If unpleasant symptoms such as a white or yellowish coating appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue, as well as pain, dryness, and elevated temperature, a disease such as stomatitis can be diagnosed. It is caused by the development of bacteria and viruses that affect the oral cavity in both adults and infants.
In advanced cases, wounds begin to form on the mucous membrane. A popular drug for getting rid of this disease is nystatin, which effectively fights fungal colonies in the affected areas and eliminates the cause of the disease.
Nystatin tablets
Effective treatment of stomatitis in adults
Treatment of stomatitis in adults largely depends on the type of this disease, as well as concomitant diseases that provoke the appearance of ulcers and inflammation in the mouth. The most interesting thing is that the diagnosis of stomatitis is still carried out visually: the patient undergoes tests only if other, more serious diseases are suspected. Effective therapy for stomatitis is possible, but only if the type of disease is correctly determined. Recovery usually occurs within one or several weeks, but there are also more severe forms when long-term rehabilitation is required for complete recovery. Let's look at the main types of disease and drugs for the treatment of stomatitis in adults.
Side effects and contraindications for use
Side effects from the antifungal agent occur quite rarely, according to patient reviews. Gastrointestinal upset may occur - vomiting, diarrhea, nausea. Also, allergic manifestations in the form of skin itching and chills can be caused.
Manufacturers indicate the following contraindications, in cases of which it is necessary to stop taking nystatin and find an alternative treatment:
- Pregnancy in the 1st trimester and lactation period.
- Individual intolerance to components and the occurrence of allergic reactions.
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder in chronic or acute form.
- Pancreatitis and stomach ulcers.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
Treatment of stomatitis after detection can be carried out many times (once a year or more often), since once settled in our body, the herpes virus remains there for life. Herpes stomatitis is characterized by the accumulation of reddish transparent blisters on the lips and inside the mouth, so it is quite easy to detect. Especially often, herpetic stomatitis manifests itself against the background of decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency, hypothermia and stress. Remember that herpetic stomatitis in adults is contagious, so you should avoid tactile contact.
Types of drugs
- Antiviral agents.
- Immunostimulants (as a preventative measure).
- Ointments (including to eliminate visual manifestations of the disease).
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
A type of stomatitis that is caused by a special type of fungus – Candida albicans. Very often, candidal stomatitis begins with glossitis, which is why its second name is stomatitis on the tongue. Treatment in this case requires fairly prompt treatment, since in adults it is quite painful and is accompanied by a burning sensation in the mucous membrane and sore throat. On the inner surface of the lips and cheeks, as well as on the tongue, characteristic foci of inflammation appear, covered with a white cheesy coating.
Treatment methods
- Treatment of common diseases (if detected).
- Antimicrobial therapy.
- Preventive rinses.
Description of the drug
Nystatin is designed to destroy yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida in the body. The active ingredient of the drug is called nystatin. It is an effective natural antibiotic with a large number of double bonds in its structure. Thanks to this, the substance penetrates and is embedded in the membrane of the pathogen cell, which in turn is destroyed .
Also, the medication contains ingredients such as talc, titanium dioxide, calcium stearate, magnesium carbonate, etc.
With regular use of the drug, further proliferation of bacteria and fungi is blocked, and a barrier is created for their spread to other organs. Over time, the oral cavity is gradually cleared of lesions, persistent plaque disappears, and damaged areas of the mucous membrane quickly heal and regenerate.
Advice. To avoid relapse of candidal stomatitis, nystatin is used for prophylactic purposes.
Prevention helps to avoid illness, but it should be remembered that an antifungal drug is an active agent, so it must be used strictly according to the instructions and as prescribed by a specialist.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
A distinctive feature of this type of stomatitis is the appearance of so-called aphthae on the oral mucosa. These are small round ulcers with redness at the edges, the touch of which causes unpleasant painful sensations. Often occurs as a result of the activity of microorganisms (in particular, staphylococcus). Treating aphthous stomatitis at home is only recommended if it is not caused by a more severe illness. Often aphthous stomatitis occurs with problems with the immune system, liver and gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment methods
- Allergy therapy.
