Diagnosis and treatment of thrush at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Diagnostics
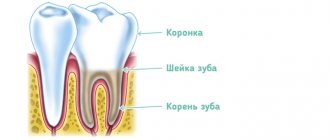
Diagnosis of vaginal candidiasis begins with interviewing the patient.
Some gynecological (bacterial vaginosis, inflammatory processes in the female reproductive system) and concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, candidiasis and intestinal dysbiosis, etc.) are important. It is not uncommon for thrush to develop after long-term use of antibiotics, hormones, or immunosuppressants. Upon examination, a characteristic clinical picture is revealed - a white coating on the inflamed mucous membrane of the genital organs, copious, curdled discharge. Examination of a vaginal smear reveals fungal flora. If necessary, a culture is carried out to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs (cultural analysis). Among additional studies, examination for sexually transmitted infections, diabetes mellitus and diagnosis of intestinal microflora may be recommended. Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Treatment
How to cure thrush?
General and local antimycotic therapy Gynecologists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital provide effective treatment for thrush in women. Today there are many medications to combat candidiasis: oral medications, creams, vaginal tablets, suppositories for thrush. Among the most popular drugs for vaginal candidiasis are flucostat, fluconazole (oral tablets), clotrimazole (vaginal tablets or cream), pimafucin (suppositories) and many other drugs. Your doctor should choose the optimal treatment regimen for you.
Reducing the role of predisposing factors To avoid relapses, it is necessary to identify and eliminate factors contributing to the disease. If possible, stop taking glucocorticosteroids and cytostatics. For diabetes mellitus, adjust blood glucose levels with medication. Restore normal microflora in the intestines. In addition, you need to take antibiotics with caution. Exacerbation/recurrence of thrush after or during a course of antibiotic therapy is common. Therefore, taking antibiotics must be combined with taking antifungals and probiotics. It is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, maintain immunity, and avoid stressful situations.
Sexual life with thrush Many people are interested in whether it is possible to be sexually active with thrush and its treatment? You can protect yourself with a condom. To achieve good results, it is often recommended to undergo treatment of vaginal candidiasis together with your sexual partner.
Treatment of vulvovaginitis in girls
For nonspecific bacterial vulvovaginitis in girls and adolescents, it is advisable to begin treatment by eliminating the source of infection in the body and the factors that provoke inflammation, for example, chemical and food. Thus, in some cases, to eliminate vulvovaginitis, it may be necessary to treat chronic diseases of the oropharynx and nasopharynx, pyelonephritis, helminthiasis, caries, etc.). Detailed instructions on the sequence of treatment of vulvovaginitis are contained in the textbook by Olga Evgenievna Baryaeva “Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs in girls and young women.”
As noted in the manual, the main goals of treatment are the elimination of the inflammatory process and the normalization of vaginal microbiocenosis. The therapeutic process may include instillation of the vagina with antiseptic solutions, such as chlorhexidine bigluconate 0.05%, nitrofural, octenisept, miramistin, etc.
Also, in most cases, antibacterial therapy is carried out taking into account the sensitivity of the isolated microflora to antimicrobial drugs. In parallel with antibiotic therapy, antimycotic and antihistamine drugs, as well as eubiotics or probiotics, are prescribed. Thus, in order to avoid the development of candidiasis, antimycotic agents are additionally used, interferon suppositories can be prescribed rectally or intravaginally for 10 days to correct immune disorders, and probiotics, prebiotics and combination drugs can be used to normalize the intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics.
To make the patient feel better, applications of ointments with anesthetic, astringent and desensitizing properties in the area of the external genitalia may be additionally prescribed. Herbal baths are used for the same purposes. It is important to give preference to herbal remedies that have antiseptic and astringent properties (oak bark, chamomile, etc.).
The criteria for cure in such cases are the absence of the pathogen in a smear taken no earlier than the 21st day after antibiotic therapy, and positive dynamics of AT titers.
When identifying a specific infection (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis), it is important to use during therapy exactly those antibacterial drugs to which the found microorganisms are sensitive. It is also necessary to examine for the presence of infection and, if necessary, treat other members of the patient’s family. In some cases, for example, with recurrent trichomoniasis, it is advisable to resort to vaccine therapy that can activate specific and nonspecific immunological reactions of the body. The criteria for cure for trichomoniasis are the absence of clinical manifestations and negative results of microscopic and cultural studies 7–10 days after the end of therapy.
Treatment of gonorrheal vulvovaginitis in girls must be carried out by a dermatovenerologist. In this case, preschool-age patients attending children's institutions are given 3 provocations and 3 cultures every 10 days for 1 month after treatment to establish cure. The criteria for cure of gonorrhea in children are a normal clinical picture and negative results of repeated laboratory tests after three provocations. Vaccine therapy is used in cases of ineffectiveness of antibiotics or in cases of relapse of the disease.
Finally, when urogenital chlamydia is detected, they resort to complex therapy involving antibacterial and antifungal drugs, interferon, and immunocorrectors in accordance with the identified pathology.
