How does the infection manifest and why is it dangerous?
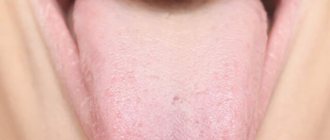
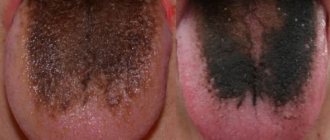
The most striking symptom of oral candidiasis is a white, loose coating on the mucous membrane. It mainly covers the tongue, cheeks, and may affect the gums and palate. Plaque can be easily scraped out; the tissue underneath is prone to redness and may bleed. Other signs of the disease include:
- unpleasant taste;
- dry mouth;
- burning;
- the appearance of cracks in the corners of the lips;
- difficulty or painful swallowing;
- unpleasant sensations with habitual movements of the tongue.
Candidiasis can be acute or chronic. In most cases, it is the acute form that manifests itself; the chronic form is typical for carriers of HIV infections and smokers. Depending on the degree and form of the disease, other symptoms may be observed, so even if one or two appear, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Kinds
- The most common is simple or, as it is also called, flat leukoplakia . It is usually discovered by chance during an examination by a dentist, since the patient does not experience any subjective sensations. A burning sensation occurs extremely rarely, and the appearance of the mucous membrane may change. If the disease affects the tongue, loss of taste may occur.
- Hairy leukoplakia of the tongue resembles stomatitis. The shape of the spot that appears, as well as its size, can be different, the color - from pale gray to white. The surface of the mucous membrane at the site of the lesion becomes slightly rough, which can be felt to the touch. On the cheeks it appears as solid or broken lines. It can also be found on the lips, where it looks like thin paper pasted on.
- Verrucous leukoplakia is the second stage of the development of the disease. The keratinization thickens, the affected area seems to rise above the nearby tissues. When you touch it with your fingers, you feel a compaction.
- Erosive form . Untimely diagnosis of the two previous stages of the disease leads to a worsening of the situation - the person feels pain when exposed to any irritants, erosions or ulcers are visible in the mouth.
- Soft leukoplakia is a type of cancer. Its distinctive feature is peeling of tissue in the area of the lesion. To clarify the diagnosis, a histological method of studying cells is required.
- Tappeiner's leukoplakia . This form of the disease affects people who abuse smoking. According to studies, daily smoking 10 cigarettes a day increases the chance of developing the disease by 50 times (as the number of cigarettes increases, the risk also increases)
The disease begins with the formation of lesions on the roof of the mouth (sometimes they appear on the gums). The mucous membrane changes its color to a pronounced gray or bluish, which is noticeable to the naked eye, folds appear on it. Reddish nodules may begin to appear, which is accompanied by infectious inflammation of the oral cavity (caused by the accumulation of salivary gland secretions in the tissues).
Causes of oral candidiasis
How does the disease occur? The fungus Candida lives in the body from birth and, under certain circumstances, provokes illness. What becomes the trigger for infection:
- weakened immunity;
- taking antibiotics;
- long-term use of removable dentures, especially if they do not fit tightly;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- smoking;
- oncology;
- use of inhalers for asthma;
- excess simple carbohydrates in the diet;
- pregnancy period;
- infancy or old age.
It can be seen that there are many reasons, often they act together, less often - individually. In general, oral candidiasis is rare in adults. It mainly affects children in the first years of life and older people. Among these categories, the prevalence of the disease reaches 10%.
Traditional treatment
If you detect plaque on the surface of the tongue or a feeling of bitterness in the oral cavity, you can resort to alternative treatment:
Salted water for mouth rinse
- A decoction of flax seeds helps with gastritis. To prepare 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the raw materials, leave for an hour and drink;
- to treat gastritis and other problems with the gastrointestinal tract, take infusions of various herbs (1 tablespoon per 220 ml of boiling water) - plantain, linden, yarrow;
- to remove plaque, the oral cavity is rinsed with an infusion of oak bark, chamomile, mint, and sage;
- Regular consumption of garlic (not recommended for gastritis). Helps in the fight against viruses and bacteria;
- rinse with salted water (1 tsp per glass). Destroys pathogenic microflora in the mouth and eliminates unpleasant odor;
- Cleaning your tongue with lemon. A small slice or juice diluted with water is used;
- use of soda. The abrasive qualities of the product will help remove plaque on the tongue, for which use a damp cotton swab;
- aloe, viburnum and honey in equal quantities. The mixture is consumed 1 tbsp. l. before meals, which is especially useful for gastritis;
- 1 tbsp. l. flaxseed oil mixed with 3 tbsp. l. vegetable juice (beetroot, tomato) and drink before lunch;
- juice from two lemons is mixed with 200 g of honey, 50 ml of olive oil. The product is taken 1 tsp. before breakfast.
