Minor defect?
Grinding of teeth in a child may seem like a minor deviation from the norm only at first glance. It’s good when this phenomenon is temporary and at the age of 5–6 years, bruxism in a child goes away on its own. But if your first-grader continues to grind his teeth at night, don't hesitate to seek medical help. Otherwise, even the permanent teeth that will replace the milk teeth will be at risk.
Helping children with bruxism
Whether the cause is physical or psychological, children can control bruxism by relaxing before bed—for example, taking a warm bath or shower, listening to soothing music for a few minutes, or reading a book. For infants who are teething, you can offer them a pacifier. She will calm the baby and give a light massage to the gums.
If you are teething or have an ear infection, ask your doctor to prescribe the correct dose of ibuprofen to relieve discomfort.
If teeth grinding is caused by stress, ask about what is upsetting your baby and find solutions.
In rare cases, when stressful situations cannot be resolved within the family circle and sleep problems arise, the help of a psychologist is required. He will help you find the cause of stress and prescribe the right course of treatment.
Symptoms of childhood bruxism
- Headache in the morning
- Feeling of fullness in the ears
- Complaints of pain in the back
- Unmotivated irritability and tearfulness
- Restless sleep with frequent crying
- Lack of appetite
- Rapid tooth wear (this symptom can only be determined by a dentist during an examination!)
Attention!
A high temperature and grinding of teeth in a child may be a reaction of the body to a routine vaccination carried out the day before.
Diagnostics
Most children who have this problem during night or daytime sleep do not even know about it. Therefore, most often, parents diagnose the problem.
Some signs:
- Teeth grinding when your baby sleeps;
- Complaints of pain in the face or jaw after waking up in the morning;
- Pain when chewing.
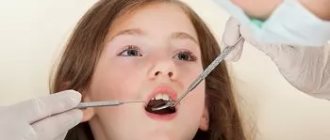
If you experience any of these signs, contact your dentist to examine your mouth for wear and damage. Spray air and water on teeth to test sensitivity.
If damage is found, the dentist may ask your child several questions, such as:
- How do you feel before bed?
- Are you worried about anything at home or at school?
- Are you angry with someone?
- What do you do before bed?
The exam will help the dentist understand whether the cause is anatomical (misaligned teeth) or psychological (stress). Select an effective treatment plan.
Causes of teeth grinding in children
Switching to artificial feeding
Teeth grinding in a child aged 8–10 months may be associated with early weaning from the mother's breast. This is extremely stressful for the baby. According to statistics, it is male “artificials” who most often suffer from bruxism. In this regard, increased attention should be paid to ensuring that the baby receives breast milk in full for as long as possible. To do this, the mother is advised to maintain a drinking regime, regularly express excess milk and avoid worries.
Teeth cutting or changing teeth
Teeth grinding during the day, which parents can notice by a specific sound, usually appears after the eruption of another baby tooth. The child is simply curious about new sensations, and he “plays”, deliberately creating friction between the teeth. As a rule, he quickly gets bored with this, but years later, when baby teeth are replaced with permanent ones, the picture may repeat. Read more about teething in this article.
Dental pathologies
When a child turns one year old, teeth grinding may indicate the presence of some abnormalities in the functioning of the dental system. An incorrect bite, inflammation of the jaw or pathological development of the joint are reasons to “grind” in order to more conveniently position the teeth in the mouth. Only an orthodontist can determine the specific cause. Read more about this here.
Stressful situations
If the day has come and a child of 2–3 years old does not stop grinding his teeth, this is a signal of a problem in his nervous system. In this way, the baby reacts to the stress he has experienced. The trigger for this can be both strong negative emotions (separation from a favorite toy, starting a visit to kindergarten or “eviction” from the parents’ bed), as well as positive ones that lead to strong overexcitation (outdoor games, the arrival of relatives with other children, etc.) .
Sleep disturbance
If a child has difficulty falling asleep, snores, mumbles in his sleep, suffers from enuresis or somnambulism, this may cause teeth grinding at night. Inadequate sleep negatively affects the child’s body and is a trigger for spasms of the masticatory muscles. The task of parents is to ensure that the baby gets enough sleep.
Wrong diet
Sometimes the reasons for teeth grinding in a child’s sleep lie on the surface - the parents themselves are responsible for this, having failed to create an optimal feeding regime. In order not to provoke involuntary contractions of the masticatory muscles, the last meal should be completed 2 hours before going to bed. Kefir is allowed 1 hour before bedtime.
Avitaminosis
Are you looking for reasons why your child grinds his teeth during the day? Analyze how much vitamins and minerals he receives from food during breakfast, lunch, afternoon snack and dinner. A deficiency of B vitamins, coupled with insufficient intake of magnesium and calcium into a growing child’s body, can lead to overstrain of the masticatory muscles. Only a pediatrician should determine the required dosage of a particular vitamin after an examination.
