When a person starts to have a toothache, he consults a doctor with the sole purpose of stopping the pain. It is not for nothing that toothache is recognized as the most difficult to bear. No stoic can withstand it for a long time. If a tooth is treated, it will no longer cause pain. Following this logic, the patient goes to the dentist.
Sealing
The specialist does what he's supposed to do. Cleans the canals, removes the source of infection or necrotic fragments of tooth tissue, sanitizes the oral cavity, and places a filling. All this is unpleasant, painful, and does not bring pleasure. But now the treatment ends, the doctor did everything to make the tooth stop hurting. However, after some time, the tooth begins to hurt again under the new filling that was installed according to the rules. Why does this happen, and what to do in this case.
Tooth hurts after root canal filling
Why does it hurt?
The first thing you need to understand is the impact on the enamel coating of a tooth or its underlying tissue (dentin) with a drill drill or any instrument penetrating into the tissue, and even more so, cleaning the canals is a real surgical intervention. In the process of working with a drill, the dental nerves are usually affected by an anesthetic injection; when it stops its effect, the pain becomes obvious and can be felt quite strongly for a short time. The surgical wound heals, the body recovers, this should take a certain period of time, such pain after filling the canal is considered normal.
Toothache after root canal filling is acceptable
How to understand at what point a deviation from the norm occurs, and when you need to seek help or take independent auxiliary measures?
By the way. There are certain criteria by which they calculate whether it is normal or deviation. With a natural pain reaction, it is enough to wait for some time. If something goes wrong and the pain continues and even intensifies, the algorithm of actions will be different.
Criteria for determining pain norm.
- The nature and level (depth) of the treatment performed.
- The presence of complications after treatment, or non-standard reactions of the patient’s body.
- Duration of pain.
- Dynamics of pain.
- Nature of pain.
Pain may indicate complications after surgery
What causes pain? They are divided into objective and subjective. The second category includes typical medical errors, errors in diagnosis, incorrect treatment or insufficiently high technology of the clinic’s equipment.
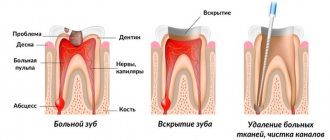
Caries or pulpitis
Deep caries
Unfortunately, very often, even in expensive dental clinics, it happens that the doctor incorrectly identifies the patient’s problem. For example, deep caries is confused with chronic pulpitis. Yes, they are similar and have almost identical manifestation. But if caries is suspected, especially when the doctor, with the best of intentions, seeks to avoid root canal treatment, this mistake can cost the patient not only a long period of pain, but also tooth loss. If you apply a filling for any form of pulpitis or periodonitis without cleaning and filling the canal, the tooth will hurt deep down until the inflammatory process reaches its culmination stage and tooth extraction is required. Thus, paradoxically, the first cause of pain may be that the doctor did not fill the canals.
Pulpitis
Burn pain
It would seem like getting a burn in the dentist's office? Overheating and tooth burns are a problem mainly in small budget clinics that have outdated equipment that does not provide for the use of water-air cooling.
During treatment, tooth enamel may burn
If the fragment of tooth tissue processed by the drill is not cooled enough, it overheats and burns the pulp tissue. As a result, a necrotic area is formed, which in the future will cause pain under the filling. The killed tissue will decompose, giving inflammation of the pulp, periodontitis, pulpitis and further, as in the previous paragraph.
- Tooth hurts under temporary filling
Overbite
Few patients take this source of pain seriously. After filling the canal, a closing filling is applied to the dentin. At the moment of biting, a tooth from the opposite row presses on the filling. If the bite level is normal, the pressure is distributed over the entire dentition. But if it is too high, the entire jaw puts pressure on the filled tooth.
Overbite filling
By the way. Patients, and even doctors, tend to believe that a protruding filling will “wear in” over time. This is a big misconception; modern filling materials are durable. It may take years to “grind in.” And at this time, each bite will not only cause pain in the tooth, but also injure the peri-root tissue. As a result, traumatic periodontitis will develop.
