Dry mouth is an unpleasant sensation that can be a symptom of serious illnesses. If dry mouth occurs constantly or frequently, it is necessary to understand the cause that is causing it and, if necessary, begin treatment. Elimination of dry mouth, as a rule, is achieved only as a result of treating the underlying disease, which should be the true goal. In any case, the feeling of dry mouth is another reason to pay attention to your health.
Dry mouth is caused by insufficient hydration of the oral mucosa, mostly due to insufficient saliva production. In medicine, dry mouth caused by a cessation or decrease in saliva production is called xerostomia.
.
Quite often, dry mouth occurs in the morning or at night (that is, after sleep).
Symptoms associated with dry mouth
Dry mouth in most cases manifests itself as a complex of symptoms described as:
- "viscosity" or "stickiness" in the mouth;
- thirst;
- irritation of the oral mucosa (burning and itching), the appearance of a bright border of the lips, cracks on the lips and in the corners of the mouth;
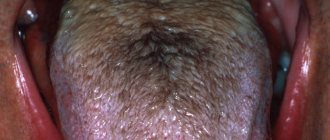
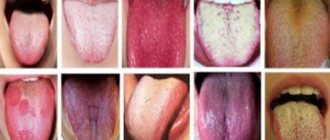
- dry tongue. The tongue turns red and becomes rough. It becomes more difficult to speak, chew and swallow. Decreased taste perception;
- dry throat. The voice becomes hoarse and more hoarse;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Diseases of the respiratory system.
Diseases of the respiratory system are a large group of diseases and conditions that can cause dry throat and require mandatory treatment under the supervision of an ENT doctor. Typically, such diseases are accompanied not only by dryness, but also by other symptoms: runny nose, frequent pain, cough and sore throat. If these symptoms appear, you should definitely contact an ENT doctor for an examination.
What diseases of the respiratory system cause dry throat?
- Acute respiratory viral infections, flu, colds. In addition to a dry throat, the patient has the following symptoms of colds and acute respiratory viral infections: fever, cough, nasal congestion, pain in muscles and joints, weakness, loss of appetite. Treatment is symptomatic: lowering the temperature, eliminating cough and runny nose with medications, as well as drinking plenty of warm fluids.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Based on the nature of the changes in the mucous membrane, catarrhal pharyngitis is distinguished, when swelling of the tissues is observed, hypertrophic, when the mucous membrane thickens, and atrophic pharyngitis, when the mucous membrane, on the contrary, becomes thinner. Attacks of dry cough, red throat, discomfort during swallowing, sore throat - all these symptoms are signs of pharyngitis. Pharyngitis can simultaneously be paired with tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils) or laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx). In this case, the patient is diagnosed with tonsillopharyngitis and laryngopharyngitis. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drugs, gargling, irrigation with antiseptics and physiotherapy (to consolidate the positive results from the action of the drugs and speed up the recovery process).
- Tonsillitis. The acute form of tonsillitis is called tonsillitis. If a sore throat is not treated in time, the disease will become chronic, with exacerbations occurring up to several times a year. Unlike pharyngitis, tonsillitis affects not the pharyngeal mucosa, but the palatine tonsils (tonsils). A sore throat occurs with acute pain in the throat, high body temperature, and a white coating or purulent accumulations appear on the tonsils. An effective means of combating sore throat is high-quality antibiotic therapy prescribed by an ENT doctor and physiotherapy performed in an ENT clinic. Chronic tonsillitis is not as severe as a sore throat, but its symptoms also cause the patient considerable discomfort: elevated body temperature, bad breath, sore throat. On the tonsils, purulent plugs are noticeable - accumulations of compressed streptococcus. Plugs support inflammation in the tonsils, so it is imperative to get rid of them. Effective therapy for chronic tonsillitis should be comprehensive and include treatment with medications, rinsing the tonsils from plugs and physiotherapy. In the absence of proper treatment, tonsillitis causes complications in the heart, kidneys and joints.
- Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, which is accompanied not only by dryness, but also by severe itching, barking cough, hoarseness in the voice and itching in the throat, as if the throat is being “teared” from the inside. The treatment regimen for laryngitis includes taking antibacterial or antiviral agents, antiseptic drugs, antitussives, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Also, during treatment it is necessary to give up alcohol, smoking and avoid overstraining the vocal cords. Moisturizing and softening the throat is achieved by drinking plenty of fluids (herbal teas, fruit drinks, compotes, etc. are suitable)
- Pharyngomycosis (or fungal pharyngitis) is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, the causative agent of which is a fungal infection. Often the disease occurs due to uncontrolled use of antibiotics. The disease occurs with dryness, severe burning, discomfort and pain in the throat. A cheesy coating is noticeable on the mucous membrane of the throat. Therapy consists of taking antifungal, anti-inflammatory drugs, gargling and irrigating the throat with antiseptic drugs. Physiotherapy is an excellent addition to drug therapy.
Causes of dry mouth that are not pathological
In some cases, dry mouth is not associated with a medical condition. For example:
- Dry mouth can occur in the morning and at night due to intoxication. This is a typical situation after drinking too much the night before.
- When nasal breathing is impaired, a person breathes through his mouth during sleep. The mouth is slightly open, and the oral mucosa dries out faster. Nasal breathing can be impaired due to a runny nose, nasal polyps, or a deviated nasal septum. A similar situation occurs with snoring. The cause of snoring in most cases is a decrease in the tone of the soft palate. Muscle weakening develops with age. This is why older people snore more often, and their oral mucosa becomes dry. This reason explains dry mouth in the morning in the elderly in most cases.
- If you don't drink enough fluids in hot weather, you shouldn't be surprised by dry mouth. A similar effect can be caused by eating highly salted foods.
- Many medications can cause dry mouth.
- Smoking is another common cause of dry mouth.
- Dry mouth can be one of the symptoms of menopause.
Diseases that may cause dry mouth
Dry mouth can be caused by high fever and intoxication due to various infectious diseases (flu, sore throat, etc.). Diseases associated with large loss of fluid as a result of vomiting or diarrhea (cholera, dysentery) can also cause dry mouth. In such cases, dry mouth is one of many symptoms and does not attract special attention.
If dry mouth is combined with diarrhea, flatulence, belching, nausea and pain in the left side of the abdomen, then this may indicate pancreatitis.
Dry mouth in combination with a bitter taste, heartburn, white or yellow coating on the tongue can indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract such as gastritis, duodenitis, cholecystitis.
Dry mouth can also occur with:
- diseases of the salivary glands;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis);
- neoplasms of the oral cavity (benign and malignant);
- damage to nerve endings that contribute to the functioning of the salivary glands;
- anemia;
- vitamin A deficiency;
- systemic diseases (scleroderma, Sjogren's disease, cystic fibrosis).
Help and treatment tactics
At home
Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications for dry mouth, recommends proper drinking regimen and lozenges that stimulate salivation . If your mouth dries out under stress, and the cause is psychological, working with a psychologist helps [5].
In the hospital
Sometimes it is impossible to eliminate the cause of dry mouth at home. This happens if the elimination of xerostomia requires surgery, radiation therapy or complex treatment of systemic diseases [7]. If you are experiencing dry mouth, contact a specialist and they will tell you how to get rid of it.
List of sources
- Morozova S.V., Meitel I.Yu. Xerostomia: causes and methods of correction // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/kserostomiya-prichiny-i-metody-korrektsii/viewer (access date: 02.21.2020).
- Arakelyan M. G., Tambovtseva N.V., Arzukanyan A.V. Main causes and clinical manifestations of xerostomia // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osnovnye-prichiny-i-klinicheskie-proyavleniya-kserostomii/viewer (access date: 02.21.2020)
- Everything you need to know about dry mouth // https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/187640.php#symptoms (access date: 02/21/2020).
