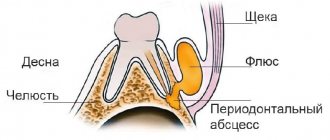
Primary self-help
But sometimes a tooth reminds itself suddenly: on the road, on vacation, late in the evening, when there is no immediate opportunity to see a doctor, nor the strength to endure any longer. In such a situation, you can use tips for quickly combating toothache:
- Rinsing. Warm rinsing helps clean the aching tooth from pieces of food, plaque and bacteria. The most effective recipes: a solution of soda or salt, a few drops of iodine or a furatsilin tablet in a glass of water, a light pink solution of potassium permanganate. Infusions of herbs also help well: chamomile, peppermint, sage, calendula, calamus, individually or in a mixture. You need to rinse every time after eating, as well as every hour. You can also make baths from infusions of these herbs for 15-20 minutes.
- Dental floss. You can try to gently clean the interdental space while the pain subsides using dental floss.
- Clove oil. A drop of this oil should be applied to the aching tooth using an ear stick.
- Strong alcohol . If there are no contraindications, you can rinse your mouth with vodka, whiskey, cognac or any other strong alcohol. The gums will absorb some of the alcohol, which will dull the pain.
- Painkiller. You can take any over-the-counter painkiller according to the regimen indicated in the annotation.
- Massage. You can try for 3-5 minutes to massage the area between the index and thumb on the side of the diseased tooth or the top of the auricle.
These steps will help ease the pain enough to allow you to wait until dental clinics open.
It is important to remember that neither these nor any other express methods will get rid of the cause, so without a visit to the dentist, the tooth will remind itself again and again.
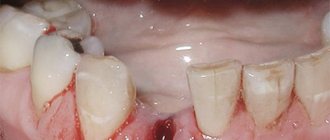
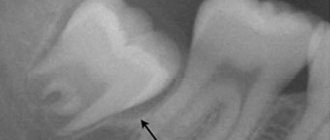
Is it possible to remove tartar at home?
On the Internet and in printed publications you can find many recipes for removing stones yourself at home. This includes a mixture of black radish with lemon juice, decoctions of walnut bark, and other incredibly practical remedies that can be found in any garden.
But the problem is that they practically don't work. Decoctions of herbs and plants can have a positive effect on the soft tissues of the oral cavity, yes. But they won’t be able to cope with mineral deposits. Daily brushing will help remove bacterial biofilm, but not tartar. Attempts to soften mineral plaque with acid, as was done 25-50 years ago, will also not lead to anything good and can cause pain in already inflamed gum tissues and increase the sensitivity of the enamel.
Mineral tartar, unfortunately, cannot be completely removed at home. Not strawberry paste, not a mixture of black radish with lemon, not walnut bark decoctions, not soda, not a swab with hydrogen peroxide. Not a single one, even the most advertised brush or paste, can destroy mineral structures. But scratching, erasing healthy enamel or causing its increased sensitivity is quite possible.
The only effective and safe way to remove mineral plaque (tartar) from the surface of the enamel is to consult a dentist.
What not to do
There is a lot of “harmful” advice that will only worsen the situation. So, what not to do:
- Do not heat. Under no circumstances apply heating pads, scarves, compresses, warming tampons, etc. to a sore tooth.
- Do not apply tablets. You can often come across advice to put an aspirin tablet on a sore tooth, but this can only cause a chemical burn.
- Do not take antibiotics. In the treatment of certain dental diseases, doctors often use antibiotics. But only a specialist can develop an effective and correct regimen for taking them.
How to avoid tartar formation
Tartar prevention is a simple and affordable procedure. It will help protect not only from mineral plaque, but also from other dental diseases. To avoid the appearance of tartar, you must:
- Brush your teeth regularly. Twice a day, morning and evening, 2-3 minutes. You shouldn’t lean on the toothbrush so as not to scratch the enamel, but you shouldn’t move it like a feather either. Select the optimal pressing force;
- Use a variety of oral hygiene products. Flosses will help remove mineral plaque from the interdental spaces, irrigators - from periodontal (gum) pockets, rinses - get rid of harmful microorganisms;
- Use quality home hygiene products. Don’t skimp on toothpaste—dentist services can still cost more than the 50-100 rubles you managed to save;
- Eat 4-6 times a day, but little by little. You should not snack every few tens of minutes, especially snacks like chips, cookies or candy;
- Make it a habit to rinse your mouth with water after every meal. This will help wash away microorganisms, bacterial plaque and food particles;
- Eat more solid, healthy foods. For example, snack on carrots and apples. But you should refuse soft and high-calorie foods (cookies, cakes, etc.);
- Visit your dentist regularly.
