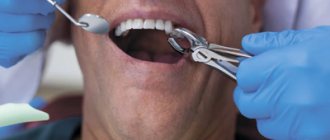
Types of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
The child’s health requires a delicate attitude, so special attention is paid to choosing the optimal method of pain relief. Three methods are used in pediatric dentistry:
- Local anesthesia
. Local anesthesia using sprays, gels and injections. - General anesthesia (anesthesia)
. Putting the patient to sleep so that the doctor can freely work in his oral cavity. - Nitrous oxide sedation
. In essence, sedation is not anesthesia. She calms the little patient, relieves stress and helps him undergo a complex operation.
At the dental clinic " Natadent"
“All of the listed methods
of anesthesia are used when treating children's teeth
. The most appropriate method is selected taking into account the expected duration and complexity of the procedure, as well as the age and personal characteristics of the child. Let's look at each approach in more detail.
How DLclinic dentistry treats children with pain relief
Since pediatric dentistry is rapidly progressing in our time, and the main vector of development is aimed at results, dental treatment for children follows the same algorithm as for adult patients, namely:
- before treatment, the tooth is isolated from the rest by means of a rubber dam (a special “rubber scarf” that is put on it), so that infection does not enter the tooth cavity, and the doctor can work in sterile conditions;
- To restore the anatomy of a tooth in cases of large amounts of destruction in children, as well as in adults, the doctor uses special means: matrices, wedges, rings, etc., due to which the effectiveness of treatment increases significantly.
If we carry out this treatment without the use of anesthesia, at a minimum, we will form a negative attitude towards the doctor in the child, and at maximum, the child will never voluntarily enter the dentist’s office again. It is very important not to neglect either quality or comfort when treating small patients.
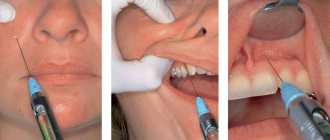
Local anesthesia
This method involves local anesthesia. In this case, the child is conscious and can communicate with the doctor and parents if they are present in the office. In dentistry for children
Most often,
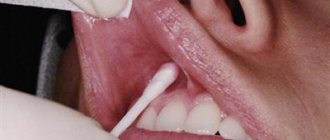
topical anesthesia
- superficial application of an anesthetic to the gums in the form of a spray or gel. This anesthesia is always used immediately before the injection (injection) into the gum. It allows you to numb the injection site and the injection of the anesthetic drug itself is painless.
If strong anesthesia is required for one or more teeth, infiltration
(numbes the mucous membrane in the area of one tooth) or
conduction anesthesia
(numbs the area in the area of several teeth) - injection of the drug into the space next to the nerve innervating the operated area. To avoid pain from the injection, this method is usually combined with the application method.
Benefits of local anesthesia:
- high safety for children;
- accessibility and ease of use;
- low price;
- local anesthesia in pediatric dentistry allows you to remove the dental nerve in one visit;
- no effect on general well-being;
- high efficiency when used correctly;
- minimum consequences and side effects
Local anesthesia in children in dentistry
is used most often because it is the fastest, simplest and most convenient method of pain relief that does not require lengthy preparations (if it is known for sure that the child is not allergic to the drug).
Types of pain relief in children in dentistry
Modern dentistry has at its disposal several pain relief techniques that can be used in young patients. They are divided into three large groups:
- local anesthesia: drugs act locally in the oral cavity: within the tissue or nerve;
- medical sedation: is not anesthesia, as such, it allows you to reduce negative mental reactions to manipulation;
- general anesthesia (narcosis): the patient falls asleep until the end of treatment.
The choice of a specific technique is carried out on an individual basis.
General anesthesia
If local anesthesia is not enough, general anesthesia can be used. It completely relieves the child of pain, vibration, loud sounds, gag reflex and other unpleasant sensations. In some situations, anesthesia may be the only available way to treat a child’s teeth.
General anesthesia in dentistry for children
provides benefits such as:
- the opportunity to work with children who are terrified of dental treatment;
- minimum stress for the child and parents;
- the ability to carry out all manipulations quickly and efficiently;
- absence of negative experiences for the child, thanks to which he will not be afraid to have his teeth treated in the future.
In pediatric dentistry
the safe drug “Sevoran” is used, which is even used as
anesthesia for pregnant women during dental treatment
and other operations. This is an inhalation drug that is supplied through a special tube directly into the trachea, without interfering with the dentist’s work in the patient’s oral cavity; after the supply is stopped, it is also excreted by the lungs without remaining in the body.
General anesthesia
Anesthesia is used in pediatric practice, but the procedure is performed only by an anesthesiologist with a preliminary examination of the child and the exclusion of contraindications. Anesthesia depresses the nervous system and can cause side effects, so it is used strictly according to indications and under medical supervision. The anesthesiologist must be highly qualified, since it is more difficult to calculate the exact dosage for a child than for an adult.
