Fluorography and radiography
Fluorography and radiography are methods of radiographic examination. Fluorography is often used for mass, routine screening of tuberculosis.
Nowadays digital fluorography is mainly used . Film fluorography is an outdated research method. Digital fluorography has a lower radiation exposure to a person, but at the same time its resolution (that is, the ability to transmit a real image) is lower in comparison with x-rays of the lungs in direct projection.
X-rays contain more information and pathological changes are more clearly visible.
The radiation exposure is low for both methods (digital devices have lower radiation exposure).
Execution steps
Interproximal radiography is one of the types of intraoral examination that allows you to obtain a picture of 1 section of the oral cavity with an image of the upper and lower dentition. To obtain the image, a special holder is secured between the closed teeth. It allows you to identify interdental caries and various changes in bone tissue due to gum disease. And also check the correct installation of crowns, dentures or fillings. An X-ray of the tooth is taken by a doctor in an office specially equipped for this. Before taking an X-ray of a tooth, the doctor gets acquainted with the problem and studies its location.
To obtain a clear image of the problem area, the patient's head is fixed in the required position. The process of visiography takes a matter of seconds, but during this time the patient is required to remain completely still. The video in this article shows how to take targeted photographs of teeth so that the image is as informative as possible. Using a digital sensor, the radiologist directs a beam of rays to the required area. The photograph is taken either from the inside of the mouth or from the face. During the manipulation, the patient does not feel any pain or discomfort.
The original digital image differs from the traditional film image because it is processed using a special program in a few seconds and transferred to the monitor screen.
X-ray and breastfeeding
Modern scientific research proves that there is no reason why a nursing mother should wean her baby off breast milk for some time due to X-rays.
Breastfeeding is NOT a CONTRAINDICATION for x-rays of any area of your body.
CT and MRI are also not contraindicated during breastfeeding.
If a contrast agent is administered, it is necessary to decide individually whether a particular contrast agent is compatible with breastfeeding. Mostly gadolinium-based contrast agents are used.
According to the website e-lactancia.org, X-ray examinations and gadolinium-based contrast agents are in the green (permitted) zone.
- X-ray does not affect the quality, quantity and taste of milk.
- There is no need to pump either before or after!
- There is no need to wean the baby from the breast after the X-ray examination. ⠀
X-ray is a short-term procedure (lasts a few seconds). The effect of radiation on the body stops immediately after the end of the procedure, the rays do not accumulate in it and radioactive substances are not formed.
Breast milk is not exposed to the negative effects of X-rays and its composition does not change.
Remember that any procedure must be justified and performed according to indications. Don't put off getting an X-ray if you need it! Late diagnosis worsens the prognosis of the disease!
More information: X-ray during pregnancy
Source:
Mohrbacher N., Stock J., La Leche League International, The Breastfeeding Answer Book, Third Revised Edition, 2008
Author: Tatyana Neeshpapa, @doctor_neeshpapa
Similar
Impact of X-rays on the human body
Modern medicine often resorts to x-ray examinations. They are widely used to obtain detailed information about internal health problems such as diseases of the musculoskeletal system and internal organs. Experts say that X-ray examination is not at all dangerous when used rationally. During such a procedure, the human body receives a tiny dose of radiation, the benefits of which largely outweigh the possible risks.
It has been proven that the body experiences quite a lot of X-ray-like effects every day. However, his immune system neutralizes their harmful destructive effect. The softest X-ray radiation is used when undergoing fluorography, which is so important during the period of rising incidence of tuberculosis. In this regard, there is no particular reason to doubt whether it is possible to do fg while breastfeeding.
A real health hazard from X-rays arises only in the case of powerful, unregulated exposure. Doctors say that the real probability of causing harm to the body from undergoing an x-ray is normally no more than 0.001%. Such figures can reassure even particularly suspicious patients.
Why are breastfeeding women afraid to have their teeth treated?