These tips will help protect not only from tartar, but also from other dental problems. They will also have a positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract. This means that the rest of the body will say “Thank you.”
Our dental center will not only help you deal with tartar through professional cleaning using modern equipment, but will also teach you proper daily oral hygiene. The procedure will take about an hour, will be painless and calm, and immediately after its completion you will be able to delight those around you with your beautiful, confident and snow-white smile!
What should you not do if you have a toothache?
Some actions can aggravate the problem, so these should be avoided:
- Applying heat, rinsing the mouth with hot liquids. If the pain is acute, this indicates an inflammatory process or an infectious lesion. In this case, heat increases blood flow to the sore spot, which can make the problem worse. In addition, neighboring teeth may also suffer from this;
- Increased bed rest. If you experience pain in a tooth, you should not lie down a lot, and this is also due to the flow of blood to it, which increases blood pressure. It is recommended to endure the pain, if not on your feet, then at least in a sitting or semi-sitting position. Of course, this is not a recommendation that answers the question of what to do if your tooth hurts at night, because sleeping even half-sitting is uncomfortable. In such a situation, the best ways are to rinse your mouth and take painkillers at night;
- Mechanical impact on the tooth and tissues around it. Eating and hygiene procedures should be done as carefully as possible, trying to avoid the sore spot.
All these methods of what to do if a tooth hurts are aimed only at relieving symptoms, but they do not help get rid of the disease that caused them. Therefore, as soon as pain makes itself felt, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor who will identify the problem and help solve it.
Did you like the article?
Rate: ( 5.00 out of 5)
Loading…
Simple Ways to Reduce Chronic Pain
Contents Factors that increase pain
Factors that reduce pain
For several centuries until the mid-20th century, doctors relied on the biomedical model of disease. Pain was perceived as a process associated exclusively with organic damage to organs and tissues. When accepting a patient with pain, the doctor was confident that the location of the pain indicated the cause of its occurrence. The doctor's job was to find and eliminate the cause of the pain, and if it was not found, he could not help the patient. Doctors did not assume that knee pain could be associated with changes in the brain, and its intensity and nature of manifestation are influenced by many factors.
In the 70s of the 20th century, a biopsychosocial model of the disease appeared, which began to take into account the patient’s personal experiences, emotions, behavior and society. Under the influence of this model, the idea of pain also changed. Pain began to be perceived as a psychophysiological phenomenon, in the control of which the brain participates.
Pain is always subjective, and each person feels it differently, depending on age, gender, genetics, psychological factors, physical activity, mental activity, traditions of the country of residence, social factors, attitudes, habits and neuroplasticity - the ability of the brain to change under the influence of experiences experience.
Any pathology, inflammation or injury, for example, a cut on a finger, triggers pain according to the following scheme: injury or inflammation acts on pain receptors (nociceptors) located in organs that transmit a signal through the nervous system to the brain. In addition, modern research shows that the brain has its own systems that can modulate and change the perception of pain. This is carried out by the opioid, serotonin, and noradrenergic systems. The more endorphins, serotonin, and norepinephrine produced by these systems, the stronger the inhibition of pain. Even in the presence of serious pathology, these systems can work on the principle of inhibition, and then the pain will be felt weakly. But under the influence of various factors (fear, anxiety, depression), the reverse process can occur, and then with the slightest damage a person will experience severe pain.
This idea of pain confirms that the brain is not just an important organ that solves mental and psychological problems. It has a colossal resource that is activated in different situations and can work in two modes - to enhance and to reduce the sensation of pain.
If we cut our finger, we don't run to the emergency room for pain relief. Sometimes we don't even feel pain because inhibition begins in response to the signal from the finger. The stronger the pain, the stronger the protection from it.
Guide to pain relief Answers to the most common questions that arise from patients and their loved ones when prescribing strong analgesics Guzel AbuzarovaDiana Nevzorova
Anesthesia
The behavior of people with severe wounds, trauma, and burns is a vivid example of how pain-relieving systems can work. The first few minutes after injury, a person may act as if he does not feel pain - continue to move and even run.
The reason is that in response to injury, there is a colossal release of endorphins, serotonin and norepinephrine, which block pain. This mechanism has evolved in humans for salvation in life-threatening situations. Of course, the blocking of pain soon ceases, and then pain shock occurs.
Factors that increase pain
In addition to diseases of organs and tissues, the perception of pain is influenced by the environment. A person is in the external environment, it is impossible to separate him from his environment, from his family and society as a whole. Psychological and social factors play a huge role in the perception of pain.
