Dental diseases of the teeth are a group of pathologies that affect the enamel, gums, oral cavity, as well as the jaw and chewing muscles. Dentists call them harmless to humans, since the mortality rate is negligible. However, it is these disorders that determine the patient’s overall well-being: they affect self-esteem and an internal sense of comfort.
Experts recommend not to let the situation get worse and to closely monitor the condition of your teeth. Due attention allows you to avoid serious complications, as well as promptly identify defects that need correction.
In this article we examine in detail the most common problems, as well as methods of treating them.
Basic terms in dentistry: names and causes of inflammatory diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
It plays a vital function in the digestion process: it is responsible for grinding food and influencing its subsequent breakdown by enzymes. In addition, there is a huge number of microorganisms that create natural microflora, but are considered opportunistic. This nuance determines the fact that any dental disorders progress extremely quickly.
Among the key factors in the occurrence of dental diseases are:
- poor hygiene;
- mechanical injuries and damage;
- chronic illnesses;
- metabolic disorders and abnormalities;
- the presence of thermal irritants in the body;
- bad environment;
- hereditary predisposition.
The branch of medicine that studies the emergence and development of pathologies is called etiology. It is partially correlated with diagnostic procedures, as it helps in determining pathogenesis.
Nuances of oral care for children over 7 years old and adolescents
At this age, it is necessary to strengthen and improve children’s ability to care for their teeth and oral cavity.
- During adolescence, teeth should be brushed at least 2 times a day, after breakfast and before bed. The toothbrush is placed at an angle of 45 degrees to the surface of the tooth. The head of the toothbrush usually grips 2-3 teeth. Sweeping movements are made from the gums to the cutting edge of the tooth.
- A toothbrush for a schoolchild should be selected according to age; the bristles should be soft with rounded ends.
- The choice of toothpaste depends on the age of the child and the severity of caries. To strengthen the enamel and eliminate caries in the white spot stage, it is possible to use remineralizing agents. You should entrust the selection of suitable toothpaste to your dentist.
- Interdental spaces are the most difficult to reach area for oral hygiene. Dental floss does a job that a toothbrush cannot do. It is designed to remove food fragments and plaque from interdental spaces.
- A balanced diet with a predominance of foods that are good for teeth is encouraged.
- Using mouth rinses to maintain fresh breath serves as an additional means of oral care. A properly selected mouthwash in combination with toothpaste provides maximum care for the child’s teeth and gums, reducing the risk of caries.
- A visit to the dentist for early diagnosis of caries and its complications is necessary twice a year, if there are problems - more often (3-4 times a year).
- Using an irrigator is the only way to remove all plaque and food debris from hard-to-reach places. This is a device that delivers a stream of liquid under pressure to certain areas of the oral cavity. It is she who penetrates hard-to-reach places, removing food debris, bacteria and plaque from there. The kit may include different attachments: for cleaning the tongue, for caring for dentures and braces, and also for cleaning gum pockets [4].
List of sources
- Prevention of dental caries as the most important aspect of preserving the dental health of children, Kuzmina E. M., Lysenkova I. I., Moscow State Medical and Dental University, 2007 // URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/profilaktika-kariesa -zubov-kak-vazhneyshiy-aspekt-sohraneniya-stomatologicheskogo-zdorovya-detey (date of access: 08/08/2020).
- Treatment of dental caries in children and adolescents, Zykeeva S.K., Bilisbaeva M.O., Vestnik KazNGU, 2022 // URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/lechenie-kariesa-zubov-u-detey- i-podrostkov (date of access: 08/09/2020).
- Prevention of dental caries. Methodological manual, G. I. Boltromyuk, Irkutsk: IrGUPS MK ZhT, 2016. —– 42 p. // URL: https://www.irgups.ru/sites/default/files/mkzht/mp_profilaktika_kariesa.pdf (access date: 08/09/2020).
