From this article you will learn:
- does it hurt to put a crown,
- stages of prosthetics,
- how much does it cost to put crowns on teeth – prices 2022.
Making and installing a crown on a tooth is a complex procedure consisting of many stages. In this article we will talk about many subtle points that affect the aesthetics and service life of your crowns. These points relate to both mistakes when choosing the type of crowns by the patient himself, and mistakes made en masse by dentists at the stages of their manufacture.
For example, most of the complaints from patients about the quality of prosthetics relate mainly to 2 things. Firstly, poor aesthetics, and the fact that the crowns stand out against the background of neighboring teeth. Secondly, the quality of therapeutic preparation of teeth for crowns. The latter leads to complications - pain, suppuration, the need for re-treatment and even tooth extraction.
Does it hurt to insert teeth?
Typically, patients are interested not only in how a crown is placed on a tooth, but also how painful it is. The most unpleasant stages here, of course, are preparing teeth for prosthetics (i.e., treating them, filling root canals), and sometimes also the process of taking impressions. If already dead teeth are used for crowns, then turning them is completely painless and does not even require anesthesia. If living teeth are ground down, a local anesthetic is first injected.
The only painful moment that I myself (being a dentist) have personally experienced is when, when taking an impression, the doctor performs gum retraction. Retraction refers to the widening and deepening of the gingival sulcus, which is accompanied by a small degree of separation of the soft gum tissue from the tooth. This is done in order to make a more accurate impression of the neck of the tooth, and it is better to do this immediately under anesthesia.
How is a crown installed on a tooth?
If you decide to put a crown on a tooth, then it will be useful for you to know what stages of this process you will have to deal with. In the process of placing a crown on a tooth in dental clinics, the following stages can be distinguished...
Initial consultation with an orthopedist (prosthetist) −
During the initial consultation, the doctor, assessing the condition of the teeth externally and using x-rays, must offer possible prosthetic options, and the patient, accordingly, must approve one of the options. Based on this, a treatment plan is drawn up, which may take into account -
removal of non-viable teeth,- preparing teeth for crowns (filling, depulping),
- choice of the type of crowns, for bridges - the number of supporting teeth, etc.
- The cost of making crowns and treatment in general is calculated, the deadline for prosthetics is determined, after which the patient must sign a treatment plan and a contract for the provision of services.
Important: at this stage the patient must choose one of the types of artificial crowns offered to him. Choosing the type of crown is not easy for the average patient, and there are a lot of pitfalls that the dentist will never tell you about. Articles to help you choose -
→ Pros and cons of metal-ceramic crowns → How to choose crowns for front teeth
Preparing teeth for prosthetics −
In some cases, crowns can be placed on living teeth. This is preferable because dead teeth are more fragile, and therefore, if the teeth are left alive, this has a positive effect on the service life of the crowns. In what cases can teeth be left alive? As a rule, we are talking about large chewing teeth. This is due to the fact that large teeth have a greater distance from the surface of the enamel to the pulp of the tooth (than single-rooted teeth) and, therefore, the risk of thermal burn of the pulp when grinding the tooth for a crown will be much lower.
Moreover, under crowns made of metal-free ceramics, even the majority of single-rooted teeth can be left alive. This is due to the fact that under ceramics the tooth is ground down by 1.0 from the side surfaces, and under metal-ceramics – on the same surfaces by 2.0 mm. Therefore, metal-free ceramics also allows you to increase the service life of the tooth itself under the crown.
When using metal-ceramic prosthetics for single-rooted teeth, the nerve is almost always removed. If this is not done, then turning such a tooth can lead to a thermal burn of the dental pulp, i.e. neurovascular bundle. In this case, after some time, its inflammation will develop, and the crown will then have to be removed and the tooth re-treated. If the tooth under the crown is destroyed by a carious process (there is pulpitis or periodontitis), then planned depulpation of the tooth and treatment of inflammation at the apex of the root are required.
When depulping a tooth, it is carried out -
- removal of a nerve from a tooth,
- instrumental treatment and expansion of root canals (Fig. 2),
- the canals are filled with gutta-percha (Fig. 3),
- after which a filling is placed on the crown part of the tooth (Fig. 4).
Important: if the crown part of the tooth is destroyed by 1/2 or more, the tooth must be strengthened with a pin fixed in the root canal (otherwise the crown can easily fall out along with the filling). There are 2 main methods for restoring severely damaged teeth.
