Not everyone manages to keep their teeth intact throughout their lives. When teeth are lost, the patient loses the ability to smile beautifully, and he experiences disturbances in speech and chewing functions. Orthopedic dentistry is designed to solve these problems. Restoration of the structure and functions of the masticatory apparatus occurs through the installation of orthopedic structures. Modern designs for prosthetics completely replace lost teeth. They are adaptive, hypoallergenic, and have a long service life.
Indications for installation of a prosthesis
The general indication for prosthetics is damage or absence of a certain number of dental units. Dental defects lead to ineffective chewing of food. The bite is disturbed, the aesthetics of the smile suffers. The most common indications for prosthetics are the following disorders:
- Adentia (complete or partial loss of teeth). Restoration of the dentition is carried out by removable prosthetics or implantation of dental units.
- Complete or partial destruction of the coronal part of the tooth, in which filling is impractical. When preserving the root, a pin structure or stump tab is used.
- Pathological abrasion of enamel, which is a systematic violation of the enamel layer of dental units. The loss of hard dental tissues leads to malocclusion.
- Traumatic damage to teeth. The patient may be offered various options for restoring the dentition, depending on the severity of the situation.
- Pathology of the alveolar process leading to serious malocclusion. A frequent consequence of partial edentia, leading to the restructuring of the alveoli and a decrease in the functionality of the dentition.
- Single and multiple dental defects. The patient can be offered various design options depending on the existing problems.
Types of prostheses
Modern orthodontics offers many types of dental restoration. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages and is used to solve a particular problem. The type of prosthesis and method of prosthetics are selected by the attending physician together with the patient, based on the clinical situation, budgetary capabilities and patient preferences. Orthopedic structures are distinguished by the method of fixation, the material of manufacture, the defect being replaced, and the type of fastenings in the oral cavity.
Classification by method of fixation
Based on the method of fixation, a distinction is made between removable and non-removable structures. A very special type is fixed dentures on implants.
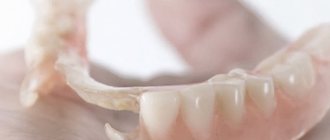
- Removable structures. They can be removed from the mouth independently. They solve the problem of the absence of one or more units in the dentition. Inexpensive and easy to care for.
- Fixed structures are permanently fixed in the oral cavity. They are durable, strong and efficient. They have a higher cost.
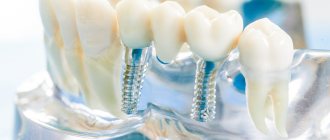
- Implantation is the most complex and expensive type of prosthetics. Implants are a multi-component structure that is inserted into the bone tissue of the jaw and replaces the root part of the teeth. On their basis, the restoration of the dentition is carried out.
Classification by material of manufacture
In modern dentistry, many materials have been developed for the manufacture of prosthetic structures. Here are the four main types:
- Plastic structures are made from polymerized acrylic. This lightweight and durable material is inexpensive and available. The lightweight porous structure ensures a tight fit, which significantly reduces the adaptation time. Under heavy loads, plastic prostheses are prone to loosening and are therefore short-lived. Used for temporary use.
- Nylon prostheses are made from soft, hypoallergenic synthetic material. They are secured in the mouth using special clasps. The disadvantage is its short service life. The chewing load is distributed unevenly, which can lead to bite problems.
- Zirconium dioxide structures. Zirconium dioxide is a durable natural mineral, naturally enriched without the presence of synthetic impurities. Used for the preparation of fixed dentures. It has many advantages: it holds the chewing load well, its shade is close to natural enamel, and it has low thermal conductivity. Zirconium dentures are not used to treat severe malocclusions, since a strong crown begins to destroy neighboring teeth.
- Ceramic dentures are made from specially treated ceramics with the addition of lithium disilicate. The crown material is very durable and reliable, its structure is closest to tooth enamel. Ceramic dentures have the highest aesthetics, therefore they are used for prosthetics in the smile area.
Classification of dentures according to the volume of the replacement defect
Depending on the clinical situation, the patient may be indicated for a complete or partial denture:
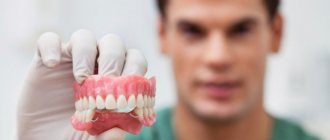
- Complete dentures are removable or conditionally removable structures used in the absence of all units in the dentition. A complete denture simulates the entire dentition. The base of the prosthesis rests on the gums and helps fix the structure in the oral cavity.
