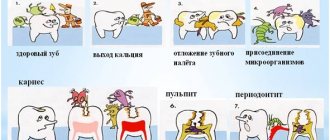
For children's teeth, caries is even more dangerous than for adults. The enamel of baby teeth is thinner and is destroyed very quickly, so carious cavities can develop into pulpitis or periodontitis in a baby in just a matter of weeks. That is why experts recommend that parents carefully monitor the condition of their dear children’s teeth.
Regularly inspect the surface of your teeth for the appearance of carious spots and remember that proper prevention can effectively protect baby teeth from this disease, and you from unnecessary troubles and worries. What is it made of? Let's talk about this in more detail.
Important components of the prevention of dental caries in children
In general, all preventive measures can be divided into three types:
- antenatal – carried out during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, they are aimed at the correct formation and development of tooth buds;
- endogenous - a set of measures to saturate the baby’s teeth with the necessary mineral components from the inside, ensured by consuming properly selected food products or taking medications;
- exogenous – thorough and regular oral hygiene, carried out both at home and in the doctor’s office.
All three types of caries prevention are equally important, so you should not think that only proper nutrition or high-quality teeth cleaning can protect you from tooth diseases. Only an integrated approach brings success, and the use of preventive measures should begin during pregnancy.
What needs to be done?
Of course, the best option would be to sanitize the oral cavity before pregnancy.
. But this is not enough. You should definitely see a dentist throughout your pregnancy.
How often should you visit the dentist during pregnancy?
- First visit
- 6-8 weeks (from the moment of the first appearance at the antenatal clinic) - II visit
- 16-18 weeks - III visit
- 26-28 weeks - Final visit
- 36-38 weeks
The dentist will provide you with warmth and understanding, assistance and support throughout the entire period of pregnancy, which will help maintain the dental health of you and your baby.
Oral care is an integral part of maintaining your health during pregnancy.
A dentist will help you take proper care of your oral cavity if you contact him promptly and regularly visit him.
But you yourself must take a number of steps to maintain oral health:
1. Correctly and regularly carry out the teeth cleaning procedure, which was taught to you by a dentist.
2. On the recommendation of a doctor, it is necessary to use additional hygiene products:
- floss threads;
- dental elixirs;
- chewing gums containing sweeteners, especially xylitol.
3. Eat rationally.
Antenatal prevention of caries in children - take care of your baby in advance
The degree of resistance of the teeth to the development of caries depends on how mineralized the buds of children's teeth are during pregnancy. The following will help ensure proper intake of minerals into the child’s body:
- Correct diet for the expectant mother and strict selection of products
Reduce your consumption of sweets and flour products as much as possible and generally reduce the amount of carbohydrates in your diet, while at the same time introducing mandatory daily consumption of foods containing calcium (this includes all dairy products).
- Timely completion of comprehensive medical examinations both during pregnancy planning and during it
They will prevent the development of a deficiency in the mother’s body of certain elements necessary for the baby.
- Oral hygiene
Do not be lazy to regularly clean the surface of your teeth with brushes, and the spaces between them with dental floss.
- Monitoring the condition of a pregnant woman's teeth
Visit the dentist's office regularly, and also take care to prevent the development of dental diseases and promptly sanitize carious lesions.
- Routine professional teeth cleaning
It should be carried out only on the recommendation of specialists and strictly in a certain trimester of pregnancy.
- Use, if necessary, vitamin-mineral complexes that reduce the deficiency of nutrients
Please note that they can only be taken after consultation with the gynecologist.
You shouldn’t relax in the fight against caries even after the baby is born. First of all, ensure that your baby maintains the necessary oral hygiene.
What do you need to know?
When does fetal teeth develop?
From 6-10 weeks of pregnancy, the formation of the rudiments of all milk teeth begins.
From the 20th week of pregnancy, the baby teeth of the fetus become mineralized and acquire a characteristic appearance and shape. During this same period, the rudiments of permanent teeth are formed.
Changes in the oral cavity during pregnancy
It is known that during a normal pregnancy, the acid-base balance of saliva changes in the acidic direction, the amount of saliva decreases and calcium deficiency develops. All this contributes to an increased risk of developing caries.
In addition, during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, bleeding and swelling of the gums increases. Salivation also decreases, which contributes to the retention of food debris on the teeth, which subsequently turns into dental deposits that irritate the gums, causing bleeding and inflammation.
The role of hygiene in the prevention of dental caries in children
Quite often, parents begin to pay attention to oral hygiene issues only after the baby has his first tooth. But you need to start caring for the first teeth long before they appear, literally from the first months of a child’s life.
For this purpose, experts recommend using special sanitary napkins for infants, for example, ASEPTA baby wet wipes. They will help to carefully and efficiently clean the gums, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks, significantly reducing the number of bacteria in the oral cavity.
For children whose first teeth have already erupted, we can recommend using a soft toothbrush and toothpaste from the ASEPTA baby series, designed for children aged 0 to 3 years. It does not contain abrasives or fluoride, the ingestion of which is highly undesirable for a child, and at the same time carefully cares for the surface of baby teeth, providing protection against caries.
To prevent caries in children, we can also recommend a procedure for remineralization of enamel and its deep fluoridation. It is carried out by specialists and, as a rule, already in cases where caries is detected at the spot stage.
An equally important place in preventive measures is given to the preparation of the child’s correct diet.
