From this article you will learn:
- what types of dental bridges are there?
- pitfalls when choosing,
- how much does it cost to put a bridge on teeth – price 2022.
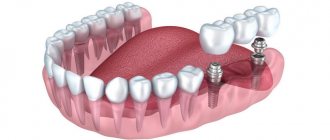
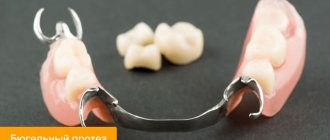
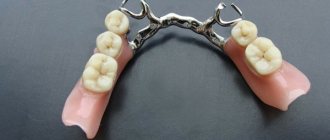
A bridge is a non-removable structure consisting of dental crowns connected into a single unit, which is used to replace missing teeth. Fixation of such a prosthesis can be carried out either on teeth ground for crowns (located on the sides of the dentition defect), or supported by dental implants. As for the length of bridges, they can be from 3 to 14 units long (the number of crowns in the prosthesis).
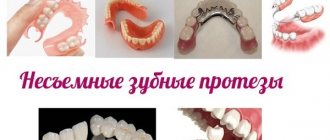
There are many options for bridges. Bridges supported by teeth ground for crowns can be made of metal-ceramics, metal-free ceramics (for example, zirconium dioxide and Emax glass-ceramics), metal-plastic, or only metal. Bridges supported by implants can only be made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. This article will help you choose a dental bridge, taking into account the location of the missing teeth, as well as your requirements for aesthetics and reliability.
Options for fixing bridges –
Bridges with fixation on teeth ground for crowns can only be used for defects in the dentition of no more than 1-2 teeth in a row. If you are missing 3 or more teeth in a row, a regular dental bridge cannot be installed, because... chewing pressure will lead to overload and loosening of the supporting teeth. In this case, either a bridge supported by implants is indicated, or a less preferable option is the manufacture of a removable denture.
Today, there are many options for making bridges. And this is not only the aesthetically acceptable types of prosthetics listed above - such as metal-ceramics or metal-free ceramics. A dental bridge can also be made - 1) from metal-plastic, 2) entirely from metal, 3) from plastic reinforced with fiberglass or metal mesh, 4) from fiberglass and a composite filling material.
How to put a bridge on teeth -
Installing a bridge on teeth is carried out as follows... The teeth located on the sides of the missing one will act as support for the bridge. If only 1 tooth is missing, crowns are usually taken on one tooth on each side of the missing one. If 2 teeth are missing in a row, then a total of at least 3 teeth are taken under the bridge supports (one on one side of the dentition defect, and two on the other).
How to put a bridge on teeth: diagram and photo
Installing a bridge requires grinding down the supporting teeth for crowns, and here it must be taken into account that for different types of artificial crowns the thickness of the preparation will differ. For metal-ceramics, teeth are ground from the chewing surface by 2.0-2.5 mm, from the lateral surfaces by 1.5 mm (Fig. 4). For crowns made of metal-free ceramics - only 1.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively (Fig. 5). Moreover, the more tooth tissue is preserved under the artificial crown, the longer its service life will be.
Schemes for preparing teeth for crowns –
Moreover, please note that in the gingival zone, the tooth crown is ground in such a way that a so-called “ledge” (i.e., a step, Fig. 6) is formed along the entire perimeter of the tooth stump. The service life of the crown will largely depend on the quality of the ledge formation, because poor/inaccurate fit of the crown to the neck of the tooth in the area of the ledge - leads to the gradual entry of bacteria under the crown and the beginning of decay of the tooth tissue. And this happens very often.
Preparation of supporting teeth for prosthetics –
In many cases, teeth under artificial crowns are subject to depulpation, i.e. the nerve will need to be removed. This is due to the fact that deep in the tooth there is a neurovascular bundle (pulp), and the more tissue is ground off when preparing a tooth for a crown, the higher the risk of nerve injury. Accordingly, because Under metal-ceramics, more tooth tissue is ground off - here it is possible to leave mainly only large molars alive (they have a greater thickness of hard tissue around the nerve).
But for ceramic crowns, almost 2 times less tooth tissue is ground off, and in this case, almost all the teeth can be left alive. Keeping your teeth alive is very important because... after removal of the neurovascular bundle, the tooth stops receiving moisture and nutrition from the inside, which leads to an increase in the fragility of the hard tissues of the tooth and reduces its service life. The cost of removing nerves and filling root canals will depend on the number of root canals in the supporting teeth, and on average will be (for 1 tooth) –
- tooth with 1 root canal – from 2500 rubles,
- tooth with 2 channels – from 3800 rubles,
- tooth with 3 channels – from 5,000 rubles.
