- What are root canals?
- What are roots, how many roots do teeth have?
- How many canals in a tooth
- Indications for dental canal treatment
- Canal diseases
- Pus in the dental canal
- Endodontics
- Stages of root canal treatment
- Canal filling methods
- Canal treatment under a microscope
- Possible complications after endodontic treatment
- Prevention of dental canal diseases
- Choosing a paste for prevention
- Tooth canal treatment: price
What are roots, how many roots do teeth have?
The roots of the teeth are located in the jaw under the gum, bone formation, 70% of the entire tooth, thanks to them the teeth are firmly held in the jaw and cope with chewing everyday loads.
The number of roots does not equal the number of tooth crowns. The total number of roots is different for each person, it is individual. It differs depending on the location in the oral cavity, race, age, and load taken.
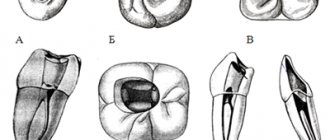
Number of roots in different teeth:
- 1 root has incisors and fangs,
- 1-2 roots have premolars,
- 3-4 roots at molars,
- Wisdom teeth can have up to 5 roots.
Roots are also present in baby teeth; they are the attachment of the teeth to the jaw; one tooth can have three roots. During the change of teeth, they dissolve, giving way to growing permanent ones, so the fallen baby teeth do not have “roots”.
Factors influencing the anatomical features of the dentition
The structure of teeth is determined by nature itself. So, it is clear that, for example, sevens need more roots than fives, since they withstand a greater chewing load. A developed root system provides them with strength and endurance.
The anatomical structure of the teeth of the lower and upper jaws is different. This is due to the uneven load performed by the functions. There are fewer canals in the lower teeth. In dental practice, there are also cases when they are absent altogether. This may be due to obliteration due to age-related changes. They provoke disorders and inflammations, neoplasms, and incorrect treatment that was carried out previously.
Indications for dental canal treatment
Root canal treatment
- a necessary procedure in case of inflammation, helps to save the tooth. Since tooth canals are treated endodontically, a number of indications and contraindications must be taken into account. You should immediately contact a dentist for treatment when the tooth hurts when pressing on it, if there is pain in the cheek, swelling of the gums, and the tooth reacts to cold and hot.
You should consult a doctor if you have symptoms:
- Inflammation, there is a risk of pulp damage
- Deep caries, there is a risk of developing pulpitis, periodontitis, and abscess.
- Pulp chamber injury
- Toothache and swelling of the gums.
- After dental treatment, after a few days, painful sensations arise and do not go away.
Contraindications:
inflammation of the tooth root and maxillary sinus, root fracture, narrowing of the canals, destruction of the alveolar process.
If it is impossible to pass through the canal, it is removed or treated with mummifying paste.
Features of the structure of teeth, their roots and canals
There are no two identical root dental systems, which is explained by the purely individual structure of a person’s teeth. In addition, the root system of incisors, canines and molars is arranged in accordance with their purpose:
- Ones and twos (incisors) are needed for biting food.
- Fours and fives (premolars) perform the initial chewing function.
- Sixes and sevens completely grind food.
Based on this, it becomes clear that the seventh tooth requires more nutrients than the fifth. It must be strong and hardy, therefore it has a more developed channel system. Despite the fact that the 6th tooth in the lower jaw performs the same functions as the seventh, it usually has fewer canals. This is due to the fact that there is less chewing load on it.
For a detailed study of the structure of the dentofacial apparatus of a particular patient, radiographic examination is used.
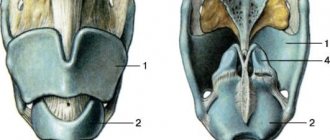
Tooth structure
Each dental unit consists of:
- crowns - the area above the gum;
- neck - the area between the crown and the root;
- root - the area under the gum.