- Antiseptic therapy (treatment of aphthae with anti-inflammatory solutions, gels and ointments).
- Dental treatment and sanitation of the oral cavity (after dental treatment, stomatitis occurs less frequently than in the presence of carious lesions).
- Immunotherapy.
- Diet.
Instructions for the use of nystatin in the treatment of stomatitis
Due to the fact that the active substance acts only on the affected object and does not penetrate into the integument, nystatin can be successfully used to treat adults and children of any age. However, the maximum duration of use should be no more than two weeks, 2-3 times a day, according to the recommendations of a specialist. According to the age of the patient, there are nuances of antifungal therapy and duration, depending on the severity of the localization, which should be strictly adhered to.
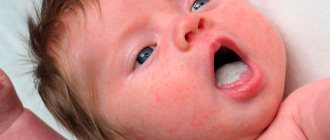
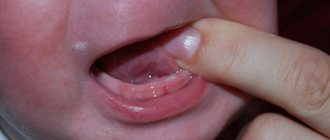
In a child under one year old
Newborn infants have their own characteristics of thrush. This may include the detection of a dense, whitish plaque in the mouth in the form of spots on the mucous membrane and tongue. Such appearances are quite painful and can provoke the child’s whims, fever, loss of appetite, fatigue, and poor sleep. In order for parents to quickly get rid of symptoms and not provoke complications, they need to follow a competent course of therapy.
For children under one year of age, nystatin is prescribed in the form of an aqueous solution. To prepare it, you need to take 1 tablet and carefully crush it. Next, the powder is mixed with oily vitamin B 12, and the resulting suspension is used to treat the affected and surrounding tissues in the mouth. The procedure is usually done 2 times a day. It is recommended to first treat the tissue with a decoction of chamomile, which is applied to cotton wool and try to remove as much plaque from the mucous membrane as possible.
What thrush (candidal stomatitis) looks like on a child’s tongue.
If the vitamin is not available, the solution is prepared using boiled water. To do this, take 300 ml of boiling water and dissolve one tablet of the drug in it. After the liquid has cooled to a comfortable temperature, you need to take a clean bandage, wrap it around your index finger, soak it in the solution and carefully treat the desired surface in your mouth.
Make sure your hands are clean and free of bacteria . You can apply antiseptic to your hands for this purpose. Manipulations are carried out after each meal, no more than 6 times a day.
Nystatin can also be prescribed in tablet form for up to a year. The dosage will be ¼ of a whole tablet; it can be given in a crushed state. After taking the child, it is forbidden to feed and drink for half an hour, so as not to provoke vomiting and to allow the substance to work. It is more advisable to take nystatin after breastfeeding.
In children from one year old
Children over a year old are prescribed nystatin in tablet form. The drug relieves the symptomatic manifestations of the disease and promotes a speedy recovery. The dosage is prescribed according to the following scheme:
- From 1 to 3 years, the dose is 250,000 units.
- From 3 to 13 years, the dose is 250/400,000 units.
The given daily dose, agreed with the doctor, should be divided into 3-4 doses during the day. Nystatin tablets need to be dissolved behind the cheek so that the active substance is evenly distributed in the oral cavity and creates a protective barrier. After resorption, it is not recommended to drink water or eat for 30 minutes.
Advice. If the child categorically refuses to carry out the procedure because of the bitter taste of the powder, you can use nystatin ointment 5%. It is used to treat the affected areas of the skin 4 times a day for 1-2 weeks until complete recovery is achieved.
In adults
For adults suffering from stomatitis in the mouth, complex treatment is necessary, which involves the use of both tablets and ointments. The so-called ulcerative stomatitis can be the cause of a previous infection, as well as as a consequence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular disorders, or due to bad habits and improper oral hygiene. The oral mucosa becomes covered with deep, painful ulcers, the body temperature rises to low-grade fever, and dehydration is felt.
An antibiotic for adults (from 13 years old) is prescribed in a dosage of 250/500,000 units, 3-4 times a day after meals, for 10-14 days. Adults should not chew the tablets; they should be swallowed with plenty of water.
