Dry throat is one of the most unpleasant symptoms indicating diseases of the nasopharynx and sluggish painful processes inside the body. This is a fairly broad symptom that accompanies many diseases - from the common cold and ARVI to an acute allergic reaction or diabetes. Despite its apparent insignificance, a dry throat can be a marker indicating the presence of serious health problems. A patient suffering from a dry throat becomes more irritable and psychologically susceptible to pathogens, provoking the appearance of increasingly painful reactions.
Dry throat - symptoms of the phenomenon
Dry throat is a rather vague formulation; the main symptoms of this painful process can be several factors from this list:
- General feeling of fatigue, weakness.
- Hoarse voice, tension in the vocal cords.
- Pain in the throat muscles, worse when talking.
- A painful dry cough during which no mucus is coughed up.
- An increase in temperature due to the body's immune response.
- Enlarged tonsils and severe redness.
In addition, dry throat is often accompanied by symptoms that accompany a cold - such as a runny nose, swollen lymph nodes, and pronounced inflammatory processes.
How to get rid of a sore throat?
Non-drug methods.
Before you get rid of a sore throat, you need to find out the exact reasons that caused it. In situations where the diagnosis of a cold is beyond doubt (there are other typical symptoms), and the infection itself is relatively mild, you can limit yourself to non-drug therapy and the use of safe medications, preferably natural remedies.
Even a slight sore throat should not be left unattended - if left untreated, the disease can “go downhill” involving the lower respiratory tract in the inflammatory process or become chronic, intractable. For non-drug treatment of sore throat, the following is also used:
- warm drink. It is recommended to take warm (not hot or cold!) liquid, with a temperature of about 40°C. For non-allergic inflammation, irritation of the laryngeal mucosa can be prescribed with herbal decoctions, tea with honey, milk with a small amount of butter and soda (on the tip of a knife). If you are prone to allergies, it is preferable to use heated mineral water, tea, or plain boiled water. The liquid should be drunk in small sips, holding it in the mouth for some time, as often as possible;
- rinsing with warm alkaline solutions, decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs;
- warming, distracting and physiotherapy (foot baths, inhalations, FUF, etc.).
Medication methods. In cases where it is not possible to get rid of a sore throat for a long time (a week or more) or if other alarming symptoms are noted (high temperature, severe weakness, severe cough), it is recommended to consult a doctor and, after prescribing, use medications:
- products for topical use - lozenges and lozenges, throat sprays, antiseptic solutions for rinsing;
- agents for systemic use – anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antimicrobial, etc.
Dry throat due to bacterial infections
One of the most common causes of dry throat. Infectious diseases accompanied by fever, cough, runny nose and other unpleasant symptoms most often cause a feeling of dry mouth due to damage to the soft tissues of the oral mucosa. In this case, it is unnecessary to fight dry mouth - you need to eliminate the cause of the disease, not its symptoms. By focusing on fighting the infection with antibiotics and other medications, you will not only increase the body's resistance level, but also get rid of all unpleasant symptoms in one go.
Physiological factors.
Physiological are so-called household, non-infectious causes that are associated with the impact of unfavorable external factors on the body or with a person’s lifestyle. In this case, there is no need to treat the throat: by eliminating the influence of such a factor, the discomfort in the throat disappears. Physiological reasons include:
- Too dry air in the room, which occurs at the height of the heating season or during prolonged use of the air conditioner. Buying a humidifier usually solves the problem.
- Polluted or dusty air. This problem is faced by people living in places with poor environmental conditions or working in “harmful” industries, who are forced to constantly inhale fumes, gases, dust, etc.). This also includes passive smoking.
- Overstrain of the vocal cords. If you regularly subject your vocal apparatus to excessive stress, a dry throat is a typical situation for you. Typically, this problem is faced by representatives of speech professions - artists, singers, teachers, announcers, tour guides, call center employees, etc. To learn how to safely use and not overstrain your vocal apparatus, it is recommended to visit a phoniatrist. A phoniatrist is an ENT doctor who specializes exclusively in the human vocal apparatus. The phoniatrist will show you effective exercises for the vocal cords and give the necessary prescriptions.
