When is it time to sound the alarm? Symptoms and stages of tooth decay
There are a number of signs that should alert you. Having noticed one or two of them, a person should become concerned and see a specialist. This:
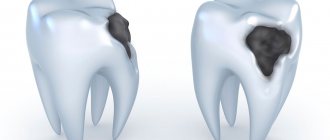
- 1. Accumulation of plaque on tooth enamel. Barely noticeable yellowish spots.
- 2. Bad breath, even the smell of rotten breath. With severe caries, the smell will be very noticeable.
- 3. Dark spots on the enamel. Painful sensations when eating hot or cold, sweet foods.
- 4. If you ignore the above-mentioned manifestations of ill health, the situation gets worse. Next, black areas appear in the area of the neck of the tooth or on the root itself, but the latter can only be detected during an X-ray examination.
- 5. Frequent aching painful sensations appear, and even if you regularly rinse your mouth with herbal infusions and take painkillers, the destructive processes are in full swing.
- 6. The pain intensifies (especially when a stream of cold air hits the tooth), and the pulp begins to die.
- 7. The nerve bundle is affected, the pain becomes especially severe.
- 8. Then, if the person never went to the hospital, he notices with surprise and relief that the pain goes away. However, in reality, the inflammatory process does not stop - the disease spreads to the root area.
Causes of the disease
There are a number of reasons leading to tooth root inflammation:
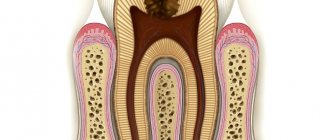
- Deep caries. As you know, at the initial stage, caries is a stain that, without proper treatment, quickly deepens and covers an increasingly larger area of the tooth. Thus, caries passes through layers: enamel, then dentin, and later reaches the inner layer - the pulp. After this, pathological microorganisms can go down the root canal and cause an inflammatory process there. There is also a retrograde type of spread of infection - that is, the spread of pathogens occurs from the roots of the teeth.
- Poor quality dental care. Many people know that regardless of whether you want to remove tartar, put a filling, or just undergo a preventive examination, it is important to contact experienced dentists. Sometimes it happens that poor-quality dental care leads to periodontitis, for example, if the doctor unsuccessfully placed a filling/crown or chose the wrong treatment tactics for pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve of the tooth). There is drug-induced periodontitis, which is formed when chemicals, such as filling materials, enter the periodontal tissue. In the event of an allergic reaction, allergic periodontitis may occur.
- Injuries. Periodontitis often occurs as a result of injuries to the jaw or teeth. Sometimes the development of periodontitis is provoked by an accidental, strong bite of a hard object (for example, a fork).
- Serious inflammatory processes in the body. Sometimes inflammation of the tooth root occurs due to general intoxication of the body, when the infection spreads through the blood or lymph. Often periodontitis also occurs against the background of poisoning of the body.
Complications and consequences that will not keep you waiting if your teeth are not treated
A far-fetched fear is extremely harmful: because of it, patients often take the situation to extremes and go to the doctor only when the disease spreads to neighboring teeth and gums, and serious intervention is required.
Deterioration of the general condition of the body
There is a misconception that bad teeth have no effect on the body as a whole. And that “one day the moment will come...” - the teeth will be cured, and there can be no complications. The immune system actually copes with the infection up to a certain point, and the problem is localized in the oral cavity. But one day the strength of the immune system weakens, because... he receives no help from outside. General intoxication of the body develops, which is poorly diagnosed, but manifests itself very clearly.
Intoxication is expressed in constant fatigue, fluctuations in body temperature, etc. The prolonged presence of rotten teeth leads to the following consequences:
- 1. Cardiac dysfunction. Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, which can only be treated surgically;
- 2. Loss of appetite. Impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to the entry of harmful microorganisms into it with saliva. Development of gastritis, food intoxication;
- 3. Frequent headaches due to tooth decay at the base of the root;
- 4. Many doctors are sure that bad teeth can cause problems with bone tissue and harm the musculoskeletal system. Arthrosis and polyarthritis often develop;
- 5. It has been scientifically proven that rotting of large chewing teeth leads to hair loss on the back of the head; destruction of small chewing units leads to baldness of the temporal part;
- 6. Rotting of any bone in the skull leads to brain damage;
- 7. Hearing impairment;
- 8. Poor condition of the skin;
- 9. An advanced putrefactive process spreads to the sinuses and can provoke chronic tonsillitis, hyperplasia of nasopharyngeal tissue, etc.
Pulpitis is a consequence of caries
The most common complication of caries is pulpitis. In fact, it is a natural consequence of caries and does not threaten a healthy tooth. With pulpitis, the dental nerve becomes inflamed; the disease is characterized by particularly severe pain when pressing on a tooth (biting on food).