Dental bridge: before and after photos
Important: if the adjacent teeth from the missing one do not have fillings and are alive, then prosthetics with a bridge and grinding down the adjacent teeth for crowns is actually a very bad idea. The price of a dental bridge of 3 units made of ceramics or good metal-ceramics (taking into account the cost of preparing teeth for prosthetics) is almost always higher - when compared with the cost of installing 1 economy-class implant.
A dental bridge should be done only if the adjacent teeth from the missing one have large fillings (taking up more than 1/2 of the tooth crown in volume), and also if the nerves have been removed from them. Remember that the service life of the best crowns will be, at best, no more than 10-15 years, and what will happen to the supporting teeth after this time, and whether they can be re-used with prosthetics is still a big question. Your own living teeth (as opposed to artificial crowns) can last you much longer.
Why does the bridge have this name?
What it is becomes clear if you clarify the meaning of the word “adhesion”. Adhesion (from the Latin adhaesio) is the ability of dissimilar materials to stick to each other. Thus, a bridge of this type is not attached to ground support units using crowns, but is “glued” to the teeth adjacent to the defect. It is called Maryland, or even Manhattan, because of the shape of the structure - an artificial tooth-base and “wing” plates extending from it on both sides.
%akc61%
Its difference from a conventional bridge is that it is fixed by means of these thin plates, which are located on the side of the tongue and are attached to the inside of two supporting elements. This attachment is almost invisible in the oral cavity.
Read more about classic dental bridges in the material “Review of bridge models: for what cases are they suitable, how much do they cost and how long will they last?”
Dental bridge: what material is best to choose from?
If we are talking about prosthetics of the front teeth, then according to statistics, most patients are dissatisfied with the bridges made for them.
As we said above, it is very difficult to make artificial crowns similar in color and transparency to neighboring teeth and, of course, good aesthetics today can be achieved mainly only by using metal-free ceramics - 1) Emax glass ceramics, 2) zirconium dioxide. But we also don’t forget about metal-ceramics, although there is one problem with it when prosthetizing the front teeth. Modern metal-ceramics in some cases can look almost as aesthetically pleasing as metal-free ceramics, but for this it is necessary - 1) to use expensive ceramic masses, 2) metal-ceramics must be made with the so-called “shoulder mass”. But this raises the cost of a metal-ceramic bridge to 20,000 rubles (for 1 Unit/crown). And this is practically the cost of 1 unit of pressed ceramics “Emax”.
Below we will talk in detail about which bridge is optimal for the front teeth (in terms of materials and budget). But with prosthetics with bridges in the area of chewing teeth, the situation is much easier, because here functionality is more important than aesthetics. And in this case, we have a number of optimal solutions, including more affordable ones, although the gold standard for chewing teeth is now expensive bridges made of monolithic zirconium dioxide.
Below we compare the following types of bridges -
- bridges made of metal-free ceramics (zirconium dioxide, E.max),
- metal-ceramic dental bridges,
- solid bridge made of cobalt-chrome alloy,
- adhesive bridge prosthesis.
Types of bridge structures and materials used
There are quite a few types of fastenings and materials for adhesive bridge prosthetics. The most commonly used materials for these restorations are base metals, composites, fiberglass2, ceramics and plastics. There are several types of adhesive bridges:
- fiberglass or elongated metal plate - a beam, the middle of which is a crown of composite material, and the edges are strips glued to the supports. At the same time, the plates also have small holes into which dental glue penetrates for better adhesion to the enamel,
- a fiberglass pin and two plates that are connected with a special tape. An aesthetic dental crown is fixed on top, which can be made from various lightweight materials,
- a fiberglass or ceramic bridge with inlays, to secure which the cavities of neighboring teeth formed after caries treatment are used. The “wings” of the bridge are glued not to the inside of the teeth, but from above; they are placed in the cavity of the supports and correspond to their anatomical shape. Such a prosthesis is similar to restorative dental inlays combined with each other with a crown in the center, replacing the missing element.
In each situation, the doctor individually selects the design that will be most reliable for the patient. This largely depends on the condition of the adjacent teeth and the location of the unit.