- Lebedev M.V., Zakharova I.Yu., Kerimova K.I. Xerostomia (dry mouth syndrome) 2022 // https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/kserostomiya-sindrom-suhogo-rta/viewer (access date: 02.21.2020).
- Dry Mouth // https://medlineplus.gov/drymouth.html (access date: 02/21/2020).
- Rad M, Kakoie S, Brojeni FN, Pourdamghan N Effect of Long-term Smoking on Whole-mouth Salivary Flow Rate and Oral Health // https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3429961/ ( access date: 02/21/2020).
- Dry Mouth or Xerostomia // https://www.cancer.net/coping-with-cancer/physical-emotional-and-social-effects-cancer/managing-physical-side-effects/dry-mouth-or-xerostomia ( access date: 02/21/2020).
Eliminate dry mouth
If dry mouth is caused by drinking alcohol and smoking, then it can only be eliminated by getting rid of the bad habit. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of salty and sweet foods. Pay attention to how you breathe - through your nose or mouth. If nasal breathing is difficult, the cause must be diagnosed and nasal breathing restored. To do this, you will have to see a doctor. It is also important to monitor the humidity in the room.
Dry mouth can be the first symptom of many diseases. Therefore, if you often experience a feeling of dry mouth, it is necessary to understand its nature, determine the cause and, if necessary, consult a doctor and begin treatment for the disease that caused this symptom.
HOW TO REDUCE THE MANIFESTATIONS OF HYPOSALIVATION
The unpleasant sensation of dry mouth is said to begin when there is a decrease in normal saliva production of 45 percent or more. Also, a feeling of dry mouth is possible when the normal composition of saliva changes. However, this condition is not always the primary one because other symptoms encountered in this patient population are often perceived as more important. Dry mouth can manifest as dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), oral discomfort, loss of taste and prolonged chewing, and can have a significant negative impact on quality of life. Hyposalivation also causes difficulty speaking, and the feeling of discomfort in the mouth can be increased in those who wear dentures. Patients with dry mouth may develop lesions and cracks in the oral mucosa, and bad breath may become another unpleasant feature. Xerostomia can lead to malnutrition and even decreased social interaction. Patients with dry mouth also have a higher risk of developing tooth decay. Decreased saliva production predisposes patients to overgrowth of Candida albicans, which causes oral thrush (candidiasis). In patients who have received radiation therapy to the head and neck area, widespread tooth decay appears several weeks after treatment. Approximately 90 percent of saliva is produced by the major salivary glands, the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands. The remaining 10 percent is secreted by hundreds of minor salivary glands under the oral mucosa. It is believed that healthy people produce about one liter of saliva per day.
Causes of xerostomia
Quite often, drug treatment can be the main cause of dry mouth or a contributing factor to the development of xerostomia: by reducing the secretion of saliva (hyposalivation), or by changing the composition of saliva. More than 500 medications are thought to cause dry mouth, including cancer chemotherapy. The risk of xerostomia increases with the number of medications a patient takes. Listed below are some of the most common medications that cause dry mouth. For example, opioids can cause dry mouth, as can tricyclic antidepressants, antihistamines, and diuretics. Drugs with antimuscarinic properties can significantly reduce saliva production. Nasal congestion and subsequent mouth breathing can lead to dry mouth, lips and throat.
