A pediatric orthopedic dentist specializes in dental prosthetics for the youngest patients. Pediatric orthopedics is not the most common branch of dentistry, and therefore finding a real professional in this matter can also be difficult. A good doctor must not only thoroughly study the structure of the jaw apparatus in children, he must perfectly master prosthetics and dental restoration in children. In any clinical situation, the doctor must do everything possible to restore dental elements rather than give preference to installing a denture. The activities of a pediatric orthopedic dentist will be discussed in more detail below.
Dentist orthopedic dentist: who is he and what does he do?
In modern dental clinics there are many highly specialized doctors who provide medical care only for a certain type of diseases of the maxillofacial system.
A dental surgeon performs all necessary operations, an orthodontist corrects the bite using braces, a periodontist treats periodontal inflammation, and an orthopedic dentist does almost everything related to prosthetics, namely, installs dentures to restore teeth. This article will tell you in more detail about the most popular dentist - an orthopedist, and will also help you understand other specialties of dentists, which you can make an appointment with at the Dr. Stepman" on Universitetskaya metro station, Lomonosovsky Prospekt.
Objectives of orthopedic dentistry
Unfortunately, teeth do not have the ability to recover. And the main task of dental orthopedics is to improve and improve the methods used in prosthetics.
In addition, orthopedic dentistry performs the following tasks:
- for the treatment of diseases of the maxillofacial apparatus using various designs;
- to restore the main functions of the patient’s dental system (chewing, speaking, swallowing);
- to keep the remaining teeth healthy;
- to ensure the aesthetic appearance of artificial and restored teeth.
Each clinic that provides orthopedic dentistry services, except for the office of an orthopedic dentist, must be equipped with a dental laboratory.
The main examination methods in such a clinic are: interview, collection of anamnesis data, examination and assessment of the condition of the oral cavity, panoramic photographs of the jaws.
Dentists: what are they?
Dentistry is a fairly broad area of medicine, which is divided into several specific areas: therapy, surgery, orthopedics, orthodontics, periodontics and others. Depending on the chosen qualifications, skills and abilities, each doctor has his own area of responsibility and set of actions performed.
To understand which dentist to contact in various situations and what is the difference between an orthopedist and an orthodontist, a surgeon and a therapist, you should know the features of their activities.
Specialists often work together and closely interact with each other, because the patient may need a set of measures aimed at completely restoring the problem area of the oral cavity.
Dental prosthetics as an art with a long history
If you are worried about searching for reliable dental prosthetics, then we hasten to please and reassure you - you are on the website of the best private dental clinic in Russia. Our clinics have confidently taken the place of the all-Russian leader in prosthetics
and implantation since 2016.
1,120
dental clinics from
106
took part in the all-Russian ranking “Best Dentistry in Russia” for 2020, according to the Kommersant Publishing House and the expert magazine Startsmile .
The quality of the clinics' work was assessed using more than 240 (!) criteria
. The TOP rating of the best dentists in Moscow and Russia helps people from different parts of the country choose dentistry where they are guaranteed to receive the highest quality medical care.
Dentist-therapist
It all usually starts with this dentist. People come to him when they are worried about toothache or other symptoms associated with the maxillofacial area. He conducts diagnostics and an initial examination, establishes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment, and gives referrals to specialized specialists. His competence includes standard problems: caries, infectious diseases and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Dentist-therapist:
- cleans channels;
- removes nerves;
- installs seals;
- removes tartar and plaque;
- restores teeth;
- performs sanitation of the oral cavity before prosthetics or other dental procedures.
Dental prosthetics technology
Currently, computer modeling is actively used in prosthetics, which allows one to obtain an accurate diagnostic picture and calculate the most suitable prosthetic parameters for each patient. Innovative technologies are 3D models that significantly speed up and simplify work for both the doctor and the patient, and the prosthetist. Computer modeling allows you to take into account all the nuances and create the most functional prosthesis. This technology is not available in all dental clinics in Moscow, but at CELT our orthopedists use it effectively.
Preparation for prosthetics consists of treating all acute and compensating for all chronic diseases of the oral cavity, as well as the nasopharynx. Often, prosthetics require preliminary preparation by an orthodontist - for example, correction of a malocclusion or, after consultation with an orthopedist and surgeon, installation of an implant. In addition, at the preparation stage, the doctor prescribes images, conducts diagnostics, draws up a treatment plan and selects the appropriate prosthetic technique. Before performing the procedure, the specialist conducts diagnostics to ensure that there are no serious problems. Contraindications to prosthetics may include caries, gum inflammation and other pathologies. If you have a chronic disease in the acute stage, you need to wait until relief comes. You cannot perform work if your teeth are crooked or have an abnormal bite. You must first undergo treatment with an orthodontist.
