Cysts in the human body are closed cavities, a kind of capsule, with contents. Their localization can be very different, but dentistry deals with the treatment and prevention of cysts located in the oral cavity. They can range in size from microscopic, in which case they are very difficult to detect with the naked eye, to impressive, which significantly complicates the quality of life of patients. The causes of cysts and methods of their treatment often depend on where exactly they formed.
Let's consider each of the options in more detail.
Content:
- Why does a cyst grow in the oral cavity?
- Types of oral cysts
- Signs of a cyst
- Examination of patients who have a cyst in their mouth
- How to treat
- Treatment of cystic formation at home
- How to reduce the likelihood of developing education
Sometimes, when visiting a dentist, a patient hears a strange diagnosis - mucocele.
More simply, it sounds like an oral cyst. Underneath this disease lies a cavity tumor neoplasm containing mucous contents. It is benign and develops due to obstructed outflow of secretions produced by parenchyma cells. The peculiarity of mucocele is that it does not have a strong epithelial membrane. Usually localized on the mucous membrane of the lower lip or under the tongue. It can also form in the chewing area. Neoplasms of the submandibular zone are very rarely encountered in dental practice.
Conducted studies demonstrate that most often young people under the age of thirty experience mucocele. The disease also occurs in adolescent children.
The reason for the appearance of a cyst on the back of the throat
The development of congenital cysts is caused by pathologies of intrauterine development. It is hereditary in nature or is caused by the expectant mother’s abuse of smoking and drinking alcohol during pregnancy.
Acquired cysts are due to the following reasons:
- non-compliance with oral hygiene measures; hereditary predisposition; disruption of the immune system; harmful production conditions; structural features of the pharyngeal and palatine tonsils; hormonal disorders; smoking and alcohol abuse; long stay in places with poor ecology.
Most often, these pathological formations appear in people who have chronic inflammatory processes in the pharyngeal cavity.
Why does a cyst grow in the oral cavity?
Most often, doctors are unable to determine the exact cause of the disease. It is believed that its development can be caused by:
- repetitive trauma to the mouth;
- inflammatory pathologies of the oral mucosa;
- congenital obstruction of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands.
Some doctors are inclined to believe that frequently appearing cysts of the sublingual salivary gland indicate a non-standard structure of the latter. There is also a dysembryogenetic version of the origin of tumors. But dentists give the main importance to the traumatic factor. Thus, blisters on the inside of the lower lip often form due to the habit of constantly biting it.
The pathogenesis of the disease can be described as follows:
- The excretory duct of the salivary gland becomes blocked for a certain reason.
- Internal hydrostatic pressure increases. The mucus accumulates and cannot come out.
- Throughout the day, the mucous secretion permeates the surrounding tissues.
- Swelling forms and the blood vessels are compressed. Tissue permeability is impaired.
- A capsule consisting of connective tissue is formed. She is gradually growing.
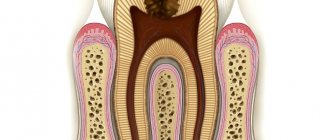
Why do cysts form on teeth?
Dental cysts are a polyetiological disease. Slow inflammatory reactions around the apical zone of the root can cause the development of radicular tumors. A follicular dental cyst is formed due to a disruption in the development of the dental germ of a permanent tooth from the dental sac.
The reason for the disruption of the development of the tooth germ is chronic periodontitis of temporary teeth, due to which the division of epithelial cells occurs around the crown of the unerupted segment. The pathogenesis of a retromolar cyst involves the formation of a bone pocket. Due to inflammation, it closes to form a cavity.
Provoking factors leading to the formation of a cyst under a tooth:
- complicated course of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- incorrectly installed orthopedic design;
- maxillofacial injuries;
- tooth root fracture;
- complicated infections of ENT organs;
- pathology of teething, etc.
Types of oral cysts
Based on their origin, mucoceles are:
- true;
- extravasal.
The first ones lack their own membrane and are covered with a gland capsule. They occur due to blockage of the duct and accumulation of mucus. The second are post-traumatic. They are formed when the tightness of certain structures is broken and the mucous secretion enters the surrounding tissues.
According to the localization criterion, the neoplasm is classified into:
- Sublingual. It is located in the hyoid-maxillary muscles or submandibular region. During rapid growth, it grows very quickly and then causes serious discomfort.