The specialist must carefully monitor the height of the bite, since the patient himself, by feeling, cannot accurately determine whether it is too high. The treatment takes place under anesthesia. There is numbness in the mouth. Feelings are blurry and unclear.
To check the bite filling, use special paper, similar to a copy.
Important! If, after filling, the tooth hurts when pressed, you need to go to the dentist and grind the filling down to a comfortable level.
Shrinkage of the filling
Another reason that most patients are not even aware of is polymerization stress. Happens when installing light-curing composites (so-called light fillings). They subsequently shrink and begin to hurt. This happens because a special lamp is used to harden the filling material. After its exposure, the composite material decreases in volume. Of course, this is not at all the shrinkage that occurs if you wash woolen fabric in boiling water, but even a slight decrease in the volume of the filling causes stress on the surrounding tooth walls. If the filling is multi-layered, the tension is greater, the stress is greater. A light filling may hurt for several weeks, or may cause discomfort for a long time.
Close-up view of light filling
Preparation stages:
- Treatment of carious cavities is a necessary procedure in order to avoid infection getting to the root. This also allows access to estuaries.
- Pulp removal - this procedure can be carried out using several methods, most often it requires two visits. At the first stage, the pulp is necrosis; at the second, it is directly removed.
- Determining the length is a particularly important stage, since each tooth in an individual patient has its own individual characteristics, both length and relief.
- Processing with mechanical instruments - at this stage, the channels are passed through to expand them. This is the main step towards quality filling. A canal that is not completed to its full length can never be adequately healed.
- The final stage is filling with gutta-percha.
It is important to take into account that the last stage directly depends on the previous ones, and if all standards are not followed, it cannot be carried out.
Channel length measurement
Root canals must be filled exclusively to the apex of the root. What happens if you ignore this point?
The canal will not be completely sealed; unfavorable microflora will begin to multiply in it. This will further lead to inflammation, complex periodontitis and then the tooth will need to be removed.
It will be over-sealed - in this case, there may be various complications. If it is a tooth on the upper jaw, gutta-percha can enter the nasal sinus - this will be odontogenic sinusitis. Another complication may arise due to damage to the nerves - neuralgia, severe pain, and subsequently inflammation.
Therefore, through trial and error, the dentist is obliged to take measurements from beginning to end.
Mechanical restoration
The next stage is mechanical processing of the cavity. The main task is to make the tooth suitable for further filling. To do this, it is necessary to remove all narrowings and expand the channel as much as possible. This is done in two ways.
In interaction with the endodontic handpiece - the so-called Pro-files. These devices rotate in the cavity of the root canal, thereby removing all unwanted tissue and expanding it.
With the help of a hand instrument, the dentist independently rotates such instruments in the tooth.
Gutta-percha filling
The final stage is filling with gutta-percha.
There are several methods for this:
- Thermofil system - filling is carried out with heated material, and already in the canal it begins to harden. This is a highly effective method, but it also has disadvantages. This is a difficult procedure to carry out, expensive and requires high professionalism of the doctor.
- Single paste method - this method involves filling the canal with a plastic material. To date, a more dangerous filling method is not yet known, since complications occur in almost every case.
- Lateral condensation method - this technique is the safest and allows you to get good results. In this case, the canals are filled very tightly with gutta-percha, thereby guaranteeing that the entire canal is filled.
In case of pulpitis and periodontitis, the quality of treatment is assessed not only by the patient’s complaints. In addition to pain, a feeling of fullness and discomfort, a control image can tell a lot.
A mandatory conclusion of dental filling is radiographic control. It is carried out both before the procedure, during the treatment process, and after filling. In the picture you can see the quality of the work performed, and if necessary, re-sealing occurs.
What hurts if there is no nerve?
All of the above cases can be attributed to partial filling. What if all the root canals are closed with fillings, and the nerves from them have been previously removed? Where does the pain come from if the tooth is “not alive”?
