In this article
- In what cases does dental caries develop: risk factors
- Prevention of dental caries: primary, secondary and tertiary
- Methods of primary prevention of caries
- The role of nutrition in preventing dental caries
- How to reduce the adverse effects of carbohydrates on teeth
- Strengthening the immune system and reducing stress factors as methods for preventing dental caries
- Drug prophylaxis
- Sealing dental fissures as caries prevention
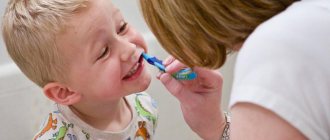
- Personal oral hygiene as protection against caries
- How to brush your teeth correctly to avoid caries?
- Chewing gums as caries prevention
According to official statistics from the World Health Organization, almost 100% of the world's population has dental caries. Modern dentistry offers effective methods for treating this disease, but prevention plays the most important role in preventing caries.
In what cases does dental caries develop: risk factors
The condition of teeth is one of the main indicators of the overall health of the human body. Therefore, preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of caries development are an important element of comprehensive health improvement. To protect teeth from carious lesions, it is necessary to understand what contributes to the development of the disease.
There are three main risk factors:
- dental plaque and the microbes it contains;
- increased amount of sugar in food;
- lack of fluoride in food and water.
In addition to these main factors in the development of caries, to varying degrees, the risk of pathology may depend on the level of solar radiation, gender and age, climatic and geographical living conditions. The likelihood of illness increases with pathological pregnancies, systemic and acute infectious diseases, during radiotherapy and other influences that weaken the immune system. An important risk factor is insufficient or improper dental and oral hygiene.
Comprehensive prevention of caries in adults involves influencing the main risk factors using different methods. Thanks to such preventive measures, it is possible to eliminate or reduce the risk of developing dental caries.
How to avoid caries?
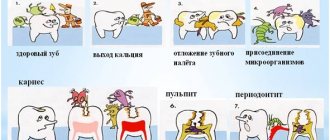
Depending on the depth of damage to hard tissues, there are 3 stages of caries - initial (spot stage), medium, deep. The rate of destruction of dental structures varies. In adults, the disease is predominantly sluggish and chronic. Children are more often diagnosed with an acute form of the disease with rapid destruction of dental structures. Inattention to the condition of teeth leads to progression of the disease. A carious lesion from the spot stage very quickly passes into the middle form, when dentin is destroyed and a visually noticeable defect is formed - a carious cavity.
How to avoid caries? Simple methods of primary prevention will help with this, most relevant when there is no visible damage to dental tissues.
Prevention of dental caries: primary, secondary and tertiary
In modern dentistry, there are three important stages of caries prevention. Primary prevention helps prevent the development of dental caries. It involves performing procedures that eliminate the factors and causes that provoke the disease. Secondary allows you to detect the disease at an early stage and take measures that will stop its development and prevent its reappearance. Tertiary is a set of measures after the main treatment. It can be aimed at restoring dentition, chewing function, or the lost appearance of teeth.
How to identify caries?
The simplicity and reliability of determining caries very much depends on the stage of its development, as well as the localization of foci of destruction on the dentition. At home, at the stage of a carious spot, when the pathology is located in the cervical, rib or root zone, it is almost impossible to visually notice the disease. Only a clear outer location on the visible part of the enamel suggests the presence of a small area of chalky color.
During the transition from the basic stage to classic superficial caries, the affected area acquires a more pronounced whitish tint, while the localization loses its shine compared to the rest of the enamel - active demineralization and destruction of the outer layer of the tooth begins, which is still focal. Over time, the diseased tooth begins to react to too cold, hot, sour, sweet foods and drinks, forming a temporary pain syndrome.
In medium and deep forms of the disease, the pathology is visible to the naked eye - these are darkening, holes and black cavities, partial tooth destruction, etc.
A particularly important stage in the effective fight against caries is considered to be the earliest possible diagnosis of the problem - only an experienced dentist can carry it out properly, through both a thorough visual examination using a special mirror and instrumental research techniques. Most often in modern dentistry, the following is used to solve this problem:
- 1. Radiography. A photograph of the internal structure of the dentition and surrounding areas gives, with correct interpretation, a clear and unambiguous picture of the development of caries and the exact localization of lesions;
- 2. Coloring. A simple method performed in a regular dental office. The procedure is carried out using fuchsin or methylene blue - areas of superficial damage to the enamel change their color;
- 3. Transluminescence. Illumination of the inside of the dentition using a powerful light source. Allows you to detect internal and hidden forms of caries inside the tooth;
- 4. Cold thermal diagnostics and drying of the enamel surface. Two alternative methods involve treating potential affected areas with a cold reagent or drying them, respectively. In the first case, the patient will feel a slight pain syndrome, while in the second, the area of potential destruction loses its shine. Both methods are suitable for identifying superficial or medium caries, including in hard-to-reach places.
Methods of primary prevention of caries
They are divided into endogenous (impact on internal factors) and exogenous (impact directly on the tooth surface).
Endogenous prevention measures include:
- complete, balanced, varied diet;
- activities aimed at strengthening the immune system;
- elimination of stress factors;
- taking vitamin and mineral supplements and saturating the body with fluoride, calcium and other microelements necessary for dental health.
