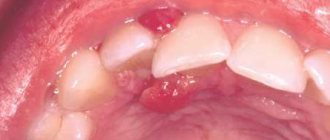
Most people associate dentistry only with dental diseases, forgetting that the soft tissues of the oral cavity can also have pathologies, causing discomfort and pain. Moreover, some gum inflammations can be dangerous to a person's overall health. Often, bumps appear on the gum tissue - this is what purulent neoplasms or fistulas on the gums are commonly called. A lump on the gum is a symptom of a serious complication that occurs for many reasons, which only a dentist can identify.
Content:
- Reasons for the formation of lumps on the gums
- Infections that cause bumps on the gums
- Bumps in the mouth of a non-infectious nature
- Lump at the base of the tooth after installing a permanent crown
- How do doctors treat a lump on the gum?
A change in the structure and shade of the oral mucosa is a reason to visit the dentist.
If a lump appears above the tooth - whether it hurts or not - it means there is some kind of problem. Such neoplasms do not just arise. This symptom may indicate various diseases. Most likely, the inflammatory process occurs in the gums, but without a preliminary diagnostic examination, the presence of systemic pathologies that manifest themselves in this way cannot be ruled out.
Possible reasons
Dentists say that in most cases, a lump on the gum is a consequence of poor oral care. Plaque can accumulate not only on the enamel, but also on the gums. Soft deposits are a favorable environment for the development of various pathogens. If plaque is not removed in a timely manner, inflammation may occur.
Doctors distinguish the following neoplasms.
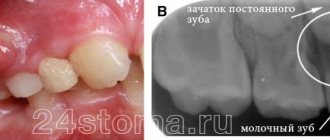
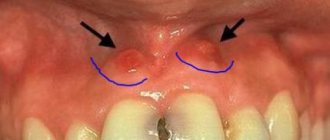
- Fistula. Formed against the background of advanced caries. Most often it forms on the upper jaw. It affects not only the mucous membrane, but also bone tissue. It is a red or pink growth with pus or exudate.
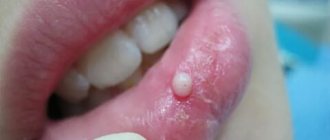
- Exostosis. A hard, white lump consisting of boney substance. As a rule, it forms after tooth extraction. At the initial stage it does not cause discomfort, but as it grows, unpleasant sensations appear.
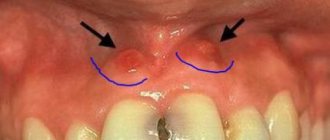
- Epulis. The ball on the stem is gum-colored. Formed from soft or hard tissues in the area of the alveolar process. It can be fibrous, angiomatous, giant cell and acanthomatous. The clinical picture is similar to gingivitis.
- Flux. Inflammation of the periosteum tissue. A lump appears near a tooth affected by caries or pulpitis. Accompanied by acute pain radiating to the ear and temple.
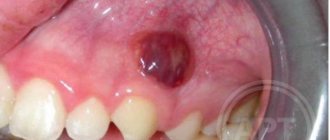
- Cyst. A growth filled with dead cells or pus. May be light or dark in color. Appears against the background of dental diseases and inflammatory processes occurring in the gums.
Reasons for the formation of lumps on the gums
When speaking about a lump under a tooth, dentists mean a dense, white or red growth. There may be purulent masses inside it. The disorder is usually caused by damage to periodontal tissues. What led to its occurrence remains to be determined by the dentist.
The described “growths” are of two types:
- infectious;
- non-infectious.
In the first case, they arise due to the abnormal activity of pathogenic microorganisms, in the second they are associated with mechanical damage to tissues, chemical burns and other unfavorable external factors.
More often than not, a lump on the gum forms precisely because of an advanced infectious process , but this does not mean that doctors can use standard schemes in their work. First, the doctor studies the features of clinical symptoms and draws up a detailed medical history, then carries out the necessary treatment measures and selects medications that will definitely help.
A lump on the gum: what is it and what diseases can it indicate?