Ointment based on nystatin 5% helps with severe forms of the disease. The product is applied directly to the lesions, that is, ulcers, in order to form a protective film. Manipulations are carried out no more than 3 times a day, otherwise side effects will occur. After application, you should not drink water or eat for half an hour.
Treatment of ulcerative stomatitis
Ulcerative stomatitis very often occurs due to poor oral hygiene and bad habits (especially smoking). Often this type of stomatitis at its onset is confused with periodontitis and gingivitis, since it is characterized by inflammation of the gums, a grayish coating around the teeth and death of soft tissues. Often accompanied by fever and fever. One of the few forms of stomatitis, which often requires treatment by a doctor, and in the most advanced cases, surgical intervention.
Treatment methods
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Antibacterial treatment of affected areas.
- Surgical intervention (in severe cases, removal of areas of dead tissue and gum grafting).
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is also called prosthetic stomatitis, since it occurs due to unsatisfactory care of the orthopedic structure, when many pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in the area of contact between the prosthesis and soft tissues. After treating foci of inflammation, it is necessary to carry out complete cleaning and antibacterial treatment of the prosthesis or replace it. This type of stomatitis should not be confused with allergic stomatitis, which develops against the background of an allergy to the prosthetic material. In this case, the prosthesis must be changed to a hypoallergenic one.
Treatment methods
- Anti-infective therapy.
- Mouth rinse.
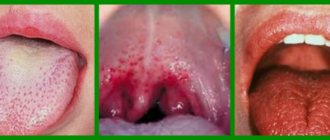
Symptoms of stomatitis
The manifestation of stomatitis can be different.
This depends on the form and stage of development of the disease. The first symptom is redness of the oral mucosa in a certain area. The spot does not rise above the level of the mucous membrane, has a round or oval shape and may be pinkish or whitish in color. Next, the area around the affected area becomes swollen, hyperemic, and pain appears. Aphtha appears at the site of the spot. Aphtha (from the Greek aphtha - ulcer) is a superficial defect of the mucous membrane, having a round shape and a grayish fibrinous coating. If you remove necrotic plaque from the surface of the aphthae, the ulcer will begin to bleed [5]. Most often, aphthae are located along the transitional fold, on the lateral surface of the tongue, on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips.
In severe forms, the amount of fibrinous plaque on the surface of the ulcer increases, and an infiltrate appears at the base of the aphthae (an accumulation of cellular elements of blood and lymph in the mucous layer). With such a clinical picture in the oral cavity, the patient experiences pain, burning, itching, bad breath, increased salivation, and eating becomes difficult. Body temperature rises to 38 ℃, weakness appears.
A feature of the disease is frequent relapses. Repeated rashes may appear after a few days or every few months. It depends on the ability of the immune system to fight infection.
In the most severe cases, stomatitis manifests itself in the form of ulcers on the mucous membrane. An ulcer is a deep defect of the mucous membrane, in which the entire thickness of the mucous membrane is affected. The ulcer is surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate, the edges of the ulcer are uneven, scalloped (jagged) [5]. When ulcers appear in the oral cavity, the general condition also worsens. The submandibular lymph nodes on the affected side may become inflamed. On palpation they will be enlarged and painful.
With candidal stomatitis, a white coating appears on the tongue and gums; when trying to remove the plaque, the affected areas begin to bleed. There is also an unpleasant taste in the mouth and a burning sensation. If candidal stomatitis develops against the background of diabetes mellitus or immunodeficiency conditions, it always has a chronic course.
With viral lesions of the oral mucosa, pain occurs, which intensifies during eating and when talking. The mucous membrane turns red and swells, then small blisters appear on it. The bubbles quickly open and aphthae form in their place. In moderate and severe forms, body temperature rises to 37-40 ° C, general malaise, weakness, and headache are noted.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is caused by the body's immunological response to contact with an allergen. The role of the latter can be played by anything: food products, new oral hygiene products, dentures, animal hair and much more. At risk are patients who are predisposed to allergies or suffer from various autoimmune diseases. A distinctive feature of allergic stomatitis is the acute onset of the disease, accompanied by an increase in temperature, severe pain and putrid odor from the mouth, which does not disappear even after thorough brushing of the teeth.
