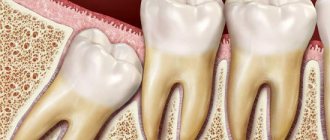
Tooth extraction in dentistry is divided into simple and complex. When extracting a tooth with one root, such manipulation is considered simple. If the tooth has a complex root with several branches, then the procedure for removing it will be complex and is carried out using special tools and techniques.
In what cases is dental surgery difficult?
Complex manipulations regarding tooth extraction include the following situations:
- with disconnected roots that are excessively curved inward or directed in different directions;
- when the problem tooth is located in the affected bone;
- in the complete absence of a crown, when there is nothing to grab onto with forceps;
- if a filling was previously installed in the tooth, which can crack under the mechanical influence of forceps;
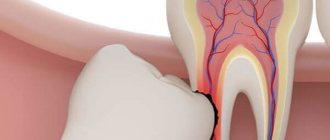
- when the tooth is impacted or dystopic;
- removing the "eight"
These are the main clinical features in which it is impossible to get rid of a diseased tooth using a standard simple procedure. Moreover, in each specific case the reasons for complex extraction may be individual.
Removal methods
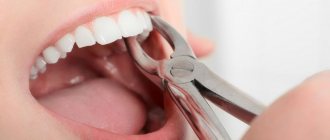
Today, there are 4 techniques for extracting molars: simple, surgical or complex, atraumatic and according to the indications of an orthodontist. A simple method is usually understood as extracting a tooth that has completely erupted above the surface of the gum. In this case, removal occurs using special forceps. First, the tooth is slightly loosened from side to side and then removed.
The surgical method is intended for more complex cases, for example, to remove impacted or hard-to-reach, decayed teeth. In this case, the specialist cannot limit himself to using only forceps; a scalpel and other devices necessary for dissecting soft tissues will also come to the rescue. After such an operation, the resulting wound can take quite a long time to heal, which will cause a lot of inconvenience in everyday life.
Atraumatic removal is the most progressive method, which is painless and fast. First, the doctor administers the required dose of local anesthetic and then removes the tooth without using forceps. The cost of this procedure is quite high, but the risks of complications and infection in the wound are minimal.
Cases when complex surgery is necessary
It often happens that the only possible way to get rid of a defect formed by a complex tooth is to remove it.
Indications for this type of procedure are as follows:
- the formation of periodontal tumors and edema, accompanied by soreness of the mucous membranes and gums;
- numbness of the face resulting from damage to the nerve endings of a diseased tooth;
- with an increased risk of curvature of adjacent teeth;
- in the presence of diseases caused by improper positioning of the tooth.
Surgeries to remove problematic teeth are contraindicated for those who suffer from pathologies of the cardiovascular system, with poor blood clotting, patients who have undergone a hypertensive crisis, in the presence of infectious or viral processes in the body, as well as other individual contraindications.
How much does tooth root removal cost?
As a rule, the price for tooth root removal is determined based on the complexity of the case, and can vary greatly depending on the segment of the clinic, the qualifications of the doctor and other factors. Standard removal starts at an average of 3,000 rubles, complex removal will cost at least 5,000 rubles. Your attending physician will help you make more accurate calculations based on the diagnostic results. In any case, the sooner you go to the clinic, the less likely it is that complications will develop, especially since modern dental offices have all the capabilities to carry out the procedure efficiently and minimize the unpleasant consequences of tooth root removal.
Preparing for dental surgery
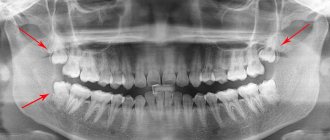
If a patient is faced with the removal of a complex tooth, then an experienced doctor will not perform such manipulations without prior preparation. An x-ray is required before the operation. This is necessary to clarify the location of the tooth in the bone, as well as to evaluate the tissues surrounding it.
When a patient has an inflammatory process, it is first cured by taking antibiotics.
Complications after pulling out problem teeth rarely occur, but to avoid them, the procedure should be trusted to a highly qualified doctor.
How is preparation carried out for tooth extraction and subsequent implantation?
Since the quality of implantation depends on how carefully the dentist removes the tooth, each patient is required to undergo thorough preparation for this procedure, which includes a preliminary examination and some preparatory manipulations:
- The degree of tooth destruction, the presence or absence of structural anomalies in the implantation area are assessed;
- Additional instrumental research methods are carried out: X-ray, CT. With their help, the doctor assesses the condition of the bone tissue, as well as the roots of the tooth, including their location in relation to the paranasal sinuses;
- Instruments for tooth extraction and the optimal method of pain relief for the patient are selected;
- A set of treatment measures is prescribed in the presence of concomitant dental pathologies;
- If necessary, professional teeth cleaning is performed, which can effectively reduce the risk of infectious complications during the rehabilitation period;
- The day before tooth extraction, in many cases antibiotic therapy with a broad-spectrum drug is prescribed;
Before tooth extraction, it is also very important to ensure the correct psychological attitude of the patient. To do this, the doctor must explain to the patient in detail how the procedure will be performed, why certain manipulations are performed, and what results should be expected after tooth extraction and implant installation. In addition, the patient must be explained what kind of anesthesia will be used during the operation and how it works.
