Types of pediatric anesthesia How does it work?
Signs of proper sedation Drugs Indications Contraindications Possible complications Alternatives Most people associate going to the dentist with fear and stress. And if we are talking about a child, then the whole family is afraid of the visit. Therefore, the promises of dental clinics about dental treatment under anesthesia for children, without pain, in their sleep, sound like a balm. What is meant by “pain-free treatment” and is it as safe as we are told?
Sedation
– this is inhibition (depression) of the nervous system in order to relax and reduce anxiety. It does not exclude the use of local anesthesia, but simply helps overcome the fear of treatment. This is the main difference between dental treatment under sedation in children and the use of anesthesia.
But the word “sedation” did not catch on among the people, and gradually even dentists began to use expressions like “treatment of children’s teeth under anesthesia” in order to be understood by a wider audience. In this case, what is often meant is not general anesthesia, but rather sedation, a condition in which consciousness is suppressed while all protective reflexes are preserved and the possibility of contact with the patient is preserved.
Types of anesthesia for children during dental treatment
Depression of consciousness can be deep, medium and superficial.
Medicines can be administered in different ways:
- Orally
. This is how we take regular pills. - Intravenously
. Oddly enough, some children are more comfortable with an injection than with a mask on their face. - Inhalation
. This is the most common way of administering drugs. Nitrous oxide is most often used.
Do I need to prepare my child for sedation?
In principle, no. You should not overeat before the procedure. It is better to refrain from strong emotions the day before.
If in doubt and want to be on the safe side, you should take a general blood test and do an echocardiogram. You can show the doctor your medical card or tell in detail about past or chronic illnesses.
Is it worth telling the baby about the upcoming treatment? Here each parent decides for himself.
Some experts advise not to tell anything, because they themselves will tune their patient to the desired wavelength. Some children are so anxious that they don’t trust anyone except their dad and mom. Then it’s worth informing in advance what will happen in the doctor’s office. You can promise a prize to the bravest, and when it's all over, go to the toy store.
How it all happens
Treatment of children's teeth under anesthesia begins with an acquaintance and conversation with the doctor. Sometimes they play cartoons in the office, and some clinics offer toys. Then he is allowed to examine the mask, is asked to try it on, and they begin to supply pure oxygen, to which nitrogen is gradually added, increasing its concentration. After a couple of minutes the child falls asleep. After this, sensors for monitoring his condition are connected to him and treatment begins.
The duration of dental treatment in a dream varies depending on the defect, complexity of the process and other factors. At the end, they are given oxygen again. After the procedure is stopped, the child wakes up gradually. He is under the supervision of doctors for at least an hour in a specially designated room. That day it is better for him to stay at home and not visit the children's group.
When using tablets or intravenous drugs, the algorithm of action is the same, only without a mask and oxygen.
Sedation is not anesthesia
Anesthesia is used in pediatric dentistry. But this requires serious reasons, thorough preparation and follow-up. In some cases, dentists issue special referrals for treatment under anesthesia. Not every clinic can provide such therapy.
Sedation cannot be called anesthesia either. It does not block pain, so the anesthetic injection is not canceled. But the calmed baby won’t even notice him.
The procedure is very common and loved by dentists, as well as parents, who have already tried it and are convinced that there are practically no risks. We leave the “practically” remark for extreme cases, because all children are different, and in any case an individual approach is needed.
What drugs are used
Nitrous oxide or other drugs are used for inhalation anesthesia. The instructions for use of such drugs list as side effects: respiratory problems, cardiac depression (depending on the dose), nausea, vomiting. But worst of all, with a genetic predisposition, a dangerous disease can develop
[1] – hyperthermia. The chances of this happening are slim, but no one does genetic testing before dental treatment, so the possibility cannot be ruled out.
Other drugs are used intravenously and orally (in tablets), which also have side effects, although not as pronounced.
What is sedation: main advantages
Sedation is a technology that is aimed at normalizing the mental state and relaxing a person during therapy. The technique involves a slight effect on the central nervous system. It is carried out using “laughing gas” - a mixture of nitrous oxide (N2O) and oxygen (O2). By inhaling it, the patient’s pain sensitivity decreases, the urge to vomit is suppressed, and psycho-emotional stress is managed.
Unlike anesthesia, when a person falls into an unconscious state, under the influence of nitrous oxide he is conscious, breathes naturally, and can communicate. This is the main advantage of the technology. There is no recovery period or side effects. It is important to note that nitrous oxide is not addictive. Sedative dental treatment for children is carried out in comfortable conditions.
When is it worth treating children's teeth under general anesthesia in dentistry?
Due to the fact that the terms “sedation” and “anesthesia” are often used interchangeably, it is not always clear which procedure is being referred to.