Any step of a nursing mother can affect the health of the child, so before performing the simplest usual actions, she evaluates whether this will harm the baby. When visiting a dentist, three things may cause concern:
- To make a diagnosis, you may need an x-ray of the diseased tooth;
- During treatment, filling materials and anesthesia medications are used;
- After the procedure, a course of antibiotics may be prescribed.
A young mother may fear that x-rays and medications will make breast milk unsuitable for feeding, and just in case, she may completely refuse dental treatment and postpone going to the doctor until the time when the baby is weaned.
Features of the procedure in children
Contact intraoral radiography can be prescribed for children in cases where tooth damage cannot be examined in any other way. The technique allows early detection of disturbances in the process of teething, bone tissue diseases, and prescribing effective treatment. In addition, this method allows you to control the implementation of orthodontic manipulations if the child has problems with the formation of the jaw.
The study is carried out in the same way as in adult patients. Children under 2 years of age are recommended to undergo x-rays only in case of urgent need. For example, in case of injury during childbirth, to monitor the development of the jaw, or after a fall from a height, to assess the integrity of the teeth.
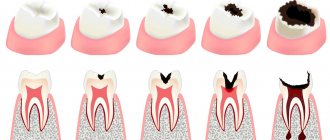
Interpretation of a dental radiograph
Only a dentist or radiologist can decipher and describe a dental image. The image shows the tooth: its root, internal canals, shape, anatomical features.
- Examines the rigidity, density and uniformity of the bone structure. Evaluates the location of each element of the dentition.
- Determines the presence of signs of clearing or darkening, indicating the development of an inflammatory process, cysts, granulomas, neoplasms.
- Depending on what the dental x-ray shows, a diagnosis is made.
Carious formations in the picture look like light areas of various shapes with unclear boundaries. The development of pulpitis is characterized by bone damage. The image shows a violation of its homogeneity in the interroot space. With the development of periodontitis, a granuloma appears in the area of the tooth root in the form of a darkened round shape with clear contours. With periodontitis, the image shows a decrease in the density of the bone structure, a decrease in the height of the partitions between the elements of the dentition, and the formation of “pockets.”
X-ray in dentistry in Kozhukhovo
In the daily practice of a dentist of any specialty, there is often a need to obtain X-ray images of the patient’s oral cavity.
X-ray images are used for correct and complete diagnosis of diseases, during treatment and to monitor its results.
The main types of research used in dentistry:
Dental (or targeted) image - for examining an individual tooth or group of teeth. It is done on a visiograph.
Panoramic photo (OPTG) - to study the entire maxillofacial area. It allows the dentist to assess not only the condition of the teeth, but also see possible pathological changes in the surrounding tissues. Done using an orthopantomograph
CT (computed tomography) is a three-dimensional model of the dental system, which allows you to very accurately determine the condition of the teeth, the size and density of the bone, and take any necessary measurements. This type of research is necessary both for complex endodontic treatment and for implantation. It is done on a computed tomograph.
Many patients wonder about the safety of dental x-rays.
Dental X-rays are significantly different from a conventional X-ray machine; the radiation exposure is much less due to the use of a narrow beam of X-rays and a short duration of radiation. For example, when taking a picture with a digital X-ray, you receive no more radiation than during a two-hour flight.
Various units are used to measure the amount of radiation. In medicine, X-ray procedures typically measure the dose received by the entire body during one procedure—the effective equivalent dose, measured in sieverts. According to SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03, when carrying out preventive medical x-ray procedures, this dose should not exceed 1,000 μSv (microsievert) per year, and a dangerous dose is 1,000,000 μSv.
What is 1000 µSv? Is it a lot or a little? 1000 μSv is approximately:
- 500 targeted images (2-3 μSv) obtained using a radiovisiograph
- 100 of the same targeted shots, but using good X-ray film (10-15 µSv)
- 80 digital OPTG (13-17 µSv)
- 40 film OPTG (25-30 µSv)
- 20 CT (45-60 µSv).