- Insufficient fluid intake. Eating foods that are too salty, sweet or spicy.
- Long-term use of certain medications (cough suppressants, antibacterials, antihistamines, diuretics, etc.).
- Uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops greatly dries out the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
- Difficulty in nasal breathing caused by structural features of the nasal cavity (deviated nasal septum, enlarged nasal turbinates, adenoids).
- Advanced age. In older people, the mucous membranes become thinner as they age, leading to a feeling of dry mouth.
- Nervous overstrain. Stressful situations provoke a decrease in saliva production, which causes discomfort. Dry mouth is not the only unpleasant consequence of stress. A person may also feel a lump in the throat and problems swallowing. This condition is temporary. After the person has calmed down or taken a sedative, the discomfort goes away.
- Tobacco smoking. The substances that make up cigarettes negatively affect the condition of the laryngopharyngeal mucosa. If you do not stop in time and do not say goodbye to the bad habit, chronic pharyngitis, chronic rhinitis, as well as malignant tumors of the larynx may develop.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, women's hormonal levels change, which can directly affect the appearance of an unpleasant symptom.
These conditions do not require specific treatment. In most cases, it is enough to eliminate or eliminate the irritating factor.
Smoking
Unfortunately, despite numerous warnings from the Ministry of Health, there are still a lot of people who smoke in Russia. Over many years of addiction, they become accustomed not only to the dubious taste of tobacco, but also to the symptoms accompanying its use - a feeling of bitterness, cough, dry mouth. The complete disappearance of dry mouth in a smoking patient is almost impossible - constant inhalation of hot smoke dries out the mucous membrane and leads to the formation of dense lumps of mucus, making swallowing and breathing difficult. If the patient is not ready to give up a bad habit, but wants to get rid of an unpleasant symptom, tissue mineral therapy is carried out - the oral mucosa is moisturized and cleansed, accumulated sputum and mucus are dissolved and disinfected by medication, after which the patient experiences relief and is relieved for a while from a constant feeling of dryness in the throat.
When your throat hurts...
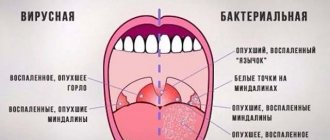
And this is how infectious and non-infectious causes of pain in the throat are distinguished:
- Infectious causes:
— Viral 70% (rhinoviruses, coronoviruses, adenovirus, influenza and parainfluenza viruses…) — Bacterial 15%. The most common cause is Group A B-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) - Fungal. The main causative agent is representatives of the genus Candida. The most pathogenic Candida albicans is 50% of all cases!
- Non-infectious causes:
— Allergic — Traumatic: cold drinks, ice cream, hot food, tobacco smoke from active and passive smoking, excessive consumption of spices, mustard, horseradish — Burns and injuries of the larynx
— Neuralgic conditions
— Benign and malignant neoplasms;
— Diseases of other human organs and systems
— Exposure to an irritating factor: gastroesophageal reflux, postnasal drip
Infectious causes of pain
Viral causes include primarily acute respiratory diseases, infectious mononucleosis, influenza, measles, and rubella. In addition to pain in the throat, the patient complains of the following symptoms: headaches, runny nose, nasal congestion, cough, fever, weakness, loss of appetite. Etiological diagnosis is difficult, especially in routine practice. In this situation, doctors are forced to rely on literature data. In most cases (20-30%), it is not possible to accurately identify the virus that caused the disease in a given person. Data from successful verification of the diagnosis place rhinoviruses in 1st place in the etiology of ARVI of the upper respiratory tract (30-50%). It should be noted that the influenza virus causes only 5 to 15% of cases of all acute respiratory viral infections.
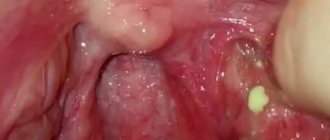
Lesions of bacterial etiology are the cause of a sore throat in 50% of cases. Bacterial infections are most often localized in the tonsil area (acute tonsillitis). Their characteristic symptoms are: severe pain in the throat; weakness and decreased performance; increased body temperature; redness of the palate, white plaque on the tonsils; enlarged lymph nodes.
