What role do baby teeth play?
It was not by chance that nature provided for the replacement of temporary teeth with molars. Baby teeth help the baby switch to a regular adult diet, stimulate the development of jaw bone tissue and create favorable conditions for the teething of a permanent set. If there had not been such a change, then the molars simply would not fit on a small child’s jaw and would not be able to fully perform their immediate functions.
How to go to the dentist, remove a baby tooth and not scare your baby?
It is recommended that a child’s baby teeth be removed by pediatric dentists: it will be painless, safe and timely. For everything to go smoothly, a visit to the dentist should be associated with something pleasant and calm. Modern dentistry has a friendly atmosphere, new painkillers have appeared, and instruments (especially in children's offices) do not inspire fear.
Finally, our advice: don’t worry and don’t let your child worry. The calmer you are about going to the dentist, the calmer your baby will behave. Stay nearby in the dentist's office, because parental support is extremely important to him.
Treat or remove?
To this question, the simplest answer that comes to mind first is to remove it, since this will help solve all the problems in one visit to the dentist’s office. However, if you dig deeper, it will be obvious that the simplest solution is not always the right one.
The consequences of premature loss of a baby tooth are quite serious:
- Earlier removal of temporary teeth leads to the fact that the remaining ones try to fill the vacated space and, in short periods of time, move towards the empty space. Because of this, molars can erupt in the wrong places and lead to severe malocclusions, which will require complex, lengthy and expensive orthodontic treatment.
- After the removal of a baby tooth, the bone tissue of the jaw ceases to experience the necessary load, which is why the rate of its growth and development decreases. Subsequently, such processes can lead to the fact that when the molars erupt, they will not have enough space, and they will grow crookedly and overlap each other.
- Long-term absence of chewing teeth and insufficient processing of food during chewing can cause the development of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- For a school-age child, the absence of front baby teeth can become a serious psychological problem, which will complicate relationships with peers and negatively affect the formation of personality.
It is because of these consequences that in modern pediatric dentistry, when it comes to removing or treating, if possible, preference is given to the second option.
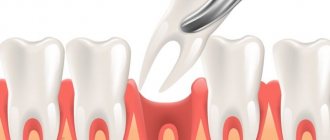
Removal of baby teeth: features of the procedure
The procedure for removing temporary children's teeth has certain subtleties due to the peculiarities of their structure. Removing a baby tooth is a last resort, since early loss of primary teeth negatively affects the permanent bite
During the natural process of changing teeth, sooner or later children's temporary teeth fall out on their own, and permanent teeth appear in their place. However, sometimes situations arise when it is necessary to remove a child’s baby tooth ahead of time. Let us consider in what cases there is a real need for the removal of a temporary tooth, as well as the features of the procedure for extracting baby teeth.
What are baby teeth used for?
The appearance of temporary teeth in children is due to natural necessity. After all, the jaws of a small child are still too small to accommodate a permanent set of “adult” teeth. However, the baby needs a chewing apparatus here and now so that he can switch to a regular diet with dense foods. Another function of baby teeth is to promote the proper development of jaw bone tissue, preparing the conditions for the appearance of a permanent set of teeth. And this requires regular “chewing” load, which helps the formation of the jaw apparatus.
It is obvious that baby teeth have very important functions. Therefore, the common belief that there is nothing wrong with the early loss of a temporary tooth is completely erroneous. And competent pediatric dentists always carefully evaluate whether it is worth extracting a baby tooth, or whether efforts can be made to save it.
Treatment of a temporary tooth is preferable to extraction
At first glance, the desire to get rid of a diseased baby tooth according to the principle “no tooth, no problem” seems quite reasonable. Moreover, everything can be solved literally in one visit to the doctor, and modern paid dentistry for children has all the means for effective pain relief. Ultimately, a molar will grow in place of the baby tooth anyway. However, in fact, premature loss of a baby tooth can result in a whole host of problems in the future.
Consequences of early loss of a temporary tooth:
- malocclusion . Removing a baby tooth will free up space into which neighboring teeth will gradually begin to move. In the future, when a molar tooth erupts in place of the temporary one, it will not have enough space for normal growth. The result will be a crooked arrangement of the dentition with malocclusion. And correcting a bite in children is a fairly lengthy and complex treatment;
- developmental disorder of the maxillofacial apparatus . Extracting a baby tooth will cause the bone tissue to experience insufficient load, which will slow down its growth and development. In the future, this may cause the fact that there is not enough free space for the proper growth of molars, and the teeth will begin to grow crookedly;
- problems with the digestive system . If one of the chewing teeth has been removed, the consequence will be insufficient chewing of food for a long period. This can cause a number of chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- speech disorder . The front teeth are part of the speech apparatus, and the absence of one or more teeth will certainly affect the development of speech;
- psychological problems . The absence of a tooth in the “smile zone” can cause certain difficulties in communicating with peers and negatively affect the child’s self-esteem.
Obviously, the early loss of primary teeth does not remain without consequences, and sometimes quite serious ones. That is why dentists primarily consider the treatment of baby teeth in children, and only in the absence of alternatives - removal.
What is taken into account when removing children's teeth?