Upper respiratory tract diseases
Coughing and grinding of teeth in a child along with nasal congestion are a characteristic manifestation of sinusitis or bronchitis. In this case, bruxism will go away as soon as the disease that caused it is cured. If you notice that your cough does not go away, despite all the traditional measures taken to combat it, then do not delay a visit to an infectious disease doctor.
ENT diseases
Grinding of a child's teeth at night is also one of the main symptoms of adenoiditis - inflammation of the tonsils. The complex of unpleasant sensations caused by an increase in the size of the adenoids literally forces you to grind your teeth. The first thing that should alert parents in this situation is a constantly slightly open mouth.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky claims: bruxism in children is more likely to occur if their parents suffered from it in childhood!
Treatment of teeth grinding
If a baby grinds his teeth in his sleep, special treatment is not always needed. If a symptom of lower jaw tremor appears in a one-month-old baby, this is an alarming sign. The mother should pay attention to how the baby takes the breast, at what time the jaw spasm or trembling of the chin appears. A consultation with a neurologist is required. It is possible that during pregnancy or childbirth the baby suffered a brain injury or suffered from hypoxia.
When a 7-8 month old baby begins to grind his jaws, the pediatrician may recommend a gel for easy teething. Experienced mothers purchase cooling silicone teethers in advance, against which the infant scratches his gums.
If the analgesic effect of cooling or dental gel is insufficient, the baby is given paracetamol or ibuprofen syrup. They relieve inflammation from the gums, eliminate pain and swelling.
In autumn and winter, a 4-5 month old child experiences calcium deficiency. At this time of year, the number of sunny days decreases, and the need for the mineral increases. Calcium is absorbed from milk if there is enough vitamin D in the intestines. It is produced under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. If there is a lack of sunlight, the vitamin is low, so it is necessary to take it in the form of an aqueous solution of drops. Vitamin D will not harm a one-year-old baby or schoolchildren in the winter. The dosage of the drug is selected by the pediatrician individually, so as not to cause a state of hypervitaminosis, which is dangerous for the kidneys.
Treatment of creaking, which often appears after overexertion or stress, is carried out with sedatives. For children, the doctor may prescribe sedatives of herbal origin or herbal teas with mint, valerian, motherwort and other combinations.
If the pediatrician cannot determine why the child continues to grind his teeth, an examination by a dentist is necessary. The doctor will grind off the protruding fillings and check the function of the temporomandibular joint. For periodontal inflammation and caries, he will prescribe special treatment. An incorrect bite is a reason to contact an orthodontist. He will select a mouthguard to protect your tooth enamel from being worn away. If the bite is defective, the use of braces or a corrective plate will be required, which is removed at night.
If there is a repeated creaking or the appearance of convulsive contractions in other muscle groups, be examined by a neurologist. The result of the electroencephalogram may indicate a mild form of epilepsy. For treatment, the doctor will prescribe anticonvulsants. They will help reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. If you refuse therapy, this phenomenon will occur more often and more severely.
What to do if your child grinds his teeth?
- The first step is to make an appointment with a dentist and pediatric neurologist. The first will give practical recommendations on how to prevent enamel wear, the second will determine why the child has teeth grinding.
- Monitor the psychological microclimate in the family. The child should be honest about his worries and be sure that he will receive help from his parents.
- Adjust your daily routine. An hour before going to bed, the child should be occupied with a calm activity to avoid overstimulation of the nervous system.
- Balance the children's menu. The daily diet should include solid vegetables and fruits - the load on the masticatory muscles during wakefulness will lead to their relaxation during sleep.
- Teach self-control. In the form of a joint game, practice every day following the simple rule: “Lips are closed, teeth are apart.” This way, the baby will not form the bad habit of clenching his teeth during the day, even at the moment of strong excitement.
Why does a child grind his teeth in his sleep: reasons
Experts are not always sure about the causes of bruxism. There are several options why children experience grinding at night:
- Incorrect bite. This is when the upper and lower teeth are not aligned properly;
- Other babies do it as a response to pain, such as ear pain or teething. Children may grind to relieve pain;
- If you have a disease - epilepsy, cerebral palsy. Or the child is taking certain medications that may develop grinding;
- During adolescence, teeth grinding at night can be caused by smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Heredity. Bruxism can be passed on to children if parents suffer from this disease;
- Another reason is stress. This is usually nervous tension or anger. For example, your child may be anxious about a test at school or because of a change in their routine;
After the age of six, many children outgrow teeth grinding.
