Teething is a process characterized by the axial movement of teeth from a non-functional position (from the bone jaw tissue) to a functional position (on the surface of the alveolar process and gums). Most often, the formation of a temporary bite causes a lot of inconvenience, not only to the baby, but also to his worried parents. In this article from the “Pediatric Dentistry” section, we will try to figure out in what order baby teeth erupt, and what symptoms accompany the development of this process.
First signs
It is advisable to recognize the onset of teething in a child in time in order to be able to provide him with the necessary help. As a rule, symptoms of the upcoming appearance of the first tooth in a baby appear within a few days - in most children this period lasts up to several days and ends with the eruption of the outer shell of the gums.
Parents can recognize that their baby is starting to teethe by the following signs:
- The appearance of sudden changes in the child’s behavior: sleep disturbance, irritability, crying, refusal to take the breast or pacifier;
- The formation of increased salivation, often accompanied by the appearance of rashes around the baby’s mouth, chin, and chest due to excessive saliva;
- At the site of tooth eruption, the gums swell and become swollen;
- The child bites everything that gets into his hands, trying to relieve the irritating itching that appears in the gums.
What does a baby tooth look like?
Externally, baby teeth are very similar to molars. The differences that exist between them are described in detail in the table above and are practically invisible to anyone except the dentist.
The milk bite consists of:
- 8 single-rooted incisors;
- 4 single-rooted canines;
- 4 double-rooted lower molars;
- 4 three-rooted upper molars.
What is the name of the first tooth that appears in the jaw? Typically, bite formation begins with the lower central incisors.
What you need to know about deadlines
With the correct development of the newborn’s body, teething occurs at certain times according to the principle of pairing. Usually identical teeth erupt at the same time - this applies to pairs of central and lateral incisors and canines.
At birth, there are 20 follicles in both jaws of the baby - 10 for each jaw, which are the rudiments of temporary teeth. The newborn also has 16 permanent tooth buds. Another 16 primordia begin to form after birth.
The order of eruption of baby teeth:
Important:
Here are the average dates for teething in newborns. However, the development of each organism is strictly individual, so it is possible that these dates may shift in one direction or another in approximately 50% of cases. Therefore, do not panic if deviations from the given deadlines are insignificant.
There are cases when a baby was born with the first tooth. This makes breastfeeding much more difficult, so you need to get appropriate advice from your doctor.
With artificial feeding, there may be a delay in teething, while a breastfed baby's teeth erupt earlier in 10 cases out of a hundred. In addition, the delay in the eruption of baby teeth is influenced by the condition of the mother during pregnancy - for example, toxicosis, infectious diseases, stress, as well as diseases suffered by the baby.
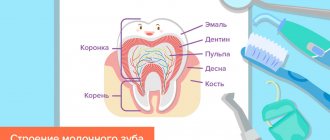
Structure
The structure of a baby tooth is significantly different from a molar tooth. Its enamel and dentin are thinner, their layers are 0.1-1 mm and 0.5-1.5 mm, respectively.
They are much smaller in size than molars, but the incisors are more convex in shape. Their root canals are wider, which increases the risk of bacteria entering and multiplying with subsequent inflammation.
The pulp of the front and chewing milk teeth in children occupies a larger volume than in the molar; on this topic, you can find many photos about the structure of a child’s jaw, what it consists of, and diagrams of the roots of the dentition in an adult and a child. In addition, children's teeth are characterized by a low degree of mineralization, and therefore are more vulnerable to caries. By the way, even adults sometimes have baby teeth, but usually no more than one.
What should you pay attention to when teething?
The above symptoms of the onset of teething are characteristic of almost all infants. However, some children have additional symptoms that need to be taken seriously:
- Temperature increase;
- Formation in the mouth of small watery blisters with cloudy or clear liquid;
- Increased redness and inflammation of the gums;
- Inflamed oral mucosa, accompanied by the formation of slight erosion.
In a healthy baby, when teething, contrary to popular belief and the advice of “experienced” relatives, the temperature does not rise. If this happens, it means that the child’s body is simultaneously exposed to some kind of inflammatory disease.
Most often, the listed signs indicate the development of a viral form of stomatitis or ARVI, which is not surprising given the child’s desire to put everything in his mouth. Therefore, you need to show the child to the doctor. If the pediatrician does not detect signs of an acute viral infection, take your baby to a dentist so that he can determine what form of stomatitis your child has caught and prescribe adequate treatment. Unfortunately, pediatricians are most often incompetent in this situation.
How to recognize the symptoms of gingivitis in children?
The clinical picture is not always bright. In addition to certain discomfort and pain in the oral cavity, children experience bleeding gums, itching or burning in them, and bad breath. Babies may develop a fever, significantly increasing their suffering.
