The appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth, medically called “halitosis,” is a signal of trouble in the growing organism. Kaliningrad residents can notice this symptom when communicating with a child, laughing or kissing.
In most cases, odor occurs due to poor hygiene, which disrupts the balance of microflora in the mouth and increases the number of pathogenic microorganisms. During the decomposition of bacteria, compounds of hydrogen sulfide and nitrogen are formed, which are exhaled along with the air.
In this situation, the problem can be solved with the help of hygiene and does not pose any danger to the child’s health. However, there may be other reasons for the appearance of a specific odor from the mouth. In what cases should parents be wary - we will find out further...
Risk factors affecting fresh breath
Let's start by identifying the reasons that negatively affect healthy breathing. At the same time, we note that microflora imbalance can occur even in healthy children. This happens for a number of reasons:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules, as we have already outlined;
- dry mouth due to insufficient saliva;
- insufficient water and fluid intake;
- breathing through the mouth, out of habit or due to nasal congestion;
- oral infections (untreated caries, gum disease, etc.);
- consumption of foods with a pungent odor (garlic, onions) or those that provoke fermentation (legumes, grapes);
- taking medications;
- hormonal imbalance;
- smoking (relevant for teenagers).
Thus, in most cases, the cause of bad breath is problems in the oral cavity, infections and poor diet.
Preventing bad breath
It is always easier to prevent a problem than to treat it, so parents should pay great attention to prevention. To do this, you should follow a number of recommendations:
- Ensure proper oral hygiene. Even a baby under one year old needs to clean his teeth. It is important to ensure that the child does not fall asleep with a bottle in his mouth, or to offer him clean water at night. At 3 years old, the child should already master the technique of brushing his teeth. It is worth making sure that he pays enough attention to each of them.
- Read the recommendations of experts regarding children's diet and apply them to your baby. Replace sugar with honey. Ensure proper drinking regime, offering the child not juices, compotes, but clean water.
- Visit the dentist in a timely manner. Most often, at 2 years old, the baby’s primary dentition is fully formed. Starting at this age, you need to visit the dental office once every 3-4 months. The doctor will be able to identify diseases in the early stages and provide timely treatment.
- Seek help in a timely manner for ENT diseases, stomach problems and other diseases. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose and prescribe the correct treatment.
Following these recommendations will not only prevent the problem of bad breath, but will also protect the child from many health problems.
How to distinguish a normal smell from a problematic one?
If an unpleasant symptom occurs exclusively in the morning and goes away after brushing your teeth, then we are talking about a physiological norm. If bad breath is observed after hygiene procedures and becomes protracted, then this deviation requires the closest attention from parents.
In addition, it is worth noting that the above risk factors can be eliminated. However, if hygiene is maintained, respiratory infections and specific foods are excluded, and the unpleasant symptom persists for a long time, this is a good reason to consult a doctor.
In this case, altered breathing can signal very specific diseases. Let's look at which ones further...
Treatment of unpleasant odor
In most cases, osostomy does not require special treatment. It is enough to systematically thoroughly brush your teeth and gums, review your diet, limit your consumption of sweets, give him enough liquid per day, and the unpleasant symptom will disappear on its own. If after a few days it does not disappear, you need to consult a specialist, undergo an examination and determine the cause of halitosis.
Parents should be especially concerned about the smell of acetone emanating from the baby - in this case, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance or take the baby to the hospital to prevent the occurrence of acetone syndrome.
List of diseases that can be detected
Despite the fact that halitosis is not a disease, it is an important diagnostic symptom by which a specialist can assume the presence of a certain disease in the body. Suspected health problems may include:
- diseases of the nose and nasopharynx: sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis;
- food allergies or respiratory rhinitis causing nasal congestion;
- dental diseases of teeth and gums;
- Gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, increased stomach acidity, intestinal dysbiosis, etc.;
- endocrine disorders: diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, etc.
As can be seen from this impressive list of diseases, solving breathing problems can fall within the competence of a variety of highly specialized specialists: otolaryngologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist.
What to do if a small child has terrible breath during an acute respiratory viral infection
When seasonal viral diseases (including sore throat) occur, severe inflammation occurs in the baby’s nasopharynx. It can appear on the tonsils, throat, nose (with sinusitis), lungs, depending on the specific disease. As a result, the inflamed areas become covered with plaque and pus, which creates stale, unpleasant breath. But don’t worry, halitosis goes away as soon as the children recover. Doctors always prescribe regular rinsing with antiseptic solutions (furacilin, rotokan and others), they quickly get rid of stench.
What can a smell “tell”?
