Seal
One of the most popular procedures in modern dentistry is the installation of crowns. The method allows you to save a damaged tooth, restore its function, and restore the attractiveness of your smile. But sometimes after orthopedic treatment, discomfort, sharp or dull pain, and sensitivity to temperature occur under the crown. In this case, discomfort may appear both in the coming days after prosthetics and several years later. What should be done in this case?
First of all, you need to understand what is causing the pain. If very little time has passed after treatment and the discomfort is not too great, do not worry. Such pain is residual in nature. As a rule, specialist intervention is not required - 3-5 days after treatment, the discomfort goes away on its own. It’s worse when the tooth starts to hurt months or even years after prosthetics. In this case, you cannot do without a visit to the clinic.
Khashchenko Stanislav Sergeevich is a dental surgeon with extensive experience.
Indications for nerve removal
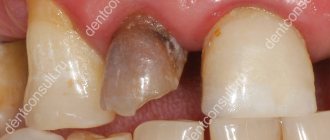
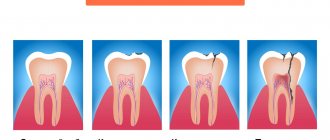
- Caries has reached the pulp. Initially, caries appears on the enamel, then moves to dentin, then to the pulp. Inflammation increases: acute pain occurs. To eliminate the pain and save the tooth, you need to remove the nerve.
- Injuries of various types: impact, fracture, chip. With such mechanical impact, traumatic pulpitis develops. The integrity of the tooth is damaged, the infection penetrates into the pulp. Inflammation occurs and pain appears. Treatment involves removing the nerve.
- Retrograde infection. When inflammation occurs at the apex of the tooth root, it then spreads to the nerve.
- Orthopedic treatment. Before placing a crown, in some clinical cases it is necessary to remove the nerves. To avoid complications, a severely damaged tooth is first treated: the nerves are removed.
- Asymptomatic pulpitis (chronic). The patient does not have acute pain, but the nerve is infected. The patient's complaints may include mild pain in the past.
How does the nerve removal procedure work?
The patient usually consults a doctor with acute tooth pain. If damage to the dental nerve is confirmed by visual examination and x-ray examination, a decision is made to remove it (depulpation).
In some cases, it is possible to save the nerve, but there are a number of pathologies when the affected nerve leads to complications and health problems, so it must be removed:
- mechanical tissue injury occurred;
- the tooth is severely damaged due to deep caries;
- diagnosed with pulpitis or periodontitis;
- prosthetics are planned.
The nerve may be partially removed (amputation) or completely (extirpation). During amputation, the root part of the pulp remains intact; the operation concerns only the coronal zone. When treating adult patients, complete removal of the nerve is usually practiced.
The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia in several stages:
- The area of the affected tooth is isolated with a latex film to prevent saliva from entering the treated area.
- The carious cavity is processed, the pulp chamber is opened, and its walls are leveled.
- The dental pulp is removed using special instruments.
- The tooth canals are expanded and washed with antiseptics.
- The dental canals are filled. Sometimes a temporary filling is installed, which, in the absence of pathologies and pain, is replaced with a permanent one after a few days.
- After filling, a control x-ray examination is carried out to check the quality of the work.
Depulpation involves the use of high-tech methods and means that require deep theoretical knowledge from the doctor. It is not surprising that such a complex procedure can be accompanied by medical errors.
For the patient, this means the occurrence of severe pain, the development of inflammation in the tooth area, and the inability to continue their usual lifestyle. Quite often he is forced to take strong painkillers for several days in a row.
What are the methods for removing a nerve?
- Amputation . This method is rarely used: mainly in pediatric dentistry. Its essence lies in the fact that the neurovascular bundle is partially removed. The pulp remains in the roots, and only the coronal part is removed. In adults, it is used in exceptional cases, when the doctor sees that the inflammation has affected only a small part of the nerve.
