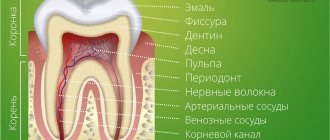
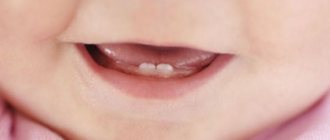
The period when a baby's baby teeth erupt is both exciting and difficult for both the child and his parents. Children are often capricious during this period, sleep poorly, cry, and all because the appearance of their first teeth is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. Since the child himself cannot tell his parents about his problem and always reacts the same way to any type of discomfort, it is difficult for mom and dad to differentiate the signs of teething under the child’s behavior.
In this article, especially for young parents, we have collected as much useful information as possible about the eruption of baby and permanent teeth in children, so that you understand what is happening and how to act in this situation to help the baby.
When and what teeth do children erupt?
In fact, the rudiments of baby teeth are formed in children even during the period of embryonic development, and at the moment when they begin to grow and erupt, the rudiments of permanent teeth are already being prepared in the child’s jaw to replace them.
If we talk about the “gold standard”, then the teething scheme looks like this:
- 6-8 months – two central lower incisors.
- At approximately 8 months, the upper central incisors also appear.
- At 8-12 months, the upper lateral incisors appear.
- Around the same time (10-12 months), the lower lateral incisors erupt.
- At 14-20 months, the first chewing teeth appear on the lower and upper jaws (one on each side - 4 in total).
- At 1.5-2 years, the first canines erupt in the upper and lower dentition.
- At the age of 2-3 years, the following chewing teeth appear.
Despite the specified timing, each baby has his own individual teething order. So, some babies show their first teeth at 4.5 months, while others are “delayed” and, on the contrary, grow a little later than the established age. Such features depend on many factors, including gender (usually girls take the lead in teething).
Teething at three months of age: normal or pathological
When the baby is very small, parents often associate his anxiety, fever and the appearance of other undesirable symptoms with illness, but not with the appearance of his first teeth. After all, the average time for teething is within 6–8 months. But pediatric dentistry knows many cases when the process begins earlier than this time frame. Therefore, parents need to prepare to help their child at any time.
Formation of milk bite
The process of building a human bite has 5 stages, and all of them occur in childhood.
Each of the five stages is important for the final formation of the entire dental system and dental occlusion:
The first stage is from birth to 6 months (before the appearance of the first teeth).
The second stage is the period of eruption of all baby teeth in a child (6 months - 3 years).
The third stage is the period of jaw growth, preparation for the natural change of milk teeth to permanent ones (3-6 years).
The fourth stage is the time of active growth of the jaws and the eruption of permanent teeth (6-12 years).
The fifth stage is 12-15 years old, when the child’s baby teeth have already changed and all teeth are permanent.
Correct formation of the primary dentition is one of the main conditions for the development of a correct permanent dentition in a child.
How many teeth should a child have?
By the age of three, a child usually already has a full set of twenty primary teeth, and until about 6 years old, their number remains unchanged. Adolescents aged 13 to 18 years should normally have from 28 to 32 molars (depending on the presence of eights, which may erupt after 21 years or not appear at all).
Symptoms of baby teeth erupting
Each baby reacts individually to the eruption of baby teeth, however, there are characteristic symptoms by which parents can understand that this is happening:
- heavy salivation;
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- itching
Severe itching and sometimes even painful sensations make the child capricious. He becomes restless, which disrupts his sleep. To somehow relieve the itching, children put toys in their mouths and intensively rub their gums. Children often refuse to eat or eat with less appetite. What does the gum look like when teeth come in? Changes in the condition of the gums are one of the criteria by which parents can differentiate teething. The gums in this place look inflamed - they turn red, swell, and immediately at the site of tooth eruption they become white.
However, the biggest concerns about the child’s condition are cough, runny nose, and fever during teething. Indeed, the appearance of baby teeth in its symptoms can resemble colds, and it is difficult for parents without experience to understand whether the baby is sick or is just teething.
First of all, you need to understand that both fever and cough during teething in children are acceptable reactions. Cough, hoarseness, and runny nose are most often the result of excessive salivation. For the same reason, during teething, babies develop a rash on the chin and around the mouth.
Another frequently asked question from parents is what kind of stool can a child have when teething? During a particularly acute period of teething, babies may have weak stools, which is associated with general irritation of the nervous system and has nothing to do with eating disorders.
However, it must be taken into account that when babies are teething, they are more susceptible than usual to various infections. If unpleasant symptoms (fever, diarrhea, cough) do not go away on their own after 2-3 days, the child should be examined by a doctor.
How long does teething take for babies?
With normal development and growth, baby teeth erupt within a few days (2-8 days), and the most unpleasant symptoms usually appear within about 2 days.
