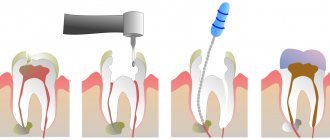
Possible reasons for the appearance of a lump on the gum after tooth anesthesia
Since the doctor makes the injection blindly, there is a risk of hitting a blood vessel. This explains why a bruise appears on the cheek or gum. In many cases it is considered the norm. Hematoma may also occur while taking certain medications that affect the blood's ability to clot. This could be, for example, Heparin, Aspirin, and many NSAIDs. A number of factors contribute to the appearance of a lump after the administration of an anesthetic:
- drinking alcoholic beverages before visiting the dental office;
- high blood pressure - hypertension;
- consuming too hot food or drinks shortly after dental treatment.
Swelling near the injection site is not considered a deviation from the norm. Often such manifestations are subjective in nature - a person may feel severe tissue swelling, although in fact the swelling is insignificant. But in some cases, these signs can lead to complications, so it is necessary to understand when the pathological process develops.
What else can be done to relieve swelling?
Additional measures can also help reduce swelling after implantation:
- Drug therapy. Take antibacterial, antihistamine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by your doctor.
- Antiseptic baths. The dentist may prescribe rinses with chlorhexidine, chamomile decoction and other means to prevent inflammation and associated tissue swelling.
- Sleep with your upper body elevated. You can use several pillows for this. In this position, conditions are created for the outflow of fluid from the surgical area.
- Elimination of irritating factors. In the first days after installation of the implant, avoid eating hot, salty, spicy foods, coffee, and alcohol-containing drinks.
- Elimination of temperature changes. You cannot take hot baths or steam.
- Reducing overloads. In the first weeks, give up sports training, and also try to avoid stress.
Why does pain occur after an injection into the gum?
Since the needle is inserted into soft tissues, it injures them and provokes discomfort. The patient may feel pain at the injection site for 1-2 days, or even more. The duration of the recovery period depends on the characteristics of the body and the perception of stimuli at the neuropsychic level.
Overly sensitive patients should be prepared for aching pain. Most often, no action is required. Usually the pain subsides on its own. In the case when it does not go away and only gets worse over time, we can talk about the development of a complication. At the same time, other signs of disturbances may occur.
Sometimes the patient thinks that the injection site hurts, but the localization is in a different place. So, after caries treatment, you may feel aching pain that radiates to the gums. Removal of a wisdom tooth is accompanied by pain in the socket, while the patient thinks that the problem is localized at the injection site.
Types of maxillary sinusotomy
There are classical (radical) maxillary sinusotomy and endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy.
Radical maxillary sinusotomy
The maxillary sinus operation is used to open the maxillary sinus through the mouth.
Radical maxillary sinusotomy is carried out using local or general (as indicated) anesthesia and includes the creation of access, excision of soft tissue, opening of the maxillary cavity and removal of polyps or foreign objects, formation of an anastomosis connecting the maxillary sinus with the lower nasal passage. The operation takes about an hour.
1 Radical maxillary sinusotomy in MedicCity
2 Radical maxillary sinusotomy in MedicCity
3 Radical maxillary sinusotomy in MedicCity
The essence of the operation
With an intraoral gairotomy, the otolaryngologist makes a horizontal incision in the soft tissues of the upper gum and moves them upward. Then, using special instruments, part of the bone plate on the facial wall of the maxillary sinus is removed. Thanks to the hole made, the sinus cavity becomes accessible for manipulation, and the otolaryngologist removes the pathological contents using a sharp spoon.
After scraping the mucous membrane, an anastomosis is formed with the nasal cavity, smoothing out the bone defect. A flap is made from the remaining free mucosa and placed on the bottom of the maxillary sinus to restore epithelization of its walls.
At the end of the operation, a tampon is placed in the sinus, which is removed into the nasal passage, and the wound on the side of the mouth is sutured. Using a tampon, sterility of the sinus is achieved and the accumulation of blood and pus is prevented.
After 48 hours, after preliminary anesthesia, the tampon is removed, and the patient is prescribed vasoconstrictor drops and sinus lavage. After a week, the sutures in the mouth are removed.
Endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy
Endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy is very popular as a minimally invasive and more gentle technique. With endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy, the lip is not dissected; the operation is performed through the nose. The procedure is virtually painless, characterized by minor swelling after surgery and does not leave scars.
Endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy. Its advantage over conventional surgery:
- low morbidity;
- minimal blood loss;
- the ability to perform surgery on an outpatient basis;
- quick rehabilitation period for the patient;
- absence of cosmetic defect after surgery.
The essence of endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy
This type of operation is performed under local anesthesia using special endoscopic equipment through the nose.
The indication for endoscopic maxillary sinus, as well as for conventional surgery, is a severe purulent process in the maxillary sinus, for which conservative treatment has proven ineffective.
