Bruxism - what is it
Uncontrolled grinding of teeth, resulting from spasms of the masticatory muscles. If you come across texts about the Carolini phenomenon, odonterism, “teeth grinding disease” - they are all about bruxism, and the names listed are synonyms of bruxism. Translated from ancient Greek, bruxism means grinding.
Dentists distinguish two types of this disease.
- Directly grinding, that is, the friction of the teeth against each other.
- Clanching is a static clenching of teeth that occurs without friction.
Bruxism is often chronic, causing discomfort to a person for many years. If left untreated, it results in complications: problems with the temporomandibular joint, chronic stress, and abrasion of tooth enamel.
It is necessary to distinguish between childhood and adult bruxism - they have many significant differences. Here we will look in detail at the course of this disease in adults. There is a separate article on childhood “teeth grinding disease”.
Night grinding of teeth.
A person does not realize that he grinds his teeth when he sleeps. Doesn't wake up from gritting her teeth and may not be aware of the problem at all. Only his relatives can talk about it.
Daytime teeth grinding.
This type of bruxism is already recognized by a person. But clenching of teeth occurs involuntarily and cannot be controlled. During daytime bruxism, a person feels discomfort, which causes periodic strong tension in the facial muscles.
What should the mother do and how to help the child?
You can help your child cope with teeth grinding at home. The task of parents is to relax the child, especially in the evening. Suitable for relieving tension:
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- correct daily routine;
- walks in the open air;
- drinking enough water;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that excite the nervous system: chocolate, coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, etc.;
- last meal – an hour before bedtime;
- hot bath before bed;
- refusal of active games, quiet activities in the evening: drawing, listening to lullabies, etc.
In addition, heart-to-heart conversations with your child can help. If the child does not speak out, he will go to bed with anxious thoughts. This will trigger an attack.
The following techniques will help reduce facial muscle tension:
- heat compresses (including for pain in the morning);
- chewing solid food;
- giving up chewing gum.
The most common consequences of teeth grinding in adults
- Increased tooth wear. Constant friction causes teeth to lose their natural height. In general, this is a natural process: with age, all people's teeth become a little shorter. But with bruxism this happens much faster. Plus, constant grinding of teeth results in frequent loss of fillings, the appearance of chips and roughness.
- Pain in the mouth. It appears due to the fact that during bruxism a person often “bites” his cheeks. Wounds and abrasions appear that do not have time to heal.
- Headache, nagging pain in the neck, ringing in the ears, dizziness. If the cause of these neurological symptoms cannot be substantiated by other diseases, then there is a high probability that these are the consequences of constant teeth grinding.
- Drowsiness, irritability, general “weakness,” fatigue. All this can appear if a person suffering from bruxism has trouble sleeping at night due to constant clenching of teeth during sleep.
A person himself can rarely understand that the cause of his health problems is bruxism. The diagnosis can be made only with the help of a special study - electromyography.
Diagnostics
Bruxism is less common in adults than in children. To begin adequate therapy, a comprehensive examination should be carried out, which will make it possible to find the root cause of this problem.
Psychotherapeutic diagnostics
The method allows you to find out why teeth grinding appeared and find the causes of the pathology at the psychosomatic level. An experienced psychotherapist assesses the extent of the progression of the disease and assists in changing the response in the event of stressful situations, since behavioral processes most often spur painful symptoms.
Electromyographic research method
Using electromyographic diagnostics, the functioning of the muscles of the masticatory apparatus is assessed at rest, as well as during active work, which makes it possible to better assess the nature of the pathology.
Electromyography reveals dental errors: inadequately selected dentures, mistakes during restoration procedures. Various studies help not only to make a diagnosis, but also to assess the possible consequences of the pathology, and provide an understanding of how to cure bruxism in adults and children in the shortest possible time.
Why do adults clench their teeth?
There is no clear answer. However, research and observations have allowed doctors to identify several hypotheses for the occurrence of bruxism.