- Extirpation . The pulp is completely removed from the tooth. After removing the nerve, the canals are cleaned, washed, and filled.
How many nerves are there in a tooth?
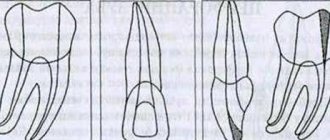
Different teeth differ from each other not only in their location in the oral cavity, shape and functions (chewing, incisor, canine), but also in their internal structure, number of roots and canals. The deeper a tooth is in the mouth, the more canals and roots it has, and most of them are in the teeth of the upper jaw.
But the number of nerves located inside a tooth may not depend on the number of canals and roots - for example, in the same tooth, different people may have one single nerve, or two, or even three (mostly again, in the far teeth, seven, six and eight). All of them are visible only during the X-ray procedure - that is why, before treating caries or, especially, pulpitis, an X-ray of the tooth
is mandatory. The doctor needs to know how many nerves there are in a particular tooth, and how badly they are damaged; depending on this, a decision will be made about their removal or treatment.
Removing the nerve of a tooth is a procedure that most dentists try to avoid until the last minute. However, it is not always possible to preserve the nerve and pulp, and here’s why.
Sequence of treatment
- Diagnostics . After the doctor has examined you and collected your medical history, an X-ray is taken. This diagnosis allows you to evaluate the structure of the tooth and plan treatment. To see the full anatomy of the root canals, a computed tomography (CT) scan is performed - a 3D diagnostic that allows you to see all the structures of the tooth.
- Pain relief . Local infiltration or conduction anesthesia is performed. Before the injection, the gums are lubricated with an anesthetic gel so that the injection is not felt.
- Setting up insulation . Root canal work should be done in clean, dry conditions. For this purpose, rubber dam (insulation) is used. It is a latex plate that is placed on the tooth. Advantages of isolation: saliva and plaque do not enter the root canals. Medicines and solutions also do not flow into the patient’s mouth.
- Preparation of hard dental tissues . The doctor uses a drill to remove the destroyed tissue. To prevent overheating of the tooth, water flows from the tip. The doctor creates direct access to the root canals.
- Nerve removal . It is performed with thin sterile instruments similar to long needles. The doctor places an instrument into the root canal and removes the nerve. Machine rotary tools may also be used. This stage is completely painless, since anesthesia was previously performed.
- Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals . The canals are washed with special antiseptic solutions and passed through with instruments. This allows you to completely remove the diseased nerve and relieve inflammation.
- Temporary filling . Root canal work is complex, so it is not always possible to treat a tooth in one visit. An anti-inflammatory paste is placed into the canals, a temporary filling is placed, and a further stage of treatment is planned.
For permanent restoration of the crown part of the tooth, ]esthetic dentistry[/anchor] will be required.
Contraindications
Doctors at the SDent aesthetic dentistry center collect all data about the patient’s condition before starting treatment. In the health questionnaire, the patient notes the characteristics of his body, and the doctor conducts a survey. Planned nerve removal is not performed if:
- high blood pressure, hypertensive crisis;
- first, third trimester of pregnancy (provided there is no acute pain);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes and facial skin;
- acute respiratory and viral diseases, etc.
What ways to get rid of toothache are there?
- Let's start with the fact that if you are experiencing severe throbbing pain, you should not endure the pain. The dentist will conduct a detailed diagnosis and be able to identify the cause; it could be damage to soft tissues or incompletely cleaned canals. Next, you will be prescribed effective treatment.
- Under no circumstances should you search the Internet for methods to relieve pain at home and self-medicate. You need to identify the exact cause and undergo treatment. Otherwise, the disease will progress and inflammatory processes will spread to neighboring teeth.
- If, in addition to pain, you experience any other unpleasant symptoms, for example, severe swelling, discharge, fever, etc., you should also consult a doctor immediately.