A special place in preparation for tooth extraction is occupied by sedation of the patient. To conduct mild sedation, the doctor must take into account the psycho-emotional characteristics of the patient, the degree of his anxiety before the upcoming manipulation. In modern dentistry, safe and effective drugs are used to provide sedation, which quickly eliminate such undesirable manifestations as severe fear, psychomotor agitation and others. Without proper psychological preparation of the patient and well-chosen sedation, painless tooth extraction before implantation is very difficult to carry out delicately and non-traumatically.
How to remove complex teeth: basic techniques
In dentistry, various methods are used to eliminate a complicated tooth, the essence of which depends on the instruments chosen for manipulation:
- removal using forceps. Compared to
in other ways, this is considered the most gentle. This technique is used in cases where the integrity of the crown is preserved. The surgeon grabs the crown with forceps and loosens it in a circular motion until the tooth root ruptures from the alveolus, after which he pulls it out; - elevator extraction. If it is located outside the dentition, it is impossible to pull it out with ordinary forceps, then this technique is used. The instrument is inserted into the periodontal fissure and rotated, as a result of which the ligaments are torn. The tooth is not pulled out of the hole, but squeezed out;
- removal with a drill. This method is used to pull out teeth with multiple roots. First, the roots are separated using a drill and then each piece is removed separately. If a resorcinol-formalin filling is installed on a tooth, then a drill is also used to pull it out.
Which method is the best? Each has certain characteristics and is selected based on the condition of the tooth, the number and depth of its roots.
Alternatives to tooth resection –
Resection in most cases is not mandatory and is the only method of treating granulomas and cysts.
Mandatory resection is required only in the presence of large cysts (for example, 1.5-2 cm or more). The latter is due to the fact that the shell of large cysts is very dense and thick, and does not completely disappear even with good conservative treatment (although the cyst itself decreases in size). Therapeutic treatment of cysts is carried out by a dentist, and the only drawback of this method is the duration of therapy and a slightly larger number of visits to the doctor. In order for the granuloma/cyst to begin to shrink and disappear, it is necessary to completely neutralize the source of infection in the root canals, and then seal the root canals with a medicinal paste based on calcium hydroxide for a period of several months.
After a few months, the doctor will take an x-ray of you to see how much the cyst has shrunk, and if everything is fine, he will prescribe you for permanent root canal filling. Until this moment, you will walk with a temporary filling. It should be noted that conservative treatment is not always effective, and the tooth becomes inflamed over and over again. Therefore, it is sometimes easier to immediately fill the root canal on a permanent basis, and the next day carry out an operation to remove the cyst.
Dystropic tooth: indications for removal
A tooth with an incorrect location in the dentition relative to its neighbors is called dystrophic. It can take the place of another, spontaneously turn, change the angle of growth, which significantly interferes with neighboring teeth and leads to the formation of a malocclusion.
Indications for extraction of a dystrophic tooth are:
- swelling of the gums and pain;
- numbness of the face due to damage to nerve endings;
- pronounced curvature of adjacent teeth;
- periodontitis or chronic pulpitis;
- when, due to a problem tooth, it is impossible to perform prosthetics;
- if a dystrophic tooth is the cause of periostitis or osteomelitis.
The removal process itself is similar to the procedure for removing an impacted tooth.
What is needed to prevent injury during tooth extraction?
The correct selection of instruments for tooth extraction before implantation is necessary in order to minimize the risk of trauma to the bone and soft tissues surrounding the tooth. Since even the slightest injury to the alveolar process of the bone makes it impossible to carry out implantation immediately after tooth extraction, dentists use exclusively modern equipment to make the process of tooth extraction as precise and non-traumatic as possible. These include:
- High quality tongs. Selecting the desired shape and bend of the forceps and using them carefully allows you to remove the tooth and tooth roots without injury;
- Periotomes. Used for atraumatic tooth extraction with delicate separation of marginal gums;
- Luxators. They are an improved version of classic elevators, significantly simplify the process of tooth extraction and make it less traumatic;
- Ultrasonic surgical devices, for example, piezotome. Allows you to minimize trauma during tooth extraction and facilitates the rehabilitation period for patients after implant installation;
The quality of the instruments determines how convenient it is for a specialist to perform the operation, which in turn is of great importance for preventing injury to bone tissue and obtaining a good result from dental implantation.