Exogenous prevention of caries is:
- brushing your teeth daily using a good toothbrush, toothpaste and floss;
- professional cleaning by a dentist twice a year;
- treatment of tooth enamel with preparations containing fluoride;
- limited consumption of sweets and other foods rich in carbohydrates;
- use of chewing gum;
- sealing fissures (natural pits and grooves) on children's teeth.
Comprehensive caries prevention measures help reduce the likelihood of its occurrence several times.
Treatment methods for caries in the spot stage
The appearance of a matte white smooth spot on the enamel is the first sign of a carious process. Such a stain means that the enamel in this place is demineralized and is more susceptible to destruction. Qualified therapy includes the following:
- professional hygiene;
- remineralization therapy, which uses drugs for the prevention of caries containing fluoride and calcium;
- regular dental examinations.
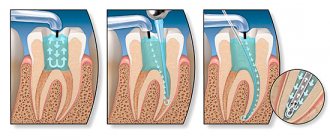
One of the latest innovations in drill-free treatment is Icon technology. After pre-treatment, a special infiltrate is applied to the affected area of enamel. The material penetrates deeply into the enamel structure, filling the defect. Excess material is removed, and the treated area is polymerized with a UV lamp. The defect is sealed, the carious process stops.
If the stain has reached the stage of pigmentation and a cavity defect has appeared on the enamel, then the affected tooth will require preparation followed by filling. The dentist selects the treatment method according to the clinical picture.
The role of nutrition in preventing dental caries
One of the effective measures to combat caries is the correct approach to nutrition. The tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive to the lack of certain food components. In particular, a lack of protein in the diet prevents the accumulation of calcium and disrupts the structure and strength of enamel. At the same time, foods that are too fatty increase the permeability of the enamel, which increases the likelihood of the formation of carious lesions.
An excess of refined carbohydrates (sweets, flour products, sugar) in the diet not only reduces the resistance of teeth to the development of caries, but also weakens the immune defense, which is also a risk factor.
To prevent caries, it is important to adhere to the following dietary recommendations:
- A sufficient amount of protein must be present in the daily diet;
- eat foods containing vitamins C, D and group B;
- be sure to eat foods rich in calcium and phosphorus (milk, cheese, eggs, fish, broccoli, legumes), as well as fluoride-containing foods (sea fish, Georgian tea);
- it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods rich in “fast” carbohydrates, eat as little sweets, cakes and refined sugar as possible;
- Avoid sticky products: they can remain on the surface of tooth enamel for up to an hour, contributing to its demineralization for a long time.
The nature of your diet directly affects the condition of your teeth. A rational, fortified, balanced diet is an effective method of non-drug prevention of caries.
Causes of dental disease
There are many reasons why tooth enamel is destroyed. The main thing is damage by microorganisms that develop in the human mouth. As a result of their activity, bacteria produce organic acids that dissolve hard tissues. Therefore, the main measure to prevent dental caries is careful oral hygiene.
Factors that cause the development of the disease also include the following:
- Excessive viscosity of saliva. If saliva is viscous, plaque from the tooth surface, where bacteria develop, is not naturally removed. Therefore, it must be removed during professional cleaning by the dentist.
- Crowded bite, in which it is important to thoroughly clean the space between the teeth.
- Poor or complete lack of oral hygiene.
- Stone formation, which also causes periodontal problems.
- Eating foods high in carbohydrates. Therefore, it is better to consume sweets in moderation.
- Exposure to harmful occupational factors. Carious lesions often develop in people working in hazardous industries.
- Injuries to the coronal part that cause the destruction process. The enamel is damaged, so it is more susceptible to negative effects.
Dental disease can be caused by a hereditary predisposition.
Most often, carious cavities develop on contact surfaces, in the blind pits of the incisors, in the cervical region, and on fissures. To prevent the development of the disease, various methods of caries prevention are used.
How to reduce the adverse effects of carbohydrates on teeth
Fermentation of carbohydrates under the influence of microbes leads to the production of organic acid, which destroys tooth enamel and contributes to the development of caries. It is impossible to completely stop eating carbohydrates, but it is quite possible to reduce the intensity of their influence on the development of caries. The following measures will help with this:
- Reducing the amount and, most importantly, the frequency of eating carbohydrate foods, so that the teeth come into contact with carbohydrates as little as possible.
- In some cases, your doctor may recommend switching from sugar to sweetener substitutes.
- Reducing the time carbohydrates spend in the mouth. This can be achieved in two ways: do not eat the sweet dish last, and be sure to rinse your mouth after eating.
- Avoid eating sweets at night and between meals.
If any of the recommendations are violated, to reduce the risk of caries, you need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
conclusions
There is a clear algorithm, following which, with a high degree of probability, you will never encounter the problem of caries.
- Regular removal of plaque and tartar is the key to healthy teeth . Good oral hygiene is the best cure for any disease related to teeth and gums.
- Proper diet . It is necessary to compose the daily menu in such a way that it contains as little flour and sweets as possible (food consisting mainly of easily digestible carbohydrates). It is also worth giving up sugary drinks (soda contains an extremely large amount of sugar). By avoiding sugary snacks, you can minimize your risk of tooth decay.