To cleanse your mouth of pathogenic bacteria, you will need professional teeth cleaning. This is relevant in cases where microprosthetics using lumineers or veneers is planned. Before performing the procedure, you need to take an x-ray and select the right treatment strategy, taking into account the individual characteristics of the client.
Dental surgeon
This doctor comes to the rescue if conventional treatments are ineffective and drastic solutions are needed that require surgical intervention.
Dental surgeon:
- removes teeth, tumors and cysts;
- eliminates acquired and congenital defects;
- opens foci of abscess and other inflammations;
- prepares the jaw for prosthetics and performs implantation;
- deals with restoration and plastic surgery of the jaw, as well as any other operations in the oral cavity.
Post-operative care
Proper oral care will help consolidate the results and avoid side effects in the postoperative period. The duration of this period does not exceed 2 weeks. Important rules to follow:
- You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day. To remove hard-to-reach stains, it is recommended to use dental floss.
- You need to rinse your mouth 3 times a day using rinses recommended by your dentist.
- The use of anti-inflammatory and painkillers should be agreed with the attending physician.
- The denture should be cleaned as thoroughly as possible. You need to pay attention to all parts, and especially in the area near the root.
Clean the superstructure thoroughly from all sides. It is recommended to carefully clean the main part of the denture with a soft toothbrush and a minimum amount of toothpaste. The presented rules apply to removable and fixed prostheses.
Be careful! Lack of care after surgery can cause inflammation and deformation of the bone tissue at the attachment site. Be sure to follow the specialist's recommendations.
Dentist-orthodontist
This doctor deals with dental disorders associated with malocclusion, which he corrects with the help of braces, mouthguards, plates and other devices. These can be genetic, congenital, age-related, acquired as a result of a disease or deformation anomaly:
- individual teeth;
- dental arches;
- jaws.
- Designs for correcting bite
There are several other important specialties among dentists:
- Periodontist. Treats periodontal diseases, which is a complex of tissues surrounding the teeth and ensuring their fixation.
- Children's dentist. It differs from an adult dentist, since milk teeth, developing jaws and the child’s psyche have their own characteristics. This requires certain knowledge for proper treatment.
- Dental Technician. Engaged in the manufacture of dentures in dental laboratories.
- But the main direction that makes it possible to restore teeth even in cases where other dentists are unable to help is dental orthopedics.
Prosthetics for complete absence of teeth
The most difficult is prosthetics in the absence of teeth.
. In this case, it is very important to approach the solution of the problem individually and coordinate all actions with the patient. Typically, CELT dentists combine various designs to achieve the desired result. Thus, it is possible to achieve what would seem to be impossible: to ensure the desired aesthetics of the smile, the comfort of wearing the prosthesis for the patient and its maximum functionality. This means that the patient does not experience discomfort, can smile freely, chew food thoroughly and talk. This has become possible thanks to complete removable dentures made of nylon or plate dentures supported by implants. The “All-On-4” technology has proven itself well, in which permanent prostheses are installed on four implants. As a result, it is possible to ensure restoration of the smile area, chewing function and reliable fixation of the prosthesis.
Orthopedics as a field of dentistry
In general, orthopedics is a large branch of the medical system that deals with disorders of the musculoskeletal system, and orthopedics in dentistry is only an independent part of it.
Dental orthopedics specializes in eliminating problems with the masticatory-speech apparatus and is based on restoring its function and integrity through the installation of dentures. This procedure is called prosthetics.
You should contact dental orthopedics if:
- Lamellar prosthesis: missing teeth - from one to completely edentulous;
- tooth decay is observed - both complete and partial;
- increased mobility or sensitivity of the teeth, and there are also other problems with the tissues and bones of the jaw - periodontal disease, periodontitis, etc.;
- there are cosmetic defects - the shape, size, color do not match or other aesthetic defects are noticeable;
- pathology of the temporomandibular joint has been established;
- This visit to the orthopedist was recommended by another dentist who, during examination or treatment, considered such a visit necessary.
- Appointments in orthopedic offices are conducted by specialized highly specialized doctors of a high category - orthopedic dentists.