What is the best way to restore a badly damaged tooth? –
The first option (Fig. 5) – patients also call it a crown with a pin or a crown on a pin. This is when a pin is screwed into an already filled root canal, and then, based on it, the crown part of the tooth is restored using filling material. Only after such restoration is the tooth ground down for a crown.
- The second option (Fig. 6-8) – the crown part of the tooth is restored using a stump inlay.
Such an inlay is cast from metal in a dental laboratory and consists of a root part (which is fixed in the canal) and a crown part, which has the shape of a tooth that has already been ground for a crown. This method provides greater reliability, strength and longer service life of the crown. Making a core inlay for a crown –
Preparation of teeth for crowns −
In common parlance - grinding teeth. The preparation process is carried out by an orthopedic surgeon, who (using a drill and a set of diamond burs) gives the tooth a certain shape. Preparation is a painful process if living teeth are ground down. In this case, local anesthesia is required. When dead teeth are ground down, anesthesia is given only if the doctor needs to strongly press the gum away from the tooth during preparation.
The tooth tissue is ground down by the doctor to the thickness of the future crown (Fig. 9-11). Crowns made of metal-free ceramics (for example, zirconium dioxide or E.max glass ceramics) require less grinding of the tooth tissue - approximately 1.0 to 1.5 mm on different tooth surfaces. But under metal-ceramics, the teeth are ground down on all sides by 1.5-2.5 mm - as a result of which almost nothing remains of the tooth. As a result of preparation, the tooth crown takes on the appearance of a “stump”.
Tooth preparation for metal ceramics –
Important: high-quality tooth preparation for a crown is a very complex and time-consuming process. The most difficult thing here is to create a ledge in the gingival part of the tooth crown. The reliability and service life of your crown largely depends on the correct formation of the ledge. It must be admitted that most doctors make a lot of mistakes at this stage. How the ledge is formed is clearly shown in the video below.
Grinding front teeth for crowns: video
Taking impressions, making plaster models of teeth –
Impressions are taken from the ground teeth using special impression compounds (Fig. 12). Subsequently, based on these casts, plaster copies of your teeth are created in a dental laboratory (Fig. 13). Such plaster models depict the patient’s teeth with very high accuracy, including those ground for crowns, and it is from such models that they are manufactured.
A very important question here is what kind of impression material you will use to take impressions. Good impression compounds are “A-silicone” or, better yet, “polyester compound”. But usually, in order to save money, alginate masses or C-silicone can be used, which will affect the quality/accuracy of crowns for the worse. As a result, crowns may not fit the ground teeth, may not fit well around the neck of the tooth, and the latter will inevitably lead to rotting of the tooth under the crown.
Taking an impression of your teeth is usually a tolerable procedure that is not accompanied by pain. However, sometimes the doctor needs to insert a retraction thread deep into the gingival sulcus in order to move the gum away from the ground tooth and thereby obtain a better impression of the teeth at the gingival margin. Gum retraction is quite painful and is best performed under anesthesia. Gum retraction also has a disadvantage - very often gum avulsion can lead to the appearance of a periodontal pocket.
But there is also a group of patients for whom taking impressions is a very big problem. For example, if you have an increased gag reflex. Of course, before the actual impression is taken, you may be sprayed on the root of your tongue with Lidocaine spray (an anesthetic), but this still does not help much. In this group of patients, it is advisable to additionally use sedatives before the procedure itself.
How dental impressions are taken in dentistry: video
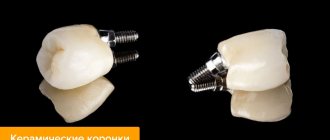
Making crowns in a dental laboratory –
So the casts were taken, plaster models were made. The dental technician begins to make your future crowns based on these models. Because While the manufacture of metal-ceramics and ceramics may take several weeks, while permanent crowns are being made, temporary crowns are usually made of plastic. They will not only restore aesthetics, but also protect sharpened teeth from destruction by the aggressive environment of the oral cavity.
The most important thing at this stage is that we recommend getting dentures only in those clinics that have their own dental laboratory (located directly in the clinic itself). This is necessary so that the orthopedic dentist has direct contact with the dental technician at the stages of making crowns, and the dental technician can always come to the office when trying on crowns.
The latter is very important if you want to get good aesthetics of the crowns, well-formed contact points with neighboring teeth, etc. Of course, none of this will help if your prosthetist's hands are growing out of a bad place, but at least it will improve your chances of receiving quality service.