- Partial dentures help restore dentition when several teeth are missing. They imitate a fragment of the dentition, replacing several nearby missing dental units or teeth lost in different parts of the jaw.
Classification of prostheses by type of fastenings
Depending on the method of fastening the prosthesis in the oral cavity, the functional load on the supporting tissues is distributed differently. The following types of orthopedic structures are distinguished:
- Lamellar dentures are a type of removable structures. Effective for partial or complete edentia. They differ in the material of manufacture and the method of attachment in the oral cavity. Attached directly to the mucous membrane.
- Bridges are non-removable structures used in cases where several dental units are missing in a row. They are attached to dental units spaced apart from each other and ground for crowns.
- Supported or clasp dentures are distinguished by a special way of transferring the load: through the supporting teeth, periodontium and mucous membrane. This method is called semi-physiological.
Prosthetics for complete absence of teeth
In cases where the client was unable to save his teeth, all-on-4 or all-on-6 implantation is used. The technology involves implanting 4 or 6 titanium pins into the jaw, which will serve as artificial roots for the future dental structure. The technology of such permanent prosthetics allows you to completely restore the dentition and restore full chewing function.
Installation of prostheses using all-on-4 technology is less reliable compared to all-on-6 technology and can become loose faster. This technique is used when it is impossible to use the all-on-6 technology and when bone tissue atrophy has developed.
The all-on-6 technology (“all on six”) is more reliable, which is especially important for prosthetics for older clients. This technique is more progressive, as it allows you to distribute the load of the entire dentition. The strength of the dental structure is ensured even in cases where bone atrophy has reached a moderate or even high degree. The all-on-6 system is also indicated if the client has periodontitis, periodontal disease and other problems with the gums and bones.
Before deciding how exactly to attach the prosthesis, the doctor will conduct an examination of the oral cavity and complete sanitation, and also check the parameters and strength of the jaw bones. It is also important to establish the presence of contraindications that do not allow all-on-4 or all-on-6 implantation.
How to choose the right dentures
The selection of a denture is made by the attending dentist together with the patient. After the initial examination, the doctor assesses the clinical situation and advises the patient, explaining what type of prosthetics is indicated for him. The patient makes a decision taking into account the doctor’s recommendations and his preferences.
Doctors at the Consilium Dent dental clinic will provide a free initial consultation on the selection and installation of orthopedic structures. After the initial examination, the dentist will select the optimal prosthetic option and advise the patient on how to prepare for prosthetics. He will talk in detail about how to care for the oral cavity during and after prosthetics. When choosing, the number of missing teeth, the condition of the tooth bed and gums, financial capabilities and the desire of the patient are taken into account.
Removable dentures. What to prefer?
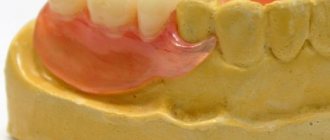
If all or a significant part of the teeth are lost, the patient will be offered the installation of a removable denture. The removable design is a plastic plate that fits tightly to the mucous membrane and follows its shape. This ensures its strong attachment in the oral cavity. Artificial teeth are attached to the plate, imitating the patient’s own lost dental units. There are two types of removable structures: partially removable and completely removable.
The best partially removable designs
Partially removable dentures are used for partial restoration of the dentition. This type of denture is indicated if only part of the teeth are missing. Plastic and nylon are used for manufacturing. Special hooks or special clasps are used as fastening means. The fasteners are quite strong and provide reliable fixation of the dentition.
Main advantages and disadvantages
Partially removable structures are universal and have many advantages:
- The chewing load is evenly distributed, which ensures the safety of the dentition.
- The oral care procedure is simple and easy.
- Durable clasps provide reliable fixation in the oral cavity.
- The prosthesis ensures complete restoration of chewing function.
- Due to the uniform load, deformation of some dental units is excluded.
Among the disadvantages are the following:
- Dentures are quite expensive.
- Not all designs are sufficiently aesthetic, so they are not suitable for restoration of a row in the smile zone.
- Dentures require periodic adjustments.