Drugs that cause dry mouth:
- Medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease
- Benzodiazepines
- Bronchodilators (ipratropium bromide)
- Antidepressants from the group of serotonin reuptake inhibitors (citalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline)
- Atropine
- Medicines to treat irritable bowel syndrome
- Drugs to treat frequent urination (oxybutynin, tolterodine, solifenacin)
- Diuretics (furosemide, thiazide diuretics)
- Antihypertensive drugs (captopril, enalapril, clonidine, lisinopril)
- Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine)
- Antihistamines
Fluid intake is important, as is the psychological state of the patient. Anxiety and chronic stress may be major contributors to dry mouth due to autonomic overactivity. Consumption of caffeine and nicotine can also contribute to dry mouth. Xerostomia is common in patients with cancer. Approximately 30 percent of cancer patients develop problems with dry mouth, which progresses in later stages of the disease. Radiation therapy to the mouth, head, or neck can cause severe xerostomia and hyposalivation. Salivary gland tissue is very sensitive to ionizing radiation and a dose >30 Gy may irreversibly alter salivary secretion depending on the location of the salivary glands relative to the radiation treatment field. Dry mouth can be caused by a variety of conditions and is not necessarily a consequence of existing cancer and its treatment regimens. There is an association of xerostomia with aging, with the prevalence tending to increase with age, accounting for approximately 30 percent of the population over the age of 65. Diabetes can cause dry mouth, as can other systemic conditions such as thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren's syndrome. Sarcoidosis and hemochromatosis are examples of rarer conditions that can lead to the destruction of the salivary glands. Transplant (eg kidney) rejection syndrome is also thought to contribute to the development of dry mouth symptoms.
Therapy and symptomatic treatment
of xerostomia
First of all, you should aim to eliminate the reversible causes of xerostomia. Talk to your doctor about your medications to determine if you can stop taking them or reduce your dosage. Alternative drugs may have less antimuscarinic properties. Any associated infections, such as candidiasis, should be treated with antifungal tablets, suspensions or gels (miconazole). For patients with mouth breathing, a short course of topical nasal decongestants (xylometazoline, oxymetazoline) may be prescribed. As mentioned above, dry mouth can be caused by excessive anxiety and/or chronic stress, so this possible cause should also be eliminated if possible.
Practical symptomatic treatment options may help. Drinking water frequently throughout the day may be sufficient for some patients. Holding ice cubes in your mouth to provide some moisture may also help relieve symptoms. Other measures include sucking on pineapple slices, taking frequent sips of cold orange juice or semi-frozen fruit juice, or using sugar-free chewing gum. Patients may find the use of olive oil beneficial, and some products containing olive oil have been shown to be beneficial for the symptomatic treatment of dry mouth. Saliva substitutes are widely used for patients with xerostomia. There are various formulations, including rinses, aerosols, chewing gums and dentifrices, and these may also play a role in stimulating salivary gland secretions. It is possible to use saliva substitutes before meals. Also, preparations containing hyaluronic acid are used to moisturize the oral cavity, sometimes in combination with amino acids.
In particular, VITA-HYAL spray (sodium hyaluronate) can be used to periodically moisturize the oral cavity during the day. Hyaluronic acid not only moisturizes the oral cavity, but also restores damaged mucous membranes, and also envelops it - preventing the penetration of bacteria through microcracks.
VITA-HYAL gel has a longer lasting effect compared to an aerosol and is usually applied to the oral mucosa in the morning and before bed. Sometimes it is necessary to apply it additionally - after eating.
It is also necessary to maintain careful oral hygiene. Some patients may be recommended treatment with pilocarpine, which stimulates the secretion of the salivary glands, but it has many side effects.
You can purchase Vita-Gial in our online store rivierabiotech.store
Which doctor should I contact for dry mouth?
If you complain of dry mouth, you can contact your dentist or general practitioner (GP or family doctor). After identifying the cause that caused the feeling of dryness, you may be redirected to an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist or rheumatologist.
Most likely, you will need to undergo various tests (general blood count, general urinalysis, blood test for thyroid hormones, biochemical blood test, serological test), and, if necessary, undergo some instrumental studies (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography).
Diagnosis of the disease
When a patient visits a doctor, the second one performs the following actions:
- Gets acquainted with his complaints, establishes from his words whether there were illnesses that could lead to this problem;
- Applies techniques to determine the amount of saliva produced;
- If necessary, urine and blood tests and ultrasound of the salivary glands can be performed.
To accurately determine the diagnosis and reasons for dry mouth, you may need not only the help of a dentist, but also a psychologist, neurologist, therapist, and rheumatologist. When developing a line to combat the problem, the participation of doctors of several specializations may also be required.