- Recommendations on oral hygiene for children from 6 to 15 years old, Moscow Department of Health // URL: https://mosgorzdrav.ru/ru-RU/health/default/card/102.html (access date: 08/09/2020 G.).
Classification: types of main dental diseases of the teeth
Conventionally, all violations can be divided into two broad categories - those associated with damage to the enamel, and those caused by processes occurring in periodontal tissues. There is another classification principle - based on “carious” affiliation:
- with existing caries lesions;
- non-carious deviations.
The second option is considered the simplest and most convenient to treat if the problem is detected at an early stage. In addition, it is easier for patients to comply with prescriptions, which simplifies the process of rehabilitation measures.
Note that congenital and hereditary pathologies stand apart. They are formed in the womb and are very difficult to correct.
Developmental and eruption disorders
What are the different dangerous dental diseases? Perhaps the most serious problems are caused by congenital or hereditary causes. In these cases, the exacerbation does not begin due to pathogenic bacteria, pathogens or other factors. Such pathologies, as a rule, play a symptomatic role. They signal about malfunctions occurring in the body and force you to take immediate action.
Edentia
A pathological process accompanied by the loss of individual units or complete rows. In extremely severe stages, complete tooth loss occurs. The disease begins to develop during intrauterine development. The main factor is poor heredity or serious illnesses suffered by the mother while carrying the fetus. Due to jaw overload, even healthy teeth can become loose.
Superset
A disease in which excess elements appear in the oral cavity, which have an extremely negative effect on the state of the bite, and provokes additional speech and chewing problems. Dentists recommend removing such units, and the sooner the better.
Fusion and Merger
A rather rare deviation, expressed in the connection of tooth buds with dental cement. The main processes unfold during the formation of elements. Only 1% of people are prone to this disease. As a rule, the disease is diagnosed as part of a temporary dentition. In adulthood, pain is approximately 5-6 times less, so patients often do not suspect the presence of a problem until a visit to the dentist.
Spear-shaped teeth
A disease that affects crowns. It is considered infrequent - it occurs in one case in a thousand. It causes both aesthetic, psychological and physiological inconvenience. Usually it is a consequence of chronic injury to the inner surface of the cheeks, lips, and tongue. In some patients it is accompanied by hypoplasia.
Impacted teeth
An ailment in which the teeth are unable to fully erupt. As medical practice shows, the problem begins to bother people due to the gums being blocked by bone layers. Another reason is premature loss of elements.
Dystopian teeth
A disease in which the incorrect location of units is recorded. The displacement occurs as a result of deviations of the alveolar ridges from the norm. It causes psychological discomfort, disrupts the beauty of a smile, and interferes with the correct functioning of the masticatory muscles.
Macrodentia and microdentia
Congenital hereditary anomalies that determine the specifics of development. Manifested in improper formation and scaling of teeth. They have a negative impact on the bite and the aesthetics of the smile. They are also extremely rare - in every 20 people (in the context of not a single state, but the whole world).
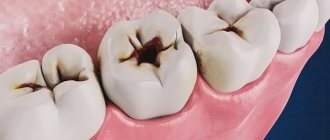
Causes of caries in adolescents
In the absence of proper oral hygiene, plaque accumulates on the surface of the teeth, which provokes the growth of pathogenic bacteria. For their vital activity, plaque bacteria use food carbohydrates, resulting in the formation of organic acids that dissolve the enamel.
In the first stages, dissolution occurs not of the harder surface, but of the subsurface layers of enamel, from where mineral components (primarily calcium and phosphorus compounds) enter the oral cavity. At this stage, a process called focal enamel demineralization is reversible [1]. With the use of preventive remineralizing measures, these damages can be restored.
If oral hygiene remains poor and no preventive measures are taken, then plaque continues to accumulate, acids constantly attack the enamel, the hard tissues of the tooth are destroyed and a cavity is formed, which can only be treated by filling.