- Bad habits
Sometimes, in order to concentrate, some people chew on a pen or toothpick. Over time, this action can become a conditioned reflex. And when a person needs to concentrate, he involuntarily clenches an imaginary toothpick between his teeth. This may explain the occurrence of teeth grinding during sleep. - Nervous stress
Often adults clench their teeth when they want to hold back in a stressful situation. If this happens for a long time, the body may develop an uncontrollable habit: the slightest overexertion - we clench our teeth tightly. This is another version of the appearance of bruxism at night in adults. - Neurological diseases
Also, people suffering from a number of neurological diseases often grind their teeth at night: epilepsy, tremor, enuresis, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease - all of them are characterized by such a symptom as bruxism. - Insomnia
If a person does not sleep normally for a long time, often wakes up at night, is more often in a state of shallow rather than deep sleep, he clenches his jaw uncontrollably because he begins to get nervous because he cannot get a good night's sleep. - Pathologies of the dental system
Bruxism can be caused by a pathological bite: it causes an uneven distribution of the load on the teeth. For treatment in this case, read the article “Bite correction in adults.” Also, the cause of clenching teeth at night may be their overcrowding. With this disorder, the teeth do not close completely. In addition, dentists studying the phenomenon of bruxism note that its cause may be the desire of people to “shorten” fillings or dentures that were installed incorrectly: a person tries to “erase” them and often begins to close their jaws tightly and move them relative to each other . Over time, this can become an unconscious habit.
For quite a long time, bruxism was considered a symptom of helminthic infestation. Scientific research has not confirmed this theory.
Possible causes of the disease
Bruxism can occur in patients of any age. If in childhood it is associated with teething and bite formation, then in adults it has several theories of origin. The disease can be a dental, psychological, neurogenic problem, and is also studied in the field of otolaryngology. Since a single cause for the development of this pathology has not been established, several theories of its development have been identified.
| Theory | Definition |
Psychological | Many doctors are of the opinion that teeth grinding at night occurs due to a violation of psycho-emotional balance. The cause of involuntary spasm of the masticatory muscles can be either negative events and stress, or strong positive emotions. During the day, patients experience emotional instability, which may also be associated with old events. |
Neurogenic | Another theory for the development of bruxism associates the disease with disruption of the central or peripheral nervous system. Its proof is the fact that teeth grinding often occurs in combination with headaches and insomnia, somnambulism, and sleep apnea (short-term cessation of breathing during sleep). Advanced forms occur against the background of nocturnal enuresis and can be complicated by attacks of epilepsy or muscle tremors (involuntary contraction of the body muscles). During the diagnosis, organic lesions of the trigeminal nerve are detected. |
Dental | Bruxism can be a consequence of pathologies in the structure and functioning of the dental system. Regardless of age, the disease can occur due to malocclusion, dental disease, or prolonged wearing of incorrectly fitted dentures or crowns. Anomalies in the structure of teeth are also included in the list of possible causes of bruxism. |
Osteopathic | Some experts consider spasms of the masticatory muscles as a protective mechanism of the body. Thus, in children this phenomenon often manifests itself after a complicated birth with possible weakness of the skull bones and sutures. Many adults who suffer from regular attacks of bruxism are often simultaneously diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Osteopathic pathology also identifies incorrectly performed dental prosthetics as one of the causes of night grinding. |
Other reasons | Another theory, which, however, has no evidence yet, is teeth grinding due to impaired nasal breathing. Thus, attacks can occur in people with a deviated nasal septum and difficulty passing air through the nasal passages. In addition, the presence of adenoids and frequent colds, which manifest as rhinitis (runny nose), may be important. |
The causes of bruxism are determined individually. It is possible that the disease will develop due to a combination of several factors at the same time. The problem of night grinding continues to be studied by leading doctors around the world. In particular, specialists from the Clinical Institute of the Brain successfully diagnose this disease and determine its causes on an individual basis.
Psychosomatic explanation of bruxism
Now one of the most common versions of teeth grinding is psychosomatic. That is, bruxism is the result of hidden experiences, long-suppressed emotions, complexes, and fears. All this can cause spasm of the chewing muscles. There is also an assumption that bruxism accompanies a number of mental disorders. Thus, scientists from Germany studying “adult” bruxism conducted a study, the results of which indicate that teeth clenching is directly related to chronic depression.
ATTENTION!
Confusion of the soul is the main cause of teeth grinding. This was the opinion of Hippocrates. And he was probably not far from the truth.
Treatment.