- Submandibular. Located in the lower submandibular region. It feels like a dense ball to the touch. Promotes disruption of the natural mechanism of salivary fluid secretion.
- Parotid. Rarely encountered in dental practice. It can be very painful when you open your mouth wide. It is formed due to impacts, injuries, after which the inflammatory process caused the closure of the salivary ducts.
- Extravasal. Most often found on the inner surface of the lip. Occurs due to mechanical damage. The inside is filled with granulation tissue.
What is a retention cyst in the mouth?
A pharyngeal retention cyst is a thin-walled cavity that is filled with purulent or serous fluid. It looks like a round dense thickening. It is formed when the excretory duct of the gland is blocked. These benign formations can be congenital or acquired.
They are formed under the influence of several factors. This may be a thickening of the secretion produced by the glandular tissue or the ingress of various small particles into the cavity. More often, this acquired formation appears in older men. Congenital retention cysts are most often detected in infancy.
Signs of a cyst
Among the main symptoms of the disease:
- The appearance of an unusual protrusion on the soft tissues of the mouth. It may resemble an abscess. It usually has a bluish color with a burgundy border, but it can also match the tone of healthy gums. The “older” the mucocele, the thinner its walls become. The “bubble” is movable; it is not fused to the surrounding tissues.
- Discomfortable sensations while chewing food. There is a feeling as if there is a foreign object in the mouth that is constantly in the way.
- An unpleasant feeling of constriction of the mucous membrane. In this case, pain does not occur.
The cyst may burst if there is a lot of pressure on it. Spontaneous opening sometimes occurs while eating. The difficulty is that afterwards it forms again - through the passage in the mucous membrane, the cleared cavity is refilled with liquid contents.
Manifestations of tonsil cysts
Symptoms of having a palatal cyst depend on its size and location. Cysts up to 1 cm in size usually do not manifest themselves, are invisible and painless. People, as a rule, do not even suspect their existence. Cysts can be discovered accidentally during routine examinations by an otolaryngologist.
You can suspect the presence of a cyst in the tonsil if you have bad breath with healthy teeth and normally functioning digestive organs. The smell comes from food particles that become trapped in the area of the cyst and begin to decompose there. As the size of the cyst increases, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- feeling of constant presence of a foreign body in the throat;
- sore throat or discomfort;
- difficulty and mild pain when swallowing solid food;
- hoarseness of voice.
Young children may begin to choke on food. If the cyst grows towards the pharynx, then a feeling of lack of air may occur, which is especially pronounced in children whose larynx is small. The existence of the cyst itself maintains chronic inflammation. The cyst excludes areas of the tonsil from immune protection.
Examination of patients who have a cyst in their mouth
Diagnosis of the described disease is simple.
The doctor examines and palpates the abnormal lesion and studies the symmetry of the face. If the mucocele has reached a diameter of more than one and a half centimeters, then its color is blue. When the lesion is opened, viscous yellow contents are released. If the resulting biological material is submitted for analysis, a large amount of salivary proteins and amylase will be found in it. If necessary, the Trommer reaction is performed to confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
During ultrasound diagnostics of the salivary gland, the doctor observes an anechoic formation of a round shape. Its borders are smooth. The fact that the patient has a mucocele is said:
- presence of granulation lining;
- absence of epithelial membrane;
- the presence of mucin and protective blood cells.
If there is doubt about the benignity of the tumor, the patient is referred to an oncologist.
Surgical intervention (opening a tonsil cyst)
In cases where drug treatment is unsuccessful or when the patient experiences obvious, persistent symptoms, the doctor recommends surgical intervention, which helps prevent relapses in the future.
Before opening the cyst, the otolaryngologist performs local application (irrigation, lubrication) anesthesia, opens the cyst with a scalpel and evacuates the contents. After the intervention, the doctor treats the site of the process with antibacterial drugs and prescribes antiseptic therapy.
If necessary, upon completion of the intervention, the otolaryngologist can take the contents of the cyst for analysis or material for histological examination.
If repeated cystic formations occur, the cyst refills with contents, then the most effective method is considered to be surgical intervention, i.e. complete removal of the cyst with its membranes.