The cariogenic effect of food and drinks on teeth in adolescents is determined by:
- frequency of consumption of sugar and other easily digestible carbohydrates;
- the amount of acid contained in the product or drink;
- the length of time the food product remains on the tooth surface;
- ability to form dental plaque [1].
Preventive measures are aimed at maximizing the elimination of all links in the pathogenesis of caries.
This requires careful oral hygiene - removal of dental plaque, limiting the content of easily digestible carbohydrates in food and increasing the resistance (i.e. strengthening) of tooth enamel in children. Kuzmina E. M., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Prevention of Dental Diseases, Moscow State Medical and Dental University[1]
Diseases associated with enamel
What are the possible dental problems due to enamel damage? In the vast majority of cases, they are associated with violations of the structure and integrity of the rows. Usually they are a consequence of internal failures in the body. They are eliminated only at the moment when the factor that provoked their exacerbation disappears.
Fluorosis
A chronic disease that develops during eruption. Accompanied by structural damage, darkening, and loss of dentin. The reason is excess fluoride, which is explained by long-term use of fluoridated water, medications, etc.
Cracks
Deviation, usually localized on the anterior chewing row. It looks like vertically or horizontally located defects of a non-carious nature. Appears due to sudden temperature changes, aggressive chemical exposure, or due to injury.
Turner teeth
An advanced form of local manifestations of hypoplasia. It is fixed long before the first eruptions and has nothing to do with carious lesions. Externally it looks like an enamel layer. Sometimes accompanied by excessive sensitivity.
Hypoplasia
Pathological phenomena of a congenital nature, which is characterized by a complete or partial absence of enamel. If we talk about the external picture, then it is worth noting depigmented or white spots, rather large grooves based on the surface, as well as small depressions. Caused by incorrect structure of hard dental tissues. If left untreated, it is complemented by acute forms of caries.
Wedge-shaped defect
Disadvantages expressed in wedge-shaped cavities in the cervical region of the units. This occurs due to the fact that certain areas of the enamel disappear, resulting in wedge holes. The problem can be registered on any element, but more often on fours and fives.
Dental problems during pregnancy
Any dental problems that arise during pregnancy are a reason to consult a dentist. Even the initial stage of caries indicates the development of an infection in the mouth, and it is potentially dangerous for the developing fetus. In addition, the doctor will recommend safe medications that replenish calcium and other minerals. It has been scientifically proven that a lack of calcium can cause pathologies in a child.
The health and peace of mind of the mother during pregnancy is the key to the health of the baby
Whatever the symptoms, any disease can be cured: there are no unsolvable problems in dentistry, and the painkillers used by doctors will make the treatment comfortable.
Other dental diseases: list of dental diseases with photos
Next, we propose to analyze ailments that may appear as a result of teething or age-related changes.
Grinding
A pathology in which there is a rapid decrease in hard tissue. Provokes thinning of enamel and damage to dentin. It can affect both individual units and full-fledged rows.
Erosion
A process in which a violation of enamel integrity is recorded. Some areas are damaged symmetrically. Main signs: changes in pigment, various cosmetic defects, painful reaction to cold or spicy food.
Pathological resorption
Loss of root tissue caused by chronic diseases, advanced periodontal disease or progressive pulp disease. It can be one-sided or combined. In the absence of rehabilitation and therapeutic therapy, tooth loss occurs.
Deposits and build-ups
They are mineralized residues that form above or below the gums. The main material for formation is food particles, the results of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as components of saliva. They trigger processes that provoke periodontitis.
List of neurotic dental diseases
Stressful periods have a particularly detrimental effect on the state of the body. In addition, as practice shows, the quality of oral hygiene deteriorates sharply. A person simply forgets about cleaning or does not do it thoroughly enough, which increases the risk of developing caries. The parallel use of sedative medications disrupts the production of saliva and causes a feeling of dryness.
Gradually, all this is reflected in psychosomatics - muscle spasms and pain are detected. The most common occurrence is excessive clenching of the jaw.