When fungal cultures are detected, we are talking about mycotic vulvovaginitis; accordingly, the basis of treatment is antimycotic drugs, used both orally and additionally intravaginally, especially in case of relapses of the disease. As a rule, two courses of treatment are prescribed with a one-week interval between them.
In addition, vulvovaginitis can be caused by a herpes virus infection. In such cases, systemic therapy with antiviral drugs orally and locally is necessary.
With atopic vulvovaginitis, the main thing is to eliminate the patient’s contact with the allergen that provokes symptoms as soon as possible. Thus, it is necessary to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, in particular, the exclusion of obligate allergens (fish, eggs, citrus fruits, chocolate, honey, strawberries, etc.), stimulants of histamine release (meat and fish broths, fried, smoked, spicy foods, eggs, cheese, fermented and pickled foods, chocolate), as well as histamine-like substances (tomatoes, walnuts). Antihistamines are prescribed in courses of up to two weeks. At the same time, it may be necessary to treat intestinal dysbiosis, which aggravates allergy symptoms due to increased absorption of allergens by the inflamed mucous membrane.
In some cases, surgical treatment is recommended - in particular, with the formation of continuous synechiae of the posterior commissure and labia minora. During the operation, a blunt separation of the adhesions is performed with a probe, after which an ointment bandage with epithelializing and keratoplasty agents is applied. In the postoperative period, it is necessary to carry out regular examinations of the patient at each washing. To avoid repeated synechiae, the posterior commissure and labia minora are toileted, and medicinal substances are placed in the wound (Actovegin 5% ointment, solcoseryl, depanthenol, ointments with vitamin A, methyluracil, etc.). In pre-pubescent girls, after the inflammatory manifestations have subsided, it is possible to use estrogen-containing creams.
At the end of treatment, patients must adhere to a number of rules to avoid relapse of the disease. Thus, it is undesirable to wear synthetic underwear and styles that do not completely cover the crotch area and gluteal folds. In addition, it is necessary to explain to the patient and her parents the importance of timely elimination of foci of infection, such as diseases of the mouth and nasopharynx, pyelonephritis, caries, etc. In this case, it is necessary to avoid the unreasonable use of antiseptic and antibacterial drugs, as well as glucocorticoids, and pay more attention to hardening.
You can learn more about the recommendations for the treatment of recurrent and acute vulvovaginitis in girls and adolescents by referring directly to the manual by O.E. Baryaeva (Irkutsk State Medical University, 2012).
Thrush during pregnancy
The development of vaginal candidiasis during pregnancy is dangerous for the expectant mother and the fetus. There is an increasing threat of the development of inflammatory processes during pregnancy, postpartum complications, and infection of the fetus, which can lead to fungal infection of its organs and even death. It is possible that the baby may become infected during childbirth. Treatment of thrush in pregnant women is complicated by the ban on taking antifungal drugs orally. Local treatment with vaginal tablets and suppositories is acceptable (Pimafucin is considered the safest among them during pregnancy). All the more important is the observance of personal hygiene rules, as well as protection from stress, proper nutrition with sufficient vitamins, walks, healthy sleep, which help strengthen the natural immune defense. If signs of thrush appear in a pregnant woman, she should immediately contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to carry out timely, adequate treatment and avoid complications.
For diagnosis and successful treatment of vaginal candidiasis, come to the Clinical Hospital on Yauza. You can see
prices for services Make an appointment
Treatment methods for urethritis in children
The main goals of therapy for inflammation of the urethra are stopping the inflammatory process and eliminating pathogenic microflora. After this, the unpleasant symptoms disappear and the child recovers. Uncomplicated urethritis can be treated on an outpatient basis. Children in serious condition, with severe intoxication of the body, as well as with concomitant pathologies of the urinary system, are subject to hospitalization.
How to treat urethritis in a child? Depending on the causes and severity of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- antifungal drugs - prescribed if the mycotic nature of the inflammation is proven; in children, candidal urethritis most often occurs against the background of decreased immunity;
- antibiotics - are prescribed if the causative agent of the disease is pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, the duration of the course of therapy is 7-14 days, after which control laboratory examinations are carried out;
- NSAIDs - have a strong anti-inflammatory effect, quickly relieve pain, improve the child’s condition, NSAIDs are usually prescribed together with antihistamines to relieve the allergic component of inflammation;
- restoratives - for urethritis, taking vitamins, antioxidants, and herbal medicines is recommended; they enhance the effectiveness of basic therapy and speed up the healing process of children;
- local treatment (irrigation, instillation, ointments for urethritis in children) - can only be used for chronic urethritis, during periods of remission; in case of acute inflammation, the use of local medications is prohibited.
After relief of inflammation, physical therapy is actively used. For inflammation of the urethra, the greatest effect is achieved by electrophoresis, microwave, ozokerite and paraffin applications. It is also recommended to take pine baths, which have a restorative and antiseptic effect.