That is, even if we take 1 image on a visiograph every day for the whole year, in addition to a couple of 3D computed tomograms per year, and the same number of OPTG, then even in this case we will not go beyond the limits of the safe permitted doses.
Several government agencies - SES, Rospotrebnadzor - are involved in the installation and monitoring of X-ray medical devices.
To approve the installation of the device, it is necessary to comply with all points of SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03. The ventilation system in the X-ray room is very important, and we approached this issue with the utmost responsibility. Also, official documents require compliance with the air exchange rate, calculated illumination values and calculated temperature values.
Is it possible to give X-rays to pregnant women?
Here's what they write to us about this in official documents (SanPiN 2.6.1.1192-03):
7.18. X-ray examinations of pregnant women are carried out using all possible means and methods of protection so that the dose received by the fetus does not exceed 1 millisievert* for two months of undetected pregnancy. If the fetus receives a dose exceeding 100 mSv, the doctor is obliged to warn the patient about the possible consequences and recommend terminating the pregnancy.
* 1 millisievert (1 mSv) = 1,000 microsievert (1 µSv)
That is, in the first half of pregnancy it is definitely not worth taking pictures, but in the second half - 1 mSv for a visiograph - this is practically without restrictions.
I would also like to add here that I have often encountered the militant obstinacy of this opinion: an x-ray at the dentist during pregnancy is an absolute evil. And after all, while “fighting” radiation at the dentist, the same people often calmly fly south to bask in the sun and eat fresh fruit. Moreover, during a 2-3 hour flight to a country with a warm climate, a person receives 20-30 μSv, i.e. the equivalent of approximately 10-15 images on a visiograph. In addition, 1.5-2 hours in front of a cathode ray monitor or TV gives the same dose as 1 picture... How many pregnant women, sitting at home, watching TV series, hanging out on the Internet, think about how many pictures they “took” while watched another program, and then discussed it with friends on the forum and social networks? Almost no one, because the average person does not associate all this with ionizing radiation, unlike an image in a doctor’s office.
Is it possible to take photographs of nursing mothers?
Can. X-rays are not the same as radioactive waste. By itself, it does not accumulate in the biological environment.
With such a load, which is necessary to work with a visiograph, nothing will happen to the milk itself.
I hope this article will help patients answer questions they have about dental x-rays.
Prevention
To avoid problems, regularly perform dental and oral health care. It's better to prevent than to treat! After all, the risk of diseases in nursing mothers is very high due to weakened immunity after childbirth. For prevention, use the following procedures:
- Brush your teeth after every meal;
- Use flossers and dental floss, special mouth rinses;
- Visit your dentist regularly;
- Change your toothbrush more often;
- Choose pastes with a high fluoride content;
- To strengthen bones and teeth, take vitamin complexes for nursing;
- Eat foods containing calcium, especially sesame seeds, cottage cheese and cheese;
- Don't drink too hot drinks, don't eat a lot of sweets. In addition, such food is harmful to lactation and the infant!
Category Pregnant Published by kosmetik-dent
X-ray of teeth
| Service | price, rub. |
| Orthopantomogram (OPTG) | 900 |
| Comprehensive services | |
| OPTG + CT 12x8.5 Promotion! | 2 700 |
| Orthodontist 1 (OPTG + TRG) Promotion! | 1 500 |
| Orthodontist 2 (OPTG + TRG + analysis and calculation of TRG) Promotion! | 3 400 |
| Therapist (OPTG + CT 5x5) Promotion! | 1 500 |
| Implantologist 1 (OPTG + 2CT 12x8.5) Promotion! | 4 500 |
| Additionally | |
| Recording to disc (CT) | included in the price |
| Printing on photo paper (OPTG) | included in the price |
| Sending by E-mail | included in the price |
| Description of the examination by a radiologist (readiness 1 working day) | check prices through the operator |
Sign up for a study by phone (812) 332-52-54