- Measures that increase the resistance of enamel to acids produced by pathogenic microorganisms should be carried out several times a year.
Strengthening the immune system and reducing stress factors as methods for preventing dental caries
The most important task of the immune system is to resist the effects of microbes. If the body's defenses are weakened (including under the influence of stress), the immune system cannot resist harmful bacteria. That is why, against the background of severe stress and weakened immunity, the risk of dental caries increases.
Prevention consists of strengthening the immune system, for which the following measures are suitable:
- quality sleep of at least 8 hours;
- physical activity: daily exercise, sports;
- hardening: water procedures, sun and air baths, cool air in the apartment;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- refusal or limitation of bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- adherence to daily routine;
- if necessary and only as prescribed by a doctor, medications to strengthen the immune system.
Caries
3939 16 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Caries: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Caries is an infectious lesion of the teeth in which demineralization and softening of the hard tissues of the tooth occurs with the formation of a defect in the form of a cavity. This is the most common disease of the dental system. Caries occurs among all age groups, but more often among adults over 35 years of age, where it accounts for 98-99%.
Causes of caries
In the oral cavity of any person there live a large number of microorganisms that are in balance and actively interact with the human body and with each other. This balance may change briefly under the influence of various factors, for example, after a teeth whitening procedure, but then the balance is restored again. If the body's defenses are reduced, the changes can be more significant and lasting.
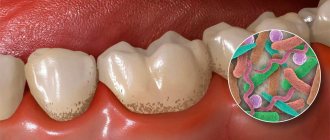
Various bacteria, fungi and protozoa live on the oral mucosa, in the ducts of the salivary glands and in saliva, in gingival fluid and oral fluid, but most of them live in dental plaque - up to 90% of all microflora.
Dental plaque is a soft sticky deposit on the surface of teeth containing a large number of microorganisms, their metabolic products, epithelial cells, leukocytes, proteins and lipids of saliva. The formation of dental plaque is a natural process, and in the absence of timely and thorough dental care, it forms within 1-2 days. As a result of structural changes in plaque, dental plaques form quite quickly. Bacteria present in dental plaque and plaques actively “exchange information”, build a large number of connections, and then stick together, forming a microbial biofilm. In a biofilm, microorganisms exchange genetic material, nutrients, and remove metabolic products. The creation of such a biofilm protects bacteria from the body's defense cells and from the action of antibiotics. As a result of the vital activity of microbial biofilm, a large amount of organic acids is formed, under the influence of which demineralization of tooth enamel begins. Small defects form, microorganisms penetrate there, destroying the enamel further, resulting in the formation of a cavity in the tooth - caries.
Carbohydrates serve as food for microorganisms, so eating sweet foods contributes to the development of caries.
In addition, predisposing factors are a decrease in the body's defenses, smoking, poor oral hygiene, and taking antibiotics - all this leads to an imbalance in the oral microflora, resulting in the proliferation of streptococci and lactobacilli, which are responsible for the production of organic acids and the development of caries.
Classification of caries
Doctors classify caries depending on the stage and location of the lesion. The stage of initial caries, in which the process does not extend beyond the enamel-dentin boundary, is called the white or chalky spot stage. This is followed by the stage of dentin caries, in which the disease crosses the enamel-dentin boundary without affecting the pulp, and the stage of cement caries with damage to the exposed surface of the tooth root in the cervical region.
Focal demineralization of enamel is characterized by the appearance of a dark pigmented spot within the enamel and is called the stage of suspended caries.
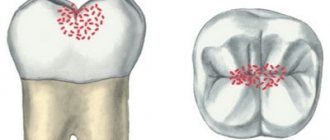
Based on the location of the cavities, there are 6 classes of the disease:
Class I - cavities localized in the area of grooves on the chewing surface of the teeth (fissures) and natural recesses of the incisors, canines, molars and premolars.
Class II - cavities located on the contact surface of molars and premolars.
Class III - cavities located on the contact surface of the incisors and canines without breaking the cutting edge.
Class IV - cavities located on the contact surface of the incisors and canines with a violation of the angle of the crown of the tooth and its cutting edge.
Class V - cavities located in the cervical region of all groups of teeth.
Class VI - cavities located on the cusps of molars and premolars and the cutting edges of incisors and canines.
Symptoms of caries
Symptoms of the disease depend on its stage. A sign of initial caries is a change in the color of the tooth enamel in a limited area and the appearance of a chalky or gray stain, lacking shine - a focus of demineralization. Then an enamel defect develops, and then a cavity. Patients with caries at the stage of cavity formation note increased sensitivity of the tooth to chemical, temperature and mechanical irritants, while the painful sensations disappear immediately after the irritant is eliminated. A defect can be seen on the visible surface of the teeth.
Further, tooth damage spreads to the underlying tissues - to the upper layers of dentin, after which, in the absence of treatment, the process captures the deep layers of dentin and approaches the pulp - soft connective tissue penetrated by blood vessels and nerve plexuses. At this stage, patients also note increased sensitivity to irritants and pain during chewing.