Uses of lemon to clean plaque on the tongue
How is oral candidiasis treated?
To begin with, let's say that treatment is necessary, otherwise the infection spreads to the pharynx, tonsils, and gums. Then the disease descends into the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, liver and causes irreparable harm to them.
When the first signs of candidiasis of the oral mucosa appear, you should contact your dentist or therapist to confirm the diagnosis. When you see your doctor, describe all your symptoms, even those that are not on the list. For example, you have noticed increased anxiety or a tendency to stress lately. Information about the medications you are taking, recent illnesses, and being around sick people is also important. To confirm the diagnosis, it is often enough to take a swab from the oral cavity and carry out the appropriate analysis. If the disease has already spread to other organs, a more thorough examination may be required, for example, endoscopy - diagnosing the condition of the esophagus and stomach using a flexible tube with a camera at the end.
How to treat oral candidiasis? Treatment can be local or systemic depending on the form and stage of the disease. When local, antifungal agents and antiseptics are prescribed. These can be sprays, rinses, gels, lozenges and more. Treatment on average takes up to 3 weeks, as a general rule - until symptoms disappear and another week. Systemic treatment is used for chronic forms or when the infection spreads to other organs. It usually involves the use of more medications that are intended to treat the directly affected areas.
Under no circumstances resort to self-medication! A fungal infectious disease has nothing to do with inflammation, so your actions are more likely to harm your body. In doing so, you can reduce the harmful effects of the infection and make you feel better. To do this, eat natural yogurt without sugar and take probiotics as recommended by your doctor. But these actions are not a complete treatment for candidiasis in the mouth!
White plaque in a child
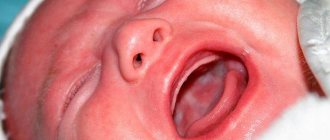
A white coating often appears on the tongue of a baby, which causes concern among young parents. What this manifestation indicates can only be said for sure by a doctor who will determine the causes of plaque in a one-month-old baby during the diagnostic process. But in some cases, if a white coating appears on the baby’s tongue, parents should not worry. This may be normal in the following cases:
if there is a thin layer of white plaque in the baby’s mouth, and it can be easily removed with a brush; a white coating on the tongue of a newborn appeared after feeding; if the baby recently drank milk or ate dairy products; if the child eats a lot of sweets (it is still important to limit sweets in order to avoid health problems in the future); if the baby does not like to brush his teeth; if staining occurs with chalk, paints, pencils.
But still, the pronounced white tongue of a newborn frightens parents. Most often, if an infant has a white tongue, we are talking about the development of thrush, which often occurs in newborns. As a rule, this happens if the child is bottle-fed, if he was born prematurely, or if he is not cared for properly. With candidiasis, a white coating may also be observed on the child's tonsils. In this state, the baby becomes restless, cries a lot, and refuses to breastfeed. Erosion appears on the mucous membrane, and the baby experiences pain.
Young mothers who do not know how to deal with such a disease should take into account that the likelihood of such a disease increases if a nursing mother consumes a lot of sweets, or if a baby who has been introduced to complementary foods eats a lot of sweets.
Also, the appearance of plaque and the causes of spots on a child’s tongue may be associated with other diseases:
Stomatitis is an inflammatory process of the oral mucosa. With stomatitis, ulcers in the mouth and a white or gray coating on the tongue may appear. The body temperature rises, the gray coating on the tongue, the causes of which are associated with stomatitis, becomes more pronounced. Ulcers, blisters, and red dots may appear on the tongue in the child’s mouth
It is important to ensure timely treatment for the baby.