One-stage prosthetics during implantation
Cases when, after tooth extraction, a patient wants to restore them as quickly as possible are not uncommon. If there are no contraindications to this procedure, CELT dentists perform one-stage prosthetics during implantation. The procedure is quite complicated and involves the removal of a tooth with the implantation of an implant and its immediate loading with a temporary prosthesis. As time passes and the implant heals, the prosthesis is replaced with a permanent one. Thus, in just one visit to the doctor, the patient not only gets rid of a diseased tooth, but also restores it.
Orthopedic dentist: what does he do?
The responsibilities of this doctor include restoring the dentition. An orthopedist, due to the consonant name and similar goals, is often identified with an orthodontist. But there is a significant difference between them - an orthodontist corrects crooked teeth and problematic bites using braces, and an orthopedist restores teeth, or rather, their outer and inner parts, using prosthetics. Therefore, he is sometimes also called a prosthetist.
An orthopedist or dental prosthetist helps in solving all of the above problems, for which it is recommended to contact orthopedic dentistry.
What troubles can you get rid of with the help of a dental orthopedist:
Constant feeling of psychological discomfort. The absence of one or more teeth spoils the aesthetic appearance of the face and even its symmetry, which makes a person feel insecure and uncomfortable. The same sensations can be caused by dental defects: chips, curvatures, crevices, etc. Especially in the “smile zone.” This is where the help of a prosthetist should come in handy.
The next problem that occurs with insufficient teeth is no less important - significant disturbances in chewing function. It needs quick recovery, because it stimulates the natural processes of the entire dental system, restoring its normal functioning: muscle tone, nutrition and blood circulation of bone tissue cells. Normal chewing function is not only beneficial for health and metabolic processes in the body, but also helps in the fight against periodontal disease.
The threat of tooth loss due to its continuous destruction. It happens that a tooth has completely healthy roots, but its outer bone tissue has already begun to deteriorate, to such an extent that the filling is no longer effective. To stop the destructive process and save the tooth, avoiding its complete loss, you need to contact orthopedic dentistry.
A dental orthopedist also treats complete edentia, which allows people who are missing all their teeth to lead a normal life.
In all these situations, veneers, inlays, crowns, dentures or other protective structures will save the situation. Their installation or prosthetics is exactly what an orthopedic dentist does.
Problems solved by a specialist
An orthopedic dentist is able to solve a number of problems faced by a person with jaw defects:
- The doctor will eliminate psychological discomfort. The absence of teeth leads to the development of a number of complexes. The person does not want to smile, speech defects appear, stiffness appears, and difficulties arise with socialization.
- An orthopedic dentist will help you get rid of physical disabilities. Gaps in the jaw cause insufficient chewing of food, which leads to problems with the digestive system, intestines and leads to weight gain.
- An orthopedist is able to relieve a person from defects in the development of the jaw apparatus - adentia. The disease is characterized by a complete or partial absence of teeth; the dentist will install a prosthesis that will help the person lead a full life.
A timely visit to an orthopedist will help eliminate jaw defects, improve health, and restore psychological comfort and confidence.
Types of dentures
The choice of type of prosthetics depends on many factors. Here the role is played by the condition, number and location of the teeth, the individual characteristics of the patient, pricing policy and other circumstances. The difference in what the orthopedic dentist does in each individual case lies in the techniques used and the prostheses used.
Microprosthetics
Suitable for situations where you need to restore a deformed or damaged tooth. The following prostheses are used:
- Veneers. The doctor places them if there are minor defects in the front teeth: chips, cracks, curvature, discoloration. Veneers are thin ceramic plates up to 0.7 mm wide that completely follow the shape of the tooth, are installed in one appointment and last up to 10 years.
- Lumineers. They are placed when, for some reason, veneers are contraindicated for the patient. These pads are slightly different from each other. The difference is that lumineers are thinner (0.3 mm), more difficult to get used to, hide defects less, and are more prone to breakage.
- Tabs. They are very similar to fillings, but they also have some differences: they last longer, are made of durable ceramics, are able to recreate the shape of the tooth, and are also used when the filling is ineffective.
Types of prosthetics
Dental prosthetics in Moscow
- one of the most popular services.