In addition to choosing the necessary tools, the experience and qualifications of the specialist are of great importance.
For an average surgeon, the remains of teeth before surgery are a hindrance and are not treated on ceremony. The result is broken bone structures of the jaw, wandering remnants of roots, unremoved cysts growing into the maxillary sinus, perforations, fistulas, osteomyelitis and much more. Not to mention the shocking post-operative pain that overtakes the patient after such punitive surgery. Entrust removal to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. Only the maxillofacial surgeon has enough theoretical and practical skills to perform tooth extraction without complications.
Extraction for acute and chronic inflammation
Quite often, the removal of a problematic tooth is accompanied by the presence of purulent foci, gum inflammation or periodontitis. In such cases, the doctor prescribes intensive therapy with the use of antibacterial drugs, and only after the inflammatory process has been suppressed is surgery to remove the tooth performed.
There are also situations when a tooth needs to be removed urgently. Only an experienced, highly qualified doctor can perform surgery in such cases.
Resection stages
- Formation of access
- the dentist cuts through the gum, exposing the jaw bone. Forms a small hole in the bone tissue (in the projection of the root apex), gaining access to the pathological focus. Often, the bone tissue has dissolved in the projection of the cyst; there is no need to cut out a hole. - Excision of tissues and correction of the apex
- the doctor removes the source of inflammation along with the dead apex of the root, cutting it off perpendicular to the upper dental axis (to the level filled with the filling mass). The empty space is filled with osteoplastic material (bone volume is restored faster). - Suturing
- suturing the wound area is sometimes performed with the installation of drainage for the outflow of ichor. Drainage is installed between the seams and is removed after 1-2 days.
Root resection takes 40-60 minutes, depending on the location of the tooth. It is easier to intervene on canines and incisors than on multi-rooted units.
Complex tooth extraction: when is it necessary?
Clinical indications for which the dentist prescribes complex tooth extraction are as follows:
- the presence of an unerupted wisdom tooth in the jaw;
- if the figure eight is incorrectly positioned;
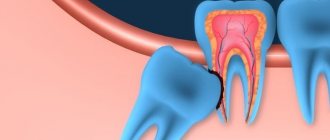
- when removing molars with two or three roots;
- with a severely damaged or twisted root;
- in case of fusion of the tooth root with the jaw bone tissue;
- in the presence of a fistula or cyst;
- with excessive fragility of the crown due to treatment with resorcinol-formalin composition.
The operation itself consists of several stages and is carried out under the influence of powerful anesthetics.
What is the tooth extraction procedure?
Removal or extraction is a dental surgical operation during which a tooth is removed from the alveolus of the jaw in whole or in part. In the first case, the crown and root part are removed, in the second, resection or hemisection is performed while preserving the dental unit.
- Complete removal - removal of the crown and roots after separation of the soft tissues and rupture of the ligaments. It is indicated in cases of loosening, significant tooth decay, jaw fractures, or the need for orthodontic (for example, braces) or orthopedic treatment.
- Resection is the excision of the apex of the affected root; it is performed when a granuloma or cyst is detected on it. Access is carried out microsurgically through the soft tissue and jaw bone in the projection of the inflamed area or neoplasm.
- Hemisection is the amputation of one of the roots of multi-rooted (chewing) teeth along with the adjacent part of the crown. It is used for inflammatory processes, the impossibility of tooth-preserving treatment, pathological features or root fractures.
Complete tooth extraction
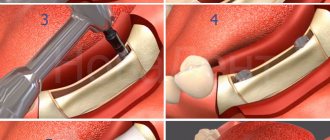
Stages of complex tooth extraction
Complex removal surgery is carried out only after x-ray diagnostics, during which the shape, length and depth of the roots are determined. If the patient has inflammation, he is prescribed treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Technique of the procedure
Wisdom tooth removal is carried out in the following order:
- the gum is separated from the neck of the tooth by making an incision in the soft tissue;
- if necessary, the interroot septum is sawed or sections of bone tissue are cut out at the location of the tooth;
- then, using forceps, the tooth is rocked and pulled out of the socket;
- Sutures are placed on the gum.
Painkillers are not required after the procedure, since the effect of the anesthetics is still present.
Features of extraction of different types of teeth
Milk and permanent teeth are removed in different ways. The methods for extracting one or more dental units located on the upper or lower jaw also differ. The removal of wisdom teeth has its own characteristics due to pain, improper eruption, and atypical location.
Removal of baby teeth
Baby teeth can be removed at any age if it is not possible to save them. The manipulation is usually performed under local application anesthesia (painkillers are applied to the gums) or an injection is given. In cases where the child is not contactable due to age - up to one and a half years - or for other reasons, general anesthesia is given.