If you were offered dental treatment for children in a dream, clarify this means sedation or anesthesia.
The main rule is that if you can avoid anesthesia, it is worth doing. Sedation is preferable, although it is also not a panacea. Studies on the long-term effects of general anesthesia show that the use of anesthesia can lead to problems in the development of cognitive functions
[2], especially if it is used repeatedly, which happens when treating children’s teeth in clinics where they take general anesthesia lightly.
There is a risk when using anesthesia
[3]:
- Airway obstructions
. This may be due to anatomical features (adenoids, enlarged tonsils), incorrect position of the jaw or tongue, or accumulation of sputum. Equipment failure can also lead to collapse. - Hemodynamic problems
. Complications include: slow (bradycardia) or, conversely, rapid (tachycardia) pulse, drop in blood pressure, puncture of a vein with a needle.
After such anesthesia, children may experience nausea, vomiting, impaired thermoregulation, muscle tremors, allergic reactions, and inappropriate behavior.
Anesthesia is recommended only in cases of absolute intolerance to local analgesics; in other situations, local anesthesia or, in extreme cases, sedation should be preferred.
Sedation does not have such a radical effect on the body, but the risks remain the same - problems with breathing and circulation.
In the vast majority of cases, complications during the use of anesthesia are caused by a doctor’s error. You need to be absolutely sure of:
- doctor's qualifications and experience;
- equipping the clinic with the necessary equipment to monitor the condition during anesthesia and to provide assistance if something goes wrong.
Although dentists have special training in the administration of sedatives, anesthesia should only be administered by an anesthesiologist.
Nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation in pediatric dentistry. Technology and application experience
Nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation (NAS), an inexpensive and effective alternative to general anesthesia, has become firmly established in the dental practice of many developed countries of the world: the USA, Germany, France, Austria, Australia, etc. Nevertheless, this technique is used in Russian (Soviet) dental practice For some reason it was not used until recently.
In Russia, as well as throughout the world, anesthesia using nitrous oxide has always been widespread. It is still widely used in surgical practice, operative gynecology, surgical dentistry, as well as for pain relief during childbirth, relief of pain attacks in acute coronary insufficiency, myocardial infarction, acute pancreatitis and other pathological conditions accompanied by pain that is not relieved by conventional painkillers. . ZAX sedation is making its way into Russian dentistry, and especially in the field of pediatric dentistry.
The article describes the main properties, indications and contraindications, as well as experience with the use of nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation in children.
To provide high-quality dental care to a child, it is necessary to create conditions in which he feels calm and comfortable. Anxiety and fear interfere with the work of a dentist, and often make it impossible or seriously affect the quality and prognosis of treatment.
Unfortunately, in our country the practice of treating children against their will is still widespread. This not only makes it difficult to carry out adequate diagnostics, but significantly narrows the choice of treatment methods and materials. Treatment of children who behave well at the initial appointment can also turn into a problem. Many pediatric dentists have encountered a situation where, during one of the visits, the child simply closes his mouth and does not allow him to complete what was planned.
With the advent of modern sedation technology, dentists can provide their patients with truly stress-free treatment.
Sedation is understood as minimal depression of consciousness, in which protective reflexes, the ability to breathe independently, and verbal contact are preserved. The choice of a sedative drug in pediatric practice largely depends on the experience of the doctor and the technical equipment of the clinic.
In the West, nitrous oxide is most often used in pediatric dentistry - oxygen sedation (NAS). Nitrous oxide is an inert gas with a subtle sweetish odor; when mixed with oxygen, it provides the safest and most harmless sedation for the patient. ZAX has been regularly used in dentistry since 1948, and currently, in 80% of cases in children, this type of sedation is used.
Nitrous oxide is supplied using special equipment. The device is a rotameter that allows you to adjust the ratio of gases in the mixture, a reserve bag, a breathing circuit with a nasal mask and a source of gases (cylinders or a centralized system). The gases exhaled by the patient are evacuated by high-speed suction.
Indications for the use of ZAX in pediatric practice are:
- The need to relieve moderate fear of dental surgery in a cooperative child. Usually these are children over 3 years old.
- The first treatment at the dentist, which allows you to form a stereotype of a non-scary treatment.
- Increased gag reflex.
- Traumatic interventions (local anesthesia, removal, preparation of carious cavity).
- Long-term treatment.
Contraindications to ZAX are:
- The child has a strong fear after a negative experience of treatment at the dentist and reluctance to contact the doctor.
- The child is too young when he is not ready to cooperate.
- Mental illnesses and intellectual disabilities that interfere with the ability to negotiate with the child.
- Impaired nasal breathing (adenoids, ARVI). The child will breathe through the mouth and will not be able to use the nasal mask.
