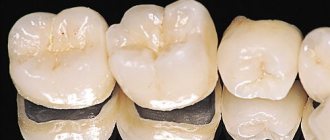
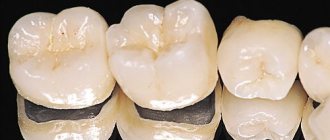
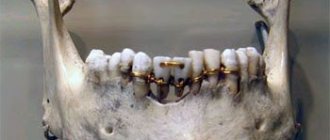
What are dental crowns
This is an artificial denture that is installed on a pre-treated natural crown. The purpose of prosthetics is to restore the anatomical shape, aesthetic appearance, and chewing function. Crowns can also be part of some other orthopedic structure: support for a partial removable or fixed denture, splinting for loosening of the dentition, etc.
Crowns on teeth
The design must meet certain requirements:
- restore the anatomical shape of the tooth, its aesthetics and color;
- support chewing and speech function;
- fit well to the neck of the destroyed tooth, make correct contact with neighboring units, as well as with teeth on the opposite side, without creating an obstacle to the closure of the dentition;
- do not interfere with the motor activity of the lower jaw;
- do not cause allergic reactions or tissue irritation.
All designs of this type have their pros and cons.
pros
Of all types of dentures, this one has a number of positive qualities, in some cases giving advantages over other types of prosthetics:
- rapid restoration of appearance and chewing function;
- large selection of materials for prosthetics;
- correct distribution of the load, eliminating the risks of abrasion of adjacent teeth and malocclusion;
- prevention of destruction of periodontal tissues and atrophy of jaw bone tissue;
- the ability to install several prostheses at once;
- if the root is partially destroyed, it is possible to install the prosthesis on a pin; if there is a complete absence of a root, it can be installed on an implant (titanium root).
Minuses
Negative qualities:
- the need to grind a tooth, sometimes a healthy one, if it performs a supporting function;
- a short period of discomfort after installation of the prosthesis; with the correct selection of material and compliance with installation technologies - very short;
- allergic reactions to certain dental materials;
- possible complications are reduced to a minimum with proper prosthetics;
- high cost of high-quality materials and insufficiently good appearance of cheap ones.
Basic requirements for material for dentures
Although a wide variety of materials are used in orthopedics, they all must meet certain requirements: to be durable, functional and attractive in appearance. That is why gold crowns and iron teeth are a thing of the past. Alas, there is no ideal alloy. Typically, more brittle ones imitate natural enamel better than harder ones. But orthopedists strive to achieve balance in everything. Regardless of what materials dentures are made from, they must:
- Withstand exposure to aggressive environments. Sour, sweet, salty - all these are chemical irritants that negatively affect the prosthesis. Maintaining its functions despite an unfavorable environment is one of the important requirements for the composition.
- Do not interact with food or change its taste
- Be comfortable to wear
- Look natural
- Have no smell or taste
Indications for installation of dental crowns
Dental crowns are installed for the following diseases and conditions:
- injuries and pathological processes of hard dental tissues, accompanied by the destruction of crowns by more than half and the impossibility of restoration with fillings - deep caries, increased abrasion, fractures and dislocations, wedge-shaped defects;
- congenital and acquired defects in the shape, height and position of teeth; congenital underdevelopment of crowns (hypoplasia);
- changes in tooth color - fluorosis, darkening after treatment;
- for support with partially removable and fixed dentures;
- as part of another orthopedic design, for example, splinting loose teeth due to periodontal diseases (periodontitis or periodontal disease).
Manufacturing technology and installation of ceramic crowns
Ceramic crowns are manufactured in advanced dental laboratories using modern equipment. After preparing the tooth, impressions are taken of it, which are analyzed by a computer program, and the resulting data is transferred to a high-tech milling machine.
Basic approaches to the manufacture of prostheses:
- Press ceramics, or pressed casting method - in this case, porcelain is applied in layers.
- Computer modeling of all-ceramic prostheses (CAD/CAM technologies).
Contraindications for installation
To place a crown on a tooth, you need to take into account not only the indications, but also the contraindications. Absolute contraindications include:
- healthy (intact) teeth; the exception is the situation when they are used as a support for other orthopedic prostheses;
- high pathological tooth mobility;
- chronic foci of infection of dental tissues that cannot be treated.
Relative:
- insufficient oral hygiene, caries - prosthetics are carried out after complete sanitation of the oral cavity;
- destruction of the crown by more than half - if the root is preserved, prosthetics are carried out after the pin is installed;
- destruction of the tooth root with its subsequent removal - prosthetics after implantation of a titanium root;
- chronic periodontitis (inflammation of the ligament that holds the tooth in the cell) - prosthetics after complete elimination of the causes of the disease - cysts, fistulas, etc.;
- not fully formed dental roots;
- severe general diseases - high blood pressure, stroke, myocardial infarction - prosthetics are possible after stabilization of the patient’s general condition.