Treatment of bruxism still remains a difficult problem. It depends largely on the time of development, causes and nature of the disease. Its treatment will be more successful the earlier the disease is diagnosed. You should not be concerned about short-term (up to 10 seconds) irregular attacks of teeth grinding. Most likely, this is not bruxism, but immediate reactions to stressful situations of a healthy person. The alarm should be sounded when such attacks become regular.
It is almost pointless to fight bruxism on your own. As soon as you suspect you have this disease, contact a sleep specialist. He will give you professional advice and prescribe competent treatment. It is important to know that bruxism in children sometimes does not require special treatment, and may eventually go away on its own by the age of 6-7 years. Bruxism in adults must be treated.
If bruxism persists in an adult, then:
- If possible, it is necessary to eliminate any existing dental problems or malocclusions.
- While sleeping, wear a special intraoral protective device (mouth guard) made of rubber or soft plastic, which is made to the shape and size of your teeth, is fixed between the teeth and prevents injury. Although this device helps to cope with bruxism, it does not cure it.
- As an additional treatment, you can use magnesium, calcium and B vitamins. Saturating the body with these microelements and vitamins can reduce the convulsive activity of the masticatory muscles during sleep.
- You can also apply a warm, damp towel to your cheeks, this will help you relax muscles that are tired from clenching your teeth.
- Learn to relax. - Since the main cause of bruxism is everyday stress, any means of relieving stress can help you - listening to music, reading books, walking or taking a bath. You may need to seek counseling to learn how to effectively cope with stressful situations.
- Psychotherapy is the best way to help, which is aimed at identifying conflicts, understanding them and developing the ability to more effectively cope with the everyday difficulties of life.
What procedures can a dentist not perform for bruxism?
Chronic teeth grinding often makes it impossible to carry out dental treatment: for some types it is an absolute contraindication, for others it is a relative one. It all depends on the severity of bruxism.
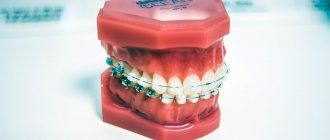
Treatment with braces.
For bruxism, dentists prefer to replace it with mouth guards. They are softer than braces and do not injure the mucous membranes, gums and tongue, which often happens if a person regularly clenches his jaw tightly. In addition, braces often break due to bruxism.
Installation of ceramic crowns
undesirable for “teeth grinding disease.” Despite the fact that modern dental ceramics are quite durable, they still cannot withstand the increased pressure that occurs during bruxism, and the ceramic crown is destroyed.
For implantation
Bruxism is considered an absolute contraindication, since the risk is too high that due to constant clenching of the teeth, the implant will become loose and fall out.
Restoration with lumineers, veneers, composites
It is ineffective for bruxism. It can be done, but it will not be possible to avoid mechanical damage to mini-prostheses. This has been recorded over many years of observations.
Minor defect?
Grinding of teeth in a child may seem like a minor deviation from the norm only at first glance. It’s good when this phenomenon is temporary and at the age of 5–6 years, bruxism in a child goes away on its own. But if your first-grader continues to grind his teeth at night, don't hesitate to seek medical help. Otherwise, even the permanent teeth that will replace the milk teeth will be at risk.
Should adults treat bruxism?
Teeth grinding is an unpleasant disease, but its severity for the patient, of course, cannot be compared with, say, a complete absence of teeth and caries. However, the long-term consequences of bruxism are still unpleasant. It may interfere with prosthetics, implantation, and orthodontic treatment with braces, if necessary. In most cases, you will simply need to get rid of uncontrollable teeth clenching, but this will require additional time and money. But, in general, we are lucky that we do not live in the Middle Ages - then the Inquisition interpreted gnashing of teeth as a symbol of connection with the devil and executed people. Today we have all the means to get rid of this disease. The main thing is not to delay your visit to the dentist and start treatment on time.
Dangerous symptoms: when should you see a doctor?
The question of when to start treatment for bruxism in children worries many parents.
As a rule, the disease goes away on its own, without any consequences, by the age of 12–13 years. This is due to the fact that by this period the formation of molars is completed. No treatment is required for this form of bruxism. However, there are times when the picture is not so rosy. You should contact your doctor immediately if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- headache and/or toothache in the morning;
- rapid wear of teeth;
- long and intense attacks at night (more than 10 seconds).
Complicated bruxism in children leads to quite unpleasant consequences, including gum disease and significant tooth wear.