Bruxism
A disorder characterized by uncontrollable grinding of teeth caused by emotional stress. As a rule, it makes itself felt during sleep. The causes of its appearance include stress, prolonged depression, and malfunctions of the masticatory apparatus.
Grinding
This is not so much a full-fledged disorder as a symptom. Occurs when muscle spasms occur when the patient clenches his jaw tightly. In the vast majority of cases, the person does not even know there is a problem. It is detected during routine dental examinations.
The main dental diseases in humans: what they are and how to treat them
Modern medical practice, implemented in the Dentika dental clinic, actively uses innovative methods of diagnosis and treatment. Almost any disease can be eliminated provided that you seek help in a timely manner, as well as follow all doctor’s prescriptions and prescriptions. Among the measures used by dentists are:
- filling;
- surgical intervention;
- prosthetics;
- implantation;
- aesthetic correction.
In addition, professional hygiene methods are used: bleaching, restoration, etc.
Prevention
Above, we examined in detail what dental diseases are called and what are the main reasons for their occurrence. Now let's talk about preventive measures to avoid serious problems and pathologies.
If you experience any strange sensations in your mouth, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your dentist immediately. He will conduct an initial examination and draw up an individual treatment program. However, in some cases it is possible not to resort to aggressive measures of influence and limit oneself to supportive manipulations.
So, what needs to be done to prevent the development of diseases?
- Do not ignore the symptoms that appear - go to the doctor immediately.
- Do not let the disease worsen, follow all dental recommendations and prescriptions.
- Get professional examinations every six months.
- Maintain hygiene at home, use only high-quality products.
- Don’t forget about professional hygiene - ultrasonic cleaning should be done once every six months to a year.
In addition, it is important to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and give up bad habits.
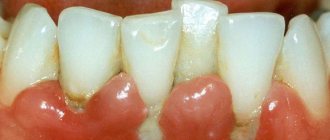
Bleeding gums
Sometimes the cause may be damage during brushing. The recommendation in this case is to temporarily use a brush with soft bristles. However, according to statistics, in 80% of cases bleeding indicates serious illness.
The first of these is gingivitis. It occurs due to insufficient or improper hygiene: dental plaque penetrates the gums, inflammation begins, and bleeding occurs. If gingivitis is not treated, it can develop into a more serious disease - periodontitis.
Bleeding indicates the onset of inflammation in the gums
Characteristic symptoms of periodontitis are inflammation and bleeding of the gums, disruption of the periodontal ligament (that is, teeth begin to loosen), and damage to bone tissue. If the disease is neglected, it will lead to tooth loss.
Let's sum it up
Dentistry studies the etiology, symptoms, and treatment features of the most common dental diseases. There are a huge number of reasons that provoke oral problems. Some of them are easily eliminated, others are subject to only partial correction. However, for both cases the rule is true: the sooner you start working on dental treatment, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. That is why it is important not to let things take their course and undergo regular medical examinations.
The role of occlusal anomalies in the “aging” of teeth
We have already written above that malocclusion is one of the main causes of pathological (accelerated) abrasion of enamel. At the same time, the more the height of the crown parts of the teeth decreases, the more pronounced the anomaly in jaw closure becomes. In fact, the process supports itself, forming a kind of vicious circle.
The situation is aggravated by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the tissues of the temporomandibular joints due to increasing loads during chewing, increased tone of the masticatory muscles, inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, which are injured by improperly positioned teeth.
You can break the vicious circle using various techniques. This can be the manufacture and installation of crowns, restoration of teeth with composite materials, the use of veneers, correction with braces or aligners. None of these techniques can be considered universal. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications, and has advantages and disadvantages that the doctor must take into account when choosing the appropriate method for correcting a person’s defect.
As you can see, adjusting the size and color of teeth is not as difficult as it seems. And the result of such a correction can make a person visually younger by several years without plastic surgery or beauty injections.