Zirconium dioxide dental bridges –
Zirconium dioxide ceramic bridges are manufactured using CAD/CAM technology, which involves milling bridges from pressed zirconium dioxide blocks on a computer-controlled machine. Sintered zirconium dioxide has a strength comparable to metal (more than 900 MPa). Thanks to this, zirconium dental bridges can be made of any length - even horseshoe-shaped bridges with a length of 12-14 teeth (which cannot be made from any other types of metal-free ceramics).
We have already said above that a zirconium bridge is the gold standard for prosthetics of the chewing group of teeth. But there are questions about the aesthetics of zirconium dioxide bridges, and when prosthetizing the front teeth, you may encounter a big problem (the bridge will stand out against the background of the patient’s own teeth). The fact is that there are 2 types of bridges and crowns made of zirconium dioxide, and they differ from each other not only in aesthetics, but also in the risk of ceramic chips.
1) “Traditional” zirconia bridges –
For such bridges, only the internal frame will be made of zirconium dioxide, which is lined with ceramic mass, or rather porcelain, on the outside (Fig. 14). And this is due to the fact that most dental laboratories use cheap versions of zirconium dioxide blocks. This zirconium dioxide has a bright white color, plus it is completely opaque, and as a result, such a material does not allow achieving a certain degree of translucency, which is characteristic of natural tooth enamel.
Crowns and bridges made from such material will have an unnatural milky white color, plus there will be no translucency characteristic of natural teeth. Therefore, in order to improve aesthetics, only the internal frame is milled from such zirconium dioxide, which gives strength to the structure, and then the dental technician, by applying layers of porcelain, gives the crowns of the bridge the final shape and color. But even despite this, the aesthetics of such crowns and bridges will be far from perfect.
Plus, this manufacturing method has another disadvantage. We have already said above that zirconium dioxide has the strength of a metal (from 900 MPa), however, the layer of porcelain mass on the surface of the zirconium frame has a strength of only 80-120 MPa. This leads to chips of the ceramic mass (according to statistics, within 6 years they occur in approximately 10% of patients). The chips are repairable, but the reliability of such repairs leaves much to be desired.
Conclusions : we do not recommend using zirconium dioxide bridges (made with a surface layer of porcelain) for prosthetics of chewing teeth, because in this case there will be a high risk of chipping. When replacing front teeth with prosthetics, this option is not very successful, because the crowns of the bridge will still have an unnatural milky tint, standing out against the background of your own teeth (Fig. 15-16). Plus, there is still a risk of chipping the porcelain lining.
The aesthetics of such structures are
Such milky-white crowns and bridges made of zirconium dioxide will look acceptable only in one case - if you are going to simultaneously prosthetize all the teeth that fall into the smile line on both the upper and lower jaws (i.e. at least the fifth teeth inclusive ). Otherwise, such a bridge will be very noticeable against the background of your own teeth.
2) Zirconium bridges using “Multi-layer” technology –
But the problem of poor aesthetics and chipping was solved by the advent of the next generation of zirconium dioxide blocks/discs. Currently, a number of manufacturers produce zirconium dioxide with “Multi-layer” technology. Discs made from such zirconium dioxide are “pre-colored”, i.e. they have a color gradient that is characteristic of the enamel of real teeth. The second difference: due to the stabilization of zirconium dioxide by yttrium, such blocks will have varying degrees of “transparency”, i.e. translucency.
As a result, crowns and bridges made from such material will have a gradient of color and transparency, which will vary from the neck of the tooth to the incisal edge (the cusps of the chewing teeth). Those. The closer to the incisal edge, the lighter and more transparent the zirconium dioxide becomes. But multi-layer technology can provide more than just good aesthetics! In this case, there is no need to use surface layers of porcelain, and therefore crowns and bridges will be made of monolithic zirconia.
Clinical case No. 1 – below you can see the aesthetics of newly made single crowns and bridges made of zirconium dioxide, made using the “Multi-layer” technology (they are not yet fixed in the oral cavity, but are on a plaster model of the patient’s teeth). The bridge prosthesis in the projection of 14-15-16 teeth is made with artificial pink gum, and the remaining units are made in the form of single zirconium crowns. With these photos we want to show a smooth transition of color and transparency.
