The state of the tongue reflects the state of the human body. That is why almost any doctor during an examination asks the patient to show his tongue. In a healthy person, the tongue has a pale pink color, pronounced papillae, and a straight fold exactly in the center. It should be soft to the touch, and moving it should not cause discomfort or pain. If you find that you have a white tongue, then there is a high probability of certain problems in the body. In this article we will talk about how dangerous the appearance of plaque on the tongue is, what causes and diseases lead to changes in the condition of the organ, and how this problem can be avoided and eliminated.
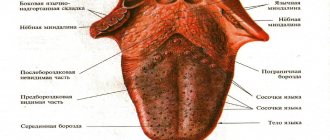
Anatomy: what does the tongue consist of?
The tongue is an organ that is part of the digestive system. It performs several functions:
- plays an important role in the formation of speech;
- helps form a bolus of food in the mouth and push it into the esophagus;
- helps us determine the taste of food.
What does language consist of? The organ is conventionally divided into two parts:
- the body of the tongue is the anterior movable part;
- The root of the tongue is the back part located closer to the larynx.
The tongue has a mucous surface on which taste buds are located, thanks to which we distinguish different tastes.
Hypovitaminosis
In the course of careful research, it was discovered that with a lack of vitamins PP and B vitamins in the child’s body, the mucous membrane of the tongue changes its color. Black plaques or spots appear.
Special cases
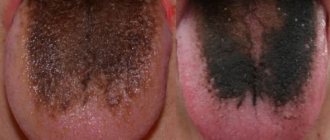
Difficult to explain cases include the so-called “black hairy tongue.” The nature of this phenomenon is still being studied, and today doctors cannot give a comprehensive explanation. The picture looks like this: at the tip and root of the tongue, the normal pink color remains, while multiple dark papillae grow on the back.
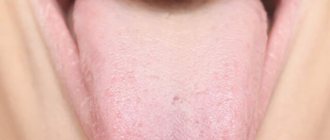
What does plaque on the tongue mean?
At different periods of time, the appearance of the tongue may change, and a coating on the tongue that has a whitish color is acceptable in a small amount. At the same time, the papillae are clearly visible through it. In summer, the thickness of the plaque may increase, and in winter it may acquire a yellowish tint.
When should you worry about tongue coating?
- if the tongue is constantly coated;
- the plaque becomes dense and completely hides the mucous membrane;
- the papillae of the tongue are poorly visible;
- the color of the tongue has changed (excessive pallor, redness, blueness);
- the plaque has a dense cheesy structure;
- unusual color of plaque - yellow, green, brown, gray, black.
With such signs, we can talk about both dental pathologies and more serious problems - acute and chronic diseases of internal organs. To get rid of plaque on the tongue, you first need to find out the reason for its appearance.
The first step is a consultation with a dentist. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will accurately determine whether the coated tongue is associated with caries, diseases of the oral cavity, and if not, he will refer you to other highly specialized specialists.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, the highest concentration of fungus is found on the surface of the inside of the cheeks, tongue, pharynx and tonsils, and palate. At an early stage of the development of the disease in children, redness of the mucous membranes is observed; they become swollen, the sensitivity of the mucous membrane increases, which is why children are often irritable, capricious, and their appetite and sleep are disturbed. The primary episode of the disease usually occurs in a more acute form; Patients may experience general symptoms: fever, headaches and dizziness, nausea or vomiting, deterioration in general health.
Some time after the onset of the disease, white grains begin to appear on the surface of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, which gradually increase in size and merge together, forming plaques, and then plaque covering large areas of the mucosa. During this stage, patients suffer from severe dryness and swelling in the mouth. The mucous membranes become painful. Burning, itching and other unpleasant sensations are most often associated with the development of an allergic reaction caused by the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and the release of toxins during their life processes. The pain intensifies when eating and swallowing food, when eating hot, sour, spicy foods and drinks. Infants often refuse to eat.
The plaque formed during candidiasis has a very characteristic appearance and resembles milk films or remains of cottage cheese. It consists of destroyed cells of the mucous membranes, food debris, bacterial mass, fibrin and keratin. Flakes, scales and plaque can also appear outside the mouth - on the edges of the lips. The spread of infection to the lips is called candidiasis. Because of this disease, the skin in the corners of the lips dries out and cracks; In some cases, the infection affects the entire surface of the lips, resulting in cracking and peeling.
In mild and moderate forms of the disease, plaque is easily scraped off, and underneath it, areas of erosion (ulceration) or maceration (softening) of the mucous membrane are found. A longer course of the disease and the lack of adequate treatment leads to deep damage to the mucous membranes, as a result of which blood appears on their surface, turning the plaque brown or brownish.
Why does plaque form on the tongue?
The most common and easily eliminated reason for the formation of white plaque on the tongue is poor oral hygiene.
However, there are other factors that influence the condition of the tongue. Among them:
- infectious diseases in the oral cavity (stomatitis, etc.);
- acute, chronic diseases and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- parasitic infection;
- candidiasis;
- kidney diseases.
Whether it is worth worrying about the health of certain organs can be judged by the color, nature and location of plaque on the tongue.
White coating on the tongue - what is it?
The main cause of plaque is poor hygiene and the resulting pathological conditions of the oral cavity. Therefore, first of all, you should see a dentist with such a problem.
In some cases, you can independently differentiate its causes by the color and location of the plaque. For example, why is the tongue white?