Some factors can open the “gates of pain” and make a person more vulnerable to it: depression, sleep disorders, chronic stress, obesity, anxiety, phobias, sedentary lifestyle, social isolation. Pain can be supported by factors such as misunderstanding on the part of loved ones, loss of role in the family, and loss of a person’s ability to adapt to environmental conditions. Doctors need to consider the influence of these factors to better understand how to build a relationship with a patient and know how to help him.
Let's say a patient with chronic pain is in difficult psychosocial conditions. This is likely to influence his pain perception and treatment. Imagine that the patient is a lonely woman who, from her window every day, sees the rusty pipes of the factory opposite her house, she has a small pension, and her neighbors are alcoholics.
Another situation is when the patient lives in the country, sees nature, children and grandchildren come to her and she does not feel lonely. And for the same diseases, but different psycho-social conditions, therapy will have different effects.
Sometimes a person's behavior pattern influences the course of his treatment. If a person is prone to catastrophizing, then when he realizes that he has chronic pain, he thinks that he will lose his job, will be left without money, he will be paralyzed, his loved ones will stop loving him and will not even visit him. Nothing terrible has happened yet, but this attitude towards the problem increases anxiety and leads to the fact that a person loses hope for effective treatment.
There is disagreement among researchers about how to approach catastrophizing. Some believe that it represents a variant of adaptation to pain. Others believe that catastrophizing falls under the category of pain coping because it increases psychological stress and can mobilize a person to action. There are also opinions that catastrophizing is not a response to pain, but a previous attitude.
Cultural background and upbringing can also influence the perception of pain.
If a person has been accustomed since childhood to taking an analgin tablet for any pain, and at some point it is not nearby, or the tablet did not help, the person’s anxiety may increase. He may think that nothing else will help him.
Factors that reduce pain
In addition to the factors that open the “gate of pain,” there are also factors that reduce pain. Some experts believe that if a person has something in pain, he needs to be prescribed pills, a blockade, injections, or surgery. However, research shows that non-drug methods can, through their effects on the brain, close the “pain gate” and reduce pain. Of course, the use of non-medicinal methods does not negate the diagnosis of pathology and the use of medications. However, when prescribing pharmacotherapy, the role of psychological sociocultural factors must be taken into account. Especially when working with patients with fibromyalgia, phantom pain, complex regional pain syndrome or joint syndrome.
These factors include a balanced diet, physical activity, meditation, placebo, good sleep, positive emotions, and social adaptation. These are simple things that we know about since childhood, and they work.
Positive emotions don't just affect our state of mind, they change how our brains work and protect us from pain. An example is Boris Kustodiev, who, after removal of a spinal cord tumor, found himself in a wheelchair. He had severe pain and paraplegia, nevertheless, in his memoirs he called himself the happiest person.
Auguste Renoir suffered from rheumatoid arthritis, a severe joint disease. He continued to work with this disease for more than 20 years. When the joints were completely functional, his hand was tied to his forearm. The pleasure of creativity allowed him to live a happy life.
“Pain is determined by how the nervous system perceives damage”
Neurologist Maxim Churyukanov on the biopsychosocial model of pain Maxim Churyukanov
Pain relief
Also among the factors that can influence perceived pain is mental activity. Immanuel Kant suffered from gout, he had severe pain, during which he continued to write scientific articles. Solving problems, reading complex texts, planning are useful for a person in terms of pain tolerance.
Physical activity also increases pain tolerance. Many American experts in recommendations for longevity recommend moving every day for 45 minutes continuously.
This is due to the fact that endogenous descending systems are activated and pain-suppressing endorphins are released no earlier than after 30 minutes of continuous physical activity. And the most interesting thing is that when muscles move, so-called myokines (anti-inflammatory cytokines) are secreted - molecules that protect us from inflammation, from pain, insulin resistance (from diabetes), from Alzheimer's disease and hypertension. (S. Schnyder, 2015). We are not talking about specific sports loads - any regular movement is beneficial for a person, and this is confirmed at the molecular level.
A study conducted by American physiologists with the participation of Buddhist monks shows that meditation also affects a person’s perception of pain. Additionally, meditation increases the volume of neurons in the insular cortex, the part of the brain responsible for making decisions and controlling situations.
The biopsychosocial approach to the perception of pain, in contrast to the biomedical one, takes into account not only the physical components, but also factors that influence a person’s perception of pain. This approach does not deny the role of treating the biological component of pain. He speaks of the need for additional influence on psychological and sociocultural factors, as well as the use of non-drug methods in pain treatment.
Recorded by Diana Karliner