- A full stomach, as nausea and vomiting may occur. The last meal should be taken 2 hours before the start of sedation.
- Hyperexcitability, since there is a possibility of a paradoxical reaction to sedation. Having some experience, the doctor, analyzing the child’s behavior during the consultation, can predict what impact the ZAX will have on the patient.
It is important to remember that successful use of ZAX is only possible in combination with the use of behavior management techniques. Trying on a mask takes place in a playful way. The doctor explains to the child in an accessible form what will happen to him. It is important to obtain the patient’s voluntary consent to wear a mask: this is the first component of success. In children's practice, scented masks and masks of various colors are used, which makes the choice and the procedure itself more pleasant.
Introduction to a state of sedation begins with the supply of 100% oxygen at a rate of 4-6 l/min, with the gradual addition of nitrous oxide. The permissible concentration of nitrous oxide is 50%. The most optimal ratio at which the planned treatment can be carried out is 30% nitrous oxide and 70% oxygen. However, adjusting the concentration of nitrous oxide depends on the effect, and in each case this is an individual indicator that is recorded in the map. After the start of inhalation, the blood is saturated with gas within 5-7 minutes. The difference between ZAX and other sedative drugs is the rapid onset of sedation and the absence of a trace effect; nitrous oxide is completely eliminated from the body within 5-10 minutes of inhalation.
For the most unpleasant and painful procedures, such as tooth extraction with a diagnosis of periodontitis, it is possible to temporarily increase the concentration of nitrous oxide up to 50%. Nitrous oxide has an analgesic effect and potentiates the action of local anesthetics. Even if the child is scared or feels discomfort, after the end of the manipulation he quickly calms down and gives the opportunity to calmly continue the treatment. The use of ZAXS allows for complex and fairly long-term treatment. For example, treatment of pulpitis followed by restoration with composite materials or standard crowns in one visit. Completion of work must be carried out on traces of nitrous oxide. The exit from the state of sedation should be smooth and ends with inhalation of 100% oxygen for 5-10 minutes. At this time, the doctor can communicate with the child, reinforcing his positive impressions of visiting the clinic. The effect of ZAX is due to nonspecific depression of the central nervous system.
Comfortable, relaxed state; pleasant mood; soft, relaxed, inhibited body movements; lack of resistance; deep breathing; decreased motor activity of the eyes, easily fixed gaze; decreased perception of sound are all symptoms of sedation. The patient may be disoriented and easily suggestible. The use of ZAX significantly facilitates the treatment process for both the child and the dentist. Children develop a positive attitude towards dental visits, which instills in them a culture of dental health. New prospects open up for the pediatric dentist to provide higher-quality, more extensive, smoother treatment!
Types of sedation: superficial and deep
The following sedative methods of relaxing and calming patients are used in dentistry:
- Superficial is the best solution in a situation where the patient requires relaxation for a short period of treatment. Indicated for adults, as well as children from the age of three. A state of pleasant slumber is achieved by inhaling oxygen mixed with nitrous oxide. The nasal mask through which the gas passes is connected to the machine. The doctor can change the ratio of components and dosage based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Deep - the medication is administered through an intravenous injection. This technique copes better with severe fear and anxiety. The technique is used for adults and children at least 15 years old. The relaxed state lasts longer than with a superficial state. The patient will need to stay in the clinic for some time and stop driving for 8 hours.
Anesthesiologists at the Refformat dental clinic in Moscow have been working with a wide variety of patients for a long time and their experience makes treatment safe. Any intervention, preparation and installation of prostheses will be comfortable and unnoticeable.
Types of pain relief in children
Before starting dental treatment, the doctor simply gets to know the child and talks about the equipment and tools in an entertaining way. After examining the oral cavity and making a diagnosis, the doctor notifies the parents in detail about the treatment plan. If a painful manipulation is required, one of the methods of anesthesia is used.
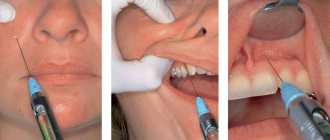
Local anesthesia
This is usually a combination of a topical spray to give the injection and an injection of anesthetic. The medicine is diluted taking into account the baby's weight. For application, a gel or solution based on lidocaine is often used. Articaine, a vasoconstrictor, is suitable for injection.
General anesthesia in dentistry for children
This is the only possible option in difficult cases. The method is used only when it is impossible to eliminate the pathology otherwise.
Alternative pain relief
In cases of moderate complexity, sedation is popular. Using the game moment, the baby is put on a mask. Inhalation calms and relaxes the child. He can follow the doctor's instructions. You can treat a child’s teeth under sedation by supplementing its effect with an injection of an anesthetic.