Types of anesthesia for treating children
In dentistry, two methods of general anesthesia are used:
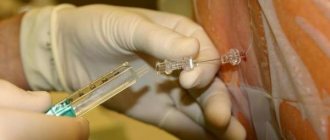
Inhalation. A mask is put on the child and an anesthetic is given. After just a few breaths, he falls into a medicated sleep. This method is more gentle, since the dosage is easier to control during the process, and side effects are rare. Sevoran is considered the most effective and safe mask preparation today.
Intravenous. For young children, an intravenous catheter is installed and Diprivan or its analogues are administered. The dosage of the drug and the duration of drug-induced sleep are established by the anesthesiologist-resuscitator. Treatment must be coordinated with parents or other guardians.
How to prepare your baby for anesthesia
Preparing a child for treatment under anesthesia is a mandatory condition that should never be neglected. You will first need to undergo a series of tests, undergo an ECG, visit a therapist and other doctors (as directed) to obtain permission for general anesthesia. It is necessary to protect your child from colds, since if an infection develops, the date of the procedure will be postponed until complete recovery.
On the day of treatment, food is prohibited for at least six hours, and drinking for four hours. It is important to make sure that the baby does not eat anything behind his back, try to distract him, for example, with a walk, reading a book, etc. The day before, you need to feed the child light but nutritious food.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Traumatic dental procedures may require general anesthesia, but this decision depends not on the parents, but on the anesthesiologist.
In what cases is anesthesia justified or even necessary:
- complex operation, large amount of work;
- children under three years of age;
- allergy to local anesthetics;
- low pain threshold;
- Dentophobia (dentophobia) - insurmountable fear;
- pronounced gag reflex;
- a number of neurological or mental diseases.
The use of anesthesia is prohibited during periods of acute respiratory infections, in case of any infectious or inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract, heart failure, heart defects, underweight, allergies to the drugs used.
Advantages and disadvantages
Treatment with anesthesia has many advantages:
- there is no psychological trauma, since the little patient falls asleep before the operation, and after waking up does not remember anything;
- absolutely painless;
- the doctor is focused on the procedure and is not distracted by the baby, which means medical errors are excluded;
- You can perform a large amount of work, including procedures of any complexity.
The disadvantages include the introduction of serious general medications into the body, which can cause negative reactions. After the procedure, the child remains lethargic for 6–8 hours and requires increased attention from medical staff and parents.
Is it dangerous to treat a child’s teeth under anesthesia?
General anesthesia in pediatric dentistry is not a whim of parents, but sometimes the only possible method of anesthesia. Temporary, as well as permanent teeth, must be treated, since infection and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity deplete the immune system, and premature loss of teeth leads to malocclusion. According to the law of the Russian Federation and a number of other countries, children under three years of age receive dental services only under anesthesia.
General anesthesia has long been safe, as it is carried out using non-toxic drugs, under the supervision of an anesthesiologist-resuscitator and modern equipment. If a child is forced into a chair and treated, the harm will be more significant than the possible side effects. Sometimes after the procedures, children begin to suffer from enuresis, stuttering, dental phobia and other disorders.
Sedation
A good alternative to general anesthesia is nitrous oxide sedation (NAS). Nitrous oxide is an inert gas, absolutely harmless and quickly eliminated from the body unchanged. The child breathes a mixture of this gas and oxygen through a nasal mask. At the same time, he relaxes greatly, and his mood improves (this state can be compared to intoxication from a glass of champagne).
Since the analgesic effect of sedation is minimal, simultaneously with it during dental treatment for children
local anesthesia
is often used. Sedation is suitable only for mild cases, but it has a number of advantages over general anesthesia:
- minimum contraindications;
- the ability to communicate with the patient;
- rapid elimination from the body;
- no health consequences;
- minimal risk of allergies.
Nitrous oxide sedation is used as an alternative to general anesthesia for the treatment and removal of primary teeth.
when anesthesia is not applicable or is excessive. Being in a relaxed state, a child can calmly spend more than an hour in the dental chair (whereas usually he can barely stand it for 20 minutes). The main condition is that the child must breathe independently through the mask.
Alternative to general anesthesia
Sedation is considered a safer alternative to general anesthesia. This procedure involves inhaling a special mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen through a mask. It makes the child feel relaxed and slightly drowsy, lifts his spirits and calms him down. At the same time, the small patient remains conscious and can interact with the dentist.
Sedation is not anesthesia, but has a slight analgesic effect. It is usually combined with an anesthetic injection. The mixture of gases is supplied through a special device that controls the duration and dosage and allows you to smoothly enter and exit the state of sedation. The effect of the procedure wears off within about 10 minutes after stopping the supply of nitrous oxide.
What type of anesthesia should I choose?