Inside the crown is the pulp, which passes into the root canals. At the end of the root there is a small apical opening through which blood vessels and nerve endings pass, starting from the main neurovascular bundle and ending in the pulp.
When a person’s pulp becomes inflamed, not only it, but also all root canals need to be cleaned of infected tissues, since they are “communicating vessels.” If even one canal is left uncleaned, pathogenic microorganisms will continue to develop inside the dental unit, which will lead to its removal. That is why the doctor must know the exact number of canals in the tooth.
How many nerves are there in a human tooth?
Thanks to the nerve, the tooth can respond to external stimuli. After removing the pulp and filling the canals, the dental unit loses sensitivity, as it is deprived of a nerve. But due to the removal of blood vessels, problems begin with its blood supply and mineralization. The crown becomes less durable and more prone to various chips and breaks. The enamel quickly darkens, and it cannot be properly bleached even with strong chemicals.
Before removing the pulp, the patient is sent for an x-ray to find out how many canals are in the operated tooth: a person has only one dental nerve in a tooth, but there may be several canals
. This preparation allows for depulpation to be carried out competently and quickly.
Types of Root Canals
There are several options for the structure of dental canals:
- in the root there is one canal passage, which corresponds to one apical foramen;
- in the root there are several canal branches that connect in the area of a single apical foramen;
- two different branched passages have one mouth and two apical openings;
- canal cavities in one root merge and diverge several times;
- three root canal passages emerge from the same orifice, but have 3 different apical openings.
There can be as many channels as there are roots, but often their number differs. Several types of canals may be present in one molar and premolar.
How many canals in a person’s teeth - table
According to statistics, the number of channels depends on the depth of the tooth.
: The deeper it is located in the jaw, the more canals it has. This is due to the increased load on the molars located at the base of the dentition.
Typically, teeth in the upper jaw have more canals. But this pattern is not observed in all patients.
The table below presents average statistical data on how many canals are in a person’s teeth above and below.
| Dental unit | Number of channel passages | |||
| Fangs | Upper | 1 | ||
| Lower | 2 | |||
| Incisors | Upper | 1 | ||
| Lower | Central | in most cases 1, less often 2 | ||
| Lateral | 1 or 2 (about the same probability) | |||
| Premolars | Upper | First | most often 2, but sometimes first premolars with 1 or 3 canals are found | |
| Second | in most cases 2, sometimes 1 or 3 | |||
| Lower | First | 1 or 2 | ||
| Second | 1 | |||
| Molars | Upper | First | 3 or 4 with equal probability | |
| Second | in most cases 3, sometimes 4 | |||
| Third | around 5 | |||
| Lower | First | most often 3, sometimes 2 or 4 | ||
| Second | usually 3, but there are roots with 4 channels | |||
| Third | no more than 3 | |||
Number of canals in teeth in the lower jaw
The teeth on the lower and upper jaws are significantly different from each other. This is partly due to the uneven load and different functions. Typically, teeth in the lower jaw have fewer canals. But each specific case requires detailed study. Therefore, the dentist first sends the patient for an x-ray, and only then proceeds to open the crown and treat pulpitis.
It is impossible to start treating caries and pulpitis based only on encyclopedic information, because:
- The 6th tooth of the lower jaw can have any number of canals - from 2 to 4;
- in the 5th tooth below there is usually only 1 canal, but in approximately 10% of patients there are quints with 2 canals;
- In the 4th tooth there is usually only 1 canal, but in about a third of cases there are 2.
The eighth tooth on the lower jaw is the most “unpredictable”. Exactly how many canals are in the wisdom tooth located below can only be determined using x-rays. Officially, there are no more than 3 of them, but during the treatment of caries, additional cavities usually open. It is precisely because of its incomprehensible structure and inconvenient location that the figure eight is most often removed.
It is impossible to treat a dental unit without studying the structure of its root and canal system. This can only aggravate the pathology and lead to complications.