As we mentioned earlier, unhealthy breath can quite eloquently indicate a certain nature of the disease. For example:
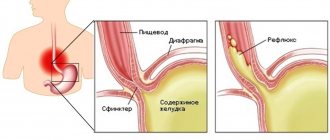
- a sour smell indicates problems with the stomach: high acidity, reflux or dysbacteriosis;
- the smell of a rotten egg - about a stomach ulcer or a violation of bile outflow;
- putrefactive – about diseases of the esophagus and low acidity of the stomach;
- acetone – about problems with blood sugar levels (diabetes) or dehydration;
- ammonia - about kidney disease, liver dysfunction and diffuse toxic goiter;
- boiled cabbage - problems with metabolism, liver and kidney diseases.
As a rule, already at the stage of collecting anamnesis and during the clinical examination, the doctor can make an assumption about the true causes of the problem.
Psycho-emotional state disorder
Sometimes halitosis can occur in children after severe excitement.
In some cases, the cause of halitosis may be hidden in the environment that surrounds the child. The fragile psyche reacts too painfully and sensitively to stressful situations, which can be almost invisible to adults, but for a child they are a serious test.
When the nervous system is overexcited, dry mouth, acetonemic crises with all their consequences mentioned above, and digestive disorders are possible.
You need to talk to your child to try to find out the root cause of worries and fears. Maybe he has problems in the children's team (conflicts in the yard, at school or kindergarten). Older children also have more serious problems. Sometimes this syndrome can occur due to failures in studies or during exams.
Children often have problems with their home environment - they experience constant fear of possible punishment for various little things - unassembled toys, something dropped on the floor, etc. He may be afraid to once again disturb adults with a question that worries him, as he may receive an irritated answer.
Such a nervous state often results in various disturbances in the functioning of the child’s body, which can result in bad breath.
If your baby is very worried, give him a slightly acidified drink and calm him down by any available means. Once the environment is normalized and stress is relieved, halitosis should disappear.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose ENT diseases, an otolaryngologist uses hardware and laboratory tests. These include:
- rhinoscopy – to examine the nasal cavity;
- radiography and computed tomography - to assess the condition of the sinuses;
- examination of nasal secretions to determine the causative agent of inflammation;
- Blood and urine tests will complement the clinical picture.
In the process of collecting anamnesis, the doctor is interested in the following questions:
- How long has the child been complaining of discomfort?
- What time of day does the smell appear and how long does it last?
- What foods did the child eat?
- how much water does he drink?
- Does the smell go away after brushing your teeth?
- What chronic diseases does he have?
- what medications does he take?
Treatment does not imply the elimination of the symptom itself, as such, but the therapy of the specific disease that provoked its appearance. If, as a result of examination and diagnostic measures, pathologies of the nose or nasopharynx were identified, the doctor will prescribe adequate drug treatment, which may include:
- antibacterial therapy (taking antibiotics);
- vasoconstrictors and antihistamines;
- special medical procedures;
- physiotherapy: inhalations, UV and UHF therapy;
If necessary, the otolaryngologist can refer a small patient to specialized specialists if the solution to this problem falls within their competence (dentist, gastroenterologist, etc.).
Preventive recommendations
In conclusion of our review, I would like to draw the attention of parents to adjusting their children's diet. Our nutritional recommendations are as follows:
- Let us remember that “bad” bacteria love a sweet environment, so it makes sense to limit the consumption of industrially produced sweets and sugar.
- As a dessert, you can offer your child natural sweets made from dried fruits and nuts, as well as fresh fruit.
- Replace carbonated drinks with pure water or herbal tea made from chamomile and mint.
- To create beneficial microflora in the intestines, a child should consume more “live” fermented milk products: cottage cheese, kefir, yoghurts.
Parents need to understand that this delicate problem requires a qualified approach, since over time it can lead not only to problems at the physiological level, but also cause social isolation of the child.
Kaliningrad residents can make an appointment with a pediatric otolaryngologist by filling out an online form on our website or by calling: +7 (4012) 357-773 or +7 (4012) 973-100.
What to do if a child has high acetone
Acetonemia itself is not a disease, but only a signal that a malfunction has occurred in the child’s body. If you find out that your child has high acetone, what should you do? It is necessary to take measures to relieve intoxication and restore glucose levels. This is indicated to us by the chemical smell emanating from the child, which is perceived differently by different people: either solvent, or acetone, or even ripe apples.
What to do if a child has high acetone?
A pediatrician will tell you how to treat high acetone: how to reduce a high temperature with acetone and get rid of other symptoms of acetonemia. Only a doctor can advise how to remove high acetone from a child’s blood. Your doctor may recommend the following steps:
- The first step is to give your child plenty of fluids. It can be almost anything: compote or tea, alkaline drink (still mineral water). It is good to alternate unsweetened drinks with sweet ones. For these purposes, you can use regular sugar and glucose solution, which is best purchased in ampoules or tablets as prescribed by your doctor.
- While the body is recovering, it is important to avoid physical activity as much as possible and take care of mental peace.
- How to reduce high acetone in a child? You should also adjust the diet of a child with high acetone and even temporarily (until the condition is completely stabilized) transfer him to a therapeutic diet.