After giving birth, almost all the mother’s thoughts are absorbed by the baby, but sometimes deterioration in well-being and discomfort in the intimate area prevent her from enjoying motherhood. The first months after the birth of a child are a time when women's health is especially vulnerable. Some nursing mothers experience itching and burning in the genital area, the appearance of a white coating and cheesy discharge. These symptoms may indicate the development of vaginal candidiasis. The question arises of how to treat thrush during breastfeeding, because not all active ingredients of medications are safe for the baby. This is why it is important to use drugs approved for use during lactation. Your doctor will help you choose the right medications.
Features of candidiasis during breastfeeding
A nursing woman may experience various symptoms of thrush: itching and burning in the intimate area, redness of the external genitalia, and the appearance of copious discharge with a sour odor. These unpleasant sensations are often accompanied by burning pain in the chest, which makes it difficult for the mother to feed the baby. With thrush, the nipples can become inflamed and red, and sometimes a whitish coating appears on them. In this case, discomfort is caused not only by the baby’s attachment, but also by contact with clothing. In some cases, thrush can also develop in infants: the oral mucosa is usually affected.
Symptoms of stomatitis in newborns
As a rule, candidal stomatitis in children begins asymptomatically, so the child does not show concern. As the disease progresses, his behavior changes - the baby refuses to eat and becomes capricious. Due to the active proliferation of the fungus, the taste of food changes, which may explain the lack of appetite.
Pronounced signs that treatment of candidal stomatitis is required in children are:
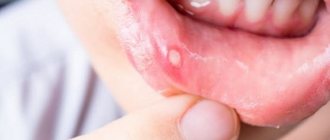
- a whitish, cheesy coating in the oral cavity - it is especially clearly visible in the morning, after waking up;
- sour breath;
- swelling and redness of the gums.
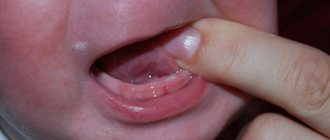
Candidal stomatitis in children has three degrees of severity. In mild and moderate forms of the disease, the white coating is easily removed, but at the same time areas of bright red mucous membranes are exposed. In severe form, the plaque is already denser. And since it is fused to the mucous membrane, it is quite difficult to remove. And if this succeeds, an eroded mucous membrane with bruises opens. Thrush in a baby’s mouth is usually clearly visible in the early stages, so prompt consultation with a doctor can prevent the development of complications.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis in children must be started in a timely manner, otherwise complications in the form of a secondary infection and the gradual spread of the fungus throughout the child’s body cannot be avoided.
Candidal stomatitis can be identified by the symptoms in the following photos:
Treatments for thrush in nursing mothers
Creams and ointments.
It is preferable to treat thrush during breastfeeding with drugs for external use, unless otherwise recommended by the doctor. Their active ingredients usually do not penetrate the systemic bloodstream, which means they are not passed on to the baby through mother’s milk. The use of creams and ointments is aimed at combating the causative agent of the disease - the Candida fungus - as well as reducing inflammation, eliminating burning, discomfort and itching. The doctor selects specific remedies in this and other cases.
Suppositories.
Drugs in this dosage form are also used topically: they are inserted into the vagina one or several times a day. The effect of vaginal suppositories can be anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antiseptic or complex. The use of such drugs for the treatment of thrush in a nursing mother is allowed under the supervision of a doctor.
Douching solutions.
The right douching product helps reduce inflammation of the mucous membranes and helps restore a healthy balance of microflora. Solutions can also reduce the unpleasant symptoms of thrush: itching, burning and discomfort in the intimate area. Douching is not difficult at all. To do this, a woman needs to lie on her back and slightly raise her legs. The solution, heated to body temperature, is injected into the vagina using a syringe or a special bottle (if the product is available in such a convenient form). The procedure takes from 2 to 15 minutes and can be done in the shower or bath.
Pills.
Treating thrush during breastfeeding with oral medications is permitted only as prescribed by a doctor. The active components of tablets and capsules pass into breast milk and can affect the baby. Systemic therapy for severe thrush is necessary; in this case, the doctor will recommend medications that will provide the greatest benefit for the mother and the least risk for the baby.
Release form
The choice of one or another drug composition depends on the location of the infectious focus. Thus, film-coated tablets are prescribed for oral administration for oral candidiasis in older children. For children from one to three years old, the pills are diluted with milk or a vitamin solution. For the treatment of oral candidiasis, newborns are prescribed an oral suspension obtained by placing several Nystatin granules in an aqueous base.
Rectal (vaginal) suppositories are mainly used as part of complex therapy for intestinal/vaginal candidiasis. Nystatin ointment is indicated for fungal skin infections. In addition to the polyene antibiotic, it contains auxiliary components such as lanolin and white petroleum jelly, which ensure uniform distribution of the drug.
Is it possible to continue breastfeeding while treating thrush?