Therefore, if you want to get decent aesthetics, then when you go to a dental clinic, you need to find out whether they use “Multi-layer” zirconium dioxide. High-quality discs using this technology: these are 2 variants of Katana® discs - UTML or STML (Japan), as well as Prettau® Anterior (Germany). The cost of one such disk starts from 16,500 rubles. For example, a disc made of ordinary white opaque zirconium dioxide costs only 4,500 rubles, and therefore many clinics, in an attempt to save on costs, work with cheap, outdated materials.
Conclusions: if you need a bridge prosthesis on implants, or a bridge prosthesis in the area of chewing teeth, then a bridge made of monolithic zirconium dioxide using the Multi-layer technology is not the cheapest, but the best option. When it comes to front teeth prosthetics, if you want to get the best aesthetics possible, there are limitations. For example, if you are planning to make a bridge or crowns on all front teeth (falling into the smile line), then Multi-layer zirconium dioxide will allow you to get the ideal aesthetic result.
However, if you need a bridge for only 3-4 teeth, then even with the help of the Multi-Layer technology, a dental technician is unlikely to be able to make such a structure absolutely indistinguishable from neighboring natural teeth. In this case, to achieve ideal aesthetics, it is worth choosing a bridge not from zirconium dioxide, but from pressed Emax ceramics. This is due to the fact that when working with Emax, the dental technician will have significantly more color options in his arsenal (than when working with any option of zirconium dioxide), which will make the bridge as similar as possible to the neighboring teeth.
Cost – for zirconium bridges, the price for 2022 in Moscow will be on average from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles (for 1 Unit/crown). Thus, the cost of a 3-unit bridge will be at least 90,000 rubles. However, in a number of clinics you may well be offered a price of less than 30,000 per unit, but in this case the bridge will clearly not be “multi-layer” or monolithic.
Fixed dentures - features and advantages
Fixed dentures are considered the most effective and inexpensive solution to restore dentition.
The most common causes of tooth decay and subsequent loss are:
- abundant carious lesions;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- dental cysts, etc.
As a result of these dental diseases, tooth crowns and roots are destroyed, teeth fall out on their own, or surgical intervention is required to remove dead hard tissues and roots. For restoration, the dentist recommends permanent dental prosthetics, the basis of which is a bridge and ceramic crowns of the latest generation.
Advantages of fixed dentures:
- Aesthetics. Fixed dentures are difficult to distinguish from your teeth. With proper selection and proper installation, the design looks harmonious in the oral cavity, and the person smiles boldly.
- Comfort. A person quickly gets used to a fixed denture and does not feel discomfort afterwards.
- There is no need to build up bone for high-quality implementation of a fixed denture. When using modern artificial roots, there is often no need to build up bone tissue. This simplifies the entire dental procedure and makes it much more affordable.
- Fast payback. The investment in fixed dentures always pays off in dental health, attractive visual effect and durability.
E.max ceramic dental bridge –
If you are planning prosthetics on your front teeth, then a dental bridge made from IPS E.max ceramics is the best option in terms of aesthetics (even compared to bridges made from Multi-layer zirconium dioxide).
The “Emax” material refers to glass ceramics, because this material consists of 70% lithium disilicate crystals. Due to the fact that the E.max glass matrix is as similar in structure and transparency as possible to natural tooth enamel, crowns, veneers and bridges made from this material can be made completely invisible against the background of neighboring teeth. Clinical case No. 1 – before and after photos
Clinical case No. 2 – before and after photos
E.max glass ceramics is practically the only material that allows achieving good aesthetics in patients with a high level of transparency of tooth enamel (if the transparency coefficient is low, then good aesthetics can be achieved with zirconium dioxide). E.max crowns require less grinding of the supporting teeth, which increases their service life. And besides, the use of this material practically eliminates the occurrence of ceramic chips.
Important points - E.max ceramics are available in several versions, but for the manufacture of bridges it is best to use “IPS E.max PRESS”. Bridges are made from this material by pressing under conditions of very high temperature and pressure, making the finished structure very strong (about 400 MPa). However, there are several limitations for E.max bridges...
Firstly, you can make bridges from E.max with a length of no more than 3 units, i.e. They can only restore a single missing tooth. Secondly, their safety margin is sufficient to restore mainly only the anterior group of teeth (the distant abutment tooth should be no further than the 5th tooth inclusive). Therefore, if you need to restore the chewing group of teeth, then a priori the choice falls on bridges made of zirconium dioxide or metal ceramics.