A person can determine for himself when caries turns into pulpitis. With caries, pain appears only if a certain irritant acts on the diseased tooth. The unpleasant sensations disappear as soon as the irritant is eliminated. With pulpitis, pain can occur on its own. It can only be eliminated by the intervention of a doctor. A pain reliever will also help, but this is a short-term measure that loses effectiveness with frequent use. Taking painkillers is allowed only when it is not possible to visit the dentist. Their effect is only to relieve or weaken the pain syndrome; they do not have a therapeutic effect.
Periodontitis
If for some reason pulpitis has not been cured, the disease develops further. The ligaments that attach the tooth to the bone are affected.
Periodontitis has 2 phases:
- 1. Acute, characterized by severe pain;
- 2. Chronic – this phase may practically not appear.
A tooth was pulled out and the bleeding doesn’t stop: what to do?
A tooth was pulled out and the bleeding doesn’t stop: what to do?
Contents: • Bleeding is a complication after dental surgery • What should not be done after tooth extraction?
• What can you do at home? • Professional help from a dentist Tooth pulled out
– the bleeding doesn’t stop, why does this happen? Tooth extraction is a dental surgery that is performed in a clinic. Any operation is accompanied by some blood loss. Tooth extraction is no exception, as damage to gum tissue and periosteum occurs.
Bleeding is a complication after dental surgery
Socket bleeding can be quite difficult to stop. This problem occurs not only immediately after the operation, it can appear within a day.
Let's look at the reasons for this condition:
1. If the problem occurs immediately after removal, then this may be due to the fact that adrenaline has stopped working, and this provokes vasodilation. 2. If bleeding began after a certain time, then a common cause is the patient’s incorrect actions, which caused damage to the clot in the socket.
Local reasons include:
• damage to a wound or gum; • violation of the integrity of the interroot septum; • inflammation that has begun in the gum area at the site of the extracted tooth; • damage to the blood vessels located under the tongue. Common causes are mainly the patient's diseases, such as: scarlet fever, sepsis, blood diseases, hepatitis, hypertension.
What should you not do after tooth extraction?
After any surgical intervention, certain rules should be followed so as not to cause undesirable consequences.
For several hours it is prohibited:
• drink alcoholic drinks of any strength, because alcohol promotes vasodilation; • smoke; • Eating; • rinse your mouth with any liquid; • steam or take a hot shower, bath; • engage in physical labor or exercise in the gym.
How long does it take for blood to bleed from the socket?
A full-fledged clot is formed within 20 - 30 minutes.
If the bleeding continues when the patient is already at home, then there is cause for concern, so it is better to call the doctor and follow his recommendations. It is worth noting that some people confuse bleeding with ichor, which can be released from the wound for several hours after the removal procedure. If the secreted liquid is colorless or yellowish with a small amount of blood mixed in, then this is ichor. In this case there is nothing to worry about.
What can you do at home?
If bleeding begins after tooth extraction, and for some reason it is not possible to contact the dentist, then you need to help yourself.
The following manipulations may help solve the problem:
• A sterile swab should be placed on the resulting depression, then clamped with your teeth and held for approximately half an hour.
• If the bleeding does not stop, the tampon should be changed to one moistened with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, which helps stop the bleeding. • You can try applying cold to the cheek from the side of the extracted tooth. Cold constricts blood vessels, which helps eliminate this problem. Just remember: you can’t apply anything cold directly to the wound, as these actions can cause complications. • If the pain in the gum area is severe, then you can take painkillers, but without aspirin. This medicine thins the blood, which may cause bleeding. If the listed remedies do not produce results, and a person develops weakness or dizziness, then a visit to the dentist should not be postponed.
Professional dental care
The doctor will assess the situation and take action to stop the bleeding. What should a patient be prepared for? If there is bleeding from the soft gum tissue, the dentist may use sutures to close the wound.
If blood flows out of a blood vessel, then a tampon soaked in a special agent is placed into the tooth wound, the vessel is compressed, and the tampon is left in the hole for 5 days.
If the use of local remedies is ineffective and the bleeding does not stop, then the doctor may prescribe general medications that accelerate blood clotting. But the use of these medications is possible only after examination and testing.
Prevention of bleeding
To reduce the risk of all kinds of complications, you must adhere to some rules before tooth extraction: • Approximately two days before surgery and after, you should definitely stop smoking. • If the patient has hypertension, it is necessary to take medications to stabilize blood pressure, and also measure it before and after this dental procedure. • If the patient is taking blood thinning medications, they should be stopped a few days before surgery as they reduce blood clotting.
How to protect yourself from complications of dental diseases
To avoid any complications, it is best to prevent the diseases themselves. There is nothing complicated here:
- 1. Brushing your teeth twice daily. In this case, it is necessary to change your toothbrush in a timely manner (usually once every three months) and carefully choose toothpaste, taking into account the doctor’s recommendations;
- 2. Regular visits to the dentist. If you go to the doctor every six months, you will be able to either completely avoid caries, or cure it at the earliest stage - quickly and without any discomfort;
- 3. If a tooth has been removed or deformed (part of it has broken off, a filling has fallen out), you also need the help of a doctor. Such violations spoil the bite, and the load on neighboring teeth will increase. They will become more vulnerable to adverse effects.