When the dental pulp becomes inflamed – pulpitis – severe toothache begins. If the disease is not treated, the pathological process can spread beyond the tooth into the bone tissue and periodontitis will develop.
Diagnosis of caries
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the oral cavity, examining the mucous membrane, establishes the presence of fillings and the degree of their adherence, the presence of defects in the hard tissues of the teeth, and notes the number of teeth removed. The dentist carefully evaluates the condition of all teeth, determines the density of hard tissues, texture and degree of surface uniformity, checks pain sensitivity, and probes the identified carious cavity. If indicated, radiography is performed.
Which doctors should I contact?
Dentists treat caries.
Treatment of caries
The main goals of caries treatment are to stop the pathological process, restore the shape and function of the affected tooth, prevent the development of complications and restore the aesthetics of the dentition. If the carious lesion is limited to the enamel, then patients may be prescribed deep fluoridation of the hard tissues of the tooth to prevent further development of the process.
If a defect occurs in the hard tissues of the tooth, conservative remineralizing treatment does not have an effect; in this case, the altered tissues are removed and the tooth crown is restored using a filling.
Complications of caries
In almost half of patients aged 35-44 years, there is a need for filling and prosthetics of the affected tooth, and doctors have to resort to tooth extraction in almost a quarter of cases. With late treatment of caries, the pathological process can spread deeper into the dental pulp, and from the infected pulp, inflammation through the tooth canal penetrates further into the bone and under the periosteum of the jaw with the development of inflammation of the periosteum - periostitis or gumboil. Tooth extraction as a result of untimely treatment, which leads to complications, causes deformation of the dentition and can even lead to pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
Dental caries can cause problems with chewing function.
Prevention of caries
To effectively prevent the development of caries, it is necessary, firstly, to prevent the creation in the oral cavity of conditions conducive to the emergence of microbial films and the carious process, and secondly, to increase the caries resistance of dental tissues. The main methods of prevention are regular oral care with proper brushing technology, the use of dental floss, the use of fluoride toothpastes, mouth rinses, reducing sugar consumption and regular dental examinations (once every 6 months).
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of “Dental caries” Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014, updated on August 2, 2022.
- A.I. Khavkin, Yu.A. Ippolitov, E.O. Aleshina, O.N. Komarova. Oral microbiota: protective or pathogenic factor? // Issues of practical pediatrics. – 2015. – T. 10. – No. 4. – P. 49-54.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Drug prophylaxis
After an in-person examination, the dentist, according to indications, may prescribe the patient one of the following methods of medicinal endogenous prophylaxis:
- additional fluoridation of food and drinking water (the amount of fluoride is calculated only by a doctor, taking into account the dose that a person already receives from food and water);
- anti-caries drugs for oral administration (usually they contain a complex of vitamins and sodium fluoride that help strengthen teeth).
There are also exogenous methods of drug prophylaxis. These include coating the teeth with fluoride varnish or fluoride gel. Fluoride varnish stays on the enamel surface for a long time, saturates it with fluoride ions, has an antimicrobial effect, and reduces pain in cases of increased tooth sensitivity. Fluoride-containing gel has a remineralizing effect on tooth enamel; it is used for applications or electrophoresis.
Do I need a dental scan?
American dentists recommend having your teeth x-rayed every year. Austin Frakt, a health economist, reviewed[] medical studies and concluded that such reinsurance is unwarranted. Cavities in the tooth form more slowly—over 2–3 years.
In Russia, preventive x-rays are not so popular. But computed tomography is suggested to be done regularly. You should also not agree to this expensive service more often than once every couple of years.
Sealing dental fissures as caries prevention
Fissures are natural depressions on the surface of teeth. Food debris accumulates in these pits, making it more difficult to remove plaque and germs from there during cleaning. In addition, in the fissure area, enamel mineralization is slowed down; its layer is thinner than on other surfaces of the teeth, so natural depressions are considered a risk zone for the development of carious lesions. The fissure sealing method is primarily used for children. Its essence lies in the fact that the recesses are closed with special sealants. As a result, food does not accumulate on the teeth, and the vulnerable spot of the tooth surface is reliably protected from the action of pathological microorganisms.
What happens if you don’t prevent caries?
- Development of pulpitis. This is an inflammation of the soft tissues of the tooth, accompanied by severe pain;
- Development of periodontitis. Through root canals, infection of the tissues located inside the tooth occurs.
- Cyst formation. The process is characterized by the destruction of bone tissue, the proliferation of granulations and the formation of cavities among them.
- Development of gumboil (pronounced swelling of the gums). The inflammation spreads to the periosteum, as a result of its detachment, a space filled with pus is formed.
Good to know. Tooth decay is one of the possible signs of diabetes. Sugar rises in the blood, and therefore in the oral cavity.
At the Saint-Dent Clinic in Moscow you can get high-quality dental services. Doctors are highly qualified and use advanced technologies and materials to provide all types of dental care. You can find the clinic's contacts here. The price list with prices is here.
Personal oral hygiene as protection against caries
Individual oral hygiene plays an important role in preventing caries. It refers to exogenous non-drug methods of prevention.
