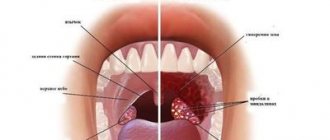
The norm is a small formation of light or white color. But a yellow coating on the tongue and bitterness already indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Any changes in the oral cavity are always scary and cause discomfort. A slight coating on the tongue is normal for both adults and children. However, if the formation has acquired an atypical hue and is accompanied by bitterness, then this may indicate signs of illness.
Plaque on the tongue: normal or not?
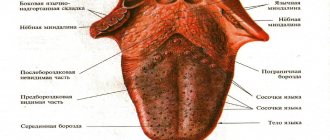
The human language is a kind of litmus test for the health of the entire organism. Normally, a healthy person should have a tongue without plaque, but this is ideal, which is rare today. If the tongue is coated, there are only two cases where you should not worry about it.
- After meal.
Eating foods such as strong tea, black coffee, red wine, blueberries, and beets causes temporary staining of the tongue and an unnatural coating on it, but both phenomena go away on their own and do not cause damage to health. - After the night.
A constant coating on the tongue in the morning is normal. At night, bacteria living in the mouth actively multiply, leaving traces of their vital activity. A thorough morning toilet will put everything in its place.
Tongue care kit from miradent.
When and which doctor to contact about a coating on the tongue
As a rule, tongue coating is not the main symptom.
And it is other symptoms that tell you which doctor you should see. If plaque on the tongue is accompanied by symptoms of ARVI, you should consult a physician. If you have symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases, contact a gastroenterologist. If there are no such symptoms, and the cause of your concern is plaque, in case of white plaque you can consult a dentist, in case of yellowish or gray plaque, you can consult a gastroenterologist. And in any case, you can consult a general practitioner - family doctor or therapist. A child with a persistent coating on the tongue should be shown to a pediatrician.
What if it's a disease?
A strong coating on the tongue and bad breath are already a reason to be wary. An experienced doctor will determine which disease the plaque on the tongue is a sign of, comparing the degree of density of the deposit, color and location.
Glossitis
One of the typical diseases characterized by plaque on the tongue is glossitis - inflammation of the tongue caused by injury or of an infectious nature. With glossitis, red spots appear on the tongue, which is why the disease is sometimes called “geographic tongue.” Read more in the article.
Gastritis
If your mouth is sour and there is a coating on your tongue, this is a sign of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Usually the plaque disappears if you follow a diet.
Thrush
With thrush, the plaque is located under the tongue. It is distributed unevenly and has the character of spots.
Chlamydia
With chlamydia, a sexually transmitted disease, a thick, sticky coating appears on the roof of the mouth and tongue as a result of a malfunction in the immune system after an attack by chlamydia.
Bronchitis and pneumonia
Plaque on the sides of the tongue will indicate an upper respiratory tract disease. In most cases, it is whitish and is easily removed by brushing your teeth and tongue, but also quickly returns to its original place.
Alcoholism
A coating on the tongue after alcohol abuse is common. People talk about this figuratively: “It’s like cats have shit in your mouth.” However, in chronic alcoholics, the dark brown coating never goes away and is localized at the root of the tongue.
Cancer
If the tongue is coated, one cannot say with certainty that a specific type of cancer is present. But it is precisely this symptom, coupled with a number of other characteristics, that indicates a complication of an oncological disease (for example, a malignant tumor in the lungs).
Plaque on the tongue of a pregnant woman, with rare exceptions, is not a sign of illness - it is the result of changes in hormonal levels.
How to remove and treat?
Note! If plaque is caused by dysbacteriosis, medications that contain live bacteria are prescribed.
They must be prescribed by a doctor; these can be tablets, capsules, powder for preparing a suspension, suppositories and microenemas.
For the treatment of dysbiosis the following are used :
- Probiotics – contain live bifidobacteria and lactobacilli (Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Acipol).
- Prebiotics - contain lactulose - a nutrient medium for beneficial microflora (Normaze, Duphalac, Lactusan).
- Symbiotes - contain live bacteria and substances for their nutrition (Bifidobak, Biovestin Lacto).
If the plaque is caused by thrush , the first thing you need to do is follow a diet.
Know! The diet should be based on fermented milk products, which will restore the balance of microflora, and the number of fungal microorganisms will again be controlled by beneficial bacteria.
also use :
- legumes;
- fruits and vegetables;
- natural fresh juices and compotes.
It is recommended to wear underwear made from natural materials , since synthetic underwear does not allow the skin to breathe.
Oral and genital very important .
Drug treatment is prescribed as the disease progresses:
- are used . They eliminate fungal colonies in the digestive tract, which have a complex effect on the rest of the body.
- Local drugs are used
- Immunomodulatory drugs . Increases the body's overall resistance to various pathological agents.
Reference! The following antifungal drugs are used:
- Nystatin;
- Pimafucin;
- Mikozan;
- Clotrimazole;
- Zalain;
- Livarol;
- Ginofort;
- Diflucan;
- Itrazol and others.
It must be said that treatment of thrush after taking antibiotics does not always necessarily require the prescription of antifungal drugs .
You should know! Sometimes microflora can be restored with proper nutrition. As soon as the microflora is restored, the coating on the tongue will disappear.
