What is flux and its types
Flux is an inflammatory process of the soft tissues of the periodontium and periosteum.
The scientific name of the disease is periostitis. It can occur on the gum under any tooth (or above it, if we are talking about the upper jaw). Caused by infection of dental tissues. The process of progression of periostitis goes through four stages (if you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner). The first is characterized by slight pain in the gums, “radiating” to the tooth. The second is the appearance of swelling and redness at the site of tissue infection (the tumor visually resembles a small sac). The third is an increase in body temperature, discharge of pus and swelling of the cheek due to inflammation. The fourth is manifested by severe throbbing pain and increased swelling. Types of flux:
- ordinary - the inflammatory process does not affect the periosteum;
- fibrous – inflammation spreads to the periosteum;
- orthodogenic – infection of bone tissue occurs (osteomyelitis);
- albuminous - a chronic form with a slight increase in temperature and periodic suppuration.
Tooth flux - what is it?
Periostitis (flux) is a rather unpleasant process that affects soft tissues and periosteum. An inflamed pouch on the gum can form after unprofessional treatment by a dentist, as a result of injury to the mucous membranes or as a consequence of their disease. There are different forms of flux, differing in the localization of inflammation. For example, with serous periostitis, the periosteum becomes inflamed, and infection with diffuse flux affects different parts of the jaw, so the pathology has to be eliminated surgically.
Causes and mechanism of flux occurrence
As already mentioned, the cause of periostitis is infection. It may be caused by the following factors:
- the presence of carious lesions on the teeth;
- injury;
- infection during treatment;
- poor oral hygiene.
And yet the most common cause of the disease is caries. If a person does not go to the dental clinic, pathogenic microflora destroys tooth enamel and then penetrates inside the tooth. Then pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute pain. If left untreated, the pain gradually stops as the nerve endings die. But the spread of infection does not stop, it reaches the tooth root, causes inflammation of the gum tissue, in which the pathological process begins with the formation of pus. Flux is formed.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth can be removed due to flux, but in modern dentistry the emphasis is on tooth-preserving manipulations. This also applies to flux. A tooth must be removed when its crown is seriously damaged and cannot be restored with a pin or inlays. If an infection occurs under the crown, then re-prosthetics are often difficult. In some cases, a tooth has to be removed because it is impossible to unfill the canals after a previous unsuccessful treatment, but this happens extremely rarely. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove a tooth based on the clinical picture.
Symptoms
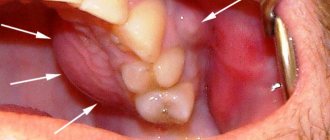
- The formation of a small lump on the gum under (above) the tooth
- Throbbing pain radiating to the back of the head, chin, temple
- Redness of the gums
- Swelling of the cheek due to inflammation
- Increased pain when touching a tooth next to a lump
- Deterioration of general condition caused by intoxication
- Temperature increase (low to high)
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
Note: sometimes swelling on the cheek occurs without any apparent reason or pain. But nevertheless, if this symptom appears, you need to consult a dentist as soon as possible. The doctors in our network of clinics have extensive experience in treating flux, regardless of its type and complexity of the clinical case.
How to avoid deletion
In order to avoid complications, the most important thing is to seek help from a dentist in time. Timely treatment will help save the tooth.
With timely, qualified assistance, swelling and pain will disappear within three days.
If therapeutic help is not enough, surgical intervention is started.
Stages of surgical treatment
- anesthesia;
- antiseptic treatment;
- removal of purulent formation and surrounding inflamed tissue;
- removal of the tooth itself;
- fixation of drainage for the outflow of pus;
- suturing.
After several days, the drainage is removed.
After removal, the main thing is to follow all the dentist’s instructions to avoid any complications.
What happens if flux is not treated?
Many patients, when symptoms of periostitis appear, hope that everything will “resolve” on its own, as people say. This is an erroneous and dangerous opinion, following which can have dire consequences. This situation can have a particularly serious impact on the child’s health, because the protective immunity at an early age is not well developed. If left untreated, the infection remains in the body, causing the emergence of new diseases, some of which can result in sepsis and death. What is most likely to happen? We list them according to the severity of the problem.