Pharyngomycosis in the vast majority of cases is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (oral thrush). Sometimes the causative agents are mold fungi (aspergillus, penicillin, geotrichum). To trigger the pathological growth of fungi, which leads to an inflammatory process, it is necessary to reduce the body's defenses. Therefore, pharyngomycosis accompanies the following diseases and conditions:
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- metabolic diseases (obesity, thyroid pathology);
- oncological diseases (during chemotherapy);
- HIV.
The disease begins in the same way as all pharyngitis - with discomfort in the throat. The fungal nature of the process can be suspected based on the characteristic itching and burning. Patients complain of constant soreness and dry mouth. Pain for pharyngomycosis is very characteristic; it intensifies with swallowing and is more intense than with a bacterial infection.
Non-infectious causes of sore throat
Pain in the throat can be a result of exposure to various allergens: food, pollen, house dust, fur and secretions of pets, etc. In addition to discomfort and pain in the throat, patients are concerned about congestion and clear discharge from the nose, sneezing, itchy eyes .
Various external factors can cause pain: mechanical injuries to the larynx, chemical or thermal burns. Hard pieces of food and bones can injure the larynx. Chemical burns can be caused by inhaling vapors of harmful substances at work or by ingesting harmful substances while eating. Thermal burns most often occur when eating hot foods or drinks.
Pain in the throat may be a manifestation of neurological disorders. Usually this condition is accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing, and headaches. This feeling can manifest itself constantly, or maybe with a certain frequency.
Other causes of sore throat accompanied by sore throat and cough: drainage of discharge from the nasopharynx due to adenoiditis or sinusitis, space-occupying formations of the nasopharynx (cyst/bursa of Thornwald); irritation of the respiratory tract by dry air, smoke, including active and passive smoking. In adults, a common cause of such complaints, often with a feeling of a lump in the throat, a “foreign body,” is an exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis associated with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, esophagitis, gastroesophageal reflux, cholecystitis, gastric ulcer. Severe dysphagia, regurgitation and pain when swallowing can be caused by varicose veins of the esophagus. Chronic pathology of the kidneys, endocrine system, blood, previous radiation and chemotherapy can lead to the formation of a chronic inflammatory and atrophic process in the pharynx. The first manifestation of hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar) may be thirst and dry mouth, accompanied by catarrhal changes in the pharynx. Similar complaints occur with Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. In patients with hypothyroidism, swallowing is often impaired, speech becomes slurred due to swelling and dryness of the tongue and lips, and it is difficult to perform pharyngoscopy.
Hypovitaminosis can also cause discomfort and pain in the throat. Vitamin A deficiency causes dryness and erosion of the mucous membranes. Vitamin B2 deficiency produces a triad of symptoms: dermatitis, cheilitis and glossitis (bright red, smooth and shiny dry tongue), accompanied by burning and pain in the mouth when talking and eating. Vitamin C hypovitaminosis occurs with dietary deficiency of ascorbic acid, inflammatory processes in the intestines and is manifested by pain, hemorrhagic and ulcerative-necrotic manifestations in the oral cavity and in the area of the palatine tonsils, mobility and tooth loss.
Diseases of the spine (cervical osteochondrosis, tuberculous spondylitis, radiculitis) can cause pain in the throat. Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve manifests itself as intense pain in the pharynx, especially against the background of chronic stress in anxious and suspicious patients. Metabolic disorders, intoxication, and trauma contribute to its occurrence. Characterized by unilateral pain in the root of the tongue, tonsil, lasting several minutes, accompanied by dry throat and subsequent hypersalivation. Neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve gives similar symptoms, but also includes a painful dry cough and spasm of the vocal folds when inhaling.
Diagnosis and treatment
As we can see, there are many reasons why your throat hurts. And to determine the real cause of this condition, an examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary. If during the diagnostic process with an ENT doctor it becomes clear that the problem is not from the ENT organs, you may need to consult related specialists: a neurologist, gastroenterologist, allergist, endocrinologist. In this case, the patient is sent for CT, MRI, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, gastroscopy, etc.
Every person who has a sore throat needs a medical examination and diagnosis. The sooner you make an appointment, the more effective the treatment will be, and the risk of complications will be minimal.