Many experts believe that there should be no pain in this case. But, since it still occurs, and in a significant number of patients, the question of the origin of pain in a tooth without nerves remains open and hotly debated.
The tooth may hurt even after the nerve is removed
In what cases can you not worry that after filling the canals under a temporary or permanent filling, pain continues?
Important! Short-term pain in a tooth where there is no nerve, even if all the work on removing nerves, cleaning and filling canals was carried out according to the protocol and without errors, is a normal phenomenon.
Table. Nature of pain after root canal filling
| How it manifests itself | Description | Cause | What to do |
| Pain during biting | After the installation of a filling, usually temporary, is completed, pain occurs several hours or days later. There are painful symptoms when biting (from pressure). | If the level of occlusion is not too high, the reason is the reaction of the peri-root tissues to the extraction of the nerve. The root canal is expanded and filling material is introduced into it. The body reacts to a stimulus. | In this case, you can do nothing. The pain lasts from 5 days to 3 weeks. Pain dynamics should be positive (gradually subsiding, until disappearance). |
| Aching pain under the filling | After the anesthesia wears off, aching pain remains under the filling. | This is also due to the body’s reaction to the removal of the nerve. The disturbed canal walls “whine.” | The pain can last from two hours to a day. If it continues longer, you should consult a doctor. |
| Jerking pain inside the canal | This type of pain is rare. It’s as if something is tugging in the tooth; the sensation may resemble the beginning of inflammation of the pulp. | It occurs exclusively as an individual reaction of the body to the expansion of the canal or to the filling material itself (its structural component). | The tooth can also “tug” from hours to days. In a maximum of a day everything should go away. |
What are root canals
The dental nerve, or pulp, is located not only inside the tooth, its crown, but also inside the roots. Root canals are elongated cavities located inside the roots of teeth. This is where the dental nerve passes within the root. The number of root canals in one root may vary. There may be two or more channels in one root. The root canal can be very thin, thinner than a human hair, so high-quality treatment can take quite a long time. The difficulty is that even with the use of modern microscopes, the doctor cannot see absolutely all parts of the root canal. Work in the deepest part of the root is carried out almost blindly, which requires experience and skill from the doctor.
How to relieve post-filling pain
Most experts advise doing nothing. If the pain is normal, it will go away on its own in due time. But, if the pain is strong and interferes with the normal flow of life, you do not have to endure it. You can use folk remedies or official medicine.
By the way. The most famous “dental relievers” have long been considered soda and salt. They have several effects at once - antiseptic, relieves inflammation, removes tumors.
Soda and salt for preparing the solution
If your tooth hurts after permanent or temporary root canal filling, rinsing is effective.
Baking soda rinse procedure
A warm, but not hot solution is made in the proportion of 5 g of soda per 200 ml of water. Boil the water first. It is advisable to carry out up to four rinses per hour, that is, every quarter of an hour.
Preparation of the solution
Salt rinsing procedure
The proportions are the same as when preparing a soda solution. You can rinse five times an hour. It is preferable to use iodized salt. If the salt is ordinary table salt, add two drops (per 200 ml of solution) of pharmaceutical iodine, with a concentration of 5%.
Salt solution with iodine
Important! Iodine is used only by patients who do not have thyroid problems and who do not have an individual intolerance to this component.
Medicines
From your home first aid kit you can use the following drugs to relieve dental pain after root canal filling: Ketorol, Ketanov, Baralgin, Nise and others.
Painkiller "Ketorol" tablets
How does the process of refilling dental canals take place?
The current level of development of medicine in the field of dentistry is quite high. But dentists make mistakes, which is why filling dental canals again is quite common. At this point in time, doctors use several methods for performing this procedure.
Mechanical methods involve the use of a special instrument - an endodontic motor and an apex locator. In this case, antiseptic agents are added to the filling material. To prevent the development of inflammation, the doctor must very carefully and completely fill the dental canal with filling material.
Medicinal methods involve the use of products with organic solvents. They are able to soften and destroy the filling in a few minutes.