Flux symptoms
Flux is an inflammatory process in the periosteum, which is accompanied by noticeable swelling of the gums and cheeks. If at the same time you notice an increased temperature, sharp pain in the area of the disturbing tooth and enlarged lymph nodes, rest assured that this is a gumboil. When you touch a tooth, pain may be felt in the ear, temple, or entire half of the face.
The formation of flux can be caused by stress, a cold, untreated pulpitis or caries, as well as an infection that has entered the body. If painful sensations accompany you throughout the day and the swelling does not subside, this may indicate the presence of pus inside the tooth cavity. In this case, you can no longer hesitate and you must urgently contact a specialist, otherwise the disease may progress to the abscess stage, which threatens the formation of phlegmon (purulent inflammation).
Important Note
: Do not under any circumstances try to open an abscess yourself!! This can lead to blood poisoning and the most severe consequences.
Consequences of untreated flux:
- abscess (abscess) - the formation of a purulent sac;
- phlegmon - an extensive inflammatory process after the rupture of an abscess;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw - inflammation of the tissues of the jaw bone;
- inflammation of the sinuses of the skull - the sphenoid, maxillary and frontal sinuses are involved in the pathological process. Sometimes the infection penetrates into the brain tissue.
Important: specialists from the “Smile” clinic network recommend starting treatment as early as possible. The faster the inflammation is stopped, the less effort will be required to eliminate the problem and restore the patient’s health.
Gums gumboil - what is it?
Before we tell you what helps with flux and what to do if it appears, we will describe this ailment. In the medical field, the disease is called periostitis. Its occurrence is promoted by inflammation of the periosteum tissue.
Visually, the pathological focus resembles an elastic sac filled with purulent contents. Its borders are red and painful. If the outflow of necrotic masses is not ensured in time, the pathogenic microorganisms contained in them can enter the systemic bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
Treatment algorithm
The treatment protocol for periostitis involves a combination of surgical, medicinal and physiotherapeutic methods:
- taking (or a course of injections) antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microflora;
- opening the purulent sac (using local anesthesia), and in difficult cases, installing temporary drainage to drain the pus;
- eliminating the cause that caused the formation of flux: treating a tooth or extracting it if therapeutic measures are inappropriate, cleaning periodontal pockets;
- treating the wound with an antiseptic (gel, rinsing) until it is completely healed;
- course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Expert advice: after opening a purulent sac, you should not apply warm compresses or take antibiotics that have not been approved by the doctor. If pain continues more than 8 hours after surgery, you should contact the clinic immediately.
Treatment methods
The attending physician should tell you after the examination how to treat gumboil and what measures need to be taken to achieve a successful result. The mechanism is approximately the same, but each clinical case has its own nuances. Today, several techniques are used aimed at eliminating the disease and its manifestations. As a rule, they come together.
Antibiotics for gumboils
Antibiotic treatment is an important stage of rehabilitation. The most effective antibiotics for fighting inflammation and infection are Metronidazole, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav and their analogues. Any tablets and antibiotics for tooth flux should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
Physiotherapy
Used as an additional measure to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Recommended procedures include electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy.
Therapeutic treatment
It is carried out if it is decided to save the tooth. This includes endodontic treatment and filling of root canals, as well as resection of the root apex if necessary. If the cause of the flux is periodontitis, then a series of manipulations are carried out to eliminate the accumulation of bacteria in the periodontal pockets.
Surgical procedures
This includes tooth extraction and periostotomy - the main procedure for treating flux. The doctor makes an incision into the purulent sac, and then installs a drain through which the purulent exudate comes out.