Our phone numbers:
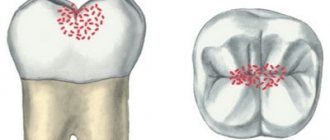
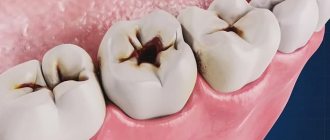
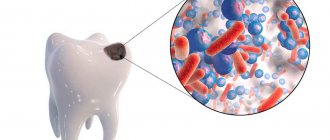
To begin with, it is useful to remember that caries is a complex, slow-flowing and slowly developing pathological process in the hard tissues of teeth, resulting from the complex interaction of unfavorable external/internal and general/local factors, as well as pathogenic bacteria, leading to the destruction of hard tissues of teeth. Caries and pregnancy are more closely related precisely through the physical condition of the mother. For example, constant pain in a tooth affected by caries (which, by the way, is not uncommon during pregnancy) leads to a woman’s inability to eat normally and a general deterioration in her emotional state. All this together can really have some negative impact on the development of the fetus.
Causes of caries in pregnant women.
- A decrease in the concentration of calcium and fluorine compounds both in saliva and in the blood due to some consumption of them for the needs of the developing embryo. Calcium is not consumed from the teeth themselves, as many people incorrectly believe. But the remineralization of enamel and its strengthening, which always occurs in other periods due to the action of saliva, can slow down or even stop during pregnancy. As a result, the enamel becomes weakly mineralized and is more easily damaged by acidic waste products of bacteria.
- Hormonal changes in the body and, again, corresponding changes in the composition of saliva, which leads to a decrease in its bactericidal properties. Simply put, the saliva of pregnant women is in some cases less effective at destroying cariogenic bacteria.
- Changes in diet – pregnant women can go to different extremes; they often develop strong cravings for sweets and starchy foods.
- Improper dental care - due to fatigue, toxicosis, worries and fuss, some expectant mothers regularly forget to brush their teeth or do not do it thoroughly.
In addition, many pregnant women manage to hear a lot of statements from friends and relatives that it is impossible to treat teeth during pregnancy, and simply do not go for preventive examinations. And as a result, they miss the moment when the tooth could actually be cured absolutely safely for the fetus.
The influence of caries on pregnancy.
Why is caries dangerous during pregnancy? Is it even worth having dental treatment during pregnancy, or is it better not to risk it?
The effect of caries on the fetus: a study conducted by American scientists revealed a clear relationship between the amount of Actinomyces naeslundii (a bacterium that has a pronounced cariogenic effect) and premature birth and the birth of a fetus with low body weight. It is assumed that these bacteria also stimulate the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (substances that cause contraction of the uterus and dilation of the cervical canal) in the body of a pregnant woman. The more the cervical canal expands, the more destruction of the fetal membranes and premature birth occur.
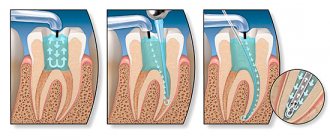
The impact of caries complications on the fetus: the simplest complications of caries include pulpitis and periodontitis. They arise due to the fact that tooth decay reaches the neurovascular bundle inside the tooth, as a result of which the latter becomes inflamed and the tooth begins to hurt. Moreover, the effect on the fetus occurs from two sides:
- firstly, inflammation of the dental pulp (pulpitis), and even more so, the spread of inflammation beyond the tooth, causing the absorption of toxins (and even pathogenic bacteria) into the blood, which are carried with the bloodstream throughout the body. The effects of this process are quite detrimental to both the woman and the development of the fetus;
- secondly, the psycho-emotional state of a woman has a great influence on the condition of the fetus. Toothache is a psycho-traumatic factor. Pain causes changes in many systems and organs, not only in pregnant women. For example, pain leads to increased release of certain hormones and changes in hormonal status. Of course, all this also adversely affects the fetus.
Prevention of caries in pregnant women
1. Preliminary sanitation of the oral cavity
To avoid dental fillings during pregnancy, it is best to cure all teeth first.
2. Oral hygiene
Despite the predisposition of pregnant women to gingivitis, careful hygiene significantly reduces this risk, as well as the risk of the formation of hard plaque. You should brush your teeth after every meal, and also use dental floss to clean between your teeth. A good helper for pregnant women can be an irrigator for washing interdental spaces, periodontal pockets and other hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity, which will minimize the risk of developing gingivitis.
3. Prevention of dental erosion
Nausea and vomiting are common in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. The low acidity level of vomit due to the high content of hydrochloric acid leads to the destruction of tooth enamel. To prevent this, you should avoid brushing immediately after nausea, because... enamel that has just been exposed to acid is most susceptible to abrasion. After each episode of vomiting, you must first rinse your mouth and brush your teeth no earlier than 30 minutes later. 4. Food
Frequent snacking between main meals is harmful. Every time you snack and don’t brush your teeth, you supply cariogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity with food, which enhances their destructive properties.
Vitamin therapy: The use of vitamins for the prevention of caries is not so common, but vitamins B1 and B6 are believed to have some anti-caries activity.
Take care of your health and the health of your child.
Dentist Trubeko A.O.
Healthy nutrition is the key to successful prevention of dental caries in children
Try to exclude sweets, flour products, as well as sweet juices and carbonated drinks from the menu. Plain water will be much healthier, and for snacks between meals, it is better to use apples, pears and other solid fruits and vegetables.
A child’s daily diet must include various dairy and fermented milk products. They will help avoid calcium deficiency and resist the development of caries.
Give preventive measures enough effort, time and attention, and your baby’s teeth will be beautiful and healthy.