Treatment methods
- Identifying the allergen and eliminating it (or minimizing contact).
- Antihistamine therapy.
- Relief of inflammation with corticosteroids.
- Taking analgesics to relieve pain.
- Local antiseptic drugs
- Diet.
Treatment of stomatitis in children
Treatment of childhood and adult stomatitis follows the same methods. At the same time, some drugs used for adults are replaced with those that are better suited for the child’s body. First of all, we are talking about antibiotics, antiseptics and drugs to enhance immunity. Children are often prescribed more gentle methods, which include the use of herbs and natural tinctures for rinsing. At an early age, dentists recommend preventing stomatitis using traditional medicine.
| Age | Type of disease |
| From 0 to 3 years | Candidal stomatitis, or childhood oral thrush. This type of stomatitis is especially common in infants. |
| 1 – 4 years | Aphthous and herpetic stomatitis caused by external infections and mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. |
| Children of primary and secondary school age | Allergic and aphthous stomatitis. |
Release form and indications for use in the treatment of stomatitis
This medicine is widely distributed, the powder has a bitter taste and a yellow color. It can be found in the form of small, biconvex, film-coated tablets for oral use. Tablets are packaged in 10 pieces in a blister pack, or 20 pieces in a glass jar, packed in a cardboard package.
There are also dosage forms in the form of a yellow polyene group ointment, produced in aluminum tubes. The ointment acts carefully and is not absorbed into the systemic bloodstream. It is usually prescribed in combination with oral nystatin for a more complete pharmacological effect.
Nystatin is used for internal and local effects on sites affected by fungal pathogens. Indications for use are appropriate in the following cases:
- Treatment of candidiasis of the mucous membrane and skin , resulting from long-term use of antibiotics when the body is exhausted, as well as due to injuries to the mucous membrane or improper hygiene.
- A prophylactic course when taking antimicrobial agents or antibiotics.
- Treatment and prevention of thrush in infants.
- For stomatitis in children and adults, the cause of which is candida.
To carry out treatment, you should initially consult a doctor, especially if a child is sick, in order to prescribe an adequate dosage and course of administration. Be sure to take into account the available contraindications given in the medication instructions to avoid possible health problems.
Nystatin ointment
Treatment of stomatitis at home
I would like to immediately note that treating stomatitis with folk remedies at home is possible, but you need to understand that in many cases it is impossible to do without a visit to a specialist and the use of antibiotics. Ignoring these points can lead to worsening of the disease and longer rehabilitation. In addition, on the Internet you can find a whole lot of “revolutionary” recipes for stomatitis, so you need to be able to separate the wheat from the chaff and understand which remedies can really help, and which are the fruit of the inflamed imagination of “couch healers”. Below we publish the most common methods of preventing and treating stomatitis with folk remedies, but please note that only an experienced specialist can draw up an optimal treatment plan.
In the case of children, treatment of stomatitis with folk remedies at home is used quite often. This is especially justified as a preventive measure, since the child’s body is more susceptible to the influence of the external environment. The most popular remedies are considered to be all kinds of decoctions, for the production of which chamomile, calendula, burdock, propolis and blackberry leaves are used. A homemade ointment is also used to treat stomatitis, which is made from novocaine, egg white and honey. Be that as it may, if your child shows signs of stomatitis, it is best to immediately take him to a specialist who can make the correct diagnosis and plan treatment.
Treating stomatitis with home remedies
| Facilities | Description |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Rinsing with a solution of hydrogen peroxide helps reduce discomfort and has an antiseptic effect. |
| Baking soda | Treatment of stomatitis in adults with soda is recommended when the disease is detected in the initial stages. A solution of the substance (a spoon in a glass of water) is recommended for rinsing. |
| Decoctions of chamomile, rose hips and calendula | They have disinfecting properties and contain vitamins and nutrients to maintain oral health. |