Anatomical features
Children's temporary teeth have certain anatomical features that doctors always take into account. In particular, the walls of the alveoli are relatively thin, and dental roots can go deep at a large angle. Therefore, for the procedure of removing baby teeth, special forceps are used that have a weakened fixation. This helps to virtually eliminate the possibility of damage to the tooth walls. The extraction technique itself is designed to extract the tooth in one movement so that the child experiences only a minimum of discomfort.
Anesthesia
Anesthesia for tooth extraction in children is not always required. If a loose baby tooth with almost resolved roots is extracted, then this procedure usually does not require special anesthesia. Most often, the child’s positive attitude and the doctor’s friendly attitude are enough.
For complex tooth extraction or nerve removal, local anesthesia may be used. The required dosage of the medication is calculated individually, taking into account the child’s parameters and the complexity of the procedure. Today's pediatric dentistry uses local anesthetics of the latest generation, which have maximum efficiency and safety. However, testing for possible allergic reactions remains mandatory.
Tooth extraction under anesthesia is a last resort option, which is suitable for small children under 1.5 years old or for children who react extremely strongly to the dental office. Modern intravenous drugs are used for this. Operations of this kind can only be carried out in serious dental clinics with a full-time anesthesiologist and a special license.
Indications and contraindications
We have already discussed possible unpleasant consequences associated with the early loss of baby teeth. Because of these consequences, there must be good reasons for removing a temporary tooth.
Indications for removal of baby teeth:
- advanced dental caries in children, leaving no opportunity for restoration of the dental crown;
- complex forms of diseases of dental and periodontal tissues (periodontitis, pulpitis), which carry the risk of death of molar rudiments;
- the presence of fistulas in the gingival tissues that cannot be treated by other methods;
- late resorption of the root of a baby tooth, interfering with the eruption of a permanent tooth;
- cases where the molar has erupted, but the temporary one is still firmly held in place.
It also makes sense to remove a loose baby tooth if it interferes with the child’s ability to eat or causes discomfort in other situations.
Contraindications to removal of baby teeth:
- childhood infectious diseases such as chickenpox, whooping cough, scarlet fever. Flu, sore throat, and acute respiratory infections may also be contraindications;
- acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity: stomatitis, gingivitis, candidiasis;
- the presence of diseases that cause bleeding disorders (leukemia, hemophilia);
- the presence of hematomas in the area where the baby tooth to be removed is located;
- severe health conditions associated with diseases such as epilepsy, heart disease, heart failure.
The decision to remove a baby tooth is made by the dentist separately in each specific case, taking into account indications and contraindications.
After milk tooth extraction
When removing a temporary tooth, the dentist must inform parents about how the child should behave after the procedure is completed. This is necessary to avoid complications and speed up wound healing.
Recommendations:
- after the tooth extraction procedure, you should not drink or eat food for 2 hours;
- for about 2-3 days, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions after meals and before bed;
- While the hole is healing, it is advisable to avoid eating spicy, salty or excessively hot foods;
- You should make sure that the child does not try to touch the hole with his hands or various objects;
- if bleeding occurs or symptoms indicate the appearance of inflammation near the hole, you must immediately go to the doctor.
Summary
The removal of baby teeth should be approached with caution, and the decision to carry out this procedure is made only by a doctor and strictly individually. It is unjustifiable to force the natural process of changing teeth: for the child, this is fraught with problems with permanent teeth in the future. It is reasonable for parents to make efforts to preserve their children's baby teeth. This requires proper oral hygiene, regular visits to the pediatric dentist, and, if necessary, timely dental treatment.
Indications and contraindications
Even though children's teeth will fall out naturally from the primary occlusion, the reasons for removing them prematurely must be quite compelling. Indications for such manipulation are strictly limited:
- Advanced forms of caries, in which the crown is so damaged that there is no technical possibility to restore it.
- Situations when the permanent tooth has already erupted, but the milk tooth sits firmly in its place and interferes with the normal growth of the root rudiment.
- The presence of a chronic fistulous tract on the child’s gums that cannot be cured by other methods.
- Severe forms of inflammation (pulpitis or periodontitis), when there is a high risk of spread of the pathological process and death of the rudiments of permanent teeth.
- Delayed resorption of the root of a temporary tooth, which interferes with the normal eruption of the permanent crown.
It is possible to remove a loose baby tooth in situations where it causes significant discomfort to the child and interferes with normal conversation and eating.
Removal is contraindicated in the following cases:
- The presence of an acute inflammatory process in the child’s mouth: gingivitis, stomatitis, candidiasis, herpetic rashes.
- If there are signs of infectious diseases of childhood: scarlet fever, whooping cough, chicken pox, as well as tonsillitis, flu or even a common acute respiratory infection.
- If the child suffers from diseases that interfere with normal blood clotting: hemophilia, leukemia.
- If the child is in serious condition and has heart failure, heart defects, or epilepsy.
- If there is a hematoma in the area of the tooth that requires removal.
In each specific case, the dentist decides whether to remove the temporary tooth or try to treat it.
«
Tooth extraction in children: indications
At the age of five or six years, the process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones begins.