Treatment of the liver after taking antibiotics involves the use of traditional methods or medications.
The following herbs are useful for cleansing the liver :
- chicory;
- corn silk;
- milk thistle;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort;
- rosehip and many others.
As for medications, the following are prescribed :
- essential phospholipids – Phosphoglyph, Essentiale Forte;
- Ursofalk and its derivatives;
- plant flavonoids - Gepabene, Galstena, Karsil and their analogues.
Important! In addition, dietary food is prescribed - it is necessary to exclude salty, fatty, fried, spicy, as well as alcoholic drinks.
Recommended to use:
- low-fat soups;
- porridge;
- seafood and lean fish;
- vegetables;
- dairy products;
- garlic;
- honey;
- dried fruits;
- nuts;
- turmeric.
Main causes of plaque
- Infection.
The main cause of plaque on the tongue in adults is infectious diseases, characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. - Impaired immune function.
When the body's protective barrier cracks, this serves as a catalyst for the activation of pathogenic bacteria, which usually occurs against the background of an increase in body temperature. - Gastrointestinal pathologies.
Various chronic ailments of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Helicobacter. Plaque on the tongue due to gastritis, if the disease is not treated, becomes denser over time and provokes bad breath. A clear sign of enterocolitis in adults is considered to be plaque on the root of the tongue. - Side effect of drugs.
Plaque on the tongue after antibiotic treatment is a common phenomenon. Medicines that include substances that inhibit the growth of certain pathogenic bacteria negatively affect the acid-base balance in the mouth, which entails an increase in the number of microorganisms “responsible” for the appearance of plaque. - The consequences of nicotine.
If you are an “experienced” smoker, then you shouldn’t be surprised by a gray or yellow coating on your tongue. Nicotine abuse has a detrimental effect on the microflora of the body in general and the oral cavity in particular.
Attention!
A provoking factor for the appearance of plaque on the tongue is also helminthic infestations, such as giardiasis. For differential diagnosis in this situation, it is necessary to take a stool test for helminth eggs.
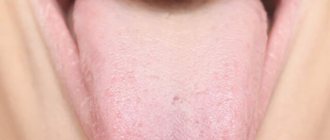
Physiological white coating on the tongue
White coating on the tongue is most often found in the morning. At night, less saliva is produced, which contributes to the activation of bacterial activity. As a result, by morning, almost all people develop a white coating on their tongue. Sometimes it is accompanied by bad breath.
As a rule, such plaque is easily removed during morning oral hygiene. When we brush our teeth, it is advisable to also brush our tongue, especially its root. Modern toothbrushes have a surface specially modified for this purpose (the other side in relation to the bristles).
However, the white coating disappears on its own as the day begins. It is erased when eating, and the greater amount of saliva released prevents it from forming again.
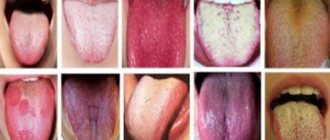
What does plaque color tell you?
White
As we have already said, a thin white mucous coating on the tongue after sleep is not a deviation from the norm. A white coating of increased density indicates constipation, and a cheesy coating on the tongue indicates the unhealthy activity of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
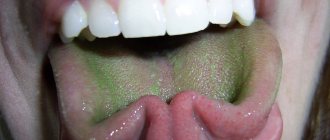
Yellow
A bright yellow coating on the tip of the tongue indicates hepatitis A (Botkin's disease). If there are problems in the functioning of the gallbladder, a yellowish coating and cracks appear on the tongue.
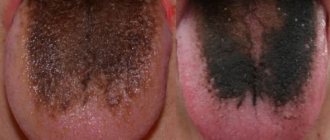
Dark
A dark coating on the tongue is a sign that something is wrong with the lungs. You don’t often see a completely black plaque: for example, in advanced stages of cholera due to dehydration of the body or in Crohn’s disease.
Diseases that cause plaque on the tongue:
- stomatitis;
- thrush (candidiasis). Caused by fungi of the genus Candida. The disease can be caused by long-term use of antibiotics or decreased immunity. With oral candidiasis, a typical manifestation is a dense milky-white coating that covers the tongue in spots. Similar spots may also appear on the roof of the mouth or gums. In severe cases, plaque covers the entire tongue as well as the walls of the throat, making swallowing and breathing difficult.
- scarlet fever. In the first days of the disease, the tongue is covered with a white-gray coating. Then the coating disappears, and the tongue acquires a crimson color;
- whooping cough. A pale yellowish coating on the tongue may be accompanied by bad breath;
- dysentery. A thick white coating is typical;
- cholera. Characterized by a dark coating (even black);
- diphtheria;
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- enterocolitis;
- pancreatitis;
- stomach cancer;
- kidney diseases;
- some other diseases.
What to do?
How to remove plaque from the tongue? To begin with, determine exactly the reason why the plaque occurs and treat the underlying disease by following the doctor’s instructions. For preventive purposes, in order to minimize the amount and density of plaque, you must follow simple rules of personal hygiene:
- brush your teeth in the morning and before bed with toothpaste and a brush that has a tongue cleansing pad;
- use antibacterial mouthwash;
- use a special spoon to clean the tongue, moving from its periphery to the front surface.
For a detailed article on how and how to properly clean your tongue from plaque, read a separate article.