Quick transition Treatment of a short frenulum of the tongue
A short frenulum of the tongue (ankyloglossia) is one of the most common minor anomalies in the development of the oral cavity.
The frenulum of the tongue is a fold of the oral mucosa that runs along the midline and connects the floor of the mouth with the lower surface of the tongue.
The function of the tongue frenulum is to fix the tongue to the soft tissues of the oral cavity, preventing tongue retraction (glossoptosis), especially during the neonatal period.
Symptoms
When crying, the tip of the baby's tongue bifurcates in the shape of a stylized heart.
The baby cannot stick his tongue out of his mouth. To test this reflex, you can run your finger over the baby's lips. Normally, the baby sticks his tongue out quite far, moving it around his lips in search of mother's milk.
Breastfeeding takes a lot of time, the baby is capricious, nervous, and clicking sounds are heard when sucking.
The baby is not gaining weight well.
A child with a short frenulum cannot reach the palate with his tongue.
There is a noticeable disturbance in the pronunciation of certain sounds during speech formation.
With a short frenulum (less than 1.5 cm), if it is attached to the soft tissues of the floor of the mouth, functional disorders do not always occur. These include difficulty sucking during breastfeeding and disturbances in sound pronunciation during the formation of phrasal speech.
Reasons for appearance
Reasons for education:
- lack of nutrients, iron and vitamin PP in the patient’s body;
- anemia;
- lack of B vitamins;
- allergic reaction to toothpaste or medications;
- chronic fatigue and constant nervous tension;
- mechanical damage to the tongue (nervous biting, chewing);
- disruption of capillary blood flow in the tongue;
- the patient has diseases such as gastritis, enterocolitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis;
- wearing uncomfortable dentures.
The main reason why the tongue is cracked is mechanical injuries due to a lack of vitamins and microelements in the patient’s body. In this case, it is enough to bite your tongue while chewing food so that a painful crack forms at its tip.
Another fairly common reason why a patient’s tongue is cracked is a malfunction in the patient’s central nervous system, which is caused by chronic fatigue, frequent stress, and lack of sleep. This is a reason to suspect a problem with the hypothalamus.
It happens that patients are perplexed: why there are cracks on the tongue, there seems to be no visible reason for their appearance. In this case, the answer to the question of why cracks appear can only be given by an experienced doctor, after a thorough diagnosis. It is necessary to do a detailed blood test to determine which microelements and vitamins are missing in the patient’s body. Quite often, correction of the nutritional system helps get rid of the disease.
Many people are probably interested in the question of what cracks mean. After all, the tongue, as is known, signals the presence of many diseases and pathological conditions of the human body. Cracks in the tongue are a sign of a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body. Quite often, cracks are caused by worms, as they deplete the human body, causing anemia and iron deficiency. They also indicate a diseased liver, since with this disease the human body does not receive many microelements important for health.
Cracks in the tongue on the side can be a sign of thyroid disease; in this case, it swells and is injured at the edges by the patient’s teeth.
Consequences of frenulum anomaly
Hypotrophy due to impaired sucking, poor weight gain in infants.
Malocclusion, the first signs of which during the period of temporary occlusion is the rotation of the central lower incisors to the lingual side.
Impaired development of the lower jaw, as a result, the formation of a distal bite.
Local gingivitis, periodontitis up to exposure of the roots of the teeth in the area of the lower jaw incisors.
Violation of the pronunciation of sounds that require raising the tongue upward: “sh”, “zh”, “sch”.
Impaired language development due to asymmetrical growth. Low mobility of the tongue impairs the articulation of some sounds. Violation of diction (clarity, intelligibility of pronunciation).
What it is
Officially, painful cracks on the tongue and along the edge of the tongue are called glossalgia. This is a fairly common neurosomatic disease.
Most common symptoms:
- dryness in the tongue area;
- itching and burning;
- swelling;
- soreness.
The insidiousness of glossalgia is that it does not go away on its own; without appropriate treatment it is impossible to get rid of a crack in the tongue.