With properly selected therapy for candidiasis, you can and should continue breastfeeding, because mother's milk is the optimal nutrition for a child in the first year of life. At the same time, of course, a nursing woman does not want to infect her baby. To reduce the risk of infection, thoroughly wash your hands with antibacterial products after using the toilet and using topical medications. If your child shows signs of thrush, you should consult your pediatrician, but breastfeeding should not be interrupted.
How long does it take to treat thrush while breastfeeding?
Of course, a nursing mother wants to get rid of candidiasis for a long time, because she has enough other worries. With proper treatment, symptoms often decrease and even disappear completely in the first days from the start of therapy. But the process of completely getting rid of thrush is quite long. To prevent the disease from returning, a course of treatment is usually necessary, which lasts 10–15 days. The exact duration of taking the medication is determined by the doctor. To ensure the effectiveness of therapy, you can take vaginal smears to determine the composition of the microflora. If the content of Candida fungi is higher than normal, it is advisable to repeat the course of treatment.
Prevention is easier than cure - measures to prevent thrush during breastfeeding
Proper intimate care.
Young mothers devote a lot of time to their baby, often to the detriment of taking care of their own health. But in order to prevent thrush from appearing, it is very important to provide proper care for the female genital organs. It is advisable to carry out hygiene procedures twice a day using intimate hygiene products. You need to dry yourself with a separate towel, which is changed every 2–3 days and washed at high temperature (60–90 °C).
Healthy lifestyle.
An important condition for preventing thrush is maintaining the balance of vaginal microflora. For this, it is important not only to properly care for the intimate area, but also to maintain immunity. A nursing mother needs to eat a balanced diet, maintain a work-rest schedule, regularly spend time in the fresh air, and engage in physical activity to the extent that her postpartum condition allows.
Tantum® Rose for thrush in nursing mothers
Tantum® Rose can be used in the complex treatment of inflammation of the female genital organs (vulvovaginitis)1, which is accompanied by candidiasis. The drug has no age restrictions and is approved for use during pregnancy and lactation1. Tantum® Rose helps restore the delicate balance of microflora in the intimate area and fights only harmful microorganisms - bacteria and fungi that cause thrush2. The product relieves the unpleasant symptoms of inflammation within 20 minutes after use3. You can choose Tantum® Rose in convenient syringe bottles for single use or in economical sachet form with powder. The prepared solution is heated to body temperature and injected into the vagina. This simple procedure is carried out 1-2 times a day1.
Bibliography
- According to the instructions for use of the drug Tantum® Rose.
- MaglianoE. At al. The role of benzydamine in the topical treatment of the so called non specific vaginitis. Int J Tiss React 1987; X1(2): 151–156.
- Czajka, R. et al. Assessment of the efficacy of benzydamine (Tantum Rosa) in the form of vaginal lavage in the treatment of perineal complaints in the early puerperium. Pol J Gyn Invest 2001; 4(2): 99–105.
Thrush in children: causes
In adolescents, the main cause of thrush is a hormonal imbalance, which occurs due to the growth and development of the child or due to disruption of the endocrine system.
Other causes that act as factors in the occurrence of childhood vulvar candidiasis:
- reduced immunity;
- antibiotic treatment (uncontrolled);
- poor or unhealthy diet (especially abuse of sweets, fast food, etc.);
- smoking and alcohol;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- improper hygiene or its complete absence;
- hypothermia;
- anatomical features of the reproductive system;
- infection from the inside (for example, from the intestines);
- after contact with household objects or in public places (swimming pool, etc.);
- during childbirth from the mother;
- excess weight (at the stage of obesity);
- anemia and other diseases;
- allergic reactions.
As you can see, there are a lot of answers to the question “Where does thrush come from in children?” Moreover, as a rule, a whole complex of problems leads to thrush. Another factor is age. In infants, thrush usually appears as a result of parental neglect, in teenage girls - as a result of changes in the hormonal system, etc.
If there is any suspicion of candidiasis or another infection, it is necessary to take the child to a doctor who will conduct an examination and prescribe a course of treatment and recovery, as well as give useful tips on how to prevent infection or relapses. The medical center employs specialists in pediatric gynecology and uses modern diagnostic equipment.
Initial appointment
At the initial appointment, the doctor examines the child’s genital organs to assess the disease and state of health. The doctor also finds out the possible causes of thrush in a child, prescribes tests to understand how to treat, since the course is prescribed individually for each specific clinical case.
Diagnosis of the disease
In some cases, tests and examinations are required:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
; - blood and urine tests;
- taking smears and culture for fungi of the genus Candida;
- stool analysis for worms and intestinal dysbacteriosis
If children are suspected of having any diseases other than thrush, additional tests are prescribed. Also, if thrush has caused a nervous shock and affects the psychological and mental development of the child, then a consultation with a psychotherapist is prescribed.
Procedure and treatment regimens for vulvovaginal candidiasis in school-age children and teenage girls
The procedure and treatment regimen are determined individually and depend on the type and stage of development of the disease, the causes of infection and the presence of concomitant diseases. A visit plan is also assigned individually, since for one patient the first consultation and follow-up appointment will be enough, while for others several appointments will be needed.