It will not be easy for even the most attentive mother to “diagnose” the disease based on such symptoms on her own. In addition, if a son or daughter has already had an unpleasant experience visiting a dental clinic, they can hide all the unpleasant signs, steadfastly enduring the discomfort.
It is advisable that by the age of 10–12 years, children already have their own dentist. Regular medical examinations with a doctor whom the child trusts will help, if not avoid problems, then at least diagnose them in a timely manner.
Possible complications
"Surprises"
The problems that nature presents when infants have their first teeth do not end with the listed troubles. Sometimes other complications are possible:
- Formation of hematomas.
A bluish-colored bubble swells on the gum. Most often it resolves over time, but sometimes if the blister is too large, surgery is required. The doctor makes a small incision on the gum to remove the bloody fluid.
- The appearance of vomiting.
This may be caused by excessive salivation. However, if vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea and fever, these may be signs of rotavirus, so it is necessary to urgently show the child to the pediatrician.
- Cough reflex.
With normal teething it does not happen. The cause of the cough may be excessive saliva secretion, which causes the baby to choke.
If a runny nose appears, take your child to the doctor
- teething probably coincided with a cold.
Important:
If your baby is experiencing fever, diarrhea and vomiting during teething, take this seriously. The cause of their appearance cannot be teething. It is urgent to call a pediatrician, since the baby’s body is at risk of intoxication due to a developing infection.
What types of gingivitis occur in children?
- Most often, catarrhal gingivitis occurs with a burn or accidental mechanical injury to the mucous membrane. It is manifested by swelling of the periodontal tissues and pain when pressing on the gums, often becomes chronic and over time can develop into inflammation of the periodontal tissues - periodontitis.
- With hypertrophic gingivitis, the mucous membrane swells, becomes purple-blue and enlarges, “creeping” over the teeth. Pus is released from the formed periodontal pocket.
- In the atrophic form, the gums, on the contrary, turn pale and recede, exposing the tooth root.
- If left untreated, catarrhal gingivitis may not become chronic, but develop into an ulcerative form. The appearance of bleeding ulcers is accompanied by severe pain and a significant increase in temperature.
How to relieve your baby's condition with medications
If your baby is bothered by sore gums and begins to behave restlessly, you can give him a mild pain reliever that is appropriate for his age.
For the youngest, it is better to use candles, and older children can be given a special suspension. These drugs, in addition to a sedative effect, have mild antipyretic properties. In addition, pharmacies sell a special anesthetic gel, a small amount of which should be applied to the surface of the inflamed gum. However, you should not get carried away with such gels, since most of them promote increased salivation and also cause numbness, which makes the baby feel uncomfortable.
Important:
Before purchasing one or another medication to alleviate a child’s teething condition, you should definitely consult a pediatrician to rule out side effects.
Caring for emerging teeth
Teething is an absolute reason for making the first visit to the pediatric dentist. During the consultation, the doctor identifies all deviations in the structure of the child’s dental apparatus, assesses the condition of the frenulum of his lips and tongue, draws up a dental care plan and a plan for preventive visits to the dental clinic.
It is advisable to brush emerging teeth twice a day. Initially, you should use a baby silicone brush or a small piece of gauze without toothpaste for cleaning. A regular toothbrush can be used when the child is one year old, and toothpaste when he reaches two years of age. In addition, it is important to pay attention to the process of enamel mineralization. In particular, it is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets and include foods enriched with calcium, phosphorus and ascorbic acid in the baby’s diet.
Prevention
Dystrophic processes in the gums can be prevented. To do this, it is necessary to take care of the baby’s oral cavity from a very early age, prevent the formation of a large amount of plaque, and also visit a doctor in a timely manner to control and prevent dental diseases.
The dental department of the SM-Doctor clinic in Moscow has experienced doctors, modern equipment and the most comfortable and friendly environment. We will find the causes of gum recession and try to eliminate them as soon as possible. Don’t delay visiting your dentist; make an appointment with SM-Doctor.
Classification
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, local (affects a small area of the dentition) and generalized (involves the entire dentition) form of the disease is distinguished.
The degree of tissue deviation from the normal position makes it possible to distinguish between mild, moderate and severe degrees of the disease. Some dentists also distinguish between physiological (associated with natural processes in the body or the anatomical features of its structure) and symptomatic forms of pathology. In the second case, it is a consequence of other dental diseases, for example, gingivitis, periodontitis, and malocclusion.
Treatment.
Providing QUALITY dental care to children from the moment the first tooth appears and up to 3 years of age is LIMITED to physiological reasons: mild excitability, restlessness, fear of unknown manipulations in the oral cavity. An attempt to cure teeth by talking to a child or holding him by force in his arms ends with POOR-QUALITY treatment, as a result of which various local complications can develop.
REMEMBER: FORCED TREATMENT WITH CHILDREN RESTRAINT CAUSES IRREPAIRABLE PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAUMA TO THE CHILD!
Like