The period of formation of the primary occlusion ends at 2-3 years, and at this moment the baby has 20 primary teeth.
Problems and complications when the first teeth appear
Sore gums, fever, poor appetite and indigestion are, although unpleasant, acceptable symptoms during the eruption of baby teeth.
In some cases, children experience complications:
- long delay - can be either a genetic feature or pathological adentia (if the child has not formed the rudiments of teeth);
- formation of a hematoma (cyst) - in this case, the gum above the growing tooth acquires a dark purple tint, then a lump or hematoma appears in this place, which may be due to both difficult eruption (the tooth cannot cope with the mucous membrane) and other reasons;
- violation of the order of teething;
- aphthous stomatitis - rashes on the mucous membrane in the form of purulent ulcers;
- enamel hypoplasia – occurs in babies under 10 months of age;
- malocclusion - improper closure of teeth, crowding, possible problems with the eruption of permanent teeth in the future.
If your baby experiences “difficult eruption” of primary teeth or you encounter the listed complications, you should definitely consult a pediatrician. If the formation of a primary occlusion is clearly incorrect, consult an orthodontist.
Why do my gums hurt when teething?
To appear on the surface, the tooth needs to pass through the jaw bone and gum tissue. Although this is a natural process, it can be painful, because the tooth “grows” through the gum and violates its integrity. The gums become sensitive during tooth eruption, and pain may occur when pressing on them. These unpleasant sensations go away as soon as the tooth moves apart the gum and looks out.
What to do when teething: advice for young parents
Now that you know what is happening to your child, you can draw up a rough action plan aimed at making the process of the appearance of the first teeth as easy as possible for the baby.
Tips for moms and dads:
- 1
Stay calm. It’s not easy for a child anyway, and your anxiety and irritation will only negatively affect the baby’s well-being. - 2
Surround your baby with love and tenderness. Remember that small children feel calm and safe only in the arms of loving parents.
- 3
Provide your baby with special gum toys that will help relieve itching and make teething easier.
- 4
Turn on the increased antibacterial protection mode (frequent ventilation, sterilization of toys, pacifiers, etc.), since during this period the child can easily catch an infection.
If your baby's gums are bothering you a lot, you can use a special teething gel. This product has a mild anesthetic effect, relieves itching and pain. Regarding the choice of gel, it is better to consult your pediatrician. He will tell you which drug is suitable for your baby’s age and has a safe composition.
What to do when the temperature rises? Doctors recommend avoiding the use of antipyretic drugs, as the body fights infections by raising the temperature. If hyperthermia is very high, you should consult a pediatrician, he will recommend what medications and in what dosage can be given to the baby. Under no circumstances use folk remedies or medications without first consulting a doctor!
When should you worry?
The listed signs of the appearance of the first baby tooth should not bother mom, dad and grandmother too much. The following symptoms may be a reason to contact your pediatrician:
- Early appearance of the first teeth. In rare cases, newborns develop teeth immediately after birth. This may indicate endocrine pathology and requires examination by an endocrinologist.
- A significant delay in teething may also indicate various metabolic disorders in children and requires medical intervention.
- Incorrect appearance order . If, instead of the baby’s first incisors, molars or fangs begin to peck, such disharmony may indicate anomalies in the baby’s development or be a consequence of illnesses that the woman suffered during pregnancy.
- Temperature above 39 degrees. When the first teeth erupt in children, the temperature rises slightly. If your baby becomes hot and the high temperature lasts for several hours, call a doctor immediately.
Formation of permanent bite
The development of permanent teeth is a long and complex process. The formation of permanent teeth begins at approximately 3 years of age, when the child’s primary bite is already fully formed.
Preparations for their eruption are ongoing, but changes occur gradually, so most often we don’t even notice them. Meanwhile, the child:
- jaws grow and expand;
- the distance between baby teeth increases (this is important, since permanent teeth are larger and by the time they erupt there should be enough space for them in the dentition).
Timing of eruption of permanent teeth in children
The order of growth of permanent teeth in children is mainly hereditary. In approximately 50% of cases, the molars (sixes) grow first. Second molars appear at 7-8 years of age. Around the same time, the incisors are replaced.
The first permanent tooth appears in children at 6 years of age, and the complete formation of the permanent dentition of the lower and upper jaw is completed at 12-13 years of age. After this, the roots of permanent teeth continue to form and this process ends by the age of 15.
Teething symptoms
Unlike baby teeth, permanent teeth in children erupt almost always painlessly and with virtually no symptoms.
In rare cases, during the teething period the child’s well-being may deteriorate:
- the child gets tired quickly;
- drowsiness appears;
- gums become inflamed;
- salivation increases, a runny nose appears;
- The gums itch where the tooth grows, and when chewing, painful sensations appear.