Local therapy and rinsing for tooth flux
For better release of pus, pain relief and reduction of swelling, gels and ointments are used topically: Metrogyl Denta, Levomekol, Cholisal. Many people are interested in how to rinse gumboil on the gums. Miramistin and soda solution are usually used for rinsing. As an alternative, you can use folk remedies: decoctions and tinctures of propolis, chamomile, sage or calendula. A tooth after gumboil is still very vulnerable: to minimize the risk of re-infection, these treatment and preventive procedures are very important.
Recommendations from prevention experts
- Timely treatment of caries
- Thorough hygienic care of teeth and gums at least 2 times a day
- Rinsing your mouth after every meal and sugary drinks
- Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination twice a year
- Have it professionally cleaned at least once a year
- Eating firm, raw fruits and vegetables daily
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers services for the treatment of dental flux in adults and children. Contacting our centers has a number of important advantages:
- highly qualified specialists;
- compliance with examination and treatment protocols in accordance with international standards;
- system of family and cumulative discounts;
- stable price of treatment, depending on the severity of the clinical case.
You can contact any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Art. Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Art. Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, address: building 34, building 1.
Do not delay your visit to the doctor, make an appointment when the first symptoms of periostitis appear. This will significantly shorten the treatment time and save costs. Our specialists will provide effective medical care regardless of the severity of the disease. We will take care of your health!
Flux and abscess: causes, diagnosis, treatment methods
Flux and abscess: causes, diagnosis, treatment methods
In modern medicine, the term “flux” as such no longer exists. The once popular word has now been replaced by “odontogenic periostitis.” However, for many, the words “tooth flux” is a more understandable term and means severe pain, swelling and something serious that urgently needs to be addressed to a doctor, and rightly so.
There are different degrees of purulent inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial area - periostitis (flux), abscess, phlegmon.
Most often they appear against the background of advanced caries.
The first stage of inflammation is periostitis (flux) of the jaw - this is an acute inflammation of the periosteum. The cause of flux is the activation of pathogenic flora: streptococci, staphylococci and other pathogenic, often putrefactive bacteria, which were in a dormant state, under certain factors begin to actively multiply and spread, triggering an acute reaction of the body aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation.
Periostitis occurs as a complication of acute or chronic, but aggravated periodontitis, which in turn appears as a result of advanced caries. Previously treated pulpitis may also be a prerequisite. Much less often, the inflammatory process can develop with difficulty in teething, injuries, as well as periodontal diseases in the presence of periodontal pockets.
Flux can also occur after tooth extraction, due to traumatic removal or incomplete extraction of roots. Sensitization and general factors play a certain role in the development of the disease: cold, overwork, stressful situations that reduce the body’s defense reactions.
Regardless of the cause, the clinical picture develops the same
Flux and its symptoms:
- constant toothache, aggravated by pressing or tapping on the tooth;
- redness and hyperemia of the gum mucosa in the area of the causative tooth
- the formation of a significant tumor in the area of the tooth, upper or lower jaw, depending on its location.
- severe pain that can only go away after taking a painkiller;
- limited mouth opening;
- signs of intoxication of the body in the form of a sharp rise in body temperature, headaches, general malaise and a feeling of chronic fatigue
Abscess – second stage of inflammation
An abscess is a purulent inflammation of tissues with their melting and the formation of a purulent cavity; functionally it is practically no different from periostitis; it forms within a day or two from the onset of the disease. The symptoms in this case are the same, but at the same time more intense. Pus, as with flux, is limited to the periosteum, but can penetrate deeper into the tissue.
Sometimes during the disease a fistulous tract may appear, through which pus will come out. An effect of imaginary well-being is created, because along with the outflow, the signs of inflammation subside. However, with this type of development, the disease becomes chronic; if the infection is not stopped, it can spread to neighboring tissues and cause a complication in the form of osteomyelitis (necrotizing inflammation of the bone).
If the abscess was not drained and the fistula never formed, purulent inflammation begins to spread to the surrounding tissues - phlegmon appears.
Phlegmon is a dangerous omission
Cellulitis is the third, most severe stage of purulent inflammation in the tissues around the tooth. In this case, the pus is not limited to the periosteum alone, but wanders freely through the tissues.