Regular brushing of teeth, tongue, removal of food debris, soft deposits contributes to the proper development and functioning of tooth enamel. The components of therapeutic and prophylactic pastes enrich the tissues of the oral cavity with calcium and phosphate salts, vitamins and microelements, making them more resistant to negative influences. Massaging the gums with a toothbrush activates metabolism, improves blood circulation in periodontal tissues, and prevents bleeding and gum disease.
Personal hygiene involves careful independent removal of plaque from the surface of teeth and gums using toothbrushes, pastes and other products.
The effectiveness of individual oral hygiene depends on several factors:
- quality and compliance of the characteristics of the toothbrush with the condition of the teeth of a particular patient;
- following proper cleaning techniques;
- the use of additional cleansing methods - irrigators, dental floss, mono-beam and orthodontic brushes, rinses.
Professional hygiene
Modern methods of preventing dental caries involve in-office hygienic cleaning twice a year. Professional hygiene is aimed at removing bacterial plaque and mineralized formations (plaques, stones) from the supragingival and subgingival parts of the tooth. Hygienic cleaning includes the following steps:
- Removal of hard and soft deposits using the AIR-FLOW method or ultrasonic scaler.
- Polishing the surface of the teeth with an abrasive paste.
- Protection of enamel with fluorine varnish.
Hygienic procedures are painless and carried out quickly. Another plus is that the dentist gets the opportunity to accurately assess the condition of the oral cavity and detect pathology at the initial stage. Each stage can be carried out as an independent procedure. But it is a complete hygiene complex that will ensure effective prevention of diseases of the teeth and gums.
How to brush your teeth correctly to avoid caries?
The toothbrush should have a small head to easily penetrate hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity, removing plaque even from distant teeth and from interdental spaces. The stiffness of the bristles is of great importance. The best choice for most adult users is a medium-hard brush. It will clean the surface of the teeth quite intensively, without damaging the gums or scratching the enamel.
However, for children and those with sensitive teeth and gums, brushes with soft bristles are needed. Regarding the correct choice of the optimal toothbrush, as well as toothpaste with the appropriate composition, it is better to consult with your dentist. He will be able to make recommendations based on an in-person examination of the oral cavity.
Even a properly selected brush and good toothpaste will not protect against caries if you brush your teeth incorrectly. Therefore, it is important to learn a technique that will allow you to most effectively clean your teeth and oral cavity from bacteria. There are several different ways to clean teeth in dentistry. One of the widely used is the standard Pakhomov method:
- The dentition is conventionally divided into segments.
- Begin cleaning from the upper right segment, from the distant chewing teeth. They alternately move from segment to segment along the upper jaw, and then move on to cleaning the lower row of teeth in a similar way.
- According to Pakhomov’s method, when cleaning the lateral front and back surfaces of the teeth, the brush moves in the direction from the gums to the edge of the tooth. Chewing surfaces are cleaned with back-and-forth movements.
- Finish cleaning with circular movements in each segment.
Please note that this cleaning method is suitable for those who use regular manual toothbrushes. There are nuances in using electric toothbrushes, and the method of using them is always detailed in the instructions. The main difference is that an electric toothbrush does not require mechanical movements; it simply needs to be moved from tooth to tooth without applying too much pressure.
After brushing your teeth with a brush and toothpaste, it is recommended to additionally clean the interdental spaces with floss or irrigator, and also use the mouthwash as a solution for the prevention of caries.
Dental caries in children
In children, identifying caries is quite simple: first, white or brown spots appear on the teeth, then the teeth begin to react to hot or cold food, and bad breath may appear. All these symptoms indicate the rapid development of the disease. If action is not taken in time, the infection can spread to several teeth at once.
Causes of caries development in children:
- The main cause of childhood caries is poor oral hygiene. The task of parents is to choose the right toothbrush for their child and teach him how to brush his teeth. Many young children are afraid of this harmless procedure, so we can recommend trying to present brushing as a game. It is necessary to accustom a child to brush independently starting from the age of 3 (before this moment, parents should brush the child’s gums and teeth).
- The infection can be transmitted from an adult to a child. As a rule, this happens if you eat with a child with the same spoon or kiss him on the lips, which is often abused by adults who are unable to cope with an overabundance of feelings.
- Genetic characteristics associated with abnormal maternal lifestyle during pregnancy. Teeth form during the first trimester, so if a woman smokes or drinks alcohol, this can affect the baby's dental development.
- Early caries, which appears in children before the age of 2 years, can be caused by poor mineralization of baby teeth.
- Various chronic diseases can also cause cavities.
- In infants, bottle tooth decay often occurs when the child eats food before bed. After eating, food residues remain on the teeth, and parents, instead of brushing the child’s teeth, put him to bed.
Chewing gums as caries prevention
Chewing gum may help prevent tooth decay by increasing saliva production. Salivary fluid washes each tooth, removing dirt and germs from it, has an antiseptic effect on the oral cavity, and neutralizes plaque acids. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to chew gum with sweeteners for several minutes after each meal, especially sweets. Remember that comprehensive preventive measures will help maintain the health and appearance of your teeth for a long time.
