Tooth extraction: swelling
Tooth extraction is a difficult operation that traumatizes the tissue surrounding the tooth. Therefore, it is not surprising that unpleasant consequences occur after tooth extraction: the most common of them is swelling. Patients often complain that after tooth extraction, the gums become swollen, swelling of the cheek or a slight gumboil appears. This is caused by partial destruction of the soft tissue around the tooth. This is unpleasant, but if the tumor is small, it goes away on its own in 2-3 days. To relieve swelling after tooth extraction, ice can be applied to the cheek for about 10 minutes. If the swelling has not gone away after a day, apply heat. Keep the heating pad for 20 minutes, then take a break for 10 minutes and put the heating pad back on.
Sometimes swelling can be caused by an allergy to the anesthesia. In this case, histamine, an antiallergic drug, will help. But if the swelling increases, then it may be a sign of inflammation that has arisen after tooth extraction. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Pain after tooth extraction
Another common complaint is that after tooth extraction, the gums, adjacent tooth, jaw, and throat hurt. As a rule, these are common symptoms after a traumatic procedure. They are caused by damage to the periodontal tissues and nerves, which goes away on its own after a few days. For example, if a temporary aching pain appears after tooth extraction, this is normal. To relieve discomfort, you can take painkillers. But if the pain intensifies, it is still worth visiting a doctor.
Bleeding after tooth extraction
Immediately after a tooth is removed, there is bleeding from the socket. This is quite normal, since blood vessels rupture during surgery. In this case, the doctor will provide you with the necessary assistance. But sometimes bleeding occurs a few hours after surgery. To stop the bleeding yourself after tooth extraction, apply a small gauze swab to the hole and lightly bite it. After 15 minutes the blood stops flowing. But if the bleeding does not stop for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
Don't be alarmed if...
- If the gums around the wound and the outside of the cheek are swollen and painful. This is a natural reaction to surgery. Swelling can be reduced with cold or ice, but it will be worst around the third day after surgery, and bruising may occur. Afterwards, the swelling and pain will subside.
- If during the first hours after surgery the gums bleed slightly. We emphasize - lightly . If the bleeding is severe and a blood clot does not form in the socket, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
- If you have a mild fever, the corners of your mouth become dry and cracked. This is also a sign that the body has begun healing the wound and fighting possible bacteria.
- If you cannot open your mouth wide for the first three days after surgery. And they shouldn't.
Pus after tooth extraction
Suppuration of the socket and periodontal tissues is caused by their infection. It can happen for several reasons. Firstly, if you did not follow the dentist's instructions regarding individual oral hygiene after surgery. Secondly, the cause may be a tooth fragment remaining in the tissues after removal. Thirdly, there is a high risk of suppuration after a complex wisdom tooth extraction, for example. If the inflammation is not treated in time, then some time after removal, suppuration, a fistula on the gum, and even a cyst may appear. If pus appears at the surgical site, consult a doctor. He will find and eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process.
Causes
Why does my breath smell after tooth extraction? There are several factors that provoke the problem:
- Patient's disregard for doctor's recommendations. After tooth extraction, the dentist instructs the patient about the rules of behavior in the postoperative period. For speedy wound regeneration, it is necessary to refrain from consuming hot and cold foods for 24 hours, as well as from rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions. Also, you should not touch the hole with your hands, so as not to provoke the destruction of epithelial tissue.
- No blood clot. During complex operations, for example, after the removal of a wisdom tooth, dry socket syndrome is often observed due to a previous infection of the alveoli. Pathogenic flora prevents a clot from forming. Complications after surgery appear within a few days. Patients report throbbing pain and swelling of the cheek.
- The presence of chronic infectious diseases in the oral cavity. The presence of pathogenic flora increases the risk of wound infection after tooth extraction. For people with chronic dental diseases, extraction is prescribed in extreme cases due to the high risk of developing negative consequences.