Further spread of the infectious-inflammatory process in the perimaxillary soft tissues usually occurs along the fiber of the interfascial and intermuscular spaces, the fiber surrounding the vessels, nerves, and salivary glands. In this case, tissue compaction occurs, often accompanied by the appearance of asymmetry of the face and neck in the form of swelling. The pain moves beyond the jaw and becomes less localized. Chewing function may be impaired due to pain and limited mouth opening. External breathing may be impaired, and signs of intoxication may increase.
Purulent lesions of the head and neck carry the risk of further spread of purulent infection into the facial muscles, cervical regions, and beyond them into the trachea and chest cavity, into the esophagus, into the heart, and can penetrate into the lymphatic system and brain tissue.
IMPORTANT! If phlegmon is not treated in time, it can be fatal!
Treatment of periostitis, abscess
The first and most important step in treating flux is visiting a doctor.
Treatment is complex: surgical - opening and draining the inflammation, and conservative drug therapy.
Stages of treatment:
- Examination, examination, including x-ray diagnostics, determination of indications for surgical treatment.
- Local anesthesia.
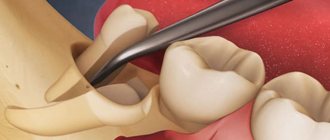
- An incision is made in the gums next to the gumboil so that the purulent contents come out, observing all the rules of asepsis and antiseptics.
- Installation of drainage for further outflow of pus - otherwise the exit from the periostitis site will close faster than it will be completely cleared.
- Removal of the affected tooth, if it is not possible to cure it, or removal of the root remaining in the hole, if we are talking about flux after removal.
- Prescription of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, painkillers.
- Control inspection and removal of drainage.
- Recommendations for home oral care.
All procedures are performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. After the examination has been carried out and the cause of inflammation has been established, an incision is first made in the area of the flux to release the accumulated pus, after which a so-called drainage - a rubber strip - is inserted into the wound. Treatment of an abscess differs from the elimination of periostitis only in the duration of wearing the drainage.
Next, the indications for tooth extraction or preservation are determined. If the tooth that was the source of infection is destroyed and has no functional or aesthetic value, then it is removed simultaneously with the opening of the abscess. This will improve the emptying of the purulent focus and will contribute to a faster elimination of inflammatory phenomena.
Tooth extraction is sometimes postponed due to perceived technical difficulties or the unsatisfactory condition of the patient.
In other cases, the tooth is preserved: its cavity is opened, the root canal is freed from decay products, and then conservative treatment of chronic periodontitis is carried out. All this is determined by the doctor and depends on the specific situation in the oral cavity. Treatment does not end there, but continues at home with the help of prescribed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. A repeat examination is scheduled on the 2nd day after surgery, the degree of subsidence of inflammatory phenomena is determined and, depending on this, additional treatment is prescribed. During dressing, local wound treatment is carried out. Around day 3-4, the drainage is removed, but conservative treatment continues.
Treatment of phlegmon is carried out in a hospital setting.
What happens after treatment?
After opening the abscess, if no complications arise, the disease enters the subacute stage. In most cases, inflammatory phenomena quickly (after 2-3 days) subside. There is a subsidence of the local inflammatory process: tissue infiltration decreases, the amount of purulent discharge from the wound decreases. As the wound is cleansed, granulation tissue appears, scarring and epithelization occur. At the same time, the severity of the general reactions of the body weakens, and health improves.
Usually, discomfort persists for the first 2 days, although the body temperature gradually begins to decrease, and the pain is no longer so obvious. A sharp improvement in condition and appearance occurs on the third day. Infiltration—tissue compaction at the site of inflammation—can persist for quite a long time. Gradually the “bump” should resolve.
The drainage - a rubber strip - should remain in the wound for some time after the procedure. It prevents the incision from closing prematurely, leaving an open path for pus to escape. It is strictly forbidden to loosen, push out, or adjust the drainage in any way. If a strip falls out, consult a doctor immediately. You should also contact your doctor if you do not feel better 12 hours after opening the flux.