Acute tonsillitis
Tonsillitis, or tonsillitis, is an infectious disease that results in acute inflammation of the tonsils. This is not only a very unpleasant disease in terms of its course, but also a very contagious phenomenon - you can get a sore throat simply by airborne droplets from any unsuccessful contact with an infected person. Inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx lead to severe dryness in the throat. As with colds, to get rid of a dry throat with a sore throat, you should treat the cause of the disease, not its symptom.
Diseases of the respiratory system.
Diseases of the respiratory system are a large group of diseases and conditions that can cause dry throat and require mandatory treatment under the supervision of an ENT doctor. Typically, such diseases are accompanied not only by dryness, but also by other symptoms: runny nose, frequent pain, cough and sore throat. If these symptoms appear, you should definitely contact an ENT doctor for an examination.
What diseases of the respiratory system cause dry throat?
- Acute respiratory viral infections, flu, colds. In addition to a dry throat, the patient has the following symptoms of colds and acute respiratory viral infections: fever, cough, nasal congestion, pain in muscles and joints, weakness, loss of appetite. Treatment is symptomatic: lowering the temperature, eliminating cough and runny nose with medications, as well as drinking plenty of warm fluids.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Based on the nature of the changes in the mucous membrane, catarrhal pharyngitis is distinguished, when swelling of the tissues is observed, hypertrophic, when the mucous membrane thickens, and atrophic pharyngitis, when the mucous membrane, on the contrary, becomes thinner. Attacks of dry cough, red throat, discomfort during swallowing, sore throat - all these symptoms are signs of pharyngitis. Pharyngitis can simultaneously be paired with tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils) or laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx). In this case, the patient is diagnosed with tonsillopharyngitis and laryngopharyngitis. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drugs, gargling, irrigation with antiseptics and physiotherapy (to consolidate the positive results from the action of the drugs and speed up the recovery process).
- Tonsillitis. The acute form of tonsillitis is called tonsillitis. If a sore throat is not treated in time, the disease will become chronic, with exacerbations occurring up to several times a year. Unlike pharyngitis, tonsillitis affects not the pharyngeal mucosa, but the palatine tonsils (tonsils). A sore throat occurs with acute pain in the throat, high body temperature, and a white coating or purulent accumulations appear on the tonsils. An effective means of combating sore throat is high-quality antibiotic therapy prescribed by an ENT doctor and physiotherapy performed in an ENT clinic. Chronic tonsillitis is not as severe as a sore throat, but its symptoms also cause the patient considerable discomfort: elevated body temperature, bad breath, sore throat. On the tonsils, purulent plugs are noticeable - accumulations of compressed streptococcus. Plugs support inflammation in the tonsils, so it is imperative to get rid of them. Effective therapy for chronic tonsillitis should be comprehensive and include treatment with medications, rinsing the tonsils from plugs and physiotherapy. In the absence of proper treatment, tonsillitis causes complications in the heart, kidneys and joints.
- Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, which is accompanied not only by dryness, but also by severe itching, barking cough, hoarseness in the voice and itching in the throat, as if the throat is being “teared” from the inside. The treatment regimen for laryngitis includes taking antibacterial or antiviral agents, antiseptic drugs, antitussives, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Also, during treatment it is necessary to give up alcohol, smoking and avoid overstraining the vocal cords. Moisturizing and softening the throat is achieved by drinking plenty of fluids (herbal teas, fruit drinks, compotes, etc. are suitable)
- Pharyngomycosis (or fungal pharyngitis) is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, the causative agent of which is a fungal infection. Often the disease occurs due to uncontrolled use of antibiotics. The disease occurs with dryness, severe burning, discomfort and pain in the throat. A cheesy coating is noticeable on the mucous membrane of the throat. Therapy consists of taking antifungal, anti-inflammatory drugs, gargling and irrigating the throat with antiseptic drugs. Physiotherapy is an excellent addition to drug therapy.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an infectious disease that is accompanied by severe damage to the oral mucosa and lymph nodes. Rarely occurs alone - most often pharyngitis is accompanied by acute inflammatory processes. A patient suffering from pharyngitis is faced not only with a dry throat, but also with an unpleasant soreness and tickling, a sensation of a foreign element in the nasopharynx, as well as a general feeling of fatigue and malaise. Most often, to eliminate the unpleasant consequences of pharyngitis, they resort to complex treatment - simultaneously with the use of medications, the patient is prescribed mineral therapy to normalize the condition of the mucous membrane in the pharynx, which is supplemented by herbal medicine (the use of medicinal herbs and infusions to irrigate the affected area of the pharynx).