Conclusion: The E.max glass-ceramic bridge is the best option if you require a 3-unit bridge in the anterior area and if you have the highest esthetic requirements. Considering that 1 crown made of E.max PRESS material will cost in Moscow in 2022 - from 26,000 rubles, then the cost of a bridge of 3 units will already be about 72,000 rubles. In the regions, the price for 1 unit may be slightly less (from 20,000 rubles). And don’t be confused by the fact that E.max is cheaper than bridges made of zirconium dioxide - it’s just that very expensive equipment is used in the manufacture of the latter, which affects the cost.
Indications for use of the Maryland bridge
A bridge structure of this type is often used only to restore one tooth in the frontal area, less often – two in a row. This is explained by the fragility of the structure, since it is not intended for heavy chewing loads1. The Maryland bridge in dentistry is used in the following cases:
- restoration of one or two missing teeth in a row without grinding adjacent ones,
- temporary prosthetics of 1–2 units for the period of implant healing or if it is impossible to immediately begin permanent bridge prosthetics,
- the need for simultaneous defect replacement and splinting due to periodontal diseases.
Read about the methods that are suitable for replacing lost front teeth in the material “What dentures can be placed in the smile area - the most complete list of solutions and their features.”
Metal-ceramic bridges –
Metal ceramics have a cast metal frame inside (Fig. 21), lined with porcelain on the outside. Unlike ceramics, metal is completely opaque, and therefore only opaque porcelain can be used to disguise it. The latter leads to the fact that metal-ceramic bridges and crowns will lack the translucency of natural tooth enamel, and their aesthetics will not be as good as that of metal-free ceramics.
The problem with aesthetics when using metal-ceramic prosthetics is somewhat reduced if you are going to prosthetize all the teeth that fall into the smile line at once (for example, at least from canine to canine). In this case, when talking, your interlocutors will see only the same “teeth”. But the problem with aesthetics is especially noticeable if a metal-ceramic bridge is installed on only 3-4 teeth, and in this case the crowns will stand out noticeably against the background of neighboring natural teeth.
Clinical case of metal-ceramic prosthetics –
The cost of 1 unit of metal ceramics varies on average from 12,000 to 18,000 rubles. Cheap metal ceramics costing from 8,000 to 10,000 rubles per unit also exist, but in this case the simplest ceramic mass (most likely of Belarusian or Russian production) will definitely be used, which simply lacks aesthetics. For 12,000 rubles per unit, you can already get bridges or crowns from Duceram ceramic mass (Germany), which at the very least provides a satisfactory level of aesthetics.
If more expensive ceramic masses are used, for example, it could be “Ivoclar” (Liechtenstein), then the cost of just 1 crown will increase to 15,000 rubles. The use of even higher quality ceramics “Noritake” (Japan) or “Vita” (Germany) will increase the cost to 18,000 rubles per unit, and therefore, if we are talking about a bridge of 3 units, then you need to multiply this amount by three. The amount of 18,000 rubles per 1 unit for good metal ceramics is not the maximum, and here’s why...
If we are talking about dental bridge prosthetics for the front teeth, then expensive ceramic mass alone is no longer enough to achieve good aesthetics. The fact is that with standard metal-ceramics, the lower edge of the metal frame (which is located just below the gum level) is not insulated with ceramics, and therefore it will always be in contact with the gum. Firstly, this leads to the gradual development of cyanosis of the gums, and secondly, to a gradual lowering of the gum level and exposure of the dark metal edge of the metal-ceramic crowns of the bridge (Fig. 24-25).
Therefore, if you are going to make a bridge on chewing teeth, all this may not be important, but in the area of the front teeth these problems will be critical. Only a type of metal-ceramic with the so-called “shoulder mass” can avoid the appearance of cyanosis, but the cost of 1 Unit of a bridge immediately increases by another 5,000 rubles (for the high complexity of manufacturing). So it turns out that for high-quality prosthetics with a bridge prosthesis for the front teeth, a bridge made of Emax metal-free ceramics can cost less than a good metal-ceramic one.
What does “metal-ceramic with shoulder mass” mean – as we said above – using a more expensive ceramic mass will not save you from the appearance of cyanosis and gum recession. For the latter, there are metal-ceramic bridges/crowns with the so-called “shoulder mass”, in which the lower edge of the metal frame is additionally insulated with ceramic mass. Ceramic insulation can be done either along the entire perimeter of the edge of the metal frame, or only on the front side of the crown (Fig. 27).