Trying on crowns –
Before the dental technician finishes his work, it will be necessary to try on the unfinished work.
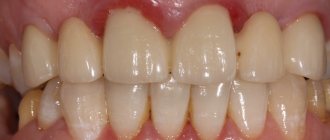
For the first time, the frame of the crowns is usually tried on, which can be either metal or made of metal-free ceramics. The second time they try on an almost finished crown, on the surface of the frame of which (after the first fitting) layers of ceramic mass, as well as dyes, were applied. It is at this stage that you can still say that you don’t like something (color, shape), and it can be corrected. Those. It is at this stage that the color is finally agreed upon, and if you have agreed on it and, moreover, signed the medical record that everything suits you, then it will be too late to make a claim. Therefore, our advice: if you are not satisfied with anything and you are ashamed to point it out to the doctor, be sure to say so, and do not sign anything until you are really satisfied with the results of the work.
After the final fitting, your crown is sent back to the laboratory where it goes through the glazing process to achieve its final look and shine. At your next visit, you will have ready-made crowns fixed with permanent or temporary “cement.”
Video of fitting of E.max ceramic crowns –
Temporary / permanent fixation of crowns –
In principle, there is no need for temporary fixation as such. It is necessary, and you should insist on it only if for some reason you are not sure of the quality of the work or something confuses you (the color/shape of the crowns, their visibility against the background of neighboring teeth). If the crowns are placed on permanent cement, they can only be removed by sawing.
If you insist on temporary fixation, and the dentist refuses you, this is also a signal to think about the quality of the work. Such cases and conflicts on this matter between the doctor and the patient are not uncommon, and here you must remember that it is you who pay the money and decide how everything should be - you too. Usually 1-2 days is enough to get used to the new crowns, determine how well the color matches the desired one, and after that come back to the clinic and have the crowns placed on permanent cement.
Put crowns on teeth: prices in Moscow
How much does it cost to put a crown on a tooth - the price in Moscow for 2021 (in economy-class and mid-price clinics) can have a very wide range. For example, you can easily see that in one clinic you can install a dental crown made of metal ceramics for 5,500 rubles, while in another the price can be 10,000 rubles. And it’s not just a matter of pricing...
The fact is that the same crowns (for example, metal-ceramic) can be made of materials of completely different quality. For example, if a cheap ceramic mass is used, then we can immediately say that the aesthetics of such a crown will be very poor. In addition, in addition to standard metal-ceramics, there is also “metal-ceramics with shoulder mass”, which is much more aesthetically pleasing than the standard version, but at the same time costs 2-2.5 times more.
Installing a crown on a tooth: price 2021
- metal ceramics - from 4,500 to 16,000 rubles.
- ceramics made of zirconium dioxide – from 14,500 to 20,000 rubles.
- from E.max ceramics – from 16,000 to 25,000 rubles.
- all-metal crowns – from 4500 rubles.
Important: if you are planning to install a crown on a tooth, the cost above does not include all possible expense items. Additionally, therapeutic preparation of teeth (if necessary) is paid, as well as the cost of making temporary crowns made of plastic. The latter are necessary to protect the ground teeth while your permanent crowns are being made.
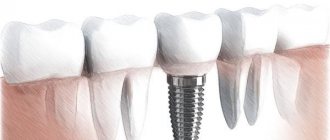
What is turning
Grinding or preparation is a procedure that involves partial removal of the hard tissues of the tooth (sometimes only enamel, and in some cases enamel and dentin) in order to give it the desired shape and the necessary roughness for installation and reliable fixation of the prosthetic structure. This is also done to ensure that the restored unit looks as natural and beautiful as possible. The required amount of tissue is usually sewn down depending on the thickness of the prosthesis. For example, before installing a crown, hard tissues are shaped into a cone. If the crown is made of zirconium dioxide, then the turning will be approximately 0.7 millimeters, if it is made of metal ceramics - about 2 millimeters on all sides.
Features of tooth preparation depend on the type of prosthesis that will subsequently be installed on the patient. For example, to fix veneers, the doctor will grind down the front, then the side and cutting parts of the enamel, and special grooves or indentations will be made on the tooth for better adhesion. But before fixing the original lumineers, the preparation will be minimal - it is enough to just give the enamel a rough surface for high-quality adhesion to the microprosthesis.