Problematic eruption of permanent teeth in children
Problems that may arise during the eruption of permanent (molar) teeth:
- 1
Growth retardation – after a baby tooth falls out, the permanent one is in no hurry to appear for 6 months or longer.
- 2
Bite pathology. It may be associated with premature eruption of permanent teeth (if the baby teeth have not yet fallen out), or lack of space on the jaw for normal tooth growth.
- 3
Hyperdentia - permanent teeth grow second row behind the milk teeth. The reason is the strong fixation of the temporary tooth in the socket, as a result of which the permanent tooth “chooses” a more convenient direction for growth.
- 4
Caries and its complications.
How to understand that teeth have started to cut?
The following symptoms will indicate that a child is getting his first baby tooth:
- severe crying, frequent whims of the baby;
- increased salivation;
- slight increase in temperature;
- frequent excitability;
- refusal of food;
- upset stomach (diarrhea).
Of course, the above symptoms individually can indicate not only that the child is getting his first teeth. For example, whims and frequent excitability in a baby can be caused by stress due to moving to a new apartment, fever by a cold, and diarrhea by an allergy to a particular product. Usually, the eruption of the first teeth in children provokes several, or even all, of these signs at once.
How to help your child: recommendations from Amel Dental doctors
To cope with the discomfort caused by the eruption of permanent teeth, it is enough to massage the child’s gums. If your gums are inflamed, a teething gel will help relieve the inflammation (your dentist will help you choose the right one).
What to do if complications develop?
- 1
Bite problems in children are easier to eliminate than in adults, so if there are defects, you should consult an orthodontist.
- 2
Caries requires immediate treatment, otherwise there is a chance that the child will lose a tooth in childhood.
- 3
If dental growth is delayed, you should immediately see a doctor. One of the main reasons for delayed eruption of permanent teeth in children is immune disorders.
Gel for teething. How to choose?
If a child becomes restless and capricious during the teething period, first of all you need to create a calm environment for him, pay him more attention, pick him up more often, hug him, and talk to him.
Pain can be relieved mechanically or with medications. You can massage the gums with a clean finger or a rubber brush, let your baby suck on a dryer or chew on a teether, especially a cooled one. There are special dental gels to relieve gum pain in babies during teething. The advantages of children's gum gels are that they quickly relieve pain.
There are many more disadvantages to using them. The main two:
- If the gel contains the anesthetics benzocaine and lidocaine, they can be dangerous to the child’s health. Such drugs provide pain relief for a short time - the medicine is washed off with saliva and swallowed. It is difficult to accurately calculate the dosage when squeezing the gel out of the tube. If you also exceed the number of applications of the medicine recommended by the instructions, you may exceed the permissible limit. An overdose of lidocaine threatens with such dire consequences as convulsions, breathing problems, heart rhythm disorders - even death.
- Herbal gels provide mild pain relief, but help relieve inflammation. Their action does not give quick results. An allergic reaction to herbal components is possible, so after the first use you need to monitor the child’s reaction.
If you still decide to use a teething gel for your baby, choose either a herbal gel or a combination drug with an anesthetic and herbs. It will help relieve acute pain and reduce inflammation. But use combination gels very carefully, only as a last resort when other methods do not work and the child is in severe pain.
It is important!
Teething is a difficult period for the baby and his parents, but it is a natural stage of growing up, which allows the transition to solid food after breast milk.
How to keep children's primary and permanent teeth healthy?
Both baby and molar teeth of a child require careful care. The health of future permanent teeth depends on how healthy the child's baby teeth were. The main concern of parents is quality care, timely treatment and preservation of baby teeth until the time comes for their natural replacement with permanent ones.
What should you do for this?
- Carefully monitor the condition of your baby’s teeth and regularly take him for examinations to the dentist in order to diagnose caries in time.
Prevention of caries is one of the main conditions for the health of a child’s future permanent teeth. You can protect your teeth by ensuring regular high-quality oral hygiene. One of the most effective measures to prevent caries in children is the dental procedure of sealing the fissures of baby teeth.
- Treat caries in a timely manner.
Unfortunately, temporary teeth have very thin enamel and not a very dense structure, so when affected by a carious infection, they are quickly destroyed. With timely diagnosis, caries is treated quickly and without complications - in dentistry, baby teeth are filled with safe materials. Thanks to modern materials and technologies in dentistry, it is even possible to restore baby teeth with severe destruction. In some cases, if the baby tooth could not be saved, and there is still a lot of time left before the permanent teeth erupt, prosthetics of temporary teeth is used.
- Take care of proper nutrition.
Food is an important source of useful vitamins and microelements, so it is important that the child’s diet is varied and balanced.
Both baby and molar teeth of a child require careful care. The habit of brushing teeth and observing the rules of oral hygiene is formed in children from the appearance of their first teeth. Maintaining the health of children's teeth requires very little time and effort, but all this effort will help your child keep his teeth healthy for a long time!