ANTENATAL PREVENTION
It is mistakenly believed that children need to take care of their oral cavity from about the age of three. In fact, the prerequisites for the occurrence of dental diseases often arise even before the baby is born. The rudiments of baby teeth begin to form already from the sixth week of pregnancy, and the rudiments of permanent teeth - from the twentieth. If during this period the fetus does not receive calcium and other microelements, the mineralization of dental tissues slows down, and the baby may subsequently have serious problems not only with milk teeth, but also with permanent teeth.
The goal of antenatal prevention is to prevent the child from developing dental diseases associated with problems in the prenatal period. To provide the fetus with the microelements it needs, a special nutritional plan is developed for the expectant mother.
In addition, if a woman suffers from periodontal disease during pregnancy, the newborn baby is at risk. In contact with the mother, the child will certainly become infected with pathogenic bacteria, and the erupted milk teeth will be affected by caries. Therefore, all actions to sanitize the oral cavity of the expectant mother should be carried out even before birth. The use of painkillers is possible from approximately 16 weeks of pregnancy.
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO VISIT A DENTIST REGULARLY?
In order to prevent the occurrence of caries, hygiene procedures alone are not always enough. If a patient has an incorrect bite or the teeth are too close together, orthodontic treatment may be necessary.
According to the accepted classification, according to the depth of damage, caries is divided into initial, superficial, medium and deep. This is an insidious disease, and it is quite difficult to independently determine it at the initial stage. The first carious spots almost do not differ in color from tooth enamel, and if you do not pay attention to them, the disease can very quickly go through all stages, completely destroy the tooth and affect neighboring ones.
Early diagnosis of caries allows for its treatment using the most gentle methods. It is very important to prevent the development of the disease and the occurrence of complications, in particular, periodontal inflammation, when no home remedies or rinses can help. Therefore, it is necessary to visit the dentist at least once every six months for a preventive examination and exogenous procedures.
The DentaLux-M dental clinic has developed an effective system for the prevention of dental diseases. Experienced doctors use the most modern equipment and new technologies.
By visiting the clinic once every six months and following your dentist’s recommendations, you will maintain a radiant smile for a long time.
The importance of treating a carious tooth
Caries usually develops slowly. At the initial stage, it looks like a white spot, which can be gotten rid of in the most gentle way possible without preparing the carious cavity - using special gels and solutions. As the pathology progresses, the infection penetrates deeper and can cause inflammation of the neurovascular bundle. At this stage, you cannot do without drilling, cleaning and filling the cavity. If caries is not treated, the tooth may completely decay and will have to be removed.
In addition, the affected unit is a source of infection and can cause chronic diseases and destruction of adjacent teeth. When the chewing function of the unit is impaired, the patient gradually develops gastrointestinal diseases. And, of course, a tooth damaged by caries looks unaesthetic.
Remember: the longer you delay visiting a doctor, the more the tooth will decay, and the more expensive its treatment will be. So, at the slightest suspicion of a problem, it is better to consult a dentist.
Proper dental care -
Unfortunately, all people understand the term “good oral hygiene” differently, believing that everything is fine with their hygiene, and that all dental problems are to blame (hereinafter on the list) - water, bad heredity, pregnancy, etc. . Below we have described in detail for you how often and how to brush your teeth correctly, as well as what hygiene products are best to use.
How many times a day should you brush your teeth?
Most people know that they need to brush their teeth twice a day. Everything is correct, but this is only the minimum value. Normally, teeth are brushed after every meal, i.e. 3 times a day. If you are afraid that your colleagues at work will call you a cleaner if they see you brushing your teeth in the toilet during your lunch break, then you need to make a choice - between clean teeth, the absence of caries and bad breath, and the respect of dirty-toothed colleagues.
If a toothbrush and toothpaste at work are unacceptable to you, then the minimum amount of hygiene that will allow you to remain Homo sapiens is “dental floss + chewing gum,” or “dental floss + mouthwash.” The most important thing in this combination is the use of dental floss, because... food gets stuck between the teeth (and we are not talking about stuck pieces of meat, but about soft food residues, which cause much more damage to the teeth, because they consist of quickly digestible carbohydrates and therefore are most quickly processed by bacteria into acid).
Diet – effective prevention of dental caries is impossible without following a diet. For example, it is very good if you brush your teeth 3 times a day after each main meal. But, if you decide to eat chocolate, cookies, sweets, nuts between main meals... the carbohydrates stick to your teeth again and bacteria immediately begin to convert them into acid. Therefore, all snacks should be eaten at the end of the main meal, and after that, immediately brush your teeth.
It is the wrong diet and frequent snacking on cookies and other carbohydrates that are the root cause of caries in children (this also applies to sugary drinks - juices, soda, liquid mixtures). Children often develop so-called bottle caries, which affects almost all teeth (when parents, to prevent the child from crying, give him a bottle of formula for the whole night or day). And without solving the problem with diet, no prevention of caries in children is simply possible.
If you are asking yourself how to get rid of caries at home, then following the recommendations of this article can almost completely save you from the appearance of new foci of caries. It's up to your willpower and motivation, because sometimes you are too lazy to get up and go straight away to brush your teeth, or finally start regularly using dental floss after every meal.
