Therapeutic toothpastes with calcium and fluoride are indicated for use if the patient has:
- signs of dental demineralization;
- poor enamel resistance to acids;
- fragility of teeth, tendency to chip;
- minor signs of caries.
The fluorides contained in such toothpastes create a thin protective layer on the crowns. All substances hazardous to enamel do not penetrate it and their negative impact is reduced several times. Incoming fluoride, when it is deficient in the body, slows down the proliferation of bacteria and, accordingly, the development of caries. The likelihood of gum inflammation is also reduced.
Why is this component so important for dental health - the benefits of the substance
The content of this element in oral care products protects against caries, makes enamel stronger, effectively removes plaque and fights pathogenic microflora. Let's take a closer look at the undoubted advantages of this component.
Prevention of caries
The enamel is constantly exposed to aggressive acids that are released with saliva. Food remains and other external factors lead to the formation of plaque, which gradually transforms into hard dental deposits, leading to the destruction of the enamel layer. As a result, a white spot first appears, which darkens and turns into a carious cavity.
Fluorine penetrates the crystal lattice of enamel, strengthens it and increases resistance to pathogenic microorganisms. It provides prevention of caries and prevents its further development, even if the disease is already at the white spot stage.
Decalcification protection
The substance promotes a process called “remyelination” - the transition of ions from the blood to the body’s tissues. Saliva, which is produced during food intake, leads to the opposite effect, that is, loss of calcium from dental tissues. When calcium and fluoride ions enter the oral cavity, they penetrate the crystal lattice of the enamel, strengthening it and preventing the destruction of hard tissues under the influence of saliva.
Strengthening enamel
The basis of enamel is calcium hydroxyapatite. By interacting with the microelement in question, this salt is converted into a new substance - fluorine hydroxyapatite. Thus, the microelement in question acts as a calcium protector, protecting it from the aggressive effects of acids in the oral cavity.
Prevention of the growth of pathogenic microflora
Pathogenic microorganisms that form plaque secrete special enzymes necessary for the breakdown of carbohydrates and their absorption. Our substance blocks the production of these enzymes, which prevents the further spread of pathogenic microflora.
This is interesting: Pencil for teeth whitening, user reviews of different models of pencils, advice from dentists
Fluoride works great against plaque
“I have been using fluoride toothpaste for a year now and am very pleased with the results! About six months ago I bought myself an irrigator, so with them, every morning cleaning feels like after professional hygiene at the dentist. I recently had a preventive examination and there were no problems with the enamel. And I myself understand that sensitivity has not appeared, the teeth are white, without spots or irregularities. It seems to me personally that all this hysteria about the harm of such products is greatly exaggerated!”
AlesyaK., Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Stopping the secretion of lactic acid
This microelement blocks excess lactic acid synthesis, thereby effectively suppressing the growth of pathogenic microflora. This acid is produced by microorganisms during their life and reproduction. Products containing this component prevent this process, thereby providing additional protection for the enamel.
Consequences of excess fluoride in the body
Do not forget that fluorine is, first of all, a toxic substance. It is added to toothpastes only in the form of compounds that can release active ions. The pastes contain sodium fluoride, sodium monophosphate, as well as tin and aluminum fluorides, and amino fluoride.
When fluoride enters the body of an adult in excess quantities, the following problems may begin:
- disruption of metabolic processes and, as a result, destruction of bones and teeth;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- increased blood pressure;
- decreased immunity.
Surprisingly, translated from Greek, the word fluorine means “destroying.” Fluorine compounds in the gaseous state are deadly. And fluorites, often added to toothpastes, are considered one of the most harmful substances for the body.
If you use fluoride paste constantly, without apparent need, the following changes may occur in the oral cavity:
- damage to the enamel, the appearance of stains on it;
- fragility of teeth;
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
Aminofluorides are the product of targeted development and long research!
Amino fluorides are also salts, but compared to sodium fluorides they have a more complex structure. They were the result of a focused search for the best compound to protect teeth from caries. The fluorine ion in the case of amino fluorides is bound into a complex amine molecule by fatty acid hydrolase. The peculiarity of these compounds is their bipolarity: on the one hand, the polar amine base is soluble in water, on the other hand, the nonpolar base is fatty. Such compounds become active on the surface, enveloping it.
Children's toothpastes with fluoride
Children's toothpastes should absolutely not contain fluoride, despite the fact that this element is necessary for growing organisms. Fluoride is added only to toothpastes for children and adolescents over 5 years of age. The thing is that young organisms perceive various components much more strongly and are many times more susceptible to fluorosis (excess fluoride).
So, now you know the benefits and harms of fluoride in toothpastes. You should not decide on the use of such means on your own. Only an experienced dentist should prescribe pastes with fluoride and calcium.
To avoid the need for medicinal pastes, take good care of your teeth and be attentive to your body. Do not get carried away with coloring products, coffee, tea and sweets. For dental health, the absence of bad habits, proper, balanced nutrition and daily thorough hygiene procedures are important.
An excellent tooth support product is ASEPTA “Remineralization” professional toothpaste with high concentrations of hydroxyapatite and thermal mud. This remedy restores tooth enamel, reduces the sensitivity of teeth and gums and accelerates the regeneration of the oral mucosa.
Why is it dangerous?
- Halogen is harmful to the condition of teeth when the body is oversaturated with it. Teeth become brittle, “spotty,” and darken. Other organs and systems suffer: bones, ligaments, muscles. The ability to learn new material, remember and comprehend is reduced.
- Halogen is very dangerous if inhaled or ingested. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur. In the future, damage to the nervous and cardiovascular systems occurs, the kidneys suffer, even death.
- If the substance enters the respiratory tract, sneezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing occur.
- Sodium fluoride in toothpaste is extremely dangerous for people suffering from diabetes and kidney failure. Accumulating in the body, it can seriously aggravate the disease.
- The fluoride content in toothpastes can also negatively affect the functioning of the thyroid gland. The functioning of the immune system decreases, a person becomes susceptible to various diseases.
- The presence of fluoride in toothpaste can become a trigger for the development of cancer. Especially if you have a predisposition to them.
- The production of collagen in body tissues decreases. The skin becomes dehydrated, becomes flabby and pale. A person looks and feels older than his age.
“Toothpastes contain fluoride that far exceeds the concentration found in natural sources.”
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova