Conservative method of treating pulpitis
The simplest option used by dentists for patients suffering from focal, acute and fibrous infections. It consists of carrying out a certain list of fairly easy and quick procedures:
- Anesthesia using local anesthetic drugs.
- Removing affected tissue using, for example, a drill.
- Treatment of the oral cavity with any specialized antiseptics.
- Applying an insulating pad.
- Installation of a temporary filling product.
The result of such operations is a whole range of positive aspects. The patient's severe inflammation is relieved, metabolic processes are restored, dentin regeneration begins, and so on.
Pulpitis of the tooth and its treatment
A characteristic sign of this pathology is inflammation in the pulp, which is located inside the tooth cavity, where blood vessels and nerves are concentrated. The cause of inflammation is the penetration of harmful bacteria into the cavity due to damage to the external dental tissues (enamel and dentin). This is the destruction that we most often owe to untimely treatment of deep dental caries: pulpitis becomes a consequence of the carious process. Much less often, it appears due to mechanical damage to the pulp, poor preparation of the tooth for filling, and unprofessional installation of orthopedic structures.
Treatment methods for pulpitis
In dentistry, two main methods are used to treat dental pulpitis in adults and children:
- biological - drug treatment of pulpitis with antibiotics and medications;
- surgical - treatment of pulpitis by amputation (partial removal of the pulp) or extirpation (in which the nerve of the tooth is completely removed).
The choice of technique remains with the dentist. The doctor studies X-ray diagnostic data, interviews and examines the patient. Based on these data, he selects the most rational method of treating pulpitis for a particular case.
Can pulpitis go away on its own?
Pulpitis is a pathological process that develops in the so-called pulp chamber, where all the nerve endings and vessels feeding the tooth are concentrated. Most often it occurs as a complication of caries, when the cavity extends deep into the tissue. But a traumatic nature is also possible, for example, in the event of a fracture or severe bruise of a tooth, or careless medical intervention that results in overheating of the pulp or opening of its chamber. Pulpitis develops extremely rarely against the background of only general somatic pathologies.
What are the symptoms?
A typical sign of the disease is aching pain. At first, it makes itself felt only when exposed to temperature stimuli, when we eat something very hot or, on the contrary, cold. As the pathology develops, the pain syndrome practically does not leave the patient, disturbing him even at night, which significantly reduces his quality of life. The pain becomes simply unbearable; due to the spread along the entire branch of the trigeminal nerve, it radiates to the temporal and ear regions.
What if the pain went away?
But what if the patient suppressed this pain for a long time with strong analgesics and finally it went away? Elimination of the main symptom contributes to the formation of the erroneous opinion that pulpitis can go away on its own. In fact, this is of course a common misconception! Temporary subsidence of pain only indicates the transition of the disease from an acute to a chronic stage. Unfortunately, it is the meager symptoms of chronic pulpitis that are one of the main reasons for late visits to the doctor and the development of complications:
- periodontitis
(an inflammatory process that begins in periodontal tissues), which is manifested by sharp pain concentrated on the affected side; upon transition to the stage of purulent inflammation, the pain becomes throbbing, purulent exudate is separated, collagen fibers are gradually destroyed, which is accompanied by severe swelling, increased body temperature and a deterioration in the patient’s general well-being; - tooth loss
- occurs as a result of the destruction of the periodontal ligaments, which are responsible for holding the tooth in the alveolus; - periostitis
(inflammation of the periosteum) with the formation of flux, characterized by severe pain and swelling (swelling of the gums and cheek), develops as a complication of periodontitis or in parallel with it; in the absence of proper treatment, a fistula tract occurs, through which purulent masses come out, after which short-term relief occurs, but the infection in the tissues persists and continues to spread; - periodontitis
(inflammation of the periodontium) is dangerous due to the gradual recession (loss) of the gums, resulting in adentia (loss of a tooth - one or several at once); - systemic diseases
(blood poisoning, phlegmon, etc.) are serious complications and occur against the background of long-term infection of the soft tissues of the face.
To avoid this, you should not wait for pulpitis to go away on its own. Toothache cannot be tolerated! It is the first signal that something is wrong. Therefore, it is important to visit the dentist on time in order to diagnose and treat the disease in the initial stages, before life-threatening complications arise.
Read more:
- Fear of the dentist
- Why does a dentist need a microscope?
Biological method of treating pulpitis
If the disease has become chronic, a biological method or conservative treatment of pulpitis with calcium is used. The process involves applying therapeutic pads containing calcium preparations. The technique is also used in the following cases:
- if the pulp was accidentally exposed during the caries treatment procedure;
- when you need to strengthen the bone partition between tooth enamel and pulp.
The specialist applies a drug for the treatment of pulpitis to the site of thinning bone tissue and thereby strengthens it. Next, the tooth is filled and monitored over time, conducting X-ray examinations at certain time intervals. The method is suitable:
- children with baby teeth;
- patients under 30 years of age during the treatment of reversible pulpitis;
- everyone who takes special care of their oral cavity.
If, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth aches, hurts when pressed or bitten, and the pain remains for a long time, intensifies at night, and becomes long-lasting, you must return to the clinic. Aching pain during the treatment of pulpitis indicates that more radical, that is, surgical, methods are needed.
Indications during pregnancy
There is a myth that it is impossible to treat teeth while expecting a baby. This misconception can have serious consequences. Infection, for example in the form of caries, through blood vessels can spread throughout the body.
It is also a mistaken belief that x-rays harm the development of the fetus. It has been proven that modern equipment has a minimal radiation dose that does not affect the body. It is much more dangerous to bring the inflammatory process to a chronic state. Therefore, you should not delay treatment of pulpitis or caries when symptoms appear.
The process of bearing a child is associated with a decrease in immunity, and as a result, with increased sensitivity to bacteria and infections. Tooth enamel in pregnant women is not as strong, because... All nutrients are aimed at the growth of the baby. Therefore, the appearance of pulpitis and deterioration in the condition of the dentition is a normal phenomenon.
The second trimester is considered the optimal period for receiving dental care. During this period, the child is protected by the placenta from harmful substances. However, if an inflammatory process occurs in the dental nerve, it is not recommended to delay treatment so as not to expose the baby to unnecessary risk.
During pregnancy, the doctor chooses a gentle treatment method, when the filling is fixed only in the dental canals. If possible, without the use of anesthesia. After childbirth, the patient is given a permanent filling. X-ray examination is carried out only in emergency cases.
How is pulpitis treated surgically?
As we have already noted, there are two possible options for surgical intervention:
- treatment of pulpitis using the amputation method with partial preservation of the pulp;
- treatment with complete removal of soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves.
If there is an objective possibility, the doctor will remove only the top of the pulp - from the crown, leaving the root part. The blood supply and sensitivity (innervation) of the tooth will be preserved. The technique is used in the treatment of children - for milk or permanent teeth that have not yet fully grown. This allows them to form normally in the future. Treatment for pulpitis can be carried out in one visit.
Treatment of acute pulpitis
The above methods are ineffective in treating exacerbations of chronic pulpitis, an acute disease when the tooth becomes a source of unbearable pain radiating to the ear, temple, and back of the head. With these symptoms, endodontic treatment of pulpitis is carried out - with cleaning of the root canals and complete removal of the pulp.
In dentistry, two modern methods of treating tooth canals for pulpitis are used: devital and vital.
- Treatment of pulpitis using the vital amputation method is carried out by removing the nerve, washing, cleaning and filling the canal.
- Devital treatment of pulpitis involves the use of medicinal pastes and requires several sessions.
These treatment methods are most often used for pulpitis on permanent teeth.
What is pulpitis?
Pulpitis is an inflammatory process in the pulp (neurovascular bundle) and root canals of the tooth. The dental crown contains a cavity pulp chamber, where there is a plexus of blood vessels, connective tissue and nerve endings. All this together makes up the pulp, the main function of which is to nourish the coronal and root parts.
Under the influence of provoking factors, hyperemia of the pulp occurs. Most often, this is caused by caries in an advanced stage. Due to damage to the crown, soft tissues are exposed and primary serous inflammation occurs (the so-called initial type). In the absence of timely treatment, the disease develops into more severe forms and can lead to irreversible consequences.
Pulpitis of primary and permanent teeth has many similarities with other pathologies, so self-diagnosis is ineffective in most cases. However, there are a number of signs that are characteristic exclusively of pulp inflammation.
Stages and stages of tooth treatment for pulpitis using the devital method
- Stage I.
The tooth is anesthetized and the carious cavity is cleaned. The pulp cavity is opened. - Stage II.
A devitalizing paste is placed into the exposed pulp and the tooth is filled for 3 to 7 days. People still call the paste “arsenic,” although it has nothing to do with this substance. - Stage III.
During your next visit, your dentist will clean the root canals according to medical protocol. - Stage IV.
If there is a risk that the tooth will crack, it is covered with a crown. If the hard tissues are well preserved or only slightly damaged, they are restored. The tooth is strengthened with a fiberglass or metal anchor pin and securely filled with photopolymer material.
The treatment time for pulpitis depends on how damaged the tooth is, the age of the patient, whether there are complications, and how many root canals should be treated.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Many patients believe that treatment for pulpitis is painful. In fact, pain accompanies the disease itself, and not the procedure for its treatment. The pulp tissue and nerves become inflamed, which causes unbearable painful sensations comparable to an electric shock. Pulp removal is absolutely comfortable, because high-quality anesthetics completely relieve the patient of pain while the doctor prepares the canals. During treatment or after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts when the internal tissues are severely inflamed. Then safe painkillers are prescribed while healing occurs (1 - 3 days).
Diagnosis of pulpitis
Correct diagnosis of pulpitis is a primary task for any dentist, since this disease can be confused with caries, trigeminal neuralgia and exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. Each of these diseases is characterized by pain symptoms, so in order for the diagnosis to be correct, it is necessary:
- identify the causes of pain;
- determine the frequency of pain;
- determine the intensity of attacks;
- conduct a visual inspection;
- carry out x-ray diagnostics.
Possible complications
If you delay visiting the dentist, inflammation can spread to the bone tissue of the tooth - periodontium. This is how one of the most common and dangerous complications of this disease begins - periodontitis, which can lead to tooth extraction. Periodontitis also occurs due to an unskilled approach to cleaning root canals.
If you are concerned about an elevated temperature after treatment for pulpitis, urgently contact a more reputable dentist, as the inflammation is progressing. Professional clinics use modern methods of canal treatment using microscopes, binoculars, visiographs, endomotors, and apex locators. These instruments prevent the risk of complications.
Unfortunately, pulpitis remains a common occurrence after caries treatment. The reason for its appearance is the same - the unprofessional actions of a doctor who violated medical protocols and made mistakes when filling. Perhaps he accidentally opened the pulp and gave bacteria access to it.
How much does tooth treatment for pulpitis cost?
The final cost of pulpitis treatment is influenced by many factors: the degree of destruction of hard tissue, the number of canals in the tooth, the presence of complications, concomitant diseases, and the chosen treatment method. If the tooth is permanent and has one canal, then the procedure in Moscow clinics will cost from 5,000 rubles. This amount includes a full range of services: x-ray diagnostics, application of anesthetic, installation of a rubber dam, treatment of caries, treatment of dental canals with cleaning, installation of a filling. Price may change if multiple sessions are required.
Phases of the disease
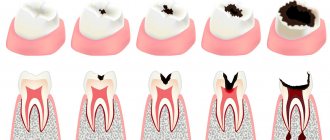
Classification of any disease contributes to quick and correct diagnosis and selection of an effective treatment method for the patient. In the case of pulpitis, everything is relatively simple, there are only two subtypes - acute and chronic.
The first type of inflammation occurs with advanced forms of caries. Bacteria destroy tooth enamel and dentin, and the infection enters the pulp. The disease is accompanied by aching, sharp pain, which intensifies with mechanical or thermal effects on the tooth. Severe pain attacks may occur at night.
Interestingly, only adults are susceptible to acute pulpitis. The anatomical structure of a child’s jaw protects him from illness.
This type can be focal or diffuse. Focal inflammation is characterized by local damage to the pulp, located close to the carious cavity. Accompanied by throbbing pain around the affected tooth. Lasts approximately 2-3 days.
Then the process moves to the next stage - damage to all tissues of the dental nerve. The pain syndrome changes from pulsating to constant, unpleasant sensations spread to the entire jaw. Pus forms in the tooth cavity. The phase lasts no more than two weeks. If timely treatment of pulpitis is not started, the pathology enters the chronic stage.