Hematoma
Description
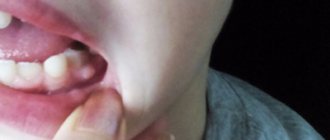
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.
Periodontitis
Description
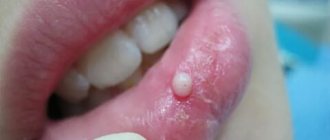
A hard lump on the gum, an abscess formed at the base of the tooth root. In the absence of therapy, it transforms into a benign tumor.
Treatment
If such compaction of the gums under the tooth appears, contact your dentist. The teeth are unfilled and root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths with medicinal herbs or soda solution are prescribed. Treatment for periodontitis may require multiple visits to the doctor.
Infections that cause bumps on the gums
Among the infectious diseases that contribute to the appearance of unusual gum growths:
- Periostitis. Inflammation of the periosteum of an acute or chronic nature. In advanced cases, it causes symptoms of general intoxication. The patient complains of a painful lump. It can either increase or decrease in size. Often there is pus inside it. Treatment consists of anti-inflammatory therapy, opening and draining the abscess. At the doctor's discretion, root canal treatment may be performed.
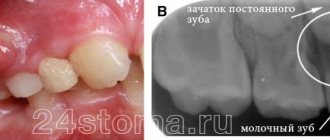
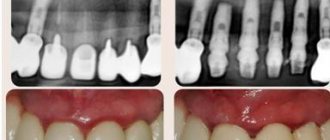
- Granulomatous periodontitis. Most often, this pathology is asymptomatic and is discovered accidentally during an x-ray for another disease. If the cyst is not localized in the area of the apex of the tooth, but is strongly displaced to the side (this is quite rare), a resemblance to a tumor can be observed.
- Radicular cyst. In advanced cases, its walls become inflamed. Then the infected contents of the tumor turn into pus. The necrotic masses are trying to find a way out. A lump appears, from which a foul-smelling liquid is released. During an in-person examination, hyperthermia and tenderness of the surrounding tissues are recorded. The situation may be complicated by symptoms of general intoxication: chills, fever, severe weakness.
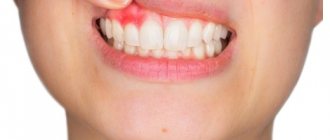
- Gingivitis. Inflammatory gum disease. They bleed and become inflamed. Deformation of the gingival margin may occur. Sometimes the inflammation becomes so severe that small benign tumors appear.
- Periodontitis. A condition in which the tissues responsible for holding the tooth in its socket weaken. As a result, the unit becomes mobile. Deep “pockets” form at its base. If food residues accumulate in them, the situation is aggravated by the formation of small round seals.
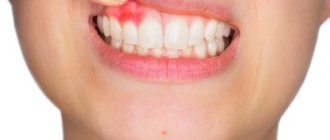
Flux (periostitis)
Description
An inflammatory process of bone tissue, which is accompanied by pain, elevated body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, and swelling of the oral mucosa. The seals have purulent contents. The cause is an infection of the oral cavity resulting from untreated caries.
Treatment
A visit to the doctor is required to treat the lump. The dentist opens the tooth, places special medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If treatment does not bring positive results, the tooth is removed.