Removable structures for complete dentures
This type of structure is used for complete restoration of the dentition in cases of total edentia. These are light and durable dentures that are in good contact with the oral mucosa. Typical denture materials used for complete dentures are nylon or acrylic. The fastenings are made in the form of so-called suction cups.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the advantages, the following should be noted:
- The designs are easy to manufacture, which determines the low price.
- In case of breakdowns or damage, they can be easily restored.
- Cover a significant part of the sky, which makes contact very reliable
- Easy to care and use.
There are also a number of disadvantages:
- The structures wear out quite quickly, since the work of the masticatory muscles is not always coordinated.
- Due to constant pressure, the volume of tissue in the jaw joint gradually decreases. This impairs the retention of the prosthesis, and it may fall out when speaking.
- If the prosthesis is not positioned correctly, pain may occur in the mouth.
Let us compare the removable structure made of acrylic and nylon.
- Acrylic processes are more affordable.
- Acrylic dentures can break over time, while nylon dentures are made of flexible and durable material, so the likelihood of breakage is minimal.
- An acrylic prosthesis does not deform; a nylon prosthesis can change shape.
- Nylon has a smooth structure, does not absorb odors, does not stain, and is non-toxic. Acrylic is a more porous material and is susceptible to staining and staining over time.
- The color of nylon is closer to the shade of natural enamel and looks aesthetically pleasing. Acrylic has a wide range of shades; it is possible to choose an option that is as close as possible to the individual shade of the teeth.
- Nylon constructions are more hypoallergenic than acrylic ones
Removable dentures without palate
Sandwich dentures are designed for partial prosthetics and are an arch made of dense polymer that imitates the jaw arch. They are fixed to the molars that are preserved on both sides of the jaw. The fasteners are telescopic crowns that fit tightly and fix the product.
The advantage of these designs is that they leave the palate and sublingual space free, which ensures the preservation of diction and the natural sensitivity of taste buds. In some patients, such prostheses cause a gag reflex, which can make wearing difficult. Such patients are recommended to opt for the clasp system.
Implant support
I would like to pay special attention to the beam fixation system supported by implants - a new word in removable prosthetics.
In the absence of favorable conditions for fixing removable dentures, an alternative to a fixed bridge is a removable denture, which is installed on implants. A complete removable denture supported by a ball or bar structure, which in turn is supported by two or more implants in the anterior jaw. (see picture)
Implants help keep the denture in place and provide better functionality and comfort. Implants can serve as a support for the fixing elements of a removable denture.
In the absence of teeth, especially in the lower jaw, it is not easy to achieve good fixation of a complete removable denture. But this problem can be solved with the help of several implants. At the end of the healing process, the implants serve as a support for the beam fastening of the removable denture. The production of such a structure takes place in a dental laboratory and requires the highest qualifications and precision from the dental technician. The beam is fixed to the implants and is a non-removable part of the combined prosthesis. The second (reciprocal) part of the beam fastening is fixed in the prosthesis. Thus, the prosthesis “snaps” onto the beam and is securely held in place.
Expert advice
There is no clear answer to the question of which prosthesis to choose in a given case. The structural features of the patient’s jaw apparatus, his age, and the severity of the problem are of great importance. Approximate recommendations are given in the table:
| Situation | Type of prosthetics |
| Clinical picture | Recommended type of prosthetics |
| Availability of dental units suitable for fastening the structure | Conditionally removable prosthesis |
| The dentition lacks a large number of dental units, and the installation of bridge-like structures or implantation is impossible | Removable prosthetics |
| Molars or incisors are completely absent from the dentition | Removable prosthetics. It is recommended to choose acrylic dentures |
| Molars and premolars are missing | Partially removable prosthetics |
| Requires installation of temporary prostheses | Partially removable prosthetics |
Basic rules of use
By following these recommendations, you will significantly reduce the period of adaptation:
- When putting on prostheses, various reactions of the body are possible. To stop an attack of nausea, drink tea or eat candy.
- Make a change to your usual menu. Food should be crushed and not rough. Any types of viscous products that can harm not only healthy teeth, but also the structure itself are prohibited.
- We recommend that you leave your dentures on at night to speed up the adaptation period.
- Hygiene should be about more than just regular cleaning. You can purchase mouthwash and other similar products.
- Use special pastes and creams for additional fixation.
- When using completely removable dentures, the patient's diction is distorted.