Of course, to avoid complications, you should immediately consult a specialist as soon as a pathological process or painful sensations are noticed.
SOS remedies against bleeding gums
Sometimes it’s impossible to get to the doctor and you need to wait 1-2 days until the appointment. In this case, several SOS tools will help.
- Rinses: chlorhexidine, oak bark decoction, LACALUT Aktiv rinses with aluminum lactate and sodium fluoride, PRESIDENT Antibacterial with plant extracts - relieve inflammation, prevent bleeding.
- Gels: Cholisal, Parodontocid - reduce pain, remove signs of inflammation.
- Pastes: Forest balm - contains oak bark, stops bleeding, strengthens gums.
All means must be used comprehensively. First, brush your teeth, then rinse (1 minute). After this, the solution is spat out and the gums are dried with gauze: this way the gel is better fixed. Then use ointments, applying with your finger to the entire inflamed surface. If saliva comes out during treatment, you should not swallow it, you need to spit it out.
After the procedure, you should refrain from drinking for 30 minutes and from eating for 2 hours. Treatment is carried out twice a day: after breakfast and at night.
The most effective remedy for diseases in which the gums begin to bleed is antibiotics. They help to quickly relieve inflammation and improve well-being. But they are available with a prescription and are taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Therefore, you won’t be able to buy and prescribe antibiotics yourself. It is better to immediately make an appointment with a specialist so as not to waste time and money on something that will not solve the problem, but will only delay the inevitable.
Ice pack
- Fill the bubble 2/3 of the volume with pieces of ice and close it tightly.
- Wrap it in a towel and apply it to the sore spot.
- If a long procedure is necessary, take cooling breaks of 10 minutes every 30 minutes.
- Watch your condition so as not to get too cold and catch a cold.
If the bleeding does not stop, for this period, stop eating food, especially carbohydrates, since this is one of the factors that activates the growth of bacteria. If bleeding is accompanied by severe pain, you can take antispasmodics and analgesics, but only after consulting a doctor.
How does a dentist stop bleeding?
If the bleeding does not stop, your dentist may do the following:
- Apply a ligature.
- Cauterize the wound surface using electrocoagulation.
- Use a hemostatic sponge, which is placed in the hole, after which cold is applied to the cheek. This gives an almost immediate effect.
- Taking drugs that increase blood clotting: vikasol, aminocaproic acid, dicinone. But the maximum effect of these funds occurs within 2-4 hours.
Important! If there is a tendency to form blood clots, as well as with diagnoses of thromboembolism and thrombophlebitis, taking medications that increase clotting is contraindicated.
If bleeding resumes a few days after tooth extraction, this may indicate the onset of inflammation. Therefore, the doctor prescribes special medications and applies a tight tamponade.
Possible complications
If left untreated, rotten teeth can lead to the development of chronic diseases of the oral cavity, pathologies of the heart, kidneys and joints, as well as neurosis and nervous tics. In people with weakened immune systems, the source of infection can cause a serious life-threatening condition - sepsis.
Insufficiently chewed food leads to bloating, flatulence, heaviness in the epigastrium or around the navel, changes in stool - diarrhea or constipation.
When pulpitis develops, the nerves going to the tooth are removed (this is called a dead tooth). It has been noticed that when nerve fibers are removed, the condition of dental tissues worsens and destruction occurs faster.
Traditional medicine methods
Alternative medicine methods, of course, can be effective, but you still need to be careful. If the problem becomes serious, it is better to contact the doctor who removed your tooth. However, in some cases the following folk advice will help:
- Apply a cotton swab dipped in aloe juice, furatsilin (in the ratio of 2 furatsilin tablets per glass of water), valerian or echinacea decoction to the wound.
- Place a brewed bag of good black tea on the hole. Tea leaves contain tannins, which constrict blood vessels and slow down bleeding.
- Apply a turunda (gauze or cotton swab) soaked in chamomile and nettle infusion to the diseased area of the gum.
Do not rinse your mouth with solutions or tinctures under any circumstances, as this has a mechanical effect on the hole. Rinsing is allowed only from the third day.
Old sinus perforation
If the defect is not detected and eliminated in a timely manner, acute inflammation will subside. Within a month, the patient develops a fistula. It connects the gum surface and the sinus cavity. Signs of a chronic inflammatory process appear. This will be a serious complication.
The patient has complaints:
- The presence of dull pain in the upper part of the cheek, of a constant nature. They radiate to the eye area and temporal region.
- Feeling of nasal congestion on one side.
- Separation of pus from the nose and from the fistula on the upper jaw.
- Swelling of the middle third of the face on the affected side.
- Air movement through the defect.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Getting fluid from the mouth into the nose.
Therapy of old processes is associated with significant difficulties. Patients are indicated for surgical treatment in a hospital.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removing foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas and granulations.
- Excision of tissues forming the fistula.
- Closing the defect.
After the operation, drug therapy with the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs is mandatory for a course of two weeks.