- 1
A white coating at the base of the tongue (in the root area) indicates high activity of bacteria or fungi. This may be due to both problems in the oral cavity and disturbances in the functioning of the intestines and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. - 2
A thick white coating on the tongue is usually caused by an infection of the tonsils, respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract.
- 3
A white, cheesy coating on the tongue is a sign of candidiasis (thrush).
- 4
A white coating on the tongue, as well as on the mucous tissues of the oral cavity, indicates stomatitis.
Yellow coating on the tongue
If your tongue turns slightly yellow in hot weather, there is no cause for concern. An alarming sign is the formation of a pronounced yellow coating on the tongue, which most often indicates serious disturbances in the functioning of the liver, gall bladder, and other pathologies of the digestive system.
Why is the tongue yellow?
- A small yellow plaque that appears in the morning and is easily removed during standard teeth brushing may indicate intoxication of the body (metabolic disorders, excess toxins). If the tongue remains clean for several hours after the procedure, then it really is a matter of toxins. To get rid of plaque, the patient needs to change his diet in order to normalize the functioning of the digestive system.
- Yellow plaque, loose in structure, combined with a specific taste and bad breath is a sign of serious disorders in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, requiring appropriate diagnosis and treatment. If such plaque appears, you need to contact a gastroenterologist.
- Yellow plaque in tandem with a high temperature may indicate inflammation of the ENT organs (pharyngitis, sore throat).
In addition, a yellow coating on the tongue inevitably appears in smokers, coffee and black tea drinkers.
Black coating on the tongue
Black plaque looks especially scary; it can occur with long-term use of antibiotics and a number of other medications, and can also indicate a number of diseases:
- infectious disease, in particular cholera;
- Crohn's disease;
- acidosis – PH disturbance;
- viral sore throat.
A dark tongue may have a purple tint, which indicates blood diseases, including anemia. A plaque with a blue tint is one of the symptoms of dangerous diseases such as dysentery and typhoid.
Treatment
Treatment for childhood gingivitis is practically no different from how adults are treated. Only medications used for them are softer and more gentle. Treatment begins with professional cleaning of hard deposits and plaque of tooth enamel - mechanical or ultrasonic.
If caries is detected during the examination, then therapeutic treatment is carried out. Gingivitis is then treated with medications with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. Measures are taken to eliminate detected pathologies (bite, frenulum, etc. are corrected).
Ointments and gels are considered effective for children under 4 years of age. For example, Cholisal ointment has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, which makes it possible to prescribe it to alleviate the patient’s condition, especially when baby or permanent teeth are cutting. Ointments and gels are applied directly to the inflamed area.
Antibiotics in tablets or in the form of injections are prescribed to children in difficult cases (the presence of infections of bacterial origin in the body). At elevated temperatures, rinses, drinking plenty of fluids, antioxidants, antipyretic drugs for children, and taking vitamins are prescribed.
Prevention measures should include regular visits to the pediatric dentist, training in oral care rules, and parental monitoring of the development of hygiene skills.
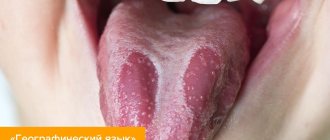
Why does the coating on the tongue have spots?
In most cases, spots on the tongue have nothing to do with dangerous conditions and diseases. However, it is imperative to find out their cause and pay attention to eliminating the causative factors.
What types of spots exist and why do they appear:
- the tip of the tongue turns red and goes numb - most likely this happened as a result of injury (burn from hot, spicy food, smoking), and problems in the intestines and heart are also possible;
- bright pink spots on the tongue - depending on the size and location, they can be caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12, folic acid or the development of scarlet fever, migratory glossitis;
- bright red spots on a pale tongue are a symptom of scarlet fever, but also appear against the background of anemia, in smokers;
- red dots combined with a whitish coating at the root of the tongue most likely indicate diseases of the digestive system.
How to remove plaque on the tongue?
- 1
Contact your dentist for advice. He will examine the oral cavity for dental diseases, carry out treatment if necessary (treatment of dental periodontitis, etc.), if plaque is associated with inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, and give recommendations on proper hygiene.
- 2
If the cause of the plaque is not related to dental health, the doctor will refer you to other specialists for examination.
What absolutely should not be done if plaque appears on the tongue:
- touch it with your hands;
- independently prescribe treatment for yourself, take medications without consulting a doctor;
- use solutions containing alcohol, iodine, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green to clean the tongue;
- take vitamins without prior examination and doctor’s prescription.
In case of plaque or rashes on a child’s tongue, you need to be careful when planning your diet and do not introduce new foods, as they can provoke an allergic reaction and aggravate the situation.
How to get rid of plaque on the tongue?
- drink enough fluids, especially in hot, dry weather;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- introduce solid raw fruits and vegetables (apples, carrots) into the diet;
- take care of the health of the digestive system - adhere to a healthy diet, which will restore the intestinal flora, improve the functioning of the liver and pancreas, and normalize the acid-base balance;
- monitor the health of teeth and gums, undergo dental treatment on time;
- observe the rules of oral hygiene.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on the results of studying the medical history and life of the child in combination with a dental examination. The patient’s complaints, the presence of somatic diseases, and whether he is taking medications that may cause the development of gingivitis are clarified.
Then the doctor conducts an external examination, paying attention to maxillofacial anomalies, the condition of the teeth and gums, and makes a diagnosis. The dentist does not require the help of other specialists, since the disease clearly manifests itself externally and does not require instrumental examination.