Types of crowns for teeth
Since dental crowns are designed for different purposes, they can be made from different materials. The orthopedist decides which crowns are best to put on the teeth in a particular case. Based on the material of manufacture, the following types of dental crowns are distinguished: metal, plastic, ceramic, metal-ceramics, glass-ceramics, zirconium dioxide, metal-plastic.
Plastic crowns for teeth
Temporary plastic crowns
Plastic (mostly acrylic) is a short-lived material, so currently a plastic crown on a tooth is mainly a temporary structure. These types of dental crowns have the following advantages:
- temporarily restore appearance, support chewing and speech functions;
- protect prepared (processed for prosthesis) teeth from pain when exposed to mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli;
- prevent displacement and loosening of prepared teeth in the absence of their support by neighboring units;
- prevent the development of pulpitis and periodontitis with preserved dental pulp.
Minuses:
- possible burn of the pulp during installation, as well as allergic reactions to acrylic and inflammatory processes of periodontal tissues;
- fragility and breakage (but repair is possible using special glue);
- color change due to food coloring;
- limited validity period (2 years) - this is enough for temporary dentures, but not for permanent ones.
Metal crowns for teeth
Metal alloy crowns
These are the very first materials used to make dentures. Metal crowns on teeth are still in demand today, provided they are used correctly. They are made from alloys of precious and base metals with the addition of nickel, chromium, cobalt and other metals. Models made of gold are also alloys, since gold is a very soft and short-lived material, and the alloy will last for decades, having a beneficial effect on all tissues of the oral cavity. Models made of steel with gold plating are no different in appearance and wearability from gold ones, but do not have a positive effect on the periodontal tissues. If the question arises, which crown is better for a chewing tooth, dentists often recommend metal. Pros of a metal dental crown:
- validity period of at least 10 years; with proper care – decades; rarely break;
- biocompatibility with tissues;
- absence of corrosion in the alloys used;
- tolerate chewing load well;
- reasonable prices.
Minuses:
- not very attractive in appearance, since they differ as much as possible from natural units; therefore, they try to place a crown on a metal tooth on the lateral (chewing) units;
- sometimes they cause allergies and galvanic (electrochemical) reactions (if there is already a tooth made of another alloy in the mouth).
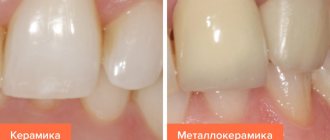
Ceramic crowns for teeth
Ceramic crowns
Ceramic tooth crowns are made from the most fragile material – pressed porcelain without any additions. They have their pros and cons. Pros of a ceramic dental crown:
- very beautiful – the appearance completely corresponds to natural teeth;
- strength;
- validity period - with proper care 10 years or more;
- completely biocompatible with tissues, do not cause allergies or gum irritation;
- do not change color when using food dyes;
- require minor grinding of hard dental tissues.
Minuses:
- fragile, breakages in the form of chips are more common than other materials;
- cannot withstand high chewing loads, so these crowns are placed on the front teeth;
- high price.
Zirconium dioxide dental crowns
Zirconium crowns
Zirconium crowns are made from the mineral zircon (silicon acid) through special processing using additives. The result is a very hard, durable material that also has the necessary plastic properties so that it can be used to make a denture. Zirconium crowns are made either from zirconium alone or by covering it with ceramics. The latter look more beautiful, so they cost more. Pros of a zirconium dental crown:
- the most durable material, service life - 15 years or more;
- zirconium crowns are beautiful - metal-free ceramics based on zirconium dioxide give a good aesthetic effect, but pure zirconium prostheses also look good;
- the possibility of manufacturing a structure for both anterior and lateral (chewing) units;
- completely biocompatible with human tissues, do not cause allergies or irritation.
Minuses:
- increased wear of teeth on the opposite side is possible;
- the top layer of ceramics may chip;
- high price.
Metal-ceramic crowns on teeth
Metal-ceramic tooth crowns have a metal alloy frame, which ensures the strength of the prosthesis, and a ceramic coating, which creates an aesthetic appearance. Advantages of a metal-ceramic dental crown:
- quite durable - service life is about 8 - 10 years;
- aesthetic appearance;
- cheaper than metal-free ceramics;
- if the frame is made of gold or platinum, then the prosthesis does not cause tissue irritation or allergies.
Minuses:
- metal-ceramic tooth crowns are not as beautiful as those made from porcelain or zirconium;
- chips of ceramics may appear;
- sometimes they darken, acquiring a grayish tint;
- frames made of base metals sometimes cause tissue irritation and allergies.
Glass-ceramic dental crowns
Glass-ceramic crowns
One of the most modern dental materials, combining high aesthetic qualities and sufficient strength. This type of dental crown is made on the basis of glass and ceramics using lithium disilicate (Empress Esthetic), lithium disilicate (E-max), zirconium silicate (Ceramage), etc. Advantages of a glass-ceramic dental crown:
- thin, therefore allowing for minimal tooth treatment;
- smooth surface and good adhesion to natural hard dental tissues - reduces the risk of developing caries;
- transparency and aesthetics - outwardly no different from the enamel of natural teeth;
- Lightweight design increases wearing comfort;
- do not change their color throughout use;
- validity period – more than 10 years;
- biocompatibility due to the absence of metal in the frame - does not cause gum irritation or allergic reactions.
Minuses:
- high price;
- hardness – can cause increased wear of teeth located opposite;
- fragility - can crack, repairing it is problematic.
Metal-plastic dental crowns
Metal-plastic crowns
A metal-plastic dental crown has a metal (usually base metal alloy) frame and a plastic covering. Temporary structures are most often made from this dental material, as it is not durable. A metal-plastic dental crown has the following advantages:
- ease of installation and repair of the structure;
- low cost.
Minuses:
- short validity period - about 2 - 3 years;
- allergies and tissue irritation may occur;
- loose fit to natural hard tissues – risk of caries and inflammatory diseases;
- color change due to the use of food coloring.
From the table you can find out which dental crowns are best suited for you:
| View | Aesthetic indicators | Period operation | Compatibility with the body | Allergy |
| Plastic | low | 2 years | not always | often |
| Metal | low | 10 or more years | not always | often |
| Ceramics | high | 10 years | high | No |
| Zirconium dioxide | high when combined with ceramics | 15 or more years | high | No |
| Metal ceramics | average | 10 years | not always | It happens |
| Glass ceramics | high | 10 or more years | high | No |
| Metal-plastic | average | 2 – 3 years | not always | It happens |
Types of removable dentures
This category includes designs that can be removed, cleaned, and put on independently, without the help of a specialist. They are indicated for complete or partial absence of teeth; they can be permanent or temporary. The following types of removable dentures are distinguished:
- lamellar;
- clasp;
- immediate dentures;
- quadrotti;
- sandwich dentures.
Removable prosthetic structures perform an aesthetic function and promote better chewing of food. The advantages of this method of prosthetics include speed of installation and relatively low cost. Permanent structures have significantly more disadvantages.
First, the gum tissue atrophies, making it necessary to replace the artificial jaw every 2 or 3 years. Secondly, plate dentures are not securely fixed in the oral cavity and can distort diction. Thirdly, the materials used wear out quickly and are not very durable. Below are detailed characteristics of each type of removable dentures.
Suction cup or plate prosthesis
An inexpensive and simplest method of prosthetics for complete or significant absence of teeth. The prosthesis consists of a base made from an individual impression and crowns. To make the base, hard hypoallergenic materials (acrylic, plastic) or soft nylon are used.
If several dental units have been preserved, the artificial jaw is attached to them using clasp hooks. In the case of complete edentia, fixation is carried out by suction of the base bed to the gum tissue. For more reliable fastening, dentists recommend using special adhesive compounds (creams, glues).
Complete removable dentures for the upper jaw have a design feature. They completely cover the palate, which increases their surface area and, accordingly, the reliability of fixation in the oral cavity. Prosthetics of the lower jaw in a similar way is undesirable, because the product, without a palatal part, is less well retained in the mouth.
Dentists do not recommend this type of prosthetics for several reasons:
- due to the high load on the gums, hard and soft tissues quickly atrophy, which leads to the need for frequent replacement of dentures;
- design features often contribute to impaired diction and can provoke an inflammatory process;
- patients complain of a long process of getting used to it, discomfort while wearing it, and gagging;
- the prosthesis is not sufficiently securely fixed in the oral cavity, restoring chewing function by no more than 65%;
- the materials used in manufacturing are not very durable; plastic can cause an allergic reaction.
Removable prosthetic structures are still in high demand because they are inexpensive, quickly manufactured, and easy to maintain.
Immediate prosthesis
Also known as a “butterfly” or “bug”, it is a temporary type of prosthetics for 1-3 dental units. It is usually installed before implantation for the period necessary for the engraftment of titanium pins. At this time, a removable denture is necessary to maintain chewing function, maintain aesthetics, and also to prevent tooth discrepancy.
The design received its name due to the similarity of its supporting part to the open wings of an insect. The base is usually made of soft materials, colored to match the gum, and the crowns are made of white acrylic plastic. The denture is attached to healthy teeth using clasps, which are almost invisible when smiling or talking. Immediate dentures are inexpensive, are manufactured in 2-3 days, and look aesthetically pleasing.
Immediate prosthesis
Clasp prosthesis
One of the highest quality modern types of prosthetics for partially edentulous patients. The design is comfortable to wear, aesthetically pleasing, and durable. In addition, the chewing load is evenly distributed between the supporting dental units, which significantly slows down bone tissue atrophy. To install this type of structure, you must have your own healthy teeth on both sides of the jaw.
The clasp prosthesis consists of three main parts:
- metal frame made of titanium, precious metals or cobalt-chromium alloy (CHC);
- a base made of nylon or acrylic, with plastic teeth;
- fixation systems (locks, clasps, telescopic crowns).
The basis of the metal frame is an arc, which serves as a load distribution and ensures the strength of the entire structure. On the upper jaw, it can be in three positions - in front, in the middle or behind - or have a closed ring-shaped shape. when replacing the lower jaw, this element has an exclusively anterior position.
The arc does not come into contact with the mucous membrane and has a small thickness. A nylon or acrylic base with crowns is welded onto it. The thickness and volume of the base are reduced due to the presence of a durable metal frame. This increases the comfort of wearing clasp structures and makes them one of the best dentures for teeth. The reliability of fixation in the oral cavity depends on the type of attachment to the supporting dental units.
On clasps
This is the name for hooks that are placed on healthy crowns, transferring pressure to them and keeping the prosthesis from moving. They are usually made of metal, but if they fall into the smile zone, they can be made of nylon (it is almost invisible). Clamp fastening has the following advantages:
- reliable fixation;
- comfort, quick adaptation;
- no need to grind your own crowns;
- affordable price (compared to other options).
The disadvantages include low aesthetic characteristics, but this only applies to metal clasps. In addition, such fastenings negatively affect the condition of supporting teeth, accelerating their destruction. The reason is the slight elasticity of the hook required to remove or put it on. As a result, it becomes mobile, gradually wearing away the enamel. But this problem can be solved by installing metal-ceramic crowns.
On locks
Fixation of the prosthesis is ensured by metal micro-locks or attachments consisting of two parts. One of them is located on the prosthesis itself, and the second is on the metal-ceramic crown of the abutment tooth. The design of this fastening is reliable and also redistributes about half of the chewing load onto healthy teeth.
The advantages of clasp dentures with attachments include:
- high aesthetics - the locks are located on the inner surface of the teeth, therefore they are completely invisible;
- reliable fixation;
- long service life - about 7 years;
- high rates of restoration of chewing function;
- no pain, discomfort, quick adaptation.
Among the disadvantages, one can highlight the rather high cost of production, which is due to its complexity. In addition, for prosthetics, it is necessary to grind down your own teeth in order to install metal-ceramics.
On telescopic crowns
The most technically complex, but the most effective way to fix the prosthesis in the mouth. The fastening element consists of two parts - a metal cap and a metal-ceramic crown. The first of them is placed on a ground healthy tooth, and the second is attached to the frame of the prosthesis. During installation, the crown is placed on the cap, ensuring the most reliable fixation. Therefore, to the question of which clasp dentures are the best, we can confidently answer that these are the ones.
The advantages of products with telescopic crowns include:
- reliability;
- durability;
- aesthetics.
The main disadvantage of this type of construction is its high cost, since it is necessary to install crowns on at least 4 abutment teeth.
Quadrotti
The name of the design comes from the Italian QuattroTi - the latest development by European scientists in the field of prosthetics. The principle of manufacturing and fixation of the prosthesis is similar to the clasp one, but differs in the material of manufacture. Instead of metal, it uses acetal - a monomer-free plastic, which is characterized by increased strength, 100% hypoallergenicity, and lightness.
Quadrotti prosthesis
This material made it possible to improve the performance qualities of the artificial jaw without compromising other significant properties. The weight of the structure has decreased, the strength is not inferior to its metal counterpart, and there is no risk of allergic reactions. In addition, Quadrotti clasps, made of acetal, are completely invisible on the teeth.
QuattroTi clasp dentures are superior to their clasp-based counterparts in the following indicators:
- aesthetics – the material for making fasteners is available in ten shades of white;
- comfort – the design is light and non-bulky, so adaptation occurs quickly and diction is not impaired;
- long service life - at least 7 years;
- hypoallergenic - unlike metal, acrylic or plastic, it is not able to provoke an allergic reaction.
Quadrotti prostheses are not inferior to their metal counterparts in strength, but have one significant drawback. Their clasps do not perform a supporting function, but only hold them, so there is no redistribution of the chewing load on the supporting teeth. All the pressure is placed on the gum tissue, which can cause pain when chewing. In addition, the price of QuattroTi is higher.
Sandwich
This is the name of a new generation of removable prosthetic structures for the upper jaw without a palate. It is a domestically developed product, made from acrylic plastics. It is recommended for patients who have retained at least two of their own teeth that will serve as supporting teeth. This type of dentures is also suitable if there are no teeth, but 2 implants are installed.
The base is fixed on the gum due to two fasteners that repeat the anatomical shape of the existing dental units. Due to the absence of the palatal part, the product is superior to the standard removable analogue in the following respects:
- does not cause a gag reflex;
- does not provoke inflammation;
- does not impede diction;
- no need to remove at night;
- no need to use adhesives;
- more durable and lighter.
The only disadvantages of the sandwich can be considered a higher cost or the need to install two implants if your own teeth are completely missing.
Which crowns are best for teeth?
All types of dental crowns have their own indications and contraindications. Certain types are used on different teeth. Recommendations about which crown is better for the chewing tooth and which for the front tooth are given to the patient by the orthopedist. But, for example, a metal-ceramic crown can be installed on any tooth.
Crowns for front teeth
Incisors and canines are always visible when talking and smiling. In total, each jaw has 4 incisors (2 central and 2 lateral) and 2 canines. Their main function is to bite food, create an aesthetic appearance and maintain correct diction. What crowns are best for such teeth? Most often, ceramics and glass-ceramics are used for crowns on the front teeth. These dental materials allow you to create the maximum aesthetic effect, as well as maintain chewing and speech function.
Crowns for lateral (chewing) teeth
These types include premolars and molars. When smiling, they are not always visible (sometimes 1 premolar is visible) and perform a chewing function. Crowns on chewing teeth are most often installed metal or zirconium. At the patient's request, glass ceramics can also be used. If the first premolars are visible when smiling, ceramics, glass ceramics or zirconium crowns are installed on them.
The final decision on which crown is best suited for a chewing tooth is made by the doctor together with the patient. Plastic or metal-plastic is most often used as a temporary structure.
Main types of metal ceramics
Metal-ceramic dentures consist of a metal base, onto which a ceramic coating is applied layer by layer and fired. Metal-plastic crowns are made in a similar way (the metal base is covered with plastic), but the plastic coating is very fragile and short-lived. Therefore, when the question arises: which teeth are better than metal-ceramics or metal-plastic, metal-ceramic structures always win. Technology using ceramics has made it possible to obtain high strength and achieve good aesthetics of dentures. Depending on the composition of the frame, such crowns are divided into two main types:
- Metal ceramics based on base metal alloys. In this case, cobalt-chromium or nickel-chromium alloys are used. They are inexpensive, but have a dark shade and can change the color of the prosthesis, shining through the ceramic layer of the coating if it is not thick enough, making it noticeable against the background of natural teeth.
- Metal ceramics based on precious metals, the most popular of which is gold. It does not distort the color of the crown; due to its yellowness, it gives the ceramic a warm tint and provides a higher aesthetic result. This is a better metal-ceramic compared to the previous option. However, such prostheses will be somewhat more expensive than them.
Thus, patients who have chosen metal-ceramic crowns can choose the best option for themselves in terms of price/quality ratio.
Installing a crown on a tooth
The process of installing a crown on a tooth is strictly regulated. It is carried out in stages. The appearance, functionality and lifespan of the prosthesis depend on how the crown is placed on the tooth and how carefully the work is done.
Inspection
Installing a crown on a tooth begins with an examination by an orthopedic dentist. He examines the oral cavity and, if necessary, prescribes x-rays. Based on the results of the inspection and examination, preparatory measures are carried out.
Treatment
A complete sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out. Treatment includes caries, gum and oral cavity diseases. In severely damaged units, the pulp is removed and the root canals are cleaned (depulpization). Professional dental cleaning is required. Only after the doctor is convinced of the complete absence of foci of infection can prosthetics be performed.
Turning
It is not easy to crown a tooth. To install a crown on a tooth, it needs to be ground - remove the surface layer of hard tissue with a thickness equal to the thickness of the future prosthesis. Structures can be made of different materials and have different thicknesses, so turning will also be carried out to different depths.
Grinding a pulpless tooth before installing a crown is painless. It is recommended to grind a living, non-pulpless tooth under local anesthesia.
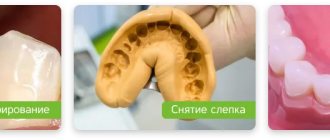
Taking an impression and making a model
An impression or impression is taken from a unit that is fully prepared for prosthetics, reflecting the condition of the prosthetic part of the dentition. For this purpose, an elastic dental material is used that retains its shape for a long time (silicone mass, dental wax, plaster).
The oral cavity is dried, the material selected for making an impression is placed in a special mold (spoon), and it is applied to the place of prosthetics in the dentition. The patient can only clench his jaws and keep them clenched for several minutes until the impression hardens. The resulting impression is washed under running water, placed in a special solution and sent to a dental laboratory. Using the cast, a plaster model is first made, it is tried on, and then a prosthesis is made from the selected material.
Fixation of crowns
The installation of the crown ends with its strengthening - fixation. First, the crown is strengthened with a temporary compound. The patient wears the prosthesis, assessing the degree of comfort, for 2 to 4 weeks. If everything is normal, the temporary fixation is replaced with a permanent one, strengthening the prosthesis with cement. If the prosthetic unit has enough natural tissue, then the prosthesis is placed directly on the treated and filled tooth. If there is not enough tissue, the prosthesis can be fixed on an inlay, a pin or an implant (titanium root).
On the tab
Fixation of the crown on the core tab
This is the best option for prosthetics. The inlay is made in the laboratory from an impression and reliably covers the damaged tooth. Even if the crown is destroyed for some reason, the inlay will not be damaged and re-prosthetics can be carried out easily. A prosthesis on an inlay can last a very long time, from 7 to 10 years or more, depending on the material of manufacture.
On the pin
Crown on pin
The orthopedist decides which crown is best to install on the chewing tooth and how to strengthen it, but most experts believe that a supporting structure in the form of a pin is most suitable. The pin is inserted into the preserved tooth root when there is significant destruction (at least half) of the crown. Before this, treatment and removal of pulp from the root canals is carried out. Contraindications for the installation of a pin are any inflammatory processes, including pulpitis and periodontitis, split roots, narrow curved root canals.
Pins are placed mainly on the lateral (chewing) teeth, but sometimes on the front teeth. The price depends on the material of manufacture. Cheaper metal ones with threads (anchors) are placed mainly on chewing teeth. More modern fiberglass ones are transparent, without threads, installed on cement.
On an implant
Crown on an implant
An implant is a titanium root that is implanted into the jawbone. Installed when the root is destroyed, on which it is impossible to install a pin. Dental implantation can take place immediately after removal of the natural root (single-stage technology) or after some time (delayed).
An adapter (abutment) is installed on top of the titanium root, onto which the prosthesis is attached. The abutment can be metal and then it will be visible through transparent metal-free crowns. Zirconium abutments can be placed on any teeth, metal ones - mainly on the lateral ones. Usually, a temporary structure is first installed, and after the implant has healed, it is changed to a permanent one.
Metal ceramics on the front teeth –
An aesthetic problem when replacing anterior teeth with metal-ceramics is associated with the presence of a metal frame under the surface layers of the ceramic mass. The first problem is that the ceramic layer must be made opaque - otherwise the metal frame will be visible through the ceramic layer. In turn, dental tissues have a certain light transmittance - enamel is capable of transmitting about 70% of light, and the dentin lying under the enamel is about 30%.
Such optical properties give natural teeth a certain degree of transparency, as well as color, which also changes from the cutting edge to the neck of the tooth. Therefore, when metal-ceramic crowns are installed on one or two front teeth, in most cases they are noticeable against the background of natural teeth. Therefore, if we are talking about budget metal-ceramics, this problem can be more or less solved only if you install metal-ceramics on all 6-8 front teeth at once, and in this case, all the front teeth under the crowns will look at least the same.
If you have a sufficient budget, the problem of color and transparency can be solved by using more expensive ceramic mass, the use of which, however, will significantly increase the cost of crowns. Among the best options (according to many of our colleagues) are the ceramic masses “Vita” (Germany) and “Noritake” (Japan), as well as “Ivoclar” (Liechtenstein). The use of a good ceramic mass allows us to minimize the difference between metal-ceramics and natural teeth, but again, only to a certain extent.
Clinical case No. 1 (before and after photos) –
In Fig. 3-4 you can see how one terrible metal-ceramic installed on all the upper teeth was replaced with almost the same terrible one (the crowns look gray, there is no gradient of color and transparency; as if they were made of plastic). More or less, the only thing that saves the situation is that all the upper teeth look the same, because... They all have the same crowns. In fact, in this case, metal-ceramics are more like cheap plastic crowns.
Clinical case No. 2 (before and after photos) –
In Fig. 5-6 you can see that all 6 lower metal-ceramic crowns - 1) have an unnatural gray-milky color, which is especially visible on the fangs, 2) there is no transparency along the cutting edge, 3) there is no color transition from the neck of the tooth to the cutting edge . The situation is saved again only by the fact that all 6 front teeth are taken under crowns - which makes them at least identical. On the other hand, we must admit that many patients are quite satisfied with this level of aesthetics.
Important: it should also be noted that the transparency of tooth enamel can vary greatly from person to person. Therefore, if the enamel is highly transparent, metal ceramics will not suit you at all. But if your teeth have low enamel transparency, then high-quality metal-ceramics may be a good option. But in any case, keep in mind that in bright natural light, the difference in color and transparency between metal-ceramic crowns and “your teeth” will be most noticeable. It is also worth considering that metal ceramics will have a stronger effect in patients with a gummy type of smile, i.e. when the crowns of the teeth are completely exposed when smiling.
Another disadvantage of metal ceramics on the front teeth –
However, the lack of a gradient of color and transparency (which can be found in most cases of manufacturing budget metal ceramics) is not its only aesthetic problem. Many patients almost immediately after prosthetics note that the gums around the crown have become bluish (Fig. 7). Also, after several years, many patients notice that the gums have receded, exposing the subgingival edge of the crown at the neck of the tooth - which looks like the “dark line” in Fig. 8.
Disadvantages of economy class metal ceramics:
Patients react calmly to such things if they occur in the area of the chewing teeth. But on the front teeth, especially if the patient has a gummy type of smile (that is, the gums are exposed while smiling) - this is a serious aesthetic problem. All this arises due to the fact that the lower edge of the metal frame of a metal-ceramic crown is usually not insulated with ceramic mass. It is the contact of the metal with the gum that leads to a change in its color, and also contributes to gum recession and exposure of the edge of the crown.
However, such problems with gum aesthetics are typical only for standard economy-class metal-ceramic crowns. There are metal-ceramic crowns with a much higher level of aesthetics - the so-called metal-ceramics of increased aesthetics.
Metal ceramics of increased aesthetics –
To create high-quality, highly aesthetic metal-ceramics, you certainly need an expensive, high-quality ceramic mass, which will significantly increase the cost of such crowns.
However, this is not enough, because in order to also exclude the appearance of cyanosis of the gums or a dark line, it is necessary to manufacture metal-ceramics with “shoulder mass” (Fig. 9). For crowns with shoulder mass, the metal frame will be insulated with ceramics, including in the area of the ledge (where the crown wraps around the neck of the tooth), i.e. slightly below the edge of the gum. Moreover, isolation can be carried out either along the entire perimeter of the cervical part of the crown, or only on its front side, which is already good. Isolating the edge of the metal frame with ceramics helps to avoid the development of cyanosis of the gums and the appearance of a dark line in the future.
Clinical case No. 3 – before and after photos
In Fig. 10-11 we see a decent option for metal-ceramic prosthetics, which was installed on the 4 upper incisors (there is even transparency along the cutting edge). Additionally, the patient had teeth whitening. As we can see, there are practically no differences in the color and transparency of metal-ceramic crowns from your own teeth (although minor flaws will still be noticeable to professionals).
It should be noted that modern metal-ceramic crowns (thanks to the latest generation of ceramic compounds) can be almost as aesthetically pleasing as ceramic ones. But this requires expensive materials, and most importantly, a highly professional dental technician who must have artistic talent. And there are only a few such technicians even in Moscow and St. Petersburg. And in any case, the cost of 1 unit of highly aesthetic metal ceramics (in clinics where the best specialists work) will be no less than 25,000 rubles.
Possible complications
Depends on how the crown is placed on the tooth. If all indications and contraindications for prosthetics are observed, the correct choice of dental material, prosthetic technique, and high-quality performance of all work, complications, as a rule, do not occur or are reduced to a minimum. Sometimes the cause of complications is the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Pain under the crown
After treatment and prosthetics, moderate pain may persist for some time (1–5 days), decreasing in intensity. But if the tooth under the crown hurts, and the pain does not decrease, but increases, tissue swelling appears, pus is released from the gums or the temperature rises, you should immediately consult a doctor - this is a sign of an inflammatory process. The cause of inflammation may be incompletely cured caries or incompletely removed pulp from the root canals. Another reason is violations during the installation of the prosthesis, its loose fit to the remains of the natural crown and infection getting under it.
Pain under the prosthesis with irradiation into the jaw also occurs when the root canal is perforated with a pin or when a small part of the instrument used to clean the root canal is broken off. What to do: you should not try to treat a bad tooth on your own; this requires urgent help from a dentist. Usually the crown is removed, the pathological process is treated, and then the crown is reinstalled (new or old, if it is not destroyed). Sometimes pathology can be eliminated without removing the crown, simply by drilling a hole in it. The hole is then repaired using photo-curing filling materials.
If the toothache under the crown is very severe, before seeking medical help, you can take a painkiller: Paracetamol 500 mg tablet, Ketorol 10 mg or Naise 100 mg.
Unpleasant smell
Indicates the presence of an infection in the mouth. This may be a slow inflammatory process, or it may be an acute one, in which case the tooth also hurts. The cause of an unpleasant odor from a tooth under a crown can also be insufficient oral hygiene, smoking and eating a lot of sweets. What to do: consult a doctor; this symptom can only be eliminated in the dentist’s office.
Allergy
Allergic reactions are most often associated with the installation of crowns made of non-precious alloys of metal and plastic (acrylic). Redness and swelling of the gums and pain appear. The allergic process is dangerous because it can quickly spread to surrounding tissues. At the same time, the tissues of the larynx swell, breathing is impaired (Quincke's edema). What to do: contact your dentist immediately. Help consists of replacing the prosthesis that has caused an allergy to a structure made of a different material. At home, the patient can take a tablet of any antihistamine: Zodak, Claritin, Tavegil, etc.
Caries
The cause of the development of dental caries under the crown is most often incompletely cured primary caries. But sometimes, even after careful treatment, caries develops again (secondary caries). This happens especially often when the crown does not fit tightly (an infection gets under it), poor oral hygiene, or consumption of large amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates. What to do: Contact your dentist as soon as possible. The product is removed, caries is treated, and then the structure is reinstalled. If it is worn out, install a new one.