At an early stage of the disease, the doctor may not notice pronounced cracks in the tongue, since they are microscopic and mainly manifest themselves as burning and pain. If you do not respond to this symptom in a timely manner, over time a crack may form at the tip or in the middle of the tongue, longitudinally, as well as cracks under the tongue and on the sides. In this case, the doctor also notes swelling and swelling of the tongue, atrophy of the salivary glands and filiform papillae on the surface of the tongue. The sooner you start treatment, the easier it is to get rid of glossalgia, so if you have cracks in your tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Congenital pathologies of the tongue and frenulum - types and features
Anomalies of the tongue can be either congenital or acquired; they are often the result of certain pathological processes occurring in the body. Currently, malformations of the main speaking organ are quite rare. Many of them are serious problems that often require surgery. Further in this article we will talk about what congenital defects of the tongue and frenulum exist, how they are corrected, and also consider in detail such a pathology as a folded tongue.
Types of congenital anomalies
Currently, in medicine and dentistry in particular, a specific list of main pathologies is identified, each of which has its own deviations. Anomalies of the development of the main organ of the oral cavity include the following disorders:
- aglossia is a rare anomaly in which the tongue is completely absent,
- microglossia - the absence of the front part of the organ, due to which it has an abnormally small size, becomes too short,
- macroglossia - in this case the organ grows excessively, which is accompanied by generalized hypertrophy of the jaw muscles,
- splitting - its two parts are separated vertically, they simply do not grow together, remaining completely separate from each other. This tongue resembles a snake's,
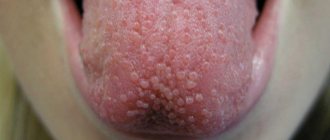
- lingual tonsils - enlarged lymph nodes in the root area of the organ,
- rhomboid glossitis - characterized by the formation of an inflamed area in the shape of an oval or diamond at the base, usually blue-red in color,
- folding is a defect in size and shape, in which deep grooves and folds covered with papillae appear on the surface of the organ,
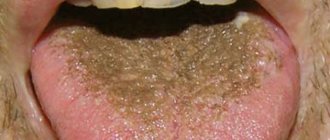
- a villous (hairy) tongue is a rather rare phenomenon, leading to hardening of overgrown filiform papillae. As a result, the area at the root turns brown or even black,
- Tongue goiter is a pathology in which thyroid tissue develops inside the organ and manifests itself as an uneven surface.
Modern medicine in most cases corrects such defects - in such situations, the problem of aesthetics and functionality is solved through surgery and plastic surgery.
Treatment
The main question that worries patients with glossalgia is how to cure cracks in the tongue. In fact, everything is not so difficult. The treatment method depends on the cause of glossalgia.
- First, it is necessary to eliminate the dental causes of tongue cracks - correct an incorrect bite, replace defective fillings, and adjust the prosthesis. Next, the patient should be carefully examined by a therapist, neurologist, and, if necessary, by an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist. And only after this should treatment for glossalgia be prescribed.
- Typically, treatment for fissures consists of drug therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment with medications is to improve blood circulation in the tissues of the oral cavity, as well as to improve general cerebral circulation. For this purpose, drugs such as trental, cavinton, nicotinic acid, and vitamin C are prescribed.
- The tone of the autonomic nervous system should also be improved; for this purpose, sedatives are prescribed - tincture of valerian, motherwort, persen.
- Additionally, the doctor may prescribe procedures such as hirudotherapy or electrical neurostimulation using a TENS device. A good effect is achieved by using electrophoresis, as well as iontophoresis of novocaine.
- If the tongue is severely painful, the doctor may prescribe local painkillers - lidocaine, dicaine.
- If the patient has cracks in the tongue, plaque and burning, it is necessary to adjust the diet. During treatment, you should completely exclude from the diet foods that irritate the surface of the tongue - such as sour juices, vegetables, pickles and marinades. You should not consume large amounts of spices, especially pepper and salt. It is advisable to quit smoking.
- After each meal, be sure to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with salted water or a decoction of medicinal herbs. Oak bark, sage, propolis, and honey have a healing effect.
Is glossitis contagious?