Indications for simple removal are:
- extensive carious lesions;
- inflammatory processes – periodontitis, pulpitis;
- the baby tooth prevents the eruption of the permanent one or does not fall out after it;
- pronounced dystopia.
The features are due to the fragility of the enamel and the weak expression of the neck. For extraction, a special tool with a loose grip is used; the extraction itself is performed in one movement.
Removal of upper teeth
Incisors and canines with one root are removed in a simple way, and multi-rooted molars and premolars are removed in a complex way. Removal of upper dental units has a number of the following features:
- teeth are removed from the alveoli more easily, since the structure of the jaw bone tissue is more porous;
- the roots are usually straight, which also makes manipulation easier;
- anesthesia acts faster and stronger;
- due to less trauma, healing after removal of a wisdom tooth (or another) is faster.
During the operation, the patient's head should be tilted back. This gives the doctor a full overview and access to the desired tooth.
Removal of lower teeth
By analogy with the upper ones, simple removal is used for single-rooted teeth of the lower jaw, and complex removal is used for chewing teeth. Due to anatomical features during the procedure, the doctor may encounter the following difficulties:
- often there are dental units with curved roots;
- increased bone density, making surgery difficult:
- low effectiveness of anesthesia (does not work for a long time, insufficient pain relief).
The patient's head should be tilted forward during removal. When removing front teeth, a straight head position is possible.
Wisdom tooth removal
This is the name given to third molars, which usually erupt in humans between the ages of 15 and 25. They are considered a rudimentary formation, therefore they often grow with displacement, quickly collapse, injure the mucous membrane, have a non-physiological crown shape, and curved roots. These teeth may remain impacted (unerupted); in case of incomplete eruption, they form a fold in the gum (“hood”), which often becomes inflamed.
Removal of a wisdom tooth with a “hood”
The listed features of wisdom teeth are a recommendation for removal. Their extraction is a complex operation for the following reasons:
- difficult access due to location;
- the need to cut the gums due to retention or destruction of the crown;
- the need for longitudinal sawing of the tooth for its gradual extraction due to curved roots.
After wisdom teeth are removed, stitches are often needed. Also, sometimes a bandage soaked in medicine is placed in the hole; it must be changed regularly when visiting a doctor.
Removal of several teeth
Simultaneous extraction of a significant amount or all dental units is carried out according to indications - before prosthetics, for periodontal disease. The order of complex and simple extraction during the operation is determined by the dental surgeon individually for each patient. The exact number of teeth that can be removed in one visit also varies individually and is determined by a combination of several factors:
- type of anesthesia - under general anesthesia, a larger volume of surgical intervention is permissible, and local drugs have restrictions on the duration of action and dosage;
- client comfort - gradual removal is possible (first on one side, then on the other, after healing, which makes it easier to eat) or simultaneously, if it is more convenient for the patient;
- difficulty of removal - when it is necessary to saw a lot of teeth, cut a significant area of the gum surface, extraction is performed in several stages;
- general health, absence of specific contraindications (reduced blood clotting, vascular and heart diseases, hypertension) - after the removal of a wisdom tooth and others, an extensive wound surface is formed, which is fraught with bleeding and infectious inflammation.
The healing process of the hole after a complex removal
Basically, tissue healing occurs after 7-10 days. It should be noted that this period is quite difficult for the patient. As soon as the effect of the anesthetics stops, aching pain immediately occurs. To eliminate it, you should take pain medication.
The swelling and redness that appears will decrease every day. If there is slight itching in the socket area, this indicates intensive tissue restoration. Removal of sutures after healing is not required since they “dissolve” on their own.
During the regeneration period after removal, it is very important not to disrupt the integrity of the blood clot formed in the socket. To do this, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- during the first 2-3 hours after surgery, do not consume any drinks, much less food;
- Under no circumstances should the well be heated, cleaned or washed;
- do not rinse your mouth for 24 hours after removal;
- When eating food, you need to chew it on the opposite side in relation to the hole.
If you follow these recommendations, the tissue will soon recover without complications.
How to avoid complications
Inflammatory processes in the postoperative period usually occur due to the fault of patients who do not follow several basic rules. The dentist will tell you what to do after removing a wisdom tooth or any other dental unit to prevent negative consequences. Standard recommendations are as follows:
- Do not touch the blood clot in the first three days so as not to damage it. This clot naturally reliably prevents infection from entering the wound.
- Follow the advice on nutrition and oral care - eat only approved foods, brush your teeth carefully.
- Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, especially in case of periodontal disease or after removing a significant number of teeth.
Complications can also arise due to the fault of the dentist. In addition to infection of the wound with unsterile instruments, there is a risk of jaw fracture, damage to nearby teeth, and incomplete removal. Such situations can be avoided; you just need to choose a clinic with an impeccable reputation. Yulisty employs highly qualified dental surgeons, so the possibility of medical error is completely excluded.