Number of canals in teeth in the upper jaw
The root system of the teeth of the upper jaw is more complex and branched. This explains the longer treatment of upper molars and the frequency of repeat visits due to incompletely sanitized dental cavities.
Features in the structure of the canal system of teeth in the upper jaw:
- The 6th tooth of the upper jaw is most often three-channel. But sometimes there are also four-channel first molars.
- The fourth and fifth teeth from above are most often two-canal, but sometimes single-canal and three-canal premolars are found.
- The 4th upper tooth usually has 2 canals, but sometimes there are premolars with 1 or 3 canals.
The “wise” eight on the upper jaw is a four-channel tooth. Third molars with 5 canals are extremely rare. However, in dentistry, even cases of the presence of eight-channel wisdom teeth located at the top have been recorded.
Canal diseases
Canal diseases make themselves felt by inflammation and pain, so you need to see a dentist. If there is internal inflammation, but there is a possibility of soft tissue necrosis.
- Pulpitis
- inflammation of the dental pulp. With pulpitis, blood vessels collapse and die.
- Periodontitis
- inflammation of connective tissues resulting from complications of pulpitis.
- Abscess
- the presence of pus in the gums, which arose as a complication of pulpitis
- Advanced caries
leads to inflammation of the tooth canals.
Types of root canals
As noted above, the internal structure of each individual element has its own individual characteristics. But there is also a classification that makes it possible to group various options for the structure of dental canals into several categories:
- for one root there is one passage and one apical foramen,
- the root has several branches that connect closer to the apical foramen,
- two branched passages with one mouth and two apical openings,
- in one root, the cavities are connected and separated several times,
- three canals emerge from the same orifice but approach three different apical foramina.
The internal structure of each individual tooth has its own individual characteristics.
The number of roots and canals may be the same, but more often their number differs. In this case, cavities of various types may be present in one chewing premolar or molar.
Pus in the dental canal
Pus can accumulate in the dental canal in case of improper therapeutic treatment, or as a complication of this treatment, tooth trauma. Pus in the dental canal
appears as a consequence of deep caries, when the carious process has reached the canal and pathogenic microorganisms began to develop, causing pain.
Pus accumulates due to infection and the development of bacteria in the dental canal, and has two exits: through the carious cavity of the tooth or through the gum. It is very important to seek help in time, since the presence of pus can lead to the following complications: spread to the tissues of the oral cavity, spread to nearby organs. The presence of pus over time can lead to a fracture of the jaw and dissolution of bone tissue.
Treatment boils down to removing the pus and rinsing the canal cavity through the tooth tissue or gum. The canal is washed daily for several days and done in the dentist's office. The patient is taking antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading. It is important to see a doctor in a timely manner because of the danger of an acute condition becoming chronic.
Depulpation: is there life after death?
Previously, if the pulp was damaged, dentists most often simply removed the diseased tooth, but today modern techniques make it possible to save the tooth, and the doctor’s goal is to try all methods and try to prevent tooth extraction. One of these methods is depulpation, that is, removal of the pulp of a tooth or, more simply, its nerve.
Depulpation is carried out under anesthesia and consists of several stages: the dentist removes caries from the tooth tissue, then opens the root canal and removes the inflamed pulp tissue. Then the doctor mechanically cleans the canals, then performs an antiseptic treatment and then seals the canals, in most cases first installing a temporary filling and only after a second visit and the results of an x-ray examination, a permanent one.
If depulpation is carried out correctly, then such a tooth will last long enough and will perform all its functions. So maybe nerves are not needed at all? The conclusion is again incorrect, because everything in our body is interconnected, and each organ bears a certain functional load; the pulp in this case provides nutrition to the tooth, without which it becomes more fragile. If the dentist makes even the slightest mistake, the tooth will immediately react to this and begin to crumble and darken, so before depulping, you need to make sure that there is no other way out.