How to remove dental crowns -
Unfortunately, we must also note the fact that sometimes situations arise when the crown needs to be removed. For crown removal, the price for 2021 will be about 1000 rubles per unit. The need to remove the crown may be due to the following reasons...
- With poor preparation of the tooth for a crown - according to statistics, in 60-70% of cases, the root canals of the teeth are filled poorly, which leads to the development of inflammation and the need for re-treatment or removal of the tooth. You can find out more about poor-quality preparation of teeth for prosthetics, what this leads to, and what to do about it here .
- With manufacturing errors - for example, the crown did not fit tightly around the neck of the tooth, and therefore, within days, the destruction of the tooth tissue began. Metal-ceramics or metal-free ceramics could chip a large fragment of the ceramic mass, which may not be repairable and require replacement of the crown (24stoma.ru).
- Scheduled replacement of crowns is necessary - all crowns have their own service life, and they will have to be changed periodically. It should be noted that high-quality modern crowns can last 8-10 years, or even more.
Removing crowns: video
And here the question always arises: does it hurt to remove the crown... It can indeed be a little painful, and therefore the procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Removing cermets, for example, is very difficult. The crown is sawed using special discs and burs, and cases of damage to the gums next to the tooth are not uncommon. We hope that the article on the topic: How to put crowns on teeth was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Personal experience as a dentist, 2. “Orthopedic dentistry. Textbook" (Trezubov V.N.), 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. "Orthopedic treatment with fixed prostheses" (Rozenstiel S.F.), 5. "Crowns and bridges in orthopedic dentistry" (Smith B .).
Possible complications after the procedure
Complications are rare after crown placement, but complications do occur. Most often this is a medical error or lack of professionalism. Therefore, the best prevention of complications is choosing a clinic with an excellent reputation. In addition, there are several diseases that do not depend on the doctor. They can be caused by medications, gastrointestinal diseases, and injuries.
Complications after crown installation
Prosthetic stomatitis (allergy)
Stomatitis, the cause of which is dentures, happens:
- allergic, this is a contact allergic inflammation, which often occurs after repeated prosthetics;
- toxic (occurs more often than allergic).
Prosthetic allergic stomatitis is a reaction to metal compounds and plastic. The more metal (a large number of bridges, crowns), the more likely an allergy. Moreover, this type can develop both immediately after installation and after 5-15 years of wearing crowns. Patients with gastrointestinal diseases and endocrine disorders are at risk. Typical complaints are swelling of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and larynx, sometimes it is difficult to breathe, the tongue swells and does not fit in the mouth, but there are no ulcers familiar to ordinary stomatitis.
If a metal, metal-ceramic or metal-plastic crown is installed, a burning sensation of the tongue, drooling, and dry mouth are noted. If you are allergic to acrylates, granular bright red foci of inflammation appear on the mucous membrane of the palate, matching the shape and size of the prosthesis. In addition, skin reactions are noted - eczema, urticaria, dermatitis.
With toxic prosthetic stomatitis, the mucous membrane is damaged, and there is massive destruction of the epithelium of kidney, liver, intestinal cells, red blood cells, and nerve cells. Most often, poisoning is caused by stainless steel; if the crown (whole or base) is made of gold or a silver-palladium alloy, the disease occurs much less frequently.
This complication appears 1-7 days after installation. Characteristic symptoms of toxic denture stomatitis:
- burning tongue;
- drooling (hypersalivation);
- unpleasant feelings in the tongue, such as tingling, rawness (glossalgia);
- nervous disorders;
- gastrointestinal disorders.
Caries on supporting teeth
The ground teeth under the crown, if the nerve is removed, dry out over time. As soon as the seal is broken, bacteria and food particles penetrate under the denture and caries develops. That is why, even if part of the tooth and the root remain, it is better to build up the support than to remove the tooth along with the nerve.
Jaw trauma and hard food lead to a violation of the integrity of the crown and further development of caries underneath it. Development is promoted by poor oral care.
Galvanic syndrome
Saliva is a complex electrolyte, and the oral cavity is an electrochemical system in which:
- saliva (liquid phase), saturated with oxygen and carbon dioxide, acts as an electrolyte;
- teeth, dentures (solid phase) act as electrodes.
If there are metallic inclusions in the oral cavity that are not covered with ceramics (insulator), the potential of the electrode system increases sharply. There is a feeling of acidity and burning in the mouth. With a galvanic symptom, the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted, which leads to a general deterioration in the patient’s condition.