General recommendations after treatment
- You can eat and drink immediately after treatment;
- Until the anesthesia wears off, you should not eat rough food;
- in the days following treatment on the side of the diseased tooth, do not chew rough, hard food;
- in some cases, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and oral baths are prescribed;
- If a temporary filling falls out, consult a doctor immediately;
- If pain occurs after placing a temporary filling, also consult a doctor immediately.
After the anesthesia wears off, the patient may feel discomfort in the area of the treated tooth. If pain, throbbing, or swelling occurs, you should consult a dentist.
Can a tooth hurt after nerve removal?
A tooth from which the nerve has been removed is called “dead.” According to logic, a tooth without a nerve cannot hurt. But tissues need time to recover after endodontic treatment. Therefore, reactive pain after dental treatment can normally persist for several days. Over time, it weakens and goes away on its own. Painful sensations usually occur when pressure is applied or while eating - they can last 1-3 days
,
a week maximum
.
The picture is completely different when the pain increases, becomes throbbing, the gums are swollen, red, swollen, and symptoms of intoxication appear - headache, fever, weakness. Such symptoms indicate the development of complications and require immediate attention to the dentist. The doctor will determine why the dead tooth hurts and provide effective treatment.
Long-term consequences after treatment
Patients often experience complications after nerve removal. This is due to many factors: lack of diagnosis, poor quality treatment, incorrect diagnosis, etc. Main consequences:
- poor canal filling. A loose filling leads to the re-emergence of bacteria that extend beyond the tooth root. A cyst forms, due to which the tooth is often removed;
- tool fragments. The complex anatomy of the canals and low-quality instruments can lead to its failure.
- removal of material beyond the root apex. If the filling material is chosen incorrectly or there is too much of it, it extends beyond the root.
- Tooth perforation occurs due to aggressive processing.
To avoid such complications, doctors at the SDent clinic recommend contacting us for medical help, as we have a staff of highly qualified doctors, an equipped X-ray room and advanced equipment!
You should immediately consult a doctor if:
- pain intensifies or persists for more than 24 hours;
- bleeding from the socket intensifies or persists for more than 12 hours;
- one or more sutures placed by a doctor are lost;
- there was a putrid odor from the mouth;
- it is difficult or painful to open your mouth;
- the increase in body temperature is significant (more than 39 degrees Celsius) or persists for more than 24 hours;
- swelling increases or persists for more than 3 days;
- mobility of adjacent teeth occurred.
Our contacts
Top Contents
- How to remove a tooth
- Wisdom tooth removal
- Root removal
- Recommendations after removal
In dentistry, there are specific indications that explain why a tooth should be removed, the main one of which is to prevent the development of inflammation, loss of adjacent teeth and general infection of the body. If you have the following conditions, your doctor will recommend extraction surgery:
- complete destruction of the crown and root;
- crown fracture;
- advanced pulpitis;
- severe periodontal damage;
- mobility grades 3 and 4;
- purulent processes (flux, cyst formation at the root apex);
- incorrect positioning, which leads to injury to the cheek or tongue;
- correction of the bite when one element interferes with others, including before installing braces.
The final decision on whether a tooth needs to be removed is made by the doctor after examination and x-ray diagnostics. If there is a possibility of restoration, the dentist will definitely use it, since the tooth-preserving approach is the basis of dental treatment.
Often the question of whether to remove or treat a tooth arises in pregnant women, since surgical intervention during this period has an extremely adverse effect on the development and health of the fetus. Doctors prefer symptomatic treatment, which alleviates the condition and allows you to delay the time before childbirth. Removing a tooth while breastfeeding is not dangerous, and the operation does not carry any risks.
Extraction is not performed if there are contraindications:
- acute infectious diseases;
- bad feeling;
- Drunk;
- mental disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, etc.
If you have chronic diseases or diseases that require special treatment, check with your doctor whether a tooth can be removed in your case. The dentist must be aware of possible risks and take all measures to prevent them.