Many of our patients (as well as patients, for example, of chiropractors or neurologists) do not even realize how interconnected the problems they are being treated with are. For example, the jaw joint hurts, the head hurts, shooting in the ear, clicking in the jaw, pulling at the base of the skull... it would seem that these are different symptoms, but the reason may be the same for everyone: TMJ dysfunction
.
Functions of the TMJ
TMJ
or
temporomandibular joint
is a joint located above the ear that connects the temporal bone to the lower jaw and the lower jaw to the skull. The muscles that are attached to this joint are actively involved in speaking, facial expressions, chewing, and swallowing. Together, muscles, ligaments, cartilage and joints make up the apparatus, thanks to which we can generally open and close our mouth, move our jaw back and forth and left and right, and the load on this apparatus is significant - comparable to the load, for example, on the knee joint.
The temporomandibular joint is the only paired and symmetrically moving joint in the human body, and problems with its functioning lead to numerous unpleasant diseases. TMJ dysfunction—limited work and mobility of the jaw joint—occurs when the joint on the right and left sides of the skull does not move synchronously or evenly. For example, to open the mouth, the patient must first move the lower jaw from side to side, “until it clicks.” Or when you open your mouth, you feel pain in your jaw or temples.
This disease has many names: arthritis (arthrosis) of the TMJ, myofacial syndrome, myoarthropathy of the TMJ, chronic dislocation of the lower jaw, Costen's syndrome (named after the American doctor who first identified this disease). This pathology is difficult to diagnose and treat, and at the same time it can cause a wide variety of pain - from headaches to neck pain.
Statistical fact: from 30% to 70% of dental patients suffer from functional pathology of the temporomandibular joint. And these are not always older people, as one might expect. On the contrary, people of all ages, including children, suffer from TMJ pain and related pain.
TMJ dysfunction was first described by otolaryngologist (ENT doctor) Kosten in 1934. Kosten studied pain and noise in the ears and burning in the nose, which intensified during or after eating, and was the first to think of linking them with malfunction of the temporomandibular joint. Subsequently, his colleagues and other doctors who examined this problem expanded and supplemented the list of symptoms. Now this list is quite extensive, and often not all symptoms can be associated specifically with TMJ problems.
Possible complications
In the absence of proper treatment, the primary dislocation of the jaw turns into an old one, and if you correct it yourself incorrectly (we strongly advise you not to do this), over time, with a high degree of probability, the need for surgical intervention will arise. This material will tell you what to do if toothache radiates to your temple.
The main complications of TMJ dislocation:
- bruxism;
Bruxism or teeth grinding leads to excessive tooth wear or complete loss.
- erasing enamel;
- pain when chewing;
- clicks;
- arthrosis
A medical consultation is required, since a jammed jaw may indicate not only a dislocation of the joint, but also a fracture, osteomyelitis of the jaw, arteritis of the facial artery, and dysfunctional changes in the jaw apparatus. And the sooner they are detected, the more positive the treatment prognosis will be. Find out why you grind your teeth in your sleep here.
If your jaw is jammed, your doctor will first try conservative methods, and if they don’t help, he will recommend other options.
Symptoms of TMJ dysfunction
- Pain in the jaw, increasing when opening the mouth, chewing, speaking, yawning;
Clicking in the joint of the lower jaw, the jaw “jams”, it does not open, does not close, or has begun to close differently;- Pain in the temples, in the eye area, visual impairment, photophobia (sensitivity to light);
- Pain, ringing and noise in the ears, in the ear area, feeling of pressure in the ears;
- Frequent headaches, dizziness, migraines;
- Sleep disorders, insomnia, anxiety, depression;
- Pain in the neck, in the lower part of the skull;
- Tooth pain from sweets, hot, cold.
This diversity in symptoms, which often makes it difficult for doctors to diagnose, is explained by the fact that the joint is connected to many important organs and parts of the body (eyes, ears, neck, head) and errors in its functioning can affect everything at once, or they can only affect something one. It is usually possible to determine that the problem is in the temporomandibular joint only in a complex manner.
In most cases, TMJ dysfunction is manifested by pain in the face, joints of the jaw, neck, shoulders, ears, crunching and clicking. Complaints of dizziness, difficulty chewing food, speech and hearing disorders, difficulty opening the mouth, “jamming” of the jaw, or even the appearance of swelling and fever are also common.