Causes of constant dryness in the nasopharynx
There are several reasons that lead to dry nasal mucosa. They are conventionally divided into two large groups:
- External . This includes climatic conditions and indoor microclimate, prolonged stay in mountainous areas. Working in hazardous industries (chemical, heavy industry, construction), as well as smoking, also contribute to increased dryness;
- Internal . These are side effects associated with taking certain medications and alcohol intoxication. These include chronic and acute diseases leading to atrophy of the mucous membranes (atrophic rhinitis, Sjögren's syndrome, scleroma, diabetes mellitus).
Dryness in the nasal cavity occurs against the background of several factors that enhance each other’s effects.
It is believed that disruption of nasal mucus secretion due to external causes is easier to correct and treat. Dryness due to allergies is considered separately, since it is at the intersection of internal and external factors. You can find out about drugs for the treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in adults here.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction of varying severity is also often the cause of an unpleasant feeling of dryness in the throat. Associated symptoms include difficulty breathing, severe pain when swallowing or breathing, and many other signs. Since at this stage of development of medicine, allergies cannot be treated, but are chronic and haunt the patient throughout life, there are several ways to avoid dry mouth:
- Using antiallergic drugs to relieve allergic reactions.
- Integrated use of mineral therapy and herbal medicine to restore normal functioning of the throat.
- Exotic treatment methods for the restoration of mucous membranes in especially critical cases - laser therapy (in this case, a photosensitive gel is applied to the damaged tissues of the throat, which, under the influence of a laser, releases oxygen and saturates the soft tissues with it, promoting their regeneration and destroying pathogenic bacteria), ultrasound and other treatment methods .
Diagnostics
The main methods for diagnosing the disease are collecting anamnesis and performing pharyngoscopy. However, such a diagnosis is not enough to determine the cause of the pathology. After the diagnosis is made, the doctor refers the patient for examinations in order to identify the factors that led to the pathology. If you look at a photo of a sore throat with atrophied mucous membrane, it will help even a non-specialist to visually recognize the pathology in life.
Without fail, a person is sent for a consultation with a gastroenterologist, since it has been precisely proven that most of the atrophic pathologies of the pharyngeal mucosa develop due to the reflux of acid from the stomach into the esophagus. Sometimes the patient himself does not notice this problem, and only a specialist can determine it.
If no disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are established, a blood test for hormones and a smear to identify pathogenic microflora are indicated. In addition, a referral may be given for an allergy test.
When there is concern that the patient has begun to develop cancer, a biopsy of throat tissue is performed. It can be performed independently or in parallel with pharyngoscopy. Thanks to the procedure, a malignant process can often be detected at an early stage, when therapy is still possible.
Dry throat due to vascular pathologies
Diseases of the circulatory system and vascular pathologies are almost always accompanied by a painful feeling of dryness in the throat. In this case, the most acute symptom of the pathology is treated first. As soon as the danger to human life and health has disappeared, the attending physician can begin to get rid of dry throat. Most often, lymphotropic or capillary therapy is used for this. The essence of these methods is to normalize the functioning of capillaries that provide circulation of blood, lymph and nutrients in the damaged area of the throat. The body is saturated with useful substances, releasing large amounts of oxygen and ozone, which are destructive to most harmful bacteria. At the same time, the therapy is also of a general strengthening nature - it not only relieves the patient of the feeling of dry throat, but also prevents the appearance of similar symptoms for a long time, protecting soft mucous tissues from damage.
Differences from the subatrophic form
Subatrophic pharyngitis, the symptoms of which are minor, is the initial stage of atrophic pathology. There is no thinning or irreversible change in tissue yet. Subatrophic pharyngitis is dangerous because pronounced symptoms do not always appear, which is why many patients do not seek timely medical help. As a result, the start of therapy occurs at a time when the mucous membranes are already seriously damaged and cannot recover, and as a result, treatment is only supportive.