Glossitis is an inflammatory process in which the baby’s tongue hurts on the sides or in another area. Sometimes parents notice that the child’s tongue is swollen and there is bad breath
Small bumps, ulcers, and plaque may appear. In severe cases, the body temperature rises. If parents notice that the child’s tongue is covered in pimples, and the red pimples that appear on the child’s tongue cause discomfort and inconvenience, they should definitely consult a doctor.
Caries and complications of this disease - with the development of caries, which is not treated, a stuffy and white coating may appear in the throat.
Tonsillitis is an inflammatory process of the palatine tonsils, in which the tongue and throat are coated, and sometimes red dots appear in the child’s throat. Sometimes parents note that red dots appear on the child’s palate. It is important to treat tonsillitis promptly to prevent complications.
Laryngitis and pharyngitis are infectious lesions of the larynx and pharynx. With the development of these diseases, a thick microbial coating appears on the tongue, and general intoxication of the body is noted.
A white coating on the surface of the tongue and near it also appears with more serious ailments.
- Scarlet fever is a disease characterized by a rash. If you look into the oral cavity of a sick child, you can see a crimson tongue, on which there is a sharp increase in the papillae. In this case, the mucous membrane is inflamed, and purulent plaque is noticeable on the tonsils.
- Diphtheria – with this disease, the baby experiences a white coating in the mouth and pain when swallowing. The tonsils are pink and swollen, and a filmy coating appears on them. The anterior cervical lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (obstruction is observed with gastritis, dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis).
- Flu and ARVI.
- Chronic hypovitaminosis.
In older people
White tongue in older men and women is often associated with the presence of dentures on the teeth. Because of these devices, bacteria can develop that cause the following pathologies:
- stomatitis;
- cheilosis
Elderly people are not always able to take good care of their oral cavity. They are often diagnosed with various diseases and reduced immunity.
The appearance of plaque is facilitated by the use of steroids for the treatment of asthma, lack of vitamins, and diabetes mellitus.
How to avoid candidiasis?
To prevent the disease, you must follow a few simple rules:
- maintain oral hygiene;
- consult a dentist at least twice a year, even if there are no complaints;
- control nutrition, avoid excess carbohydrates in food;
- refrain from smoking, which can cause a chronic form of the disease.
Treatment of candidiasis of the oral mucosa can take a long time and also cause irreparable harm to health, so we recommend that you take care of yourself in advance by following preventive measures. If symptoms have already begun to appear, consult a doctor as soon as possible so that the infection does not have time to spread to other organs. You can undergo oral cavity diagnostics at Comfort Dentistry. Our specialists will tell you in detail about the prevention of common diseases of teeth and gums, and also, if necessary, provide high-quality treatment.
Why did the sky turn yellow?
The palate area, like all areas of the skin and mucous membranes on and inside the head, has an abundant blood supply due to a dense network of capillaries. The palate owes its normal color to the color of the blood flowing through them: in hard ones it is pale pink, in soft ones it is also pink, but of a more saturated dark tone. When inflamed, the color may become flaming crimson or bluish with a purplish tint. If the palate turns red and the throat hurts, this is considered normal, but the palate should not be yellow. For what reason does its color change?
The first thing that comes to mind is smoking. Indeed, the resins contained in tobacco and released when it burns stain the oral mucosa, giving it various shades of yellow and cause the formation of plaque on the palate.
But in addition to direct coloring, smoking:
- causes disorders of blood microcirculation in tissues;
- changes the composition and properties of blood.
Blood cells that contain minimal oxygen become paler, as does the area they supply. At the same time, in the region poorly supplied by them, fatigue and aging of cells increase due to chronic oxygen starvation.
And finally, once the transformations begin, they become irreversible, leading to changes in the biochemistry of tissues and the loss of their original color.
Therefore, the palate in a smoker’s mouth becomes covered with yellow spots with red dots and veins - a picture of capillary paresis.