Medical measures
Effective professional treatment for TMJ dysfunction requires eliminating the root cause of the problem. Thus, patients are advised to wear special orthopedic splints to normalize the functioning of the joint, drug therapy is carried out to relieve symptoms of inflammation, and in severe cases, surgical intervention is performed to regenerate individual areas of bone tissue. Physiotherapy is a mandatory component of the complex treatment of TMJ dysfunction.
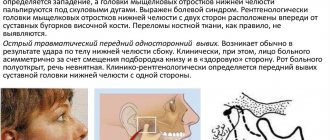
With various disorders of the TMJ, the face becomes puffy, asymmetrical, the lower jaw can be pushed forward or to the side
First of all, this is a gentle speech regime, refusal of solid food that is difficult to chew, and normalization of the daily routine. It is useful to do special gymnastics for the facial muscles, it is recommended to avoid stress, and promptly treat systemic and local dental diseases of an infectious-inflammatory nature. What to do if your jaw is jammed due to dislocation: consult a doctor (oral and maxillofacial surgeon, dentist). The specialist will straighten the joint without anesthesia in case of unilateral injury and under anesthesia in case of bilateral injury.
During medical procedures, the doctor returns the head of the joint to the fossa. So, jamming of the jaw can be associated with “local” injuries, increased load during chewing, diction and other factors causing TMJ dysfunction. If such a problem arises, you must immediately seek help from a doctor (orthopedic dentist, maxillofacial surgeon) for diagnosis and selection of a treatment strategy.
Pain in the jaw joint: causes
- Defects in the dentition - lack of teeth, overestimation of fillings;
Pathological abrasion of teeth;- Broken bite
;
- Overload of the masticatory muscles (for example, if you chew on only one side for a long time);
- Inaccurate prosthetics, errors in orthodontic treatment;
- Other anomalies of the oral cavity and jaw structure;
- Bruxism, involuntary grinding of teeth.
- Birth trauma, trauma to the skull and jaw;
- Osteochondrosis and scoliosis of the spine;
- Severe constant stress
;
- An infection in the joint cavity that provokes inflammation of the TMJ.
Diagnostics and x-ray of the temporomandibular joint
Diagnosis of TMJ when it is dysfunctional is difficult due to the variety of clinical complaints. This leads to the fact that the patient can undergo examination by different specialists for a long time, wasting time. A full examination is carried out by dentists
(primarily an orthopedist or orthodontist) and neurologists.
Diagnosis with the naked eye is difficult, and TMJ problems can only be directly noticed if the malocclusion is clearly visible. Most often, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is associated precisely with disorders of bite and jaw closure.
The most reliable and effective way is to conduct x-ray diagnostics and orthopantomogram
jaws. In some cases, an MRI may also be done.
Pain when opening a child's mouth
The peculiarity of pain in children is that the child can rarely describe the symptom in detail, as well as assess its severity. In addition, children often tend to hide from adults if they are in pain, especially if they are afraid of doctors.
Parents should pay attention to the following features:
- The child began to speak slurredly and reluctantly;
- It is painful or impossible to open your mouth wide;
- Does not eat well, tries to avoid chewing food;
- There is noticeable swelling on one side of the face;
- The baby holds on to the ear or jaw and constantly touches them.
These signs can indirectly tell parents that the baby has a sore jaw.
Treatment of the temporomandibular joint
Complex treatment of TMJ is possible only in dentistry, and is possible thanks to:
- surgery on the lower jaw;
- orthodontic treatment
(prescribing special trainers that will be worn at night and reduce pain by adjusting the load on the joint - the same trainers are recommended for bruxism) and bite correction with braces;
- orthopedic treatment
and
implantation
(insert a suitable prosthesis to restore the correct closure of the jaws).
Treatment is always prescribed individually, based on the results of an examination by an orthodontist, and is most often carried out comprehensively. It is dangerous to neglect TMJ diseases: this can lead to arthrosis, in which connective tissue grows in the joint cavity, which, in turn, threatens complete immobilization of the joint (ankylosis).
Severe pain and joint spasms can be relieved with compresses and painkillers; Stresses that provoke tension in the joint can be relieved with sedatives, but all these are half measures that do not treat the root cause of the pain.
First aid
The joint can jam spontaneously - for example, after a strong cry or prolonged chewing of solid food. It is important to know what you can do on your own to alleviate the condition before going to the doctor. So, a warm compress or a heating pad is applied to the sore joint, and then, on the contrary, ice or a cold towel. Such contrast procedures must be repeated once an hour.
To cope with pain, take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Analgin, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol). If indicated, local muscle relaxants are used (creams, ointments that relax muscles and relieve spasms).