Disease prevention
Despite the fact that dry throat itself is not an independent disease (it is just a symptom), it can and should be avoided by promptly implementing a set of preventive measures to maintain the health of the oral mucosa. You can do this as follows:
- Do not neglect daily oral hygiene. When brushing your teeth and gargling, a person easily gets rid of many pathogenic bacteria, which can cause complications and even an infectious disease if not treated properly.
- Monitor the condition of the throat mucosa. If you observe the first signs of dryness or pain, immediately consult your doctor.
- Avoid unhealthy habits, particularly smoking. Stay outdoors more often; if you need to stay indoors for a long time with dry air, use a humidifier.
- Gargle regularly.
- Conduct herbal medicine at home - prepare plant decoctions and natural teas. They have a beneficial effect on the condition of the oral cavity, relieving a person of dry throat even in the bud of the disease.
Causes of dry nose
Dry nose can be caused by both physiological and pathological reasons.
In most cases, dry nasal mucosa, the treatment of which can sometimes be very lengthy and difficult, is not a disease in the full sense of the word. Most often, dryness accompanies any disease or is a physiological condition caused by a number of physical, chemical or thermal factors.
The most common causes of dryness include the following:
- Dry cold or hot air. Most often, these are natural features of the environment that are not characteristic of humans, that is, it is usually a newcomer, a person not adapted to such a climate, who suffers from such conditions.
- Operation of heating devices and air conditioning systems. All of them, to one degree or another, greatly dry the air and provoke drying out of the mucous membranes.
- Allergic reactions. After some of them, the nasal mucosa suffers greatly, becomes dry, fragile, easily damaged and bleeds.
- Colds accompanied by severe acute or prolonged runny nose. This type of drying out is usually accompanied by extremely unpleasant sensations and the formation of painful, itchy and irritating crusts, and constant sneezing in bursts.
- Use of medications. Dryness is mainly caused by sprays designed to reduce the appearance of a runny nose. They constrict blood vessels, remove fluid from the nose and irritation, swelling, but if abused or individual intolerance occurs, they cause drying out of the mucous membranes.
- Reaction to aerosols (cosmetic or any other), as well as to the strong smell of paint, chemicals, especially those containing chlorine.
- High blood pressure.
- The use of radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer of the nasopharynx and soft tissues, eyes and ears.
- A decrease in the level of hormones in the body associated with the decline of sexual function.
- Mechanical irritation of the nasal mucous membranes associated with being in a room that is heavily smoky, dusty, or filled with tiny particles of sand or stone (for example, in places where stone processing is carried out or in construction).
- Sjögren's syndrome. This rare autoimmune disease is characterized by severe dryness of the mucous membranes of the body, including the nose.
There are many reasons for dryness and they are all different. In order to cope with this unpleasant condition, you need to know the root cause that caused it, eliminate or eliminate it, and then take measures to treat, moisturize and soften the nasal mucosa.
Drug treatment
Moisturizing sprays and nasal drops
The use of medications depends on how advanced the condition of the mucous membranes is and whether there is an underlying disease. In the latter case, you need to get rid of it by curing your runny nose, allergies, or leaving the room with dirty, dry air.
The easiest way to get rid of dryness is with the help of ready-made preparations in a spray based on purified sea water, this
- Aqua Maris
- Aqualor
- Otrivin Sea
- Salin, etc.
Please note that ordinary nasal drops for a runny nose are not suitable for this problem, as they themselves strongly provoke dryness and increased sensitivity of the mucous membranes.
If you have to work or just be in an uncomfortable environment for a long time, then to protect the already damaged mucous membrane you need to use barrier agents, that is, lubrication with healthy oils or fats. They form a thin, non-drying film on the mucous membranes, which does not allow them to dry out and become damaged. For this purpose, high-quality oils are used - rosehip oil, sea buckthorn oil, eucalyptus oil, and many others. These products are not recommended to be applied in pure form, as they can dry out the fabrics themselves. It is best to mix them with base oils: peach, almond, apricot.