The choice of a specific type of anesthesia depends on the complexity of the operation, the presence of contraindications and a number of other factors. Much is decided by the child’s character, his temperament and the presence of unpleasant experiences associated with visiting the dentist. When choosing, they are usually guided by the following criteria:
- Local anesthesia
is suitable for
removing a baby tooth for a child
, for treating caries or pulpitis. The main condition is that the operation should be short (up to 30-40 minutes). It is also chosen if other options are not available due to the age or health status of the baby. - General anesthesia is preferable if complex and lengthy treatment is required. But sometimes it has to be chosen even for simple operations, if the child experiences a panic fear of the dentist, or is allergic to all
local
anesthetic
drugs used
in pediatric dentistry
. - Sedation is used when it is necessary to suppress fear and anxiety in a child who has had a negative experience with dental treatment. It allows the doctor to calmly carry out simple but long-term treatment. Usually sedation is combined with the use of local anesthetics.
Please note that for the use of general anesthesia during dental treatment
Pediatric
presence
of qualified anesthesiologists on staff. Therefore, some clinics may recommend a certain type of pain relief based on their own limitations.
Natadent Clinic
has a license to treat children under anesthesia (we use the drug “Sevoran”), so our doctors always choose the optimal approach to both treatment and pain relief.
The use of the most modern drugs
allows us to use
anesthesia in dentistry
even
for children
under
4 years of age
, so that the child will not experience pain or discomfort.
Features of anesthesia in children in modern dentistry
Any dental procedures that may cause pain during the procedure must be performed under anesthesia. This is the only way to minimize the fear of the dentist’s chair. Even a banal injection of an analgesic into the gum is perceived very painfully by a small patient, which is why the choice of the type of anesthesia, specific drugs and dosages must be made individually.
In the process, the doctor takes into account:
- the age of the child (many drugs cannot be used in children);
- body weight (needed to calculate dosage);
- health status (presence or absence of diseases that limit the use of certain drugs, as well as the risk of allergies);
- mental characteristics (some children categorically do not accept any injections);
- the type and duration of the upcoming manipulations (it is important to understand how long the effect of anesthesia should be).
Features of dental treatment under general anesthesia
Manipulations are carried out “with four hands” - a doctor and an assistant, in order to achieve maximum accuracy. To work with filling materials, it is rational to involve a second assistant. Treatment is optimally carried out in segments, for example, first the upper right, then the upper central, etc. This allows you to reduce time, since closely spaced teeth have a similar treatment plan due to an identical diagnosis.
Sometimes, in addition to general anesthesia, the patient is given local anesthesia as indicated. For this purpose, articaine anesthetics without vasoconstrictors are used.
Contraindications to general anesthesia
Under certain conditions, general anesthesia is contraindicated:
- with decompensated heart disease;
- for renal failure and liver diseases;
- with diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- with severe forms of rickets;
- after the actual meal.
In case of increased bleeding and decreased blood clotting, before anesthesia, the patient should consult a hematologist and give the dentist permission to use this method for pain relief.
General
Many parents are so worried about their baby that they want all his teeth to be treated under general anesthesia. This approach to therapy is fundamentally wrong. There are strict indications for such treatment. Among them:
- There is a very large amount of work ahead when the child will have to spend more than one hour in the dental chair. This is possible if many teeth are neglected and you need to cure them all at once.
- Intolerance to anesthetics for local anesthesia. It's rare, but still possible. If the baby is allergic and cannot be given any of the available drugs for local anesthesia, anesthesia is used.
- Insufficient effectiveness of the administered local anesthesia. If the case is advanced and the injection given does not reduce the sensitivity of the treated area to the required level, a more serious option for pain relief is used.
- Phobia. Some children are so afraid of doctors that they faint when they see them or go into a state of panic. The doctor cannot even examine their oral cavity. Of course, you can hold the baby with six or eight hands and force open his mouth. But then he will receive serious psychological trauma. It will be difficult for a doctor to work in such an environment. Therefore, it is much more reasonable to use general anesthesia.
- Cerebral palsy, epilepsy, Down syndrome, some mental disorders. All of these are conditions in which the child behaves inappropriately or cannot control his movements. To relax the patient and ensure complete rest, a general anesthetic is used.
In order for a child to have a good attitude towards dentists and to cross the threshold of a dental clinic without fear, he needs to be taught to take care of his teeth from early childhood. First visits to the doctor can take place in the form of a game. And it’s good if a small patient has “his own” doctor whom he trusts.
Application anesthesia
Application anesthesia is a type of anesthesia that is carried out without an injection using an aerosol or gel. Most often they contain benzocaine or lidocaine. This anesthesia is used for superficial anesthesia before an injection, removal of temporary teeth if they are highly mobile, and opening of abscesses if they are located close to the surface. To do this, the doctor applies an anesthetic substance to the site of treatment. To prevent the baby from being scared, the substance may have a pleasant smell, such as fruity.
The anesthetic solution penetrates the mucous membrane and disables the surface receptors responsible for pain reactions. When applying topical anesthesia, it is important that the child does not swallow the anesthetic.