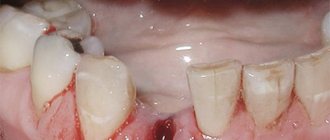
Dry socket after tooth extraction
A blood clot should remain in the socket after surgery. This is a very important part of the healing process. This clot protects the bone and nerve endings and serves to form bone tissue after tooth extraction. Therefore, you should not rinse your mouth for a day after the procedure and eat hot food - this will help the clot dissolve. But sometimes it does not form, and a dry socket appears.
Dry socket is considered a complication. It most often occurs after complex removals accompanied by significant trauma. If there is no blood clot, then the hole after tooth extraction hurts, and sometimes it seems that the ear also hurts. Often there is an unpleasant taste in the mouth. The consequence of a dry socket after a traumatic tooth extraction can be inflammation of the gums or alveolitis. Therefore, if you experience acute pain in the socket, consult a doctor immediately. He will place a tampon with a special anti-inflammatory gel on the hole. Tampons are changed until healing begins.
Tooth extraction itself is an unpleasant procedure. And if complications arise, such as alveolitis, then the patient’s mood deteriorates even more. In order to prevent its occurrence, you need to know everything about this unpleasant disease. We will tell you what you need to know about the causes of alveolitis, its types, first symptoms and treatment methods.
What it is
Alveolitis of the tooth socket is an inflammatory disease that occurs after tooth extraction as a result of infection of the wound. If the operation was difficult, with injury to the gums and the tooth socket itself, then the risk of complications increases significantly. Normally, the hole after tooth extraction heals within one to two weeks, but with alveolitis this process takes a long time.
Since the disease occurs when an infection enters the wound, in order to prevent complications from occurring, it is necessary to carefully monitor oral hygiene after the tooth extraction procedure.
Alveolitis can occur before the tooth extraction procedure as a result of infection.
Causes
Alveolitis of the socket most often occurs after tooth extraction and is considered its main complication. However, it does not always occur. In order for this complication to arise, a confluence of certain circumstances is necessary.
The main causes of alveolitis are:
- destruction of the blood clot that forms after tooth extraction and prevents infection from entering the wound;
- getting plaque, stone, or bone fragments into the hole during removal;
- unscrupulous cleansing of the hole by a doctor from granulomas and granulations;
- violation of sterility during surgery;
- too traumatic removal;
- failure on the part of the patient to comply with all the doctor’s instructions;
- reduced immunity and exhaustion of the patient’s body.
After tooth extraction, you should not rinse your mouth too vigorously, as you can wash out the formed blood clot from the hole; this threatens the entry of pathogenic microbes into the wound, which cause inflammation.
Symptoms
The first signs of alveolitis usually appear 2-3 days after the procedure. The symptoms of the disease cannot be confused with anything. This is, first of all:
- severe pain in the area of the extracted tooth;
- constant intensification and spread of pain to adjacent areas of the oral cavity;
- fever up to 38.5° C, chills and general deterioration of health;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- inflammation, swelling and redness of the gums;
- absence of blood clot;
- the presence of a specific gray plaque;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- presence of purulent exudate.
If one or more symptoms of the disease appear, you must immediately consult a dentist, since alveolitis does not go away on its own, it must be treated as soon as possible. Otherwise, complications are possible.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “alveolitis” can only be made by a doctor after a thorough examination of the patient’s oral cavity. Do not self-diagnose under any circumstances! This is a serious disease that, without proper treatment, can cause more dangerous complications, including blood poisoning. The absence of a blood clot in the socket at the site of the extracted tooth in the presence of other symptoms of the disease is decisive when making a diagnosis.
Treatment
If treatment for alveolitis is started in time, the disease usually goes away within a few days. Treatment usually consists of the following:
- thorough removal under local anesthesia of the remaining blood clot at the site of the extracted tooth;
- treating the walls of the socket with a dental instrument until slight bleeding appears;
- further treatment with a special antiseptic raster to prevent the spread of infection;
- the use of antibiotics (usually in the form of a powder that is sprinkled on the hole);
- prescription of painkillers;
- rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions;
- physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at speedy healing of the wound.
One of the most common complications of alveolitis, if not treated promptly, is osteomyelitis of the jaw bone. To prevent its occurrence, you should immediately consult a doctor as soon as you suspect some signs of alveolitis.