Depending on their needs and financial capabilities, patients at dental clinics have the opportunity to order different types of dental prosthetics
.
| Type of prosthetics | Applicable designs | Features and Benefits |
| Fixed |
| The patient is fitted with a prosthesis/prostheses that do not require removal during use. They are securely fixed to the tooth or implant using dental cement, are functional and look like natural teeth. |
| Removable |
| The patient has the opportunity to independently remove the prosthesis from the oral cavity for hygiene procedures. Removable structures need reliable fixation, so they are often used with special pastes and creams. |
| Conditionally removable |
| Such structures require removal for a short time for hygiene procedures. They are used when one or two teeth are lost. |
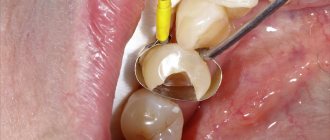
Veneers are most often made from ceramics. Veneers are thin shells that cover the outer surface of the tooth. They do not completely replace a lost tooth. Used to correct color and shape. Modern veneers are functional and perform not only an aesthetic function.
Dental crowning is a time-tested method that involves installing a special cap that replaces the natural crown of the tooth. A crown allows you to imitate the natural shape of the tooth surface. Due to its simplicity and reliability, this technique has long been in high demand.
Bridge prosthesis. This is the name for the installation of a complex structure that rests on the roots of teeth or preserved molars. The design itself is a series of dental crowns. The bridge prosthesis is considered a classic of dentures. There are temporary (performs aesthetic functions) and permanent (more functional).
Installation of dental implants is the installation of a kind of “root” made of titanium into the jaw bone tissue in the place of a lost tooth. A crown identical in shape and size to natural teeth is placed on the root. Such instructions are reliable and durable, but the procedure often requires special training.
All of the above types of prosthetics can be called effective, provided that all manipulations were carried out by a qualified specialist in a trusted clinic.
Microdental prosthetics
Removable dentures
Removable dentures are inexpensive, easy to install, and easy to care for. These dentures come in several types: plate, clasp, suction cups, butterflies. Removable structures are most often used:
- with edentia - if there are missing teeth on one or both jaws;
- for elderly people - other types of prostheses are more expensive and may not be well tolerated by the elderly;
- for children - when early loss of baby teeth can cause crooked dentition.
- Fixed structures
Fixed dentures are durable and reliable, have an attractive appearance, and are made from different materials, which makes it possible to provide prosthetics to people with any financial capabilities. These include:
- crowns are prostheses that are placed in a wide variety of situations, but most of all they are suitable for frontal single molars;
- Bridges are an excellent solution when several teeth are missing in a row;
- dentures on implants - this design will last a lifetime, but it also costs accordingly.
- Fixed orthopedic structures
Based on the results of this article, we can conclude that an orthopedic dentist treats all types of tooth loss, up to their complete absence. Today, insufficient dentition is not a problem, because to solve it you just need to go to one of the many clinics where qualified prosthetists work.
Permanent dentures
If one or more teeth are missing, the orthopedic dentist will suggest installing a fixed prosthesis. This product category includes:
- Crowns;
- Bridges;
- Implants on pins.
It is preferable to install a crown on the upper part of a molar or premolar, less often on the canines. Dentures are made in the form of a cap that is placed over the damaged tooth. The doctor uses crowns to restore chewing functions, recreate the dentition or secure a bridge prosthesis.
Bridges are used by orthopedic dentists when several teeth are missing in a row. The prosthesis is a plate of interconnected artificial teeth, which are fixed on a single base, and follows the natural shape of the jaw. Doctors create products from ceramics, cermets, plastic or other materials. The bridge is attached to the teeth or pins in the extreme parts and helps to close a large opening in the jaw row.
If the patient has a missing tooth root, the orthopedist will implant a titanium pin onto which the implant is attached. The procedure is expensive, but the prosthesis installed by the doctor does not require replacement after a certain period of time, reducing the likelihood of periodontal problems.
Removable structures help with serious jaw defects. An orthopedic dentist offers this type of prosthetics in the following cases:
- Patients with edentia;
- Children, in case of premature loss of milk teeth. The doctor will install a plate that will help form a straight jaw and protect the molars from curvature;
- Elderly people for whom the use of other types of prosthetics is contraindicated.
Orthopedists characterize removable products as easy to care for, easy to install and low cost.
With conditionally removable prosthetics, dentists replace one or more teeth. The design got its name because it is not difficult for an orthopedist to remove the prosthesis, but the patient is not able to do this on his own.
Orthopedic dentists use two types of conditionally removable prosthetics: mounting on implants or cementing.
The first type involves four pins that the doctor installs in the front of the jaw. Ball or beam fastening is used. Ball locks are easier to use, but less reliable. The beam, located inside the removable part, contains clamps that snap onto the pins, ensuring a reliable connection.
Dentists use cementation if it is necessary to glue the prosthesis to the supporting teeth. An alternative option is for the orthopedist to cut a groove in the supporting part into which the implant plate is lowered. Cement provides additional fixation.