When taking care of your own health, you should remember that not only problems with teeth pose a potential threat: problems with gums can also signal the presence of serious problems in the body. We will devote this article to a fairly pressing issue - what to do if a lump (ball) appears on the gum? We will try to thoroughly study the issue, as well as understand what diseases this symptom may signal.
What is a lump on the gum?
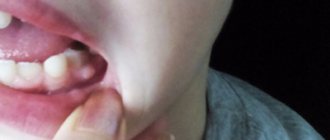
In this case, we are talking about compaction of the soft gum tissue: visually this manifests itself in the form of the formation of a ball or lump - the problem is diagnosed through a visual examination, not to mention the fact that the affected area may hurt and cause discomfort.
Any change in the color of the gum tissue is always a reason to consult a dentist. If there is a lump (ball), you should go to the doctor immediately.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of such a lump - treatment tactics depend on the correct diagnosis, which the specialists of Dr. Efremov’s Dentistry can do. But generally speaking, there are two natures of the disease - infectious and non-infectious. Let's consider both factors separately.
Infectious causes of the formation of lumps on the gums in Kirov
Infection is always associated with the activity of pathogenic bacteria, which can infect absolutely any tissue of the human body. Gums are no exception: in this case, compaction is associated with infectious inflammation, which can occur for several reasons:
- Flux or periostitis. This phenomenon can be considered a complication of diseases such as caries, pulpitis or periodontitis. The infection may well affect not only the teeth, but also the adjacent tissues, that is, the gums. The result is the formation of a lump (or ball), which is noticeable even to the naked eye;
- Acid or granuloma, which can be classified as complications of periodontitis. The apex of the root is precisely the area where, due to various complications, an abscess often occurs - pus can penetrate into the periosteum area, and then under the mucous membrane. The insidiousness of this phenomenon lies in the fact that the tissues of this area are quite elastic, so at first a person may not notice negative symptoms and not experience discomfort. Only then, when the problem becomes serious, does a ball appear - this is a real fistula, which requires immediate contact with an experienced dentist;
Periodontitis and gingivitis. When inflammatory processes form in the periodontium, in almost 100% of cases the formation of various seals is observed. In the case of gingivitis, the ball acquires a red tint, and periodontitis is accompanied by the presence of a gray lump. If you do not seek high-quality or effective treatment, the disease transforms into a flux, which becomes even more noticeable and potentially dangerous to the general condition of the body.
This is exactly what the most common cases of infectious nature of the formation of a lump on the gum look like in Kirov. Next, we will look at the non-infectious cause of this problem.
Non-infectious causes of lump formation on the gums
There are also three most common options - we will again consider them individually:
- Epulis is a small growth. Visually, epulis resembles a tumor diagnosed with gingivitis, however, x-rays and/or histological examination will help to understand the true cause of the disease. This could be malocclusion, consequences of injuries, hormonal disorders, and even the result of unprofessional dental prosthetics;
- Ecostosis is a bone growth that occurs due to jaw abnormalities. Most often, this is observed due to genetic predisposition, however, the factor of injury should also not be excluded. The fact is that bone tissue can go beyond its usual limits, resulting in a noticeable lump. As a rule, inflammatory processes are not observed in this case, however, they may well appear during mechanical damage to the growths;
- A hematoma is a blood clot in the gum area, which is a direct consequence of the injury. Although, from time to time there are cases when a hematoma forms without external influence - this is also a reason to consult a dentist to solve the problem and prevent the development of complications.
So, we looked at the three most common causes of non-infectious origin of a lump on the gum in Kirov. Next, we will find out in what cases painful sensations occur in the presence of such a ball, as well as what methods of solving the problem exist today.
If the lump hurts?
If you suddenly find a lump on your gum, however, there are no pain symptoms, this does not mean that you should refuse professional diagnosis and treatment. Yes, it is likely that everything will go away on its own, however, in most cases this is not the case - there is a risk of tooth loss!
If the lump begins to hurt, you should immediately visit the dentist; however, even in this case, it is not always possible to save the tooth.