Prevention measures
Of course, when a child grinds his teeth, parents are interested in whether it is possible to somehow prevent the development of the disease? Unfortunately, today there is no specific prevention of bruxism. But if you follow simple rules, it is quite possible to minimize the risk of its occurrence.
- Pay attention to hygiene
The banal advice is not without common sense. Judge for yourself: a common cause of bruxism is a defensive reaction to the eruption of a new tooth. During the process, the gums become inflamed and mild itching may occur. It is advisable to give your child special teethers made of safe materials so that he does not rub his teeth against each other. Also, do not ignore brushing your teeth with special fingertips.
- No stress!
Do you want your child to avoid grinding his teeth all night long and then all day long? Eliminate any nervous stress from his life. It is generally accepted that only what happens directly to him can have a negative impact on the baby’s psyche. In fact, your quarrel with your spouse or a loud conversation on the phone with a work colleague can negatively affect his mood.
- Fight bad habits
Today, any doctor will tell you that the causes of teeth grinding are both an incorrect bite and a fixed pathological reflex, for example, sucking a pacifier to calm down in a stressful situation. Therefore, it is worthwhile to gently but decisively fight childhood bad habits and promptly consult an orthodontist if necessary.
Why is night bruxism dangerous?
Should parents worry and take some measures if their baby grinds his teeth in his sleep? Yes, if:
- Child's age over 7 years
Most often, teeth grinding during sleep occurs in young children, and by the age of seven it usually goes away without a trace. If the child has already gone to school, but the problem remains, it’s time to take measures to eliminate it.
- A large number of repetitions of this condition are recorded or attacks last more than 15 seconds
In these cases, unpleasant sounds made by teeth during sleep may indicate serious disorders in the activity of the nervous system. The sooner the diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of avoiding the disease becoming chronic.
- There are signs of tooth decay or gum inflammation
If you do not take action in a timely manner, you may face much more serious problems: gum disease, premature loss of baby teeth, and malocclusion.
Bruxism becomes especially dangerous when baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. It can cause diseases that will lead to the loss of permanent teeth at an early age.
Doctors do not consider bruxism a health-threatening disorder, especially if we are talking specifically about nighttime teeth grinding. It usually goes away with age without any treatment.
If you want to help your baby cope with the problem before he outgrows it, then first consult a dentist.
About the need to treat bruxism
If teeth grinding disrupts sleep for several days, then it’s too early to sound the alarm. However, if the grinding episode becomes persistent, it is time to see a doctor. Parents need to find out why their child grinds his teeth if:
- the grinding is strong and leads to pain in the jaw and neck;
- the child continues to grind his teeth for 3 weeks or more;
- poor health, complaints about sleep and pain from any organ system;
- other symptoms appear.
Procedure for making a diagnosis:
- make an appointment with your local doctor;
- talk about changes that were noticed in the behavior and health of the baby;
- get examined by a dentist;
- as prescribed by the treating pediatrician, do polysomnography, consult with a neurologist, gastroenterologist, or otolaryngologist.
If you don't go to the hospital, you are putting your baby's health at risk. Untreated bruxism will lead to:
- chipped tooth;
- enamel microcracks;
- tooth abrasion;
- periodontitis;
- malocclusion;
- changes in jaw structure;
- dysfunction of the facial joints;
- headaches;
- neuralgia;
- spasms of the facial muscles;
- disruption of sleep and wakefulness;
- diseases of the nasopharynx.
During exacerbations of bruxism, nightmares and sleep disturbances alone will not be enough. Throughout his life, the child will face serious consequences after “childish” teeth grinding.
How is bruxism treated?
The course of treatment is selected after it is determined exactly why the child grinds his teeth. Depending on the reason, they may prescribe:
- consultations with a psychologist teaching how to independently relieve nervous tension;
- a course of psychotherapy to stabilize the emotional state;
- drug treatment against cramps of the facial and masticatory muscles, damage to the trigeminal nerve;
- therapeutic and preventive procedures for improving the health of the oral cavity;
- anthelmintic drugs.
At the same time, the pediatrician will recommend not to overexert yourself before bed, stick to a routine, get a balanced diet, take a complex of vitamins for children, and attend physical therapy to normalize nasal breathing.
Physiological explanation of bruxism
Teeth grinding occurs due to spasm of the chewing muscles, clenching of the jaws and their strong movement. The peculiarity of the disease is the fact that it occurs involuntarily. Most often this occurs during the patient's sleep at night, but some also worry during the daytime. In the first case, the pathology is called bruxism, in the second - bruxiomania. During the period of primary occlusion formation, the disease manifests itself in at least half of children. This is considered normal if it goes away by age 7.