It comes as a surprise to many people that the disease can actually be contagious. Here you need to understand that if glossitis of the tongue occurs due to non-infectious causes, for example, mechanical injuries and burns, then it is not contagious. If the cause of its development is infections, viruses and bacteria, for example, staphylococcus, streptococcus, herpes virus or candida fungi, then the pathology can become dangerous not only for you, but also for others and family members.
In addition, glossitis on the tongue may indicate that you have problems in the body, which again can be contagious to outsiders: diphtheria, helminthic infestations, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, syphilis.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 10 ratings, average: 4.90 out of 5)
language
- E.V. Borovsky, A.L., Mashkilleyson M. Diseases of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips, 1984.
Consulting specialist
Dzagurova Elina Ruslanovna
Doctor rating: 9.5 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 11 years
Clinical manifestations
Patients note swelling of the organ and an uncharacteristic crimson tint due to the translucency of the vascular network.
The tip and edges of the tongue may become covered with cracks and other erosive lesions. There may be pain and a burning sensation in the inflamed tissues. Unpleasant sensations become more intense when eating. Dry mouth appears, gums begin to bleed. High risk of developing stomatitis.
Depending on the cause that triggered the development of the disease, the patient may experience symptoms:
- With anemia: the skin becomes lemon-colored, gastrointestinal dysfunction and weight loss occur. The patient experiences nausea, numbness of the limbs, and increased fatigue. The long course of the disease leads to visual impairment, hearing impairment, central nervous system disorders, and dementia in people over 60 years of age.
- With pellagra: dermatitis develops on the skin, dementia, diarrhea, and stomatitis appears on the lining of the oral cavity. The person feels lethargic and sleeps poorly.
- With sprue: gastrointestinal manifestations, nausea, weakness, stomatitis. If left untreated, B12 deficiency occurs.
Diagnostic features
When the first manifestations of an anomaly occur, you must come for a consultation to a dental clinic. The dentist will determine the disease based on the patient’s complaints and clinical symptoms. A differential diagnosis is required with stomatitis provoked by contact with an allergen and acute atrophic candidiasis. The dentist is faced with the task of determining the cause of the anomaly and selecting therapy for the original disease.
Laboratory tests are performed. Sometimes consultation with highly specialized specialists is required.
Treatment of the disease
For this anomaly, complex treatment is prescribed. In complicated cases, in the absence of adequate therapy, glossitis can cause the disappearance of papillae and organ shrinkage, speech defects, breathing problems, and deterioration in the quality of chewing food. There is a risk of developing phlegmon and purulent melting of the mucous membrane. Such conditions are dangerous due to the development of blood poisoning and death.
Symptomatic therapy
Local antiseptic drugs can eliminate swelling. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain and relieve inflammation. Wound healing drugs are used: retinol solution, vinylin and others.
It is recommended to follow a special diet and increase fluid intake. It is useful to give preference to foods with a puree-like consistency.
Clinic of scrotal glossitis - how to identify an anomaly
It was already noted above that a folded tongue usually does not cause a person discomfort or trouble. However, against its background the following deviations may also appear:
- the formation of pronounced folds and grooves on the surface is an aesthetic problem,
- macroglossia - growth of organ tissue, against the background of which a person experiences certain difficulties while speaking and chewing food,
- thickening of the tongue
- atrophy of taste buds,
- increased sensitivity,
- burning and tingling sensations,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- the appearance of bad breath.
Folds and grooves cause an aesthetic problem
If a folded tongue causes discomfort, it is better to seek help from a dentist. The choice of treatment method will largely depend on the degree of development of the pathology.
Diagnostics
Making a correct diagnosis is not particularly difficult, so any doctor can recognize the geographic language based on the following studies:
- Collection of anamnesis, which is based on the patient’s complaints and examination data.
- General analysis .
- Bacteriological culture to detect pathogenic microorganisms and determine the causative agent of the disease.
- Polymerase chain reaction (determination of the pathogen by DNA).
- Enzyme immunoassay (presence of non-standard antibodies).
- Scraping the mucous membrane of the tongue to identify treponema pallidum (if syphilis is suspected).
- analysis to detect worms.
To differentiate from other diseases, the doctor focuses more on the movement of lesions.