Useful video - How to rinse your nose correctly:
How to treat a sore throat in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, drugs and folk remedies
If painful crusts have already formed in the nose, and the tissues are bursting and bleeding, “heavy artillery” will be required. Balms Narisan and Vitaon will come to the rescue. They soften dry and hard crusts, facilitating their painless and bloodless separation.
In the presence of an underlying disease of a viral nature, for example, influenza, Interferon, Grippferon and others from the same series will be effective. To prevent the disease and speedy recovery, oxolinic ointment is often used. The vitamin preparation Aevit also works well, which is used to lubricate the mucous membranes to speed up healing.
Nasal rinsing and inhalation
Nasal rinsing helps to quickly and effectively moisturize the nasal mucosa
Along with many medications, nasal rinsing and inhalation are very effective against dryness. If you have dry nasal mucosa, treatment of which for some reason with medications is impossible or undesirable, then you should resort to a simple remedy - rinsing. For these purposes, you can use a special teapot or use any suitable vessel. The easiest and most useful way is to rinse with physiological salt solution - it does not harm the body, since it has a composition similar to the main body fluids. The salt content in it works as a mild disinfection and means of accelerating regeneration.
To rinse, you need to make sure that the warm liquid easily penetrates into one nostril and flows freely out of the other. Then the mucous membranes are cleared of crusts, swelling, dryness and irritation disappear.
Washing with decoctions of medicinal plants also works well.
An excellent remedy is chamomile. Its warm decoction mechanically gently cleanses the mucous membranes, heals and disinfects them, and starts the process of accelerated regeneration.
Inhalation is also effective. The easiest way is to use a soda solution. Soda has the ability to soften the membranes and very quickly eliminate severe dryness and crusting in the nose.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine for dry nose recommends using aloe juice
If dry nasal mucosa is detected, treating it with traditional methods can be very simple but effective:
- First of all, it is recommended to inhale steam from decoctions of medicinal herbs, rinse with warm decoctions of medicinal herbs, and then carefully instill 2 drops of high-quality cold-pressed vegetable oil into the nostrils. You need to drip carefully so as not to get into the respiratory tract.
- Another great remedy is aloe juice. This wonderful plant will help get rid of dryness and heal inflamed and dry, cracked and crusty mucous membranes. To do this, instill 2 drops of fresh juice and lubricate the inside of the nostrils with it.
- A small amount of glycerin can be used to lubricate the nose. This substance can effectively moisturize mucous membranes. It is very useful to apply after steam inhalation, when the mucous membranes are saturated with moisture. Glycerin will help keep it in the mucous membranes for a long time.
But external hydration may not be enough, so supporters of traditional methods of treatment use internal methods. To saturate the body with moisture, drink plenty of fluids, preferably vitamin remedies: rosehip decoction, tea with raspberries and honey, lemon, alkaline mineral water, milk with honey and butter, in a word, the same set as in the treatment of colds, as well as a variety of fruit drinks, fruit, berry and vegetable juices (if you are not allergic to them).
Which doctor should I contact?
Dry throat is a fairly common symptom, so there is no clear answer to this question. It all depends on your individual clinical picture. However, if you are seriously concerned about a growing symptom and feel severe dryness in your throat, you should immediately visit an otolaryngologist, or ENT specialist - this is the specialist who deals with the treatment of the throat and will be able to advise you both on the treatment of dryness and on further medical specialist .
Dry throat is a dangerous symptom, without proper attention to which a person is recommended to face significant complications. At the first signs of dry throat, we recommend that you immediately consult your doctor to receive qualified medical care.
Call our contact center at 8 (495) 230 03 09 and we will help you make an appointment with a specialist!
Dry mouth in pregnant women
Not all pregnant women experience dry mouth while sleeping at night. Usually their salivary glands work more actively than in other periods. Therefore, dryness may indicate inflammatory processes in the body.
They are often caused by colds.
The situation of a pregnant woman may worsen if this symptom is supplemented by the appearance of a metallic taste in the mouth. If specific signs are detected, you should consult a specialist.
Dry mouth during pregnancy can occur due to frequent urination. The body simply does not have time to replenish its fluid reserves, so certain areas do not receive enough moisture.