How to treat
It is very dangerous if a person tries to remove a cystic formation on his own and, to do this, puts pressure on it or bites it. Any mechanical influences have a negative effect on the course of the disease. Due to external pressure, the liquid inside the bubble begins to flow beyond its boundaries. Afterwards it accumulates again in the inflamed area. But at the same time, the risk of infection of damaged tissues increases significantly.
Doctors most often treat mucocele surgically. If the “bubble” is localized on the lower lip, two semilunar incisions are made in its projection, after which the internal neoplasm is isolated along with all its contents. Finally, stitches and a sterile pressure bandage are applied.
If the problem concerns the sublingual area, the following can be done:
- cystectomy;
- cystsialadenectomy.
In the first case, only the cyst itself is removed. It is cleaned and cut out. In the second type of surgery, the gland is also removed.
If there is a formation in the parotid zone, a parotidectomy is performed - complete or partial. It involves excision of the cyst and part of the parenchyma. Lesions located in the submandibular area are always removed along with the gland.
If we are talking about treating a child or a weakened elderly person, the dental surgeon may decide to excise only the dome (upper part) of the abnormal structure.
Surgical removal of the cyst
There are several methods of surgical treatment of this benign neoplasm. A retention cyst is removed using one of these methods:
- Complete excision along with the contents. The patient is given general anesthesia. Then the bubble is cut out along with the internal contents. Biting. It is performed both under general anesthesia and with local anesthesia. This depends on the location of the tumor. During this intervention, part of the cyst wall is removed. Then its entire contents are pumped out. Piercing. The tissue is pierced with a needle in the place of greatest swelling on the formation. Then the fluid is removed from the cyst. The cavity is sanitized.
The last option is considered the fastest and technically simplest method. But there is a risk that the cyst will refill with contents. She reappears in the same place.
Treatment of cystic formation at home
Home therapy for oral cysts only makes sense if for some reason you cannot get to a dental surgeon in the next few days. It consists of rinsing with herbal solutions and antiseptics. You can also make compresses with anti-inflammatory herbal medicines.
If the hearth breaks through, it’s too early to rejoice. Most likely, it will soon reappear in its original place. This is how cysts work - their contents expire, but the outer layer remains.
Under no circumstances should you treat a bulge on the gum or mucous membrane as a regular pimple. Any attempts to open it mechanically will not lead to anything good. But the resulting wound can become infected. Then the inflammation will spread to deeper layers in a fairly short time, and it will be much more difficult to cure.
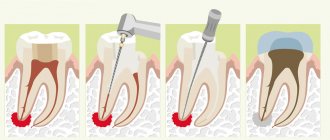
Treatment
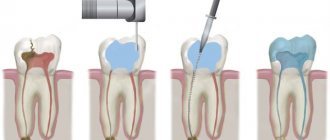
Treatment of dental cysts is carried out through surgery, laser treatment and conservative therapy. The latter has a positive effect only in the initial stages of the disease; overgrown cysts must be removed.
Surgery
To eliminate the pathology, it is not necessary to remove the entire tooth; only the tooth root on which the cyst is located is subject to resection. After removing the affected area, the dentist seals the remaining root, treats the surgical canal through which he removed the bladder with its contents, and stitches it up.
After a few days, the doctor removes the stitches and monitors the wound healing process. It is important to make sure that there are no cyst particles left in the dental canal; to achieve this goal, repeat radiography is performed.
Note! Sometimes it is impossible to remove the root along with the cyst; in these cases, the doctor completely removes the tooth. Indications for complete tooth resection are a difficult-to-reach location of the cyst and a severe course of the disease.
After surgical removal of a cyst, the patient must regularly visit the dentist and follow the recommendations prescribed by the doctor.
Conservative therapy
Tooth cyst - treatment of the disease with conservative methods is possible only in the early stages of its development. In order to eliminate the tumor, the patient is prescribed injections and rinses.
During therapeutic treatment, the dentist opens the dental canal, which leads to a cystic neoplasm, and pumps out exudate from it. The doctor does not fill the canal for ten days; during this period, the patient uses antiseptic solutions and tinctures to rinse the mouth.
Upon completion of the treatment course, the dentist treats the dental canal with medications and then fills the tooth.
Laser removal
Laser treatment is a modern method of treating dental cysts. When performing the method, the doctor opens the dental canal and uses laser irradiation to treat the area where the cystic tumor is located. The laser destroys not only the epithelium of the cyst, but also hundreds of thousands of bacteria that are inside the bladder.