As for the most acute pain in the presence of a ball (bump) on a tooth in Kirov, this may signal periostitis. If the seal only bothers you when you apply pressure or eat warm or cold food, you can most likely diagnose gingivitis or periodontitis. In turn, epulis and ecostosis may go completely unnoticed, however, there may still be a slight feeling of discomfort.
Incorrect crown installation
Separately, I would like to pay attention to such a reason for the formation of a lump as incorrect installation of the crown (we have already mentioned this factor above). There are two possible factors to highlight here:
- Incorrect or poor-quality treatment of tooth canals before prosthetics, which can lead to periodontitis (we have repeatedly spoken about the complexity of the tooth depulpation procedure);
- Incorrect measurements or poor-quality prosthesis/crown. This is also very common, since an artificial element can injure the mucous membrane of the gums, causing irritation and the appearance of seals.
Treatment depends on the cause: in the first case, it is re-treatment of the tooth canals in Kirov, in the second - re-prosthetics (if, of course, it is possible).
Treatment of lumps on the gum in Kirov
And finally, a few words about how the ball is removed and the lump on the gum is treated. The order depends entirely on the nature of the disease. For example, infectious pathologies are treated by identifying and eliminating the root cause - this is done both through mechanical manipulation and with the help of medications. If periodontal inflammation occurs, measures such as sanitation and cleaning of the oral cavity, curettage, physiotherapy, etc. may well help. As for non-infectious manifestations, here the issue is resolved on an individual basis: sometimes the disease is simply observed without any active action, and in some cases surgical intervention is required.
We invite you to Doctor Efremov’s Dentistry: sign up for a consultation and get answers to all your questions! Information by phone: 8 (8332) 255-717 . Be healthy and take care of the beauty of your smile!
Infections that cause bumps on the gums
Among the infectious diseases that contribute to the appearance of unusual gum growths:
- Periostitis. Inflammation of the periosteum of an acute or chronic nature. In advanced cases, it causes symptoms of general intoxication. The patient complains of a painful lump. It can either increase or decrease in size. Often there is pus inside it. Treatment consists of anti-inflammatory therapy, opening and draining the abscess. At the doctor's discretion, root canal treatment may be performed.
- Granulomatous periodontitis. Most often, this pathology is asymptomatic and is discovered accidentally during an x-ray for another disease. If the cyst is not localized in the area of the apex of the tooth, but is strongly displaced to the side (this is quite rare), a resemblance to a tumor can be observed.
- Radicular cyst. In advanced cases, its walls become inflamed. Then the infected contents of the tumor turn into pus. The necrotic masses are trying to find a way out. A lump appears, from which a foul-smelling liquid is released. During an in-person examination, hyperthermia and tenderness of the surrounding tissues are recorded. The situation may be complicated by symptoms of general intoxication: chills, fever, severe weakness.
- Gingivitis. Inflammatory gum disease. They bleed and become inflamed. Deformation of the gingival margin may occur. Sometimes the inflammation becomes so severe that small benign tumors appear.
- Periodontitis. A condition in which the tissues responsible for holding the tooth in its socket weaken. As a result, the unit becomes mobile. Deep “pockets” form at its base. If food residues accumulate in them, the situation is aggravated by the formation of small round seals.
Bumps in the mouth of a non-infectious nature
If we talk about dental “growths” of non-infectious origin, then we need to mention:
- Epulis. Tumor-like formation of a productive nature. It appears due to the negative influence of local irritating factors. It is caused by injuries, incorrectly installed prosthetic structures, the habit of constantly gnawing hard objects, and malocclusion. Externally, epulis is very similar to tumors caused by gingivitis. To make a correct diagnosis, dentists take x-rays and conduct a histological examination. When treating pathology, the negative influence of the provoking factor is first eliminated. After this, the oral cavity is sanitized. In some cases, it is necessary to excise the neoplasm within healthy tissue along with the periosteum.