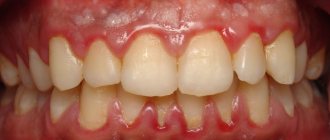
What color is the palate of a healthy person and what does it look like?
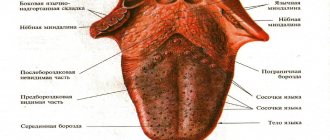
The palate of a healthy person In the upper part of the oral cavity is the human palate, which consists of two lobes: soft and hard. The hard palate is located closer to the dentition, and the soft palate is in the tonsil area.
Their structure is formed from sensitive tissues covered with a mucous membrane, which explains their tendency to immediately respond to various stimuli.
The mucous membrane of a healthy palate looks like this: it has an even color of a soft pink tone, no veins are visible on the surface. If any changes are detected, you should consult a specialist for advice.
After examining the oral mucosa and studying the characteristic signs, the doctor will give recommendations for additional examination. Based on the test results, an accurate diagnosis is made and an individual treatment regimen is developed.
You should not ignore the appointments, because a change in the color of the palate indicates that irreversible processes have begun in the biochemistry of tissues.
Source: dentoland.com
General information
Salivary fluid is approximately 95% water, while the remainder of the composition is a complex that includes enzymes, protein, acidic salt residues and other trace elements. An important function here is performed by the enzymes amylase and maltose, which help break down food particles after they enter the digestive system. The enzyme lysozyme helps maintain the natural balance of microflora, but mucin, which, by the way, is responsible for the foamy consistency of saliva, completely covers the food bolus and promotes its unhindered digestion.
Why does mucus appear on the tongue?
As a result, food passes through the esophagus without problems and enters the stomach, where the main process of digesting food and breaking it down into small particles occurs. Obviously, the degree of thickness of the salivary fluid determines how correctly the digestion process proceeds.
Epidemiology
The only source of infection is a person infected with this virus. The most dangerous are those who do not have any clinical manifestations: virus carriers are the main source of the spread of HIV infection among the population.
During a dental appointment, infection can occur in the following cases:
- when using medical instruments contaminated with blood or other biological fluid that have not been disinfected (various devices, discs, burs, probes, needles, syringes, cutting and piercing instruments, etc.);
- in the presence of wound surfaces and ulcerations in the oral cavity;
- in case of extensive contamination of the skin of healthcare workers with blood, blood getting into the eyes;
There are known examples of infection during acupuncture treatment.
(There is no airborne transmission of infection.)
The immunodeficiency virus is found in the highest concentration in the blood. Next in descending gradation are sperm, vaginal and cervical secretions of the glands, breast milk, and saliva. Blood and other specified biological fluids are factors in the transmission of HIV from an infected person to other persons.
The virus is moderately resistant outside the human body. In the external environment (biosubstrates), its infectious effect lasts up to 2 weeks, in a dried state (discharge on linen, objects, etc.) - up to 1 week. Radiation exposure and ultraviolet rays do not affect it. When boiled, the virus dies within 5 minutes; when heated to 56°C, inactivation occurs after 30 minutes. Disinfectants used in the practice of medical institutions (chloramine, calcium hypochloride, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, etc.) in concentrations provided for the disinfection of hepatitis viruses are guaranteed to destroy HIV upon direct contact of the disinfectant with contaminated blood or other human biological fluid on the surface of an object, including a hollow one ( internal surfaces of the syringe, needles, capillaries, probes, etc.).
Bacterial infections
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis develops in HIV-infected individuals both during various periods of clinical manifestations of AIDS, and without them in the presence of antibodies against the virus. Patients complain of pain and bleeding gums while brushing their teeth and eating; bad breath. Upon examination, a gray-yellow plaque (necrotic film) is found covering the gingival margin and interdental papillae. The mucous membrane in the gum area is hyperemic, swollen, and tense.
After treatment, the symptoms disappear, but there is a tendency to relapse. A prolonged course can lead to deep ulcers with damage to bone structures and necrotization of the interdental septum (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Herpes simplex on the lip.
The consequence of gingivitis is periodontitis (periodontitis) with irregular generalized destruction of bone tissue and the supporting-retaining apparatus of the tooth. Treatment of patients does not provide lasting results.