To remedy the situation, we recommend that you read aloud more often.
Fixed dentures. Which ones to choose?
Fixed prosthetic structures are firmly fixed in the patient’s oral cavity with cementing material and are not intended for self-removal. There are three main types of fixed structures: crowns, bridges, microprostheses.
Crowns
A dental crown is a non-removable orthopedic structure of a natural shape that covers the coronal part of a tooth or a separate area of its surface. Crowns are made from high-quality materials: metal, zirconium, porcelain, ceramics, plastic.
Advantages and disadvantages of crowns
The main advantage of dental crowns is that they are able to completely restore the functionality of the dentition. Other benefits include:
- strength;
- aesthetics;
- low price;
- long service life
Among the disadvantages of structures of this type are:
- metal crowns are not aesthetically pleasing enough, so they are not used in the smile area;
- it is not always possible to choose a design color that fully matches the color of natural enamel;
- in some cases it is necessary to sharpen the tooth.
Bridge structures
A bridge is a type of fixed prosthesis used to replace significant defects in the dentition. A bridge rests on two dental units spaced apart from each other and replaces several destroyed, consecutive dental units.
Advantages and disadvantages of bridges
Bridges are structures that are designed for use in cases of significant defects in the dentition. This quality determines the main advantages of the structures:
- When chewing, the load is evenly distributed, determining the long service life of the prosthesis.
- The use of a bridge helps prevent atrophic processes in bone tissue. They begin due to insufficient load on the jaw in the absence of a significant number of dental units.
- A bridge can ensure normal grinding of food during chewing, and therefore maintain the health of the patient’s digestive system.
The disadvantages of bridges include the following:
- A structure that replaces several dental units is quite expensive.
- Teeth that serve as support have to be ground down and depulped even if they are healthy.
Microprostheses
Microprostheses are microstructures made of ceramic or composite material that serve to restore the damaged part of the tooth surface. These include dental inlays, veneers and lumineers.
Microprosthetics is a gentle technology designed to preserve severely damaged teeth. It allows you to protect the front wall of the tooth and restore the aesthetics of the dentition.
Advantages and disadvantages of microprostheses
The advantages of microprosthetics are obvious:
- A microprosthesis effectively hides defects and strengthens the tooth, which prevents its further destruction.
- An ideally selected shade makes the tooth indistinguishable from other units of the dentition.
- Microprosthetics does not require grinding of teeth.
The disadvantages are:
- Microprosthetics cannot be used for carious teeth.
- The cost of the procedure is quite high.
When choosing the appropriate type of prosthetics, the dentist aims to solve the patient’s problem in the most acceptable way.
| Situation | Type of prosthetics |
| One or more incisors are destroyed | Dental crown made of ceramics |
| Completely missing dental unit | Bridge prosthesis |
| Chipped edges of the tooth | Microprosthetics (veneers) |
| Chewing teeth destroyed | Dental crown. Recommended materials: metal, metal ceramics |
Orthopedic inlays In-lay, On-lay, Over-lay
In case of minor damage to the chewing teeth, in order to maximize the preservation of the tissues of the natural teeth, not full crowns, but inlays are installed. This procedure also belongs to the group of services for dental prosthetics with fixed dentures, but is more often called microprosthetics and is used when a tooth is destroyed by 25-65%. Essentially, these are fillings made with great precision and durability.
Ceramic inlays have optimal physical and aesthetic properties. First, the inlay is modeled from wax, its color and manufacturing technology are selected, then the inlay is cast according to the wax model. Next comes its fitting, turning, fixing and polishing. Dental orthopedic inlays are fixed in the cavity using special glue. According to the manufacturing ideology, they resemble veneers; in fact, these are a kind of “veneers” for chewing teeth.
One of the modern and patient-friendly technologies in the manufacture of ceramic crowns, inlays and veneers is the CEREC technology. Chairside Economical Restorations of Esthetic Ceramic - economical restoration with aesthetic ceramics at the patient's chair. Directly in the dentist’s chair, a digital impression of the patient’s teeth is taken, the scan is processed, the crown is modeled, and it is manufactured. The whole process takes about three hours.
Which prosthesis to choose: removable or fixed?