If you do not have the opportunity to see a dentist immediately, before visiting a doctor you should rinse your mouth with a warm (but not hot!) 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide or baking soda (half a teaspoon of soda per glass of boiled water).
Medicines
After thoroughly treating the hole, the doctor usually prescribes special medications to the patient for the treatment of alveolitis. In addition to antibiotics and painkillers, antiseptic solutions for oral baths and mouth rinses are necessarily prescribed, because maintaining the cleanliness of the mouth and socket is an indispensable condition for successful treatment.
The following drugs are most effective:
- Hexicon . A modern antiseptic drug that is successfully used in dentistry. Particularly effective for stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, alveolitis. Intended for topical use. Hexicon solution is used both in the form of applications and in the form of oral baths or for rinsing the mouth.
- Corsodil . The active substance of the drug is chlorhexidine. This is an effective antiseptic that has a bactericidal effect. Used in dentistry to disinfect the oral cavity. Used externally, as a solution for rinsing, irrigation and applications. After cleaning the socket of an extracted tooth, systematically rinsing the mouth with Corsodil solution has a good effect.
- Stomatidin . An effective antiseptic with antifungal and antibacterial spectrum, which is used not only in dentistry, but also in ENT practice. It prevents the development of infections and is indicated for stomatitis, gingivitis, alveolitis, periodontal disease, tonsillitis and pharyngitis. It is used both for rinsing the mouth and for applications.
- Chlorhexidine . A proven broad-spectrum antiseptic drug that is used for disinfection not only in dentistry. Effective for treating purulent wounds, in the treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa. It is an excellent preventative against most dental diseases.
- Eludril . Created on the basis of chlorhexidine. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. Indicated for stomatitis, gingivitis, alveolitis, periodontitis, as well as for treating the oral cavity before and after tooth extraction.
Prevention
The best prevention is the patient's strict compliance with all doctor's instructions. After tooth extraction, you should not rinse your mouth too aggressively to avoid damaging the blood clot. After all, its presence in the socket is a guarantee that pathogenic bacteria that provoke inflammation of the socket or alveolitis will not get into the wound.
Alveolitis after tooth extraction
This is a serious complication caused by tooth extraction, which has several causes. This may be the presence of chronic inflammation of the tissues around the tooth - periodontitis, or a dry socket. In addition, alveolitis occurs if, after tooth extraction, a dental fragment remains in the tissues. All these factors cause infection of the hole and the development of its inflammation. 1–3 days after tooth extraction, pain occurs, followed by a specific smell from the mouth. Then these symptoms intensify, the hole becomes covered with a gray coating, and it becomes impossible to eat due to severe pain.
In this case, only a doctor will help you, who will carry out the necessary treatment and clean the hole from infection. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances - alveolitis can develop into periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), causing an abscess and phlegmon.
Painful sensations after the removal procedure are unpleasant, but inevitable. Remember, if these sensations intensify, then in this case, complications after tooth extraction should be treated by a specialist. Do not delay visiting the dental clinic, dulling the pain with analgesics. Correct and timely treatment will help you avoid more serious complications.
How to get rid of odor at home
If you have bad breath after tooth extraction, you can use traditional medicine in addition to drug therapy. With normal daily discomfort, there is no need to worry. The danger is the development of the inflammatory process. To fix the problem:
- Rinse your mouth thoroughly after eating with plain water or infusions of herbs such as sage or mint.
- To clean your tongue you need to use a specific brush.
- Avoid fast food and junk food.
- Use a decoction of chamomile and calendula. These are powerful tools for fighting inflammation. They promote wound healing. It’s not difficult to prepare a mouthwash: 1 tbsp. l. herbs are poured with 1 liter of boiling water. You need to leave for half an hour, then rinse.
- A golden mustache is often used. To carry out the procedure, squeeze the juice from the plant, then pour boiling water over it.
- Traditional healers recommend rinsing your mouth with a decoction of eucalyptus. This plant perfectly relieves the inflammatory process.