Conventional metal-ceramics and “with shoulder mass” –
As we said above, the cost of 1 unit of metal ceramics with shoulder mass will be an additional 5,000 rubles (for 1 unit). For a 3-unit bridge with shoulder mass, 2 crowns must be made, i.e. only those that will be on the supporting teeth. Accordingly, if we want a metal-ceramic bridge made of high-quality ceramics, then it will cost at least 45,000 rubles (and an additional + 10,000 rubles to this cost will also be used to create shoulder mass for crowns on abutment teeth). Total 55,000 rubles.
Important: it is worth considering that when calculating the cost of a dental bridge made of metal-ceramics, there are some other cost items. For example, the cost of temporary crowns made of plastic will be another 2,000 rubles per unit. Secondly, the cost of preparing supporting teeth for prosthetics, which can amount to another 2,500 to 8,000 rubles per tooth (depending on the number of root canals). As we see, to restore 1 missing front tooth it will be cheaper to install an economy-class implant, which even with a ceramic crown will cost you about 50,000 rubles.
A number of significant disadvantages of adhesive bridges
Despite the large list of advantages, the Maryland Bridge also has disadvantages. The disadvantages are as follows:
- relative fragility of the prosthesis: it is for this reason that dentures are not installed in the chewing zone and do not replace more than two units with them. This design is not designed for high loads, it can come off, so it is recommended to handle the prosthesis as carefully as possible, try not to bite or chew food at the site where the prosthesis is installed,
- fragility of the structure: it is used for temporary prosthetics, since the service life of even the most durable structures is no more than 3–4 years,
- incomplete restoration of a missing tooth: the prosthesis serves rather to eliminate a cosmetic defect, but does not restore functionality, that is, it cannot be fully chewed,
- complication of hygiene in the places where the prosthesis is attached and in the interdental spaces, which increases the risk of developing caries.
Despite the restoration of the row under the adhesive prosthesis, bone atrophy continues to progress at the site of the lost tooth. The lack of chewing load reduces tissue nutrition and accelerates bone loss, which over time leads to various negative consequences.
Solid-cast bridges –
A solid-cast bridge is the most cost-effective type of prosthetics.
Accordingly, its main disadvantage will be unsatisfactory aesthetics (polished metal). Therefore, solid bridges are used mainly only in the area of chewing teeth, i.e. outside the smile line. The cost of 1 unit of such a bridge will be from 5,000 to 6,000 rubles, and thus a bridge of 3 units will cost you approximately 15,000 rubles. Solid dental bridge: photo
The advantage of solid-cast bridges is that the supporting teeth are ground down for crowns to a slightly lesser extent than for metal-ceramics. Of course, this guarantees greater preservation of the hard tooth tissues under the crown, as well as a longer service life. In some cases, at the request of the patient, plastic overlays can be made on the front side of the crowns on one or all of the crowns of a solid-cast bridge. This will certainly improve the aesthetics, but it is not very reliable, and in addition, the plastic will gradually lose its aesthetic qualities.
The advantages of this type of prosthetics
Among the advantages, the following qualities of such structures have been identified:
- the adjacent supporting units, as well as the gums, are not injured when fixing the prosthesis. And this is perhaps the main advantage of adhesive prosthetics, which attracts many patients,
- fast recovery,
- there is no need for anesthesia when preparing for prosthetics,
- low cost of treatment,
- the ability to replace the prosthesis without damaging the supporting teeth,
- are non-removable, which distinguishes them favorably from immediate prostheses (“butterflies”), used as temporary structures,
- high aesthetics: when using ceramics or composite materials, crowns look natural, and the shade of the prosthesis can be precisely selected.
You can evaluate the advantages of various types of fixed prosthetics in the article on our website “Comparison of fixed prostheses.”
Combined bridges –
Because Both metal-ceramic and solid-cast bridges are made on a cast metal frame - different types of crowns can be combined in one bridge. For example, you need to make a bridge of 3 units supported by teeth 5-7 (Fig. 29). In this case, the nearest 1-2 crowns that fall into the smile line can be made with ceramic veneer (i.e., metal-ceramic), and the distant crowns that do not fall into the smile line can be made solid.
This will somewhat reduce the cost of a dental bridge, plus for solid crowns, the teeth are ground to a slightly lesser extent and, accordingly, in this case, more tooth tissue will be preserved under the crown. If you are not bothered by the fact that metal may be visible when you open your mouth wide, this is a completely worthy prosthetic option.