Prosthetic stomatitis
The appearance of painful ulcers on the gums in the area of prosthetics and their spread to the oral mucosa largely depends on how the crown is placed on the tooth. Prosthetic stomatitis is a consequence of improper design or installation of a crown, squeezing small blood vessels of the gums, leading to malnutrition and destruction of the mucous membrane. Sometimes the cause of stomatitis is the toxic effect of dental material (acrylic) on oral tissue. If an infection is added to the inflammation, stomatitis can be purulent. What to do: consult a dentist, find out and eliminate the cause of the complication.
Caring for dental crowns after prosthetics
How long the installed structure will last depends not only on the quality of dental services, but also on proper care. After installing a crown, it is important to follow these recommendations:
- You will be able to eat 2 hours after installation of the prosthesis, and drink immediately;
- For the first few days, it is better to chew solid food on the opposite side; over time, the load can be increased, but you should no longer chew nuts at all;
- after installing prostheses made of plastic or metal-ceramics, it is better to avoid taking coloring foods: coffee, beets, red wine, etc.;
- after each meal you need to rinse your mouth, using an irrigator to rinse the interdental spaces; It is better not to use dental floss, as they can damage the denture;
- brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush and toothpaste without abrasive particles; President pastes with an RDA abrasiveness rating of less than 50 units are suitable. (Preggy for pregnant and nursing mothers and Junior).
Crown care products
Polymers (plastics)
The use of polymers in orthopedics has become a real revolution. Plastic structures are still one of the most in demand. Most often, polymers are used for the manufacture of complete or partial removable dentures and as temporary structures.
Acrylic
This is inexpensive, lightweight plastic. It is resistant to chemical influences and holds its shape well. Acrylic dentures are easy to manufacture and can be repaired. Unfortunately, it is hygroscopic and easily becomes covered with microcracks in which bacteria accumulate. Acrylic systems take a long time to get used to and often cause discomfort. These shortcomings are easy to accept, but acrylic plastics contain monomers, substances that cause allergic reactions. This is the main disadvantage of acrylic. Before prosthetics, an allergy test is required.
Nylon
The problem of allergies is solved by thermoplastics - plastics that do not contain monomers. The most common of them is nylon. It is very durable, but at the same time elastic. Does not lose color even after several years of use. Nylon systems do not rub the mucous membrane and take up little space in the mouth. They get used to them faster than acrylic ones.
But nylon, as a material for removable dentures, also has disadvantages. Due to its flexibility, nylon easily peels away from the sky. The chewing load is distributed unevenly. Working with nylon is more difficult; products from it are not made everywhere.
AcryFree
Technologists have long tried to find a middle ground between acrylic and nylon, and they succeeded. A modern material for the manufacture of prostheses, AcryFree, combines the advantages of both polymers. It is tougher than nylon but softer than acrylic. Moderate hardness ensures uniform chewing load. Although AcryFree cannot stop bone loss, it does significantly slow down bone loss. Thermoplastic does not contain monomers, which means it does not provoke allergic reactions. The manufacturing method is injection molding, which eliminates the formation of micropores.
Disadvantages include a long period of adaptation, the need for special care, and the risk of clasp breakage.
Comparison of polymers
| Properties | Acrylic | AcryFree | Nylon |
| Presence of allergens | Yes | No | No |
| Price | Low | Average | High |
| Elasticity | Low | Average | High |
| Probability of failure | High | Average | Low |
| Possible repairs | Yes | Yes | No |
| Risk of loosening adjacent teeth | High | Short | Short |
Which one to choose is decided by the patient and the doctor after the examination.
How much does a tooth crown cost?
To find out how much it will cost you to install a crown on a tooth, you will need to make an appointment with a prosthodontist. During your consultation, a specialist from the St. Petersburg clinic “Yulistom” will recommend the type of crown that is most suitable for you and will evaluate the amount of work involved in preparing and carrying out prosthetics. All this will add up to the total cost of installing the prosthesis. The cost also depends on the location of the clinic, its accreditation category and the qualifications of the specialist performing the work. Only a dentist can decide which crown is suitable for the chewing tooth and which for the front one so as to have a sufficiently high quality prosthesis at minimal cost.
The price range (cost of product + cost of work) can be significant:
- metal made of base alloys - from 3,000 to 16,000 rubles;
- metal ceramics - from 7,000 to 40,000 rubles;
- ceramic – from 20,000 rub. and more.
Zirconium - an alternative to metal ceramics?
Above we compared all the advantages, disadvantages and features of both materials. Based on the information presented, we can conclude that zirconium and metal-ceramic crowns are worthy options for prosthetics, but they are designed for different groups of patients. Metal-ceramics can be used for those patients who value reliability, reasonable cost and do not need ideal aesthetics. Zirconium crowns are chosen by those patients who are most concerned about the aesthetic issue and other characteristics are not so important.