Proper hygiene scheme -
After each meal, you need to follow the following sequence: 1) flossing, 2) brushing with a toothbrush and toothpaste. If you don’t have toothpaste and a brush, you should always have dental floss and chewing gum with you. Floss will remove food debris, and chewing gum works by stimulating salivation (saliva has a certain buffering capacity that neutralizes acids in the mouth).
It is very important not only how to brush your teeth, but also when to do it. In the morning, it is best to brush your teeth after breakfast (for people with a lot of plaque and carious teeth, this can be unpleasant, so it is recommended for such patients to brush their teeth both before and after breakfast). As for all other oral hygiene sessions, teeth should be brushed within the first 5 minutes after eating.
Using dental floss –
Let's be honest - without dental floss there can be no talk of good hygiene. What do you think: why is the most common location of caries in the interdental spaces? Precisely because food debris gets stuck there, which cannot be removed by any fancy toothbrush models or even irrigators. If the instructions for a brush or an advertisement tell you that it perfectly cleans the spaces between teeth, this is all untrue and is only a publicity stunt. And this equally applies to electric, ultrasonic, and other models of brushes and attachments for them.
It is very important that you understand the following - you should use dental floss not only when you feel that a piece of meat is stuck in your teeth. After eating, so much soft sticky food debris accumulates in the interdental spaces that will not cause you any concern, but it is they (and not pieces of meat) that are the root cause of caries, because... Such food residues consist predominantly of carbohydrates that are easily digestible by bacteria.
Dental floss should be used after every meal, cleaning absolutely all dental spaces. This usually takes about 1 minute, but at the beginning (while you learn to use it) it may take longer. The thread should always be in your pocket or purse. You can use it at a party, in the restroom of a restaurant, or even just on the street. Everything will depend only on your desire to have clean teeth and a pleasant breath.
How to use dental floss correctly: video
If there are bridges on the teeth, braces -
In the presence of braces and bridges in the oral cavity, conditions are created for the retention of food debris. In the presence of bridges, food is stuffed, as a rule, under the intermediate part of the bridge, which imitates the missing tooth. Therefore, for good hygiene, an ordinary toothbrush and paste, as well as dental floss, will no longer be enough in this case (24stoma.ru).
Special devices called irrigators are designed for these purposes. Such devices deliver under pressure a thin pulsating stream of water, saturated with air microbubbles, with the help of which food debris and microbial plaque are washed away (Fig. 6). Irrigators are also indicated for patients with chronic gum inflammation, because... They also allow you to wash periodontal pockets using special nozzles.
Important: any caries you develop, even a single one, is an indicator that there are defects in your hygiene. You must understand that there is no norm for the formation of a certain number of caries lesions per year. Normally, there should be no caries at all, and if it appears, then this is a question of how correctly you brush your teeth, how regularly, whether you are familiar with dental floss, and also how correct your diet is.
When caries develops, microbial plaque and food debris remain at the edge of the corner. Adequate oral hygiene allows complete removal of both. Predisposing factors, of course, also exist. For example, a low concentration of lysozyme in saliva (this is an enzyme that inhibits the growth of plaque) is of a genetic nature, but this factor is only secondary for the development of caries.
Or the buffering capacity of saliva is too low, which does not effectively neutralize acid in the mouth. This usually occurs in patients who consume too many carbohydrates. In patients with a balanced and protein diet, the buffer capacity of saliva is always normal. Those. here again questions about your diet. Often drinking wine or fruit juices (acid), sweet soda (carbohydrates) - all this also leads to demineralization of teeth and increases the risk of caries.
Why do you need interdental brushes?
In 2015, a review of seven studies was published in which 354 patients brushed their teeth in three ways:
- only with a brush;
- brush and floss;
- brush and brushes.
Only once did scientists note that additional cleaning with a brush had advantages over brushing. But the evidence cannot be considered rigorous, since we are talking about a superficial study: the effect has not been analyzed in the long term. The same goes for comparing brushes and dental floss.
There is not enough data yet to draw conclusions about the benefits of brushes for interdental spaces.
Which toothpaste is more effective?
The good news is that brushing your teeth is still beneficial. But to prevent the development of caries, the paste must contain fluoride. A study of the results of dental examinations of children aged 5 to 16 years []confirmed the effectiveness of the use of this mineral for the prevention of caries and tooth loss. Moreover, it is better to brush your teeth with fluoride paste twice, not once: the positive effect will be more noticeable.
True, fluoride paste does not help against gingivitis and plaque on teeth. But it really protects against enamel destruction.
How and why does caries develop?
Normally, saliva destroys all harmful microorganisms in the oral cavity. This protective mechanism is provided by nature. But when a malfunction occurs in the body or negative factors actively influence it, saliva loses its protective properties. And if a large number of cariogenic microbes accumulate in the oral cavity, many organic acids are formed (lactic, butyric, formic, propionic, etc.). It is these substances that soften enamel and dentin and destroy the tooth structure. Thus, the more of these bacteria, the more acid, the faster the unit breaks down.
Caries forms on teeth if a person:
- consumes a lot of foods containing simple carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods) - such food promotes the proliferation of cariogenic bacteria;
- does not care about enriching the enamel with calcium and fluoride;
- likes to create a temperature contrast (eats cold food immediately after hot food), which negatively affects the condition of the enamel;
- rarely or poorly brushes teeth;
- neglects preventive visits to the dentist and recommendations regarding professional cleaning of units.