The advantages of laser removal are rapid tissue healing and no risk of secondary infection in the oral cavity and dental canal.
Treatment with antibiotics
In some cases, dental cysts are treated with antibiotics. Taking antibacterial drugs is an auxiliary measure to destroy an expanded infection or the main method of treatment if a dental cyst develops against the background of a primary infectious disease.
Antibacterial drugs can only be prescribed by the attending physician; the following drugs are most often used:
- amoxicillin – has a high antibacterial effect, greatly facilitates the treatment of cysts with other methods;
- Cifroploxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that actively destroys bacteria and relieves inflammation;
- tetracycline - this drug is prescribed more often than others, it actively relieves the inflammatory process, pain syndrome, and facilitates other methods of treating dental cysts.
Sometimes a doctor can prescribe topical antibacterial agents to a patient, but taking such medications is not always advisable - local drugs - antibiotics are quite difficult to distribute evenly over the diseased area.
Note! Antibacterial drugs are potent drugs that also affect beneficial bacteria in the body. You can take such medications only as prescribed by a doctor, without increasing the number of doses or dosage.
Treatment at home
Treatment of dental cysts at home is possible only as an auxiliary therapy. A cyst should not be confused with a granuloma; the latter can resolve on its own, but the cystic formation must be radically removed. Home treatment is not used to remove the cyst, but to eliminate the inflammatory process and destroy harmful bacteria.
The main goal of therapy at home is to provide an antiseptic effect. Propolis tincture, calendula tincture, eucalyptus tincture have an antiseptic effect. Tinctures are used as follows: a small amount of medicine is applied to a cotton swab and applied to the affected area, held for 5-10 minutes.
Medicines with an antiseptic effect can be used before surgery to remove a cyst and after tooth root removal. The antiseptic effect allows these medications to be used in the treatment of caries and other infectious diseases of the oral cavity.
Prevention
It is always easier and faster to prevent any disease than to cure it, so one should not forget about simple preventive rules that will help avoid the development of a dental cyst. The basic rules for preventing dental cysts are based on compliance with the rules of oral care.
How to prevent the formation of pathology:
- do not trigger the course of dental diseases such as caries, periodontitis, pulpitis; if infections occur, consult a doctor immediately;
- Brush your teeth daily and prevent the appearance of plaque, which can later transform into tartar;
- monitor the condition of the teeth and oral cavity after operations and mechanical injuries;
- visit your dentist regularly;
- monitor the condition of filled teeth and dental implants;
Patients who have had their teeth filled or have dental crowns or implants placed are advised to periodically have dental x-rays taken. This will allow timely detection of pathological changes and increase the chances of successful recovery without serious consequences.
Note! All diseases must be treated in a timely manner; inflammatory processes reduce immunity, as a result of which infections move freely from one organ to another; in addition, secondary infections can be added to already developed pathologies. It is important to monitor your health and strengthen local and general immunity.
To strengthen your immune system, strengthen your body, include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet, play sports and walk outdoors more often. It is more difficult for any infection to get into a hardened body than into a weakened body.
How to reduce the likelihood of developing education
To minimize the risk of mucocele formation, you need to follow the rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, quit smoking;
- carefully observe oral hygiene;
- rinse your mouth after every meal;
- eat a balanced diet;
- do not put foreign objects in your mouth;
- get rid of the habit of biting your lip;
- correct malocclusion;
- undergo oral hygiene every year;
- avoid trauma and chemical burns to the lips;
- promptly replace dentures;
- Follow the rules for wearing braces and caring for them.
People who follow preventive measures are much less likely to need treatment for oral cysts. If a lesion has appeared and is growing in size, there is no need to expect it to disappear on its own. This happens very rarely. It will either “deflate” or be filled again with contents and ultimately may grow to such a size that it will not be possible to do without emergency surgical intervention.
Treatment methods used for cysts in the oral cavity
For small cysts, no treatment is required. Carry out regular monitoring of educational growth. Medications are used when the tumor increases in size. The drugs help reduce inflammation and prevent suppuration.
The following treatment methods are used:
- treat the oral cavity with furatsilin solution; use antibacterial solutions for the throat (Chlorophyllipt, Tonginal, iodine preparations); take immunomodulators and vitamins; Vasoconstrictors are prescribed.
At high temperatures, antibiotics and antipyretics are prescribed.