Endodontics
Endodontics
is a branch of dentistry that studies the methods and techniques of prevention and treatment in the root canals of human teeth. Here we can draw a non-trivial analogy: a tooth is like a tree - if the roots are deep and powerful, then both the stem and crown will be strong and beautiful. Similarly, the tooth - its aesthetic beauty and health largely depend on the condition of the root canals!
Root canal treatment
necessary for complications of caries disease, namely pulpitis and periodontitis. This is the so-called primary root canal treatment. When re-treating a tooth that has been manipulated - re-canal treatment, or re-treatment.
Stages of root canal treatment
- The preparatory stage is when a diagnosis is made, a treatment plan and a method of pain relief are thought out. According to X-ray
- Preparing a carious cavity, it is opened, the dentin is removed, and access to working with the canals is opened.
- If the pulp is inflamed, a devitalizing paste is applied and a temporary filling is placed.
- The tooth cavity is opened and the pulp chamber arch is removed.
- The pulp of the crown is removed.
- Pulp extraction. The endodontist treats the canal up to the apical foramen.
- Treatment of the canal using instruments and medications.
Functions of nerves in teeth
The main function of the nerve is sensory. When bacterial damage (caries) spreads to the deep tissues of the tooth, a painful reaction occurs. Pain is the body’s signal that something is wrong and help is needed. The nerve is not located in the tooth cavity in isolation. It is part of the neurovascular bundle, a component of the dental pulp. The functions of the pulp are varied:
- tooth nutrition;
- growth and development;
- mineralization of enamel and dentin;
- immune protection.
The tooth pulp is treated and tried to be preserved in all cases where possible. It is especially important to do this in children and adolescents, since their teeth have not yet fully formed.
Canal filling methods
Canal filling
helps prevent the development of dental canal diseases. Canal treatment is a painstaking process, complicated by the fact that the dental canals themselves are narrow, the shape can be curved, which requires painstaking work to fill the entire canal. Today, dentistry has several methods for filling canals.
1. Heated gutta-percha
Gutta-percha is a hard material that becomes elastic when heated and ideally fills the canal cavity. Several methods are used to treat a tooth canal using gutta-percha:
1) liquid injectable gutta-percha;
2) continuous wave;
3) vertical condensation;
4) syringe administration of gutta-percha.
2. Lateral condensation - cold gutta-percha
A gutta-percha pin is inserted into a canal filled with sealer paste, compacted, and sealed.
3. Thermofil - volumetric filling with hot gutta-percha
A plastic rod is inserted into the canal and the canal cavity is filled with hot gutta-percha, penetrating into all branches, leaving no free space.
4. Depophoresis technology
It is used in cases of difficult access to a curved canal that was previously filled, as well as in cases where the canal contains a part of an instrument broken during treatment.
All methods are painless for the patient. After treatment, pain is possible for two weeks if the root is removed.
Features of the structure of the root system
Human teeth have a purely individual structure, so the root system of the same element may differ from person to person, including the number of canals in it and their branches. The structure of the roots is directly related to the immediate purpose of the tooth:
- incisors of the upper and lower jaws - help to bite off food,
- canines and premolars - perform the primary chewing function,
- molars - take on the main chewing load and help crush solid food as thoroughly as possible.
The photo shows teeth with roots.
The last ones in the row, sixes and sevens, and sometimes eights, require more nutrients to remain strong and wear-resistant throughout a person’s life. Therefore, premolars and molars usually have a developed canal system. But before we move on to a more detailed consideration of the structural features of the root system, let’s look at what a tooth actually consists of.
Canal treatment under a microscope
In endodontics, the method of treating tooth canals under observation of the process through a microscope is widely used. This method allows you to see much more and provide better treatment. Root canal treatment under a microscope is a convenient method for the patient and the doctor. A magnification of 30-40 times under a microscope makes it possible to see all the branches of the canals, clean the canal perfectly and seal it.