Unfortunately, many parents mistakenly believe that there is no need to treat baby teeth. This often causes the development of pathologies that ultimately lead to the need to completely remove the tooth. Here are some indications for tooth extraction in children:
- Presence of advanced caries. If caries has destroyed a tooth so much that it is not possible to restore it, the doctor, as a rule, recommends removing the tooth;
- Development of a cyst at the base of the tooth. A baby tooth injures surrounding tissues and causes inflammation;
- Difficulty with baby tooth loss;
- The presence of serious damage - chips, microtraumas;
- Referral from an orthodontist;
- The presence of periodontitis, sinusitis or fistula on the gums;
- Additional, super-complex teeth.
Permanent teeth in children are removed quite rarely, usually due to advanced caries and its complications. In addition, their removal is recommended in the following cases:
- The presence of an unerupted molar for which there is no space;
- Severe forms of periodontal disease;
- Serious injuries to permanent teeth.
Removal Features
Baby teeth in children have a number of anatomical features that the doctor must take into account when removing them:
- The wall thickness of the alveoli is much thinner.
- Often milk roots diverge deeper at a fairly large angle.
- The cervical area is very weakly expressed.
In addition, special tools are used for extraction - forceps with weak fixation, due to which the likelihood of damaging thin tooth walls is extremely low. The removal technique is to fix the tooth as tightly as possible and remove it in one movement, so as not to cause additional discomfort to the baby.
Why shouldn't you remove baby teeth yourself?
Removal of a baby tooth is considered premature if more than a year remains before a new one appears. This period is difficult to predict accurately, but you can roughly estimate it using a graph with average indicators.
Premature removal of a baby tooth is dangerous because its neighbors will try to take the vacant space. The roots of permanent teeth that are about to emerge will become crowded. The bite will change, which will take a long time to correct. Moreover, there are several strict contraindications for extracting baby teeth:
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Inflammatory diseases of the throat (ARVI, sore throat, etc.).
- It is not recommended to remove teeth for pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, central nervous system, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency and nutritional dystrophy.
So when your child's first baby teeth start to loosen, don't disturb them and let them fall out naturally. The child's body knows its business.
When a tooth is already loose, it needs to be cleaned very carefully so as not to rush things. If your child is still in kindergarten and his motor skills are not well developed, help him: take ASEPTA® Baby dental wet wipes and wipe the tooth (as well as its neighbors) from the top and sides.
Anesthesia
When a child needs to have a tooth removed, the question of anesthesia always arises. In most cases, when a loose tooth whose root has almost completely resolved is to be extracted, no special anesthesia is required. A friendly attitude from the doctor and a positive attitude from the parents are enough.
If a more complex procedure of tooth extraction or nerve removal is required, then the best option for pain relief is local anesthesia in a dosage calculated for each child individually. The latest generation of drugs are used for this, which rarely cause allergic reactions and eliminate pain as much as possible. But, despite all the advantages of such drugs, a mandatory step before pain relief is to conduct a test for a possible allergic reaction. Only in the case of a negative test can the drug be considered safe.
In exceptional cases, when the child’s reaction to a visit to the dentist’s office is extremely negative or there is a need to treat a child under one and a half years of age who is not yet fully accessible to contact, then removal under anesthesia is possible. For this purpose, drugs administered intravenously are used. This procedure is available only in large dental centers that have a pediatric anesthesiologist on staff and have received a special license to perform it.
What to do if the tooth, on the contrary, does not loosen
If a molar is already visible above the baby tooth, which is about to erupt, then this is a reason to visit an orthodontist. If such a baby tooth is not removed in a timely manner, then an expensive bite correction will be required to force the permanent tooth to fall into its proper place.
In this case, an orthopantomogram will also help, which will allow you to see where the molars are located.
What should parents do after tooth extraction?
Before removing a tooth from a child, the dentist has a conversation with the parents, in which he talks about the recommendations that should be followed after the procedure in order to avoid complications and speed up the healing process of the hole.
- The child should not be allowed to drink or eat for two hours after surgery.
- For two to three days after removal, the baby should be allowed to rinse his mouth with antiseptic solutions after each meal and before bed.
- You need to make sure that the child does not try to pick at the wound with sharp objects or simply touch the hole with his hands.
- During the healing period, it is better to avoid salty, spicy and too hot foods, which will irritate the damaged mucous membrane.
- If you experience bleeding from the socket or other symptoms indicating the development of inflammation at the site of the extracted tooth, you should immediately consult a doctor.
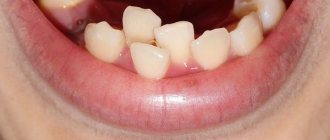
When do baby teeth start falling out?
During the first three years of life, a child grows 20 baby teeth. At this time, a temporary bite is formed: it is distinguished by a pronounced anatomical shape, thin enamel, and susceptibility to caries. After the first three years, the roots of baby teeth slowly dissolve, making room for a permanent bite. From the age of 4-5 years, baby teeth begin to fall out, and this continues until the fifth or sixth grade of school.
In most cases, the process occurs calmly and does not require third-party intervention, including medical attention. Dentists strongly advise against rushing things.