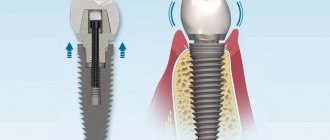
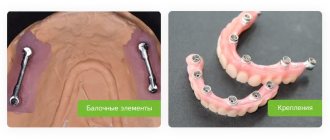
Fixed denture on titanium implants
Fixed dentures on dental implants are one of the most common systems for restoring lost teeth.
The main advantages of such solutions:
- titanium implants installed in deep bone layers preserve hard tissue around them;
- healthy supporting teeth do not require preliminary grinding and root removal;
- the average shelf life of such dentures on artificial roots is twenty years;
- the method of restoring teeth with fixed dentures is considered the most gentle and natural;
- ready-made solution for restoring edentulous teeth;
- attractive dental aesthetics.
The only caveat when installing a fixed dental structure on implants is the considerable cost of the solution.
If we compare all the existing options for fixed dental prosthetics, it is the fixed prosthesis on a dental implant that is the best solution - in terms of quality, aesthetics, reliability and durability of the teeth.
Adhesive bridge prosthesis –
An adhesive bridge is a temporary structure with a service life of up to 2 years. It is made of fiberglass tape (it stretches from one supporting tooth to another, serving as a stiffening rib), and conventional composite filling material (Fig. 31-34). Such designs are characterized by low reliability, but at the same time they can be quite aesthetic (although their aesthetics will not last too long).
Stages of manufacturing an adhesive prosthesis –
Adhesive bridges: reviews
- The advantages of adhesive dentures include: firstly, rapid production directly in the patient’s mouth in an average of 1.5 hours, and secondly, lower cost (compared to other types of bridges). The cost of an adhesive bridge will be from 13,000 rubles.
Disadvantages of adhesive prostheses –
- can be made only with a single missing tooth,
- Canines and molars (3,6,7 teeth) cannot be restored,
- low reliability (service life up to 2 years),
- To fix the fiberglass beam, it is necessary to create platforms (ledges) on adjacent teeth, thus compromising the integrity of the teeth.
Steps to install an adhesive bridge
The installation of a Maryland bridge can be carried out in one or several visits to a specialist. This is largely influenced by the condition of the supporting teeth on which the prosthesis will be fixed, as well as the features of the chosen design. The stages of manufacturing the structure will depend on the chosen technique: it is possible to manufacture the prosthesis both in the laboratory and clinically, that is, directly in the patient’s mouth.
The following main stages of adhesive-bridge prosthetics can be distinguished:
- treatment of supporting teeth: if necessary, cleaning, caries treatment, grinding or surface treatment of enamel is carried out. Minimal sanding is necessary to ensure adhesion of surfaces,
- taking impressions: used when the bridge is made in the laboratory, and not directly in the mouth during the appointment,
- production of the prosthesis: with the indirect method, it is carried out in the laboratory, especially when made from materials such as plastic and ceramics, the processing of which is impossible in the oral cavity. With the direct method, that is, directly in the oral cavity, the prosthesis is made by a doctor in one visit. The optimal material for the direct method is a light-curing composite,
- fixation of dentures: the structure is fixed using special dental cement.
Attending doctors at the Elident clinic
Mlodik Boris Naumovich
Dental surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist
Clinical experience : 26 years
Vakhrushev Alexander Viktorovich
Dental surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist
Clinical experience : 25 years
Preparation of supporting units for installation of prostheses
In most cases, natural crowns, on which a permanent bridge will be fixed in the future, are subject to pulp removal. This is due to the high probability of injury to the neurovascular bundle during turning. However, when a metal-ceramic structure is put on, there is no need to remove the nerve in large dental units, since they have denser walls.
You can also keep your natural teeth alive if you install a ceramic bridge. The ability to preserve the nerve is considered necessary, since this has a positive effect on the strength and durability of natural units.
When it is planned to install a bridge, the cost of depulpation and subsequent filling is determined by the number of root canals, and can range from 2,500 to 5,000 rubles, respectively.
If, after the loss of a tooth, healthy, living crowns remain nearby, the possibility of grinding them down for a future bridge is considered undesirable. The same goes for nearby units that previously had small seals installed. In such situations, it is advisable to install one implant: its cost will cost you less than installing a bridge.