The microscope allows you to see cracks in the canal, find all the branches of the canal, remove foreign objects, precisely treat hard-to-reach areas of inflammation, and remove the nerve. A microscope helps the dentist determine the condition of the filling, avoid damaging healthy tissue, and fill all the voids in the canal, leaving no room for infection to develop.
Possible complications after endodontic treatment
- The walls of the tooth cavity and the bottom are perforated, subject to the presence of dentin, if the instrument penetrates too deeply.
- The contents of the root canal are not completely removed in cases of obstruction, lateral branches, denticles or bleeding.
- The lumen is clogged with dentin filings, pulp residues, or an instrument that has broken in the canal.
- If the canal is bent, perforation of the root walls is possible
- The canal was not sealed thoroughly enough.
- The canal lumen was not expanded correctly.
- Filling falling out.
Complications may not appear immediately. After root canal treatment, the patient has slight sensitivity, pain, and discomfort in the area of the treated tooth and gums. If these sensations do not go away after two weeks and the pain intensifies, you should contact your doctor for an examination to determine the cause.
Prevention of dental canal diseases
Prevention of dental canal diseases begins with the prevention of diseases that precede them. It is necessary to take care of the condition of the teeth, preventing the progression of carious processes. Regular dental hygiene: brushing with a toothbrush with the right toothpaste, using dental floss, and rinsing your mouth reduces the number of bacteria and slows down the development of caries and inflammation.
Regular preventive visits to the dentist will allow you to detect the carious process in the initial stage. Do not wait until the tooth makes itself known with painful sensations. Compliance with preventive measures will not only preserve teeth for many years, but also significantly save on treatment and avoid complications caused by inflammatory processes in the dental canals.
How long can a tooth survive without a nerve?
A tooth without a nerve can darken and decay faster, since metabolic processes in it are not maintained at the same level. However, with proper treatment and subsequent care, such a tooth can live indefinitely. The dentist fills the canals (often under a microscope) and isolates the tooth tissue as much as possible from the influences of the external environment. This is called a sealed restoration. With modern crowns or inlays, the tooth lasts a lifetime.
Nerve removal at Russian-American Dental provides services for painless removal of the dental nerve, followed by canal filling and sealed tooth restoration. The tooth acquires an aesthetic appearance and a lifelong service life. You can make an appointment by calling Moscow +7 (499) 269-13-92 or. The clinic is located at st. Rusakovskaya, 28 (Sokolniki metro station).
Choosing a paste for prevention
Dental health should be taken care of from early childhood. The most effective way is prevention and regular teeth cleaning.
For daily use you need to choose a toothpaste. With a variety of options to choose from, your dentist can recommend the right one for your teeth type. To avoid the addictive effect, it is recommended to periodically change the toothpaste.
Hygienic toothpastes do not have medicinal properties and are intended for everyday use. Daily use of hygienic pastes ensures cleansing of the oral cavity from food debris after eating, removes surface plaque, and has a short-term refreshing effect.
Medicinal pastes should be used as prescribed by a doctor, since they contain high concentrations of medicinal substances, and it is not recommended to use them constantly. The use of medicinal pastes helps fight the development of caries and inflammation in the gums.
Therapeutic and prophylactic are suitable for regular use. They contain active medicinal substances and natural ingredients, but in smaller quantities.
A small amount of toothpaste (about the size of a pea) is enough to effectively brush your teeth and prevent large amounts of toothpaste from ending up in your stomach. It is important to remember that to get results from toothpaste, you must use your toothbrush correctly and change it every three months. The toothbrush is selected depending on the condition of the teeth and oral cavity.
Tooth canal treatment: price
Tooth canal treatment price
differs depending on how many roots are in the canal, whether access to them is difficult or not. The price is influenced by the technique used in the treatment process and the equipment involved (microscope).
Dental canal treatment cost
consists of many components: consultation, examination, opening access to the canal, treatment with medications. The patient needs to expect an amount of 5,000 rubles above. On our portal you can navigate prices, find great deals and trusted clinics near your home.