- Exostosis (osteophyte). A bone growth that causes the gum level to rise. Usually does not cause any discomfort. Appears after facial injuries or tooth extraction. Most often it is discovered by chance during a routine examination or during preparation for prosthetics. Therapy boils down to removing the bony protrusion and smoothing its surface.
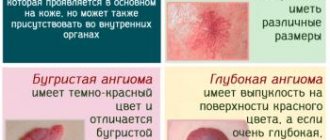
- Hematoma. It looks like a ball filled with blood. Indicates that in a certain area the capillaries or vessels of the mucous membrane have been injured, but the damage is superficial. Hematomas appear due to chemical burns, thermal and mechanical injuries. It is important to differentiate such hemorrhages from hemangiomas and vascular tumors. The latter are very dangerous and require completely different treatment.
Lump at the base of the tooth after installing a permanent crown
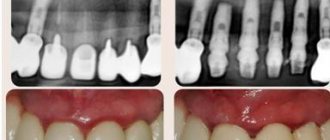
If the prosthetics are carried out correctly, the doctor did not make mistakes, no neoplasms should appear in the mouth. If, after the end of treatment, the gums swell and a painful blister forms on it, it means that something did not go according to plan.
Most likely, the doctor poorly prepared the unit for prosthetics. Depulpation must be carried out extremely carefully. There should be no air bubbles in the canals to be filled. Under no circumstances should you leave fragments of dental instruments in them. Poor depulpation creates conditions for the development of an infectious process and subsequent periodontitis.
It is also possible that the lump was formed due to shortcomings that were made at the time of fixation of the artificial unit. Then the glued structure begins to put pressure on the mucous membranes and rub the tissue. Abscesses, growths, and purulent lumps form. To eliminate these unpleasant symptoms, you need to adjust the shape of the prosthesis.
If the crown is installed correctly, it will never interfere. This needs to be understood. Only in the first hours after its fixation may an unusual sensation of a foreign body in the mouth persist. But then the person stops noticing the structure altogether.
Lump after crown installation
Improper denture fitting is a very common cause of lumps on the gums. Most often, errors occur at the tooth preparation stage, when the depulpation procedure is carried out. Poor canal filling provokes the development of infection, which, in turn, leads to periodontitis. Another common reason is a poorly made prosthesis or defects during its installation. In this case, the prosthesis injures the mucous membrane and causes swelling, abscesses and growths. Treatment almost always involves removal of the prosthesis and subsequent replacement of the prosthesis (if possible). The sooner a complication is detected, the higher the chance that it can be successfully treated. A well-installed prosthesis should not cause pain, discomfort or injure the mucous membrane. The tooth under the crown should also not hurt, since the dental nerve is killed before permanent prosthetics.
How do doctors treat a lump on the gum?
The treatment regimen directly depends on the cause of the disorder. Therefore, the patient is first offered to undergo diagnostics. It includes:
- survey, inspection;
- performing radiography;
- taking a tissue sample (if necessary).
Based on the results obtained, the doctor decides on further procedures. It can be:
- drainage and washing of purulent neoplasm;
- root canal filling;
- removal of osteophyte;
- excision of a benign tumor;
- dental crown replacement;
- conducting pharmacological therapy.
It is important that the patient strictly follows all medical prescriptions. Then the likelihood of complications will be minimized, and the oral tissues will be restored in a short time.
Treatment
Before starting treatment, you need to identify the cause of the lump. Only a specialist can do this after conducting the necessary diagnostic studies. Dental treatment will depend on the causes of the disease and the form of its course:
- the abscess can be opened and cleaned, which will prevent further spread of infection throughout the oral cavity;
- if the lump occurs due to any serious damage to the tooth, most likely the tooth will be removed;
- if a lump has formed after the removal of a tooth, the dentist will treat the hole and prescribe a number of medications.
Tooth extraction occurs only in the most extreme case, when it cannot be saved, and it causes the development of an infection in the oral cavity and its spread to neighboring teeth. The most important thing is not to self-medicate, but immediately, if a problem is discovered, contact a specialist!