The duration of endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy is 20 minutes. The opening of the maxillary cavity occurs through the nose, and not an incision is made, but a minimal puncture with a diameter of about 5 mm. An endoscopic tube is inserted into this incision, and foreign objects and pathogenic material are removed using suction. All manipulations are performed under the control of an endoscope.
The following methods of endoscopic access to the maxillary cavity exist:
- through the middle nasal meatus;
- through the lower nasal passage;
- through the anterior stack of the sinus;
- through the alveolus of the tooth (if there is a fistula);
- through the tubercle of the maxilla.
1 Diagnosis of sore throat
2 Diagnosis of sore throat
3 Diagnosis of sore throat
The use of endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy helps reduce trauma to surrounding tissues and speed up rehabilitation after surgery.
With the help of endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy, it is possible to avoid the feeling of numbness in the teeth on the operated side, which the patient experiences during a conventional operation.
Highly qualified otolaryngologists of the Multidisciplinary Clinic "MedicCity" will help you in solving various ENT problems. We possess all modern methods of diagnosing and treating diseases of the ear, nose and throat.
Complications after injection of anesthetic into the gums
Depending on the amount of blood released from the vessel and the individual characteristics of the body, it often takes 4 to 10 days for a bruise on the gum to disappear. Otherwise, this is already a complication.
| Type of complication | Features of manifestation | Symptoms |
| Accession of infection | There are always millions of bacteria in your mouth. In a normal state, they are in a certain balance, but under favorable conditions, for example, when immunity decreases, they can be activated. Thus, clotted blood becomes a nutrient medium for them. Pathogens begin to multiply. Pathogenic microorganisms can spread to periodontal tissue, the alveolar process that holds the tooth, periosteum and bone. Much depends on the type of pathogen and the location of the bruise. | Tissue infection is accompanied by the following symptoms: · painful sensations; · temperature increase – up to 39 ˚С; · weakness; · headache; Redness of the gum tissue. |
| Damage to the nerve trunk | If the doctor acts incorrectly, nerve fibers may be damaged as a result of the administration of anesthesia. In this case, it is important to contact a neurologist and maxillofacial surgeon as quickly as possible. | The patient feels a sharp pain immediately when the injection is given. It will subside for the duration of the anesthetic, but then resume again. It cannot be stopped even with the help of painkillers. If a large nerve trunk is affected, pain will be felt throughout the entire mouth, cheek and ear. It is even possible to turn off the chewing function and numbness of the face. Sometimes it is difficult to open your mouth completely; one side may sag. |
| Tissue necrosis | A very dangerous complication. The reason for its development may be the patient’s ailment, which he was silent about, vasospasm, too much anesthetic or its rapid administration. | The patient first feels a sharp, growing pain. It subsides for a short time, but this does not indicate that the danger has passed. The pain disappears due to tissue death. |
Complications after tooth extraction often occur due to the penetration of bacteria through the hole into various tissues of the dentofacial apparatus. Pus accumulates.
Symptoms of inflammation in the mouth
Inflammation of the oral mucosa involves not only its superficial layers, but also often the gums and periodontium. The latter is the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth and holds it in the bone. When these structures are damaged, the following complaints and symptoms arise: pain and redness, bleeding, swelling, the appearance of periodontal pockets, and an unpleasant odor. As the process progresses, suppuration and mobility of supporting teeth and enlargement of regional lymph nodes may appear. All of the above symptoms require specialist intervention, elimination of the cause and treatment.
Reason to see a doctor
The following symptoms require a visit to the dental office:
- severe pain at the injection site and its increase;
- significant swelling of the gums that remains after the anesthesia wears off;
- purulent or sanguineous discharge from gum tissue;
- temperature increase;
- compaction (“petrification”) of gum tissue in the affected area;
- looseness of the gums under the tooth, which was amenable to treatment, their slight displacement when exposed.
During the examination, the doctor will determine the cause of the development of undesirable effects.
Coming out of anesthesia
Most types of oral surgery are performed using anesthesia. A person can “recover” from anesthesia for several hours after the operation. Then the patient experiences ailments such as fatigue, drowsiness, and poor concentration. There are several ways to get rid of side effects of anesthesia.
- The first way is to move as much as possible, but without excessive physical activity, which can cause bleeding.
- The second way is to drink plenty of fluids, but only a few hours after the operation. It is necessary to drink ordinary mineral and always still water.
Carrying out surgical operations in the oral cavity requires subsequent special care of teeth and gums. The postoperative period will become much shorter if the listed recommendations are followed. If you experience any serious complications, prolonged bleeding, or if you cannot “bring down” the increased temperature, then this is a reason to immediately contact your dentist. Only he can help you and provide additional recommendations.