The cement filling can be removed from the canal using ultrasound and an endo-nozzle. This canal cleaning is usually carried out in one procedure.
When to see a doctor
If the pain does not decrease and does not go away within the time allotted for it according to the protocol, you should go to the doctor immediately. Without doing this, you will provoke serious complications that will lead to protracted and difficult to eliminate consequences.
Important! Especially if, after root canal filling, the gums are swollen and the pain increases, you should contact your dentist immediately.
If your gums are swollen, you should immediately contact your dentist.
To find out the cause of the pain, the specialist will conduct a palpable examination, tap the tooth (percussion), determine the viability of the pulp using electric current (ED) and prescribe x-ray diagnostics. If errors in treatment are identified or other causes of pain are discovered, the tooth must be re-treated. In emergency cases, when it is not possible to treat the tooth, it will be removed and a crown implant, bridge structure, or other recommended prosthesis will be installed in its place.
Crown on an implant
Dentist advice: how to determine how well the canals are filled?
If you have extensive carious lesions on your tooth or inflammatory processes (pulpitis, periodontitis), then, unfortunately, removal of the nerve from the diseased tooth cannot be avoided.
And at the same time, filling the canals. Root canal filling is a complex and responsible procedure. And not only because the doctor must carry out all manipulations with high precision and caution.
Even if the operation went without surprises, after a while you may encounter very unpleasant complications.
And in 60%-70% of cases, the cause of these complications is poor-quality canal filling!
The consequences of such treatment may be:
- severe toothache due to “overfilling” - when excess filling material extends beyond the upper border of the canal;
- gumboil, the development of acute abscesses, the appearance of cysts on the tooth due to “underfilling” of the canals - then an infection develops in the voids of the canal;
- complete tooth removal , which is caused by inaccurate treatment of the canals before filling and perforation of the root wall.
First of all, let's figure it out -
Painful sensations under an old filling
A situation familiar to many: a tooth was filled a long time ago, it didn’t bother me for a long time, and then it started to hurt. There are several possible reasons:
- progressive caries under an old filling;
- pulpitis (inflammation of the dental nerve) , developing as a result of untreated caries. Often this is a chronic form (periodically occurring paroxysmal pain in a tooth under a filling). Attacks occur most often at night. If left untreated, periodontitis will develop and the roots of the tooth will become inflamed;
- Periodontitis is a common cause of tooth pain under a filling. This is an inflammatory process in deep tissues. The slightest touch to a sore tooth causes terrible pain. It can radiate to the ears, head (temples and back of the head). Read on for details about why your tooth hurts and radiates to your temple. In this case, immediate assistance from a dentist is necessary. The old filling needs to be removed and the canals cleaned. The dentist places special preparations in the prepared and expanded canals that will relieve inflammation and disinfect the tooth cavity. Medicines are usually added twice. When the inflammation is removed, the doctor places a new filling. If the roots are inflamed, tooth treatment until complete recovery can be extended even for several months;
- tooth cyst It can develop over a period of time, from several months to several years. At first there are no sensations. Only in advanced cases does the tooth hurt. The cyst can lead to tooth and jaw destruction. In addition to toothache, signs of a dental cyst may include migraine, weakness, sinusitis, high fever;
- violation of the marginal seal of the filling. For various reasons, for example, due to abrasion or shrinkage of the material, the marginal fit of the filling is disrupted. Micro-cracks form between the filling and the tooth wall, where bacteria, saliva, and food debris enter. Dentin becomes infected, inflammation occurs, and recurrent caries or pulpitis develops.
- root crack. Occurs with heavy chewing load, injuries, or fixation of pins. The crack is difficult to detect, but after a while a complete vertical fracture may form in its place. The crack is difficult to diagnose, but causes pain or discomfort when stress is placed on the tooth.
A sign of the formation of a crack in the root may be a “click” heard by the patient during fixation of the pin or condensation of gutta-percha. As a rule, they remember about him after a while.
For more information regarding the causes of pain in a filled tooth, watch the video