This problem often occurs in people with reduced immunity (due to systemic disease, frequent fatigue, chronic stress), as well as in pregnant and lactating women (due to increased consumption of calcium and fluoride).
Oral hygiene
Regular hygiene procedures are one of the simplest and at the same time effective methods of preventing dental caries. After each meal, doctors strongly recommend rinsing your mouth, and best of all, brushing your teeth. This must be done within the first five minutes after eating, because it is at this time that they are most intensely affected by aggressive factors.
Hygiene procedures must necessarily include the use of dental floss or toothpicks. The floss allows you to effectively clean the interdental space from food debris, which serves as a breeding ground for pathogenic microflora. In most cases, removing such residues with an ordinary brush is not possible, so the use of thread or floss is absolutely necessary. As an additional remedy, you can use rinses - they have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects, help maintain a normal acid-base balance in the mouth and freshen breath.
The choice of hygiene products is also extremely important. An extremely effective remedy is the regular use of toothpastes containing fluoride. Fluoride exposure not only helps strengthen tooth enamel, but also has an inhibitory effect on pathogens and helps remove soft plaque. By integrating into the structure of the enamel, fluoride retains calcium in it and increases the resistance of teeth to various destructive factors.
However, fluoride-containing pastes can only be used in those regions where it is contained in water in an amount of no more than 1.2 mg per 1 liter. Otherwise, fluorosis may develop, a disease that occurs due to an excess of fluoride. If it is impossible to use fluoride prophylaxis, it is necessary to give preference to fluoride-free anti-caries pastes containing antibacterial components and a large amount of calcium.
Primary prevention of tooth decay may also include having your teeth professionally cleaned. In a dental office, a doctor can remove even the most persistent deposits, which are one of the important factors in the mechanism of caries formation. For this purpose, a wide range of means is used - from special medications to high-tech ultrasound equipment.
Professional dental treatment with fluoride –
At the beginning of the article, we already told you that the initial stage of caries develops due to exposure to acid secreted by cariogenic bacteria. This acid dissolves the surface layer of enamel - as a result of which the enamel loses calcium, i.e. demineralization of the enamel occurs. However, there are therapeutic measures that can strengthen tooth enamel by saturating it with minerals (fluorine and calcium). This process is called tooth remineralization.
Remineralization is not only professional (carried out in a dental office), but it can also be easily done independently using the right quality products. At home, you constantly use toothpastes with fluoride or calcium, which also contribute to the remineralization of tooth enamel, despite moderate concentrations of active ingredients. To strengthen enamel in children and adults, dentists most often use the method of professional fluoridation of teeth (using highly concentrated varnishes and gels).
Professional fluoridation of teeth is more effective compared to fluoride-containing therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes. For example, the fluoride concentration in dental varnish is usually 22,600 ppm, and conventional dental toothpastes contain a maximum of 1,450 ppm of fluoride. And in Colgate® Duraphat medicinal pastes (which we described above) – 2800 or 5000 ppm.
In what cases is it better to choose fluoride treatment of teeth at the dentist, and in what cases is it better to use medicated toothpastes with a high dosage of fluoride at home? Read the article on fluoridation of teeth (see link above). But in general, the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that fluoride prevention of caries should include both directions: firstly, the constant use of low doses of fluorides at home, and secondly, periodic professional applications of high doses of fluorides at the dentist (1 time in 3- 6 months).
The mechanism of action of fluorides (explanations below the picture) –
- Demineralization - when the pH of the oral fluid drops to pH 5.5 (i.e. becomes acidic) - the surface layer of enamel begins to dissolve and lose calcium and other trace elements. This is the starting point for the development of caries. A pH below 5.5 means an acidic environment, which is formed in the oral cavity under the influence of cariogenic microorganisms that “digest” food debris into organic acids.
- Remineralization - the surface of the tooth is coated with fluoride varnish, which promotes the formation of a layer of calcium fluoride (CaF2) on the surface of the tooth, from which calcium and fluoride ions penetrate into the enamel surface. There, fluoride ions bind to hydroxyapatite (the substance from which enamel is made), turning it into fluorohydroxyapatite. The latter is much more resistant to acid, and its dissolution begins only at pH 4.5 (i.e. at a higher acid concentration in the oral cavity). This ensures the anti-caries effect of fluorides.
Clinical researches
ASEPTA toothpastes are clinically proven effective. For example, clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
In addition, clinical studies have proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA ACTIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 60%, improve the overall condition of the oral cavity by 44% and reduce inflammation by 33%.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
How to stop tooth decay: correcting your bite
According to many, malocclusion is a minor cosmetic defect that does not have a major impact on dental health. In some cases this may be true; However, malocclusion can also cause uneven distribution of stress on the teeth during chewing, which, in turn, leads to premature wear. Without time to recover from mechanical stress, the enamel becomes much more susceptible to the effects of other destructive factors, which ultimately can lead to the onset of the carious process.
That is why bite correction should also be included in the list of preventive procedures. To correct it today, a wide range of technologies and methods are used - from installing braces to surgical intervention.