The prognosis of periostitis with timely radical intervention is predominantly positive. Isolated deaths are associated with late seeking of dental care.
Self-medication of flux can lead to further spread of purulent inflammation in the tissues and such serious complications as osteomyelitis of the jaw or phlegmon of the soft tissues of the face and neck.
Prohibited for inflammation:
- try to open the abscess yourself;
- apply warm compresses and dressings;
- independently prescribe antibiotics and other medications;
- take painkillers before visiting a doctor;
- drink aspirin (before and after opening).
Finally, I would like to say one thing: please do not be afraid to consult a doctor for help in a timely manner. The sooner treatment is started, the better the outcome. Take care of yourself!
Flux treatment
Treatment should take place in a specialized dental clinic. The duration and complexity of treatment depends on the area of the tooth, the location of the flux, the presence or absence of pulpitis and other diseases, as well as the stage of development of the disease - early or late.
The early stage of development is considered to be the period before the appearance of purulent discharge in the affected areas of the tooth. Most often, early treatment is accompanied by the use of antibiotics and painkillers under the strict supervision of a dentist. Remember that many antibiotics have a number of serious contraindications, and their prescription can only occur after the doctor makes sure that you are not at risk and are not allergic to certain components of the medicine.
Treatment of the late stage of development cannot be carried out without surgical intervention. At this stage of the disease, it is necessary to remove the abscess in time. The operation is performed under local anesthesia; you will not feel anything at all. After removing the abscess, relief occurs within twelve hours. The doctor prescribes painkillers and antimicrobials to the patient. It is highly undesirable to engage in heavy physical labor after surgery; it is better to avoid unnecessary stress on the body. Complete restoration of the oral cavity and body after surgery takes three days.
The most radical way to treat gumboil is tooth extraction. It is used only in the most advanced stages, when an abscess has already begun - the spread of pus into the soft tissues of the body. Pus getting into the facial muscles, neck muscles, and then the spread of pus throughout the internal organs is very dangerous. Known fatalities.
As you can see, dental flux is not a harmless, mild disease, but a serious threat to the health of your body. Do not rely on your own strength and contact the dentist at the first sign.
Prevention
To reduce the likelihood of periostitis, you must:
- Get an annual checkup at your dentist's office. The doctor will check for diseases and carry out professional oral hygiene.
- Brush your teeth two to three times a day. To do this, you need to use high-quality paste and a brush selected by a specialist.
- Treat any dental diseases promptly. After all, very often gumboil is a logical continuation of deep caries.
- Stop smoking and eat right. The diet should be rich in fresh vegetables and fruits. They will provide the body with useful elements and have a positive effect on the condition of the gums.
Summarize. If you want to find out how to quickly get rid of periostitis, be sure to visit a dentist. Don’t “reinvent the wheel” and don’t look for folk recipes. Therapy should be comprehensive, step-by-step. The doctor must be responsible for its implementation. Only then will it be possible to quickly get rid of the disease and the question of how to cure gumboil will be finally closed.
Is it possible to pierce flux with a needle at home?
Many self-medication methods are extreme, but this does not make them more effective. Some patients are confident that they can pierce the flux themselves with a regular needle, even at home.
After this, they use various rinses and lotions. However, positive results after such manipulations are extremely rare.
Under no circumstances should you violate the integrity of the gums or skin on your own. Such operations can have extremely negative consequences:
- worsening of the inflammatory process;
- an increase in the amount of pus in the abscess;
- pus can penetrate into spongy and soft tissues;
- may develop as a complication ;
- Cellulitis without proper treatment develops into sepsis.
How to quickly remove swelling from dental flux
Flux cannot be called a disease that comes from outside.
Only an experienced specialist can open the flux, since this manipulation is classified as surgical.
On the Internet you can read many reviews from people who opened the flux themselves using a needle. Even if such an “operation” was successful, it still remains extremely dangerous, so you need to consult a doctor instead of conducting experiments on your own health.