Knowledge of the advantages and disadvantages of removable and fixed structures will help you choose the optimal type of prosthetics
| Kinds | Advantages | Advantages |
| Fixed structures | High level of reliability | There is a need to grind down adjacent teeth |
| Quick adaptation to the prosthesis and comfortable wearing | Sometimes the mucous membrane rubs when worn, making correction difficult | |
| High aesthetics | While the process of adaptation is underway, changes in diction and taste of food may be observed. | |
| The chewing load is distributed evenly | High cost with good quality material | |
| Easy to care for | When installing metal crowns, a metallic taste in the mouth is possible. | |
| With proper care, a long service life will be ensured. | ||
| Removable structures | Maintenance is simple and easy | Over time, the denture may become dislodged when eating. |
| Low cost | There is a risk of developing stomatitis | |
| The installation procedure is short | In some cases it is necessary to use a fixing paste | |
| Periodontal disease is not an obstacle to installing a prosthesis | When worn, a gag reflex may occur | |
| This type of prosthesis can be manufactured quickly | When worn, the shape of the face may change |
The choice of the type of prosthesis for each patient occurs individually. Dentists recommend paying attention to removable structures for the following problems:
- with complete or partial edentia;
- if there are pathological changes in the periodontium;
- if oral care is not thorough enough;
- if there are terminal defects of the dentition.
- in case of financial difficulties.
Fixed dentures are recommended for choice in the following cases:
- when no more than one or two units are missing in the dentition;
- if there are significant chips in the enamel;
- with pathological abrasion of enamel;
- with yellowed enamel;
- if it is necessary to restore the smile area;
- in the presence of carious teeth.
What recommendations should you follow?
If you experience discomfort and pain after installing a prosthesis, you need to contact the specialist who performed this procedure. It is important to follow these tips:
- If you begin to experience discomfort immediately after installation, then you need to wait at least five hours before contacting a specialist again. This is necessary to accurately determine the areas where pain occurs.
- There is no need to try to fix something yourself, redo the design, etc. Your actions will lead to deformation of the new prosthesis and make its further use impossible.
- If ulcers or severe inflammation appear on the mucous membrane, then you don’t have to wait 5 hours and immediately seek help. Do not use any healing creams or other products that can reduce inflammation, but then the picture of the condition will be inaccurate. This will interfere with the proper treatment.
Popular questions about prosthetics
Here are collected popular questions from patients about prosthetics asked on the site forum. Experienced dentists answer.
Which prosthesis to choose: plastic or silicone?
Silicone has a short period of adaptation, is comfortable to wear, and does not rub the gums. Disadvantage of silicone: caring for them is more difficult.
Which type of prosthesis is better: a bridge structure or a suction cup prosthesis?
If there is a problem of missing several dental units in a row, the optimal choice would be a bridge. It will ensure uniform distribution of the load on the jaw, will serve for a long time, and is comfortable to use.
Which prosthesis to choose: plastic or nylon?
It all depends on which dental units need dentures. For chewing teeth, acrylic plastic is more suitable as the most durable and comfortable material to wear. Nylon dentures are suitable for premolars and incisors.
Which prosthesis design should I choose from plate-type prostheses?
If a temporary prosthesis is needed, then a removable plate structure is chosen. A fixed prosthesis is chosen in the absence of at least three dental units in a row in the dentition.
Which denture should a person prone to allergies choose: acrylic or nylon?
Nylon has more hypoallergenic properties. In addition, a nylon prosthesis is more flexible and less likely to rub the oral mucosa.
Criterias of choice
Which prosthesis is better to choose? The choice depends on the condition of the teeth in the oral cavity and their number. The dentist offers the patient the best options after studying all the problems and individual characteristics of the jaw.
If all teeth in a row are lost, preference is given to solid removable plates. This option will be the most convenient and affordable. Removable plates are easy to maintain.
The main disadvantage of non-removable structures is their high cost and the possibility of developing allergic reactions to metal alloys. The patient will not be able to clean fixed products on his own, so once every 6 months he will have to contact the dentist for professional cleaning. Home care includes mouth rinsing and regular oral hygiene.
Fixed models are optimal for partial edentia or loss of one unit. It should be noted that they are comfortable to wear and similar to natural dental tissue in terms of aesthetic indicators. The fixation of fixed dentures is much more reliable than that of removable structures, and only high-quality materials are used for their manufacture.