It is recommended to install a bridge in Moscow only when the teeth located on the border with the missing one were previously filled by 50% or were subjected to depulpation.
The use of inlays for attaching prostheses
To fix bridges, it is allowed to use special inlays made of ceramic or metal material. In this case, there is no need for total grinding of the supporting crowns: it is enough to make a small ledge on the chewing side of the dental unit.
The installation of such products is recommended only to reproduce 1 lost unit in the presence of healthy nearby crowns. In addition, due to the insufficient stability of structures on inlays, sometimes it is necessary to fix the crown at one edge.
Stages of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown
The traditional manufacturing process of metal-ceramic crowns involves the following steps:
- Determination of tooth color, characteristic features, structure of enamel, dentin, determination of the transparent layer, the presence of individual characteristics (enamel cracks, staining of fissures in the chewing group of teeth, the presence of chalky stains, enamel abrasion, etc.).
- Next comes the removal of the destroyed dental tissue and the process of preparation (grinding) of the tooth, which takes a very long time. In order to ensure that after installing a metal-ceramic crown there is no effect of the so-called “blue” gum or compression of the gingival dental papilla by the crown, the doctor must very carefully grind the tooth to create a gingival ledge (the angle on which the crown will rest). Only with this method will the work be successful.
- An impression is then taken and sent to the laboratory.
During the production of permanent metal-ceramic structures, a temporary crown is placed, which hides the defect and eliminates psychological discomfort.
- After the metal frame is made, ceramic masses are applied to it layer by layer, recreating natural teeth as accurately as possible. Next comes the artistic design of the metal-ceramic crown, taking into account the individual characteristics of the tooth.
- Then follows the fitting of an almost finished metal-ceramic crown (a metal frame with ceramics already applied, but not glazed). At this stage, the color of the crown is finally determined, because You can still make changes.
Finally, at the last visit, the permanent crown is placed. The entire process of manufacturing a metal-ceramic crown takes on average up to 10 working days.
Metal-ceramic products: characteristic features
A metal-ceramic bridge is a complex dental structure that includes a metal base and an outer ceramic layer. In this case, the prosthesis frame can be made of cobalt-nickel or cobalt-chrome alloy, and can also contain precious metals.
Currently, designs based on the use of gold alloys are especially in demand. This allows you to get the most natural shade of the crowns and use them to restore lost units in the frontal zone. In this case, the frame can have a thickness of approximately 0.5 mm.
Advantages of metal-ceramic prostheses:
- Allowed for use in the frontal zone;
- The metal bridge has a solid base, which contributes to the high reliability of the product and ensures a long service life;
- The ceramic layer is resistant to abrasion;
- Can be repaired if cracks or chips occur.
It should be remembered that before fixing a metal-ceramic bridge, the supporting crowns are subjected to pulp removal and turning.
Free consultation
Our specialists will conduct a free consultation and select the best treatment option for you.
Sign up now! Online registration
+7 (495) 649-41-19
Content
1 Indications for bridges and limitations for their use
2 Features of installing a fixed bridge 2.1 Method of grinding dental units for a future prosthesis
2.2 Preparation of supporting units for installation of prostheses
3 Bridges, before and after photos:
4 Which bridge structures should be preferred?
5 Solid structures
6 Metal-ceramic products: characteristic features
7 Ceramic fixed bridge: features 7.1 Some “cons” of zirconium bridges
8 What are the features of adhesive bridges?
9 Use of inlays for fastening dentures
10 Bridge prosthesis on implants
11 Basic rules of care
12 Price for a bridge
“Dental bridges” - indications and contraindications
Prosthetic bridges are used in the following situations:
- long-term defect in the dentition (up to 3 teeth), caused by disease or injury;
- missing tooth;
- the need for prosthetics for several adjacent teeth;
- replacement of an already installed prosthesis.
A bridge cannot always be installed; contraindications for it are:
- chronic periodontitis and other inflammatory processes in the mouth;
- bruxism;
- malocclusion;
- increased tooth wear;
- severe osteo-jaw pathology.
Bridges are not recommended for installation in the absence of two adjacent premolars (small molars) and in the absence of 4 incisors at once.
Important! Even if you suddenly discover one of the contraindications, don’t be upset and feel free to contact us. Most contraindications are relative - after preliminary treatment, prosthetic bridges are quite